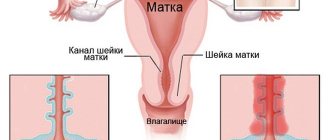
Separate diagnostic curettage (SDC) is performed to examine cellular material. The sampling is carried out separately from the cervical canal and the endometrium - the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity. The procedure is often called “cleaning”; in some cases, treatment is also carried out along with the examination, since the pathologically altered tissue is removed.
Our expert in this field:
Alimardonov Murad Bekmurotovich
Gynecologist-oncologist, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
General concepts
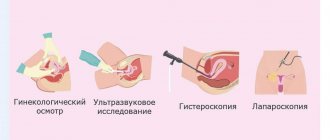
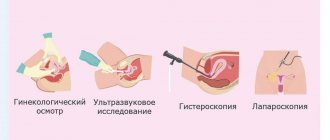
Hysteroscopy is a technique for examining the internal cavity of the uterus using endoscopic equipment and simultaneously taking a biopsy. This is not a primary intervention - it is not carried out without clear indications, it is prescribed only at the end of the diagnostic stage, after ultrasound, colposcopy and other tests.
To choose the optimal treatment method and make the correct diagnosis, the visual image provided by ultrasound is not enough; you need to know exactly which cells form the pathological focus in the endometrium, the mucous membrane lining the internal cavity.
The procedure is not considered invasive because it does not involve penetration through tissue cutting. Unlike the standard colposcopy performed during the initial appointment—examination of the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix through a microscope—the hysteroscope invades the sterile uterine space. In essence, this is the same endoscopy as gastroscopy, only the uterine cavity, unlike the stomach, normally does not contain microflora and its appearance there is not at all beneficial for the woman.
Endoscopy of the uterine cavity allows targeted diagnostics - a detailed examination and taking the most informative piece of tissue - a biopsy, simultaneously solving treatment problems - removing polypous growths, an internal fibroid nodule, or separating mucosal adhesions that interfere with normal menstruation, formed during the inflammatory process.
Preparatory marathon
Having figured out what separate curettage means and how it happens, many begin to be interested in the correct approach to the preparatory stage. The most important point here is checking with the menstrual cycle calendar.
This is necessary in order to increase the chance of success with minimal trauma. It is best to have time to carry out the intervention a couple of days before the start of menstruation. Also, operations are prescribed during the period when menstruation has already begun, and the bleeding has become quite heavy.
For doctors, even the second scenario is preferable, since the mucous membrane of the genital organs comes off naturally. For the patient, this arrangement will be less painful after the anesthesia wears off.
Before issuing a referral for manipulation, the gynecologist will definitely send his ward to undergo tests to exclude possible contraindications. To protect a woman, she will have to pass the following tests:
- coagulogram;
- completed form No. 50;
- cardiogram;
- flora smear;
- ultrasound examination of the uterus.
Separately, you will have to check your blood clotting to determine the duration of possible bleeding. It would also be useful to conduct a preliminary allergy test if the victim has never previously been subjected to anesthesia. Such careful preparation will reduce the risk of possible anaphylactic shock.
Precautionary measures also concern the prohibition of eating food at least twelve hours before the appointed time. Due to such a strict restriction, doctors try to schedule such a delicate examination for the first half of the day.
What is curettage?
Scraping the endometrium is similar to scraping; the skin of young potatoes is also scraped off, only evenly and using a special technique. The inner mucosa is completely shed during menstruation, so scraping it off is quite easy.
The term “separate diagnostic curettage” involves the removal of the surface layer of the endometrium and separately the cervical mucosa, since different pathological processes that require a different therapeutic approach can simultaneously appear and coexist in different parts of the organ - the body and cervix.
Pregnancy and childbirth after curettage of the uterine cavity
The first menstruation after curettage may occur with some delay (in some cases up to four weeks or more), which is associated with hormonal imbalance.
This is also considered normal after curettage. You should sound the alarm if your period does not come for more than two months - this is a serious reason to consult a gynecologist.
In general, most women get their period within two to three weeks, which means that in the new cycle (i.e., with the arrival of their period), there is theoretically a chance of becoming pregnant.
Childbirth after the procedure usually proceeds well.
If a woman tries to conceive a child for six months or more after curettage, but there are no results, it is necessary to undergo additional examination by a gynecologist. Curettage should not negatively affect fertility; on the contrary, this procedure is often performed as part of the complex treatment of infertility.
The pregnancy planning plan after curettage is built depending on what caused the need for the operation. If a woman sets a goal to become pregnant after curettage, she must inform her gynecologist about this. The specialist will give an adequate assessment of the situation and recommend the timing of pregnancy planning.
Indications and contraindications
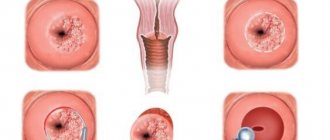
The indication for hysteroscopy with RDV is any pathology of the endometrium, which often manifests itself with bleeding outside the menstrual cycle - acyclic or after menopause. Ultrasound allows you to preliminarily determine the nature of pathological changes and their localization; an accurate diagnosis can only be obtained by studying a piece of tissue under a microscope. Inspection of the cavity through the eyepiece of a hysteroscope helps to assess the extent of the lesion and the volume of pathological tissue for curettage.
The manipulation will provide information about the causes of infertility and menstrual irregularities, and at the same time as diagnosis, destroy adhesions in the fallopian tubes that interfere with the movement of sperm.
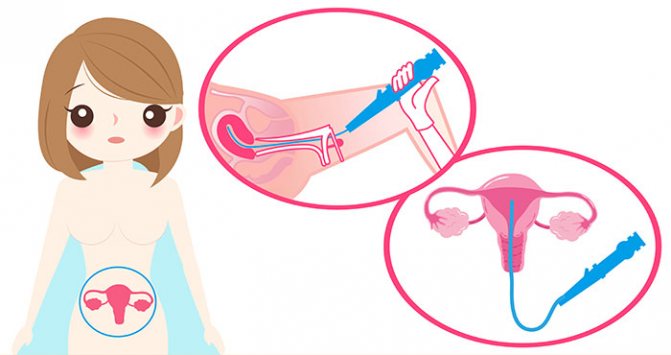
There is a need for hysteroscopy with RDV when removing synechiae - pathological adhesions of the mucous membrane that disrupt endometrial rejection and prolong menstrual bleeding. Under visual control, the exact location and optimal depth of the treatment effect is determined.
Taking a biopsy after long-term hormonal treatment will demonstrate the achieved result and allow you to decide on a further strategy.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy with RDV:
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs in the active phase;
- infections or severe pathology of other organs with significant dysfunction;
- blood clotting disorders, including with excessive formation of blood clots;
- pregnancy;
- extensive cancerous lesion of the cervix with fusion of the cervical canal.
Methodology
Hysteroscopy with RDV is performed under short-term intravenous anesthesia in a small operating room. The woman is placed on a gynecological chair, the external genitalia and the perineal area are treated with a disinfectant solution. Spoon-shaped speculums are inserted into the vagina. The neck is secured by the anterior lip with bullet forceps. The upper mirror is removed, the lower one is held by the operating nurse. Using a small sharp curette No. 1, the cervical canal is scraped out without inserting the instrument into the internal os. The scraping is placed in a test tube with formaldehyde, and the tube is sent to the histology laboratory. A smear is applied to a glass slide for cytological examination.
To determine the length and position of the uterus, probing of the uterine cavity is performed. A metal probe is inserted through the cervical canal to the fundus of the uterus. To carry out hysteroscopy with RDV, it is necessary to dilate the cervical canal, which is carried out with Hegar dilators up to No. 10-10.5. The dilators are advanced beyond the internal os, starting with small sizes. A hysteroscope tube is inserted into the uterine cavity. In practice, liquid hysteroscopy with a single-channel fluid supply and its independent outflow through the dilated cervix is more often used. After the expansion of the uterine cavity with fluid, the gynecologist sequentially examines the walls, bottom and area of the mouths of the fallopian tubes. Polyps, hyperplasia, cancer, foreign bodies, fibroids and other diseases of the uterus have characteristic hysteroscopic signs that are easily detected during examination.
After determining the localization and extent of the pathological process of the endometrium, the hysteroscope is removed. Next, the uterine cavity mucosa is scraped, removing the entire functional layer. Using sharp curettes No. 6.4, scrape out all the walls in the direction from the bottom to the internal pharynx. Control curettage of the uterine angles, where polyps are most often located, is carried out with a small curette No. 2. If the scraping is abundant with blood clots, it is washed and placed in a separate tube with formaldehyde. To control the completeness of curettage, the hysteroscope is reinserted and the entire uterine cavity is examined. The instruments are removed and the cervix is treated with iodine. The duration of hysteroscopy with RDV is on average 20-30 minutes.
Preparation
Preparation for hysteroscopy with RDV is standard - as for minor gynecological operations, these are detailed tests:
- blood and urine
- on the microflora of the genital tract,
- for common infections (HIV, hepatitis, syphilis).
This implies a complete gynecological examination and for anesthesia, an ECG and fluoroscopy of the lungs, consultation with a therapist and other specialists are required, if the state of health requires it.
On the eve of the manipulation, the colon is cleansed; before the intervention, you must refuse to eat.
Hysteroscopy with RDV requires a short hospital stay for optimal preparation and a calm attitude. The best time is three to four days before the expected menstruation, when, under the influence of hormones, the cervical canal has expanded as much as possible, and the endometrium is almost ready for rejection.
FAQ
On what day of the cycle is it better to perform RDV with hysteroscopy?
The procedure should be performed on days 5-7 of the cycle. If the indication for hysteroscopy of the uterus with RDV is an emergency condition (for example, bleeding), the intervention is performed immediately.
Recovery after hysteroscopy in the Russian Far East
In the first days, discharge and minor nagging pain in the lower abdomen are possible, which can be easily eliminated with the help of conventional painkillers. Sexual intercourse can be resumed after the discharge has stopped. In the first two weeks you should avoid visiting baths and saunas.
Where to do hysteroscopy with RDV in Moscow
Today, examination is available in almost all gynecological medical institutions. But when choosing a clinic, it is better to give preference to those equipped with modern equipment, including endoscopic equipment. Our Center not only has expert-class equipment, we have our own laboratory, so the examination result is ready in the shortest possible time. As for the price of hysteroscopy with RDV, it depends on a number of factors (type of anesthesia, type of pathology, time of hospitalization, etc.). Therefore, it is better to find out the cost of hysteroscopy of the uterus with RDV from the administrator.
Tags: Operative gynecology Uterine fibroids Adenomyosis (internal endometriosis) Intrauterine pathology Uterine fibroids with endometriosis Pregnancy and uterine fibroids Intrauterine synechiae Endometrial hyperplasia Treatment of endometrial polyps Uterine fibroids and multiple myomatosis
How is hysteroscopy with RDS performed?
The patient is taken to a small operating room, the manipulation is performed on a gynecological chair.
The woman is put under brief anesthesia - half an hour is enough for the manipulation.
It begins, like any gynecological examination, with the installation of gynecological speculum and treatment of the genital tract with antiseptics. The cervix is fixed with special forceps, its canal is expanded to the required diameter, then the hysteroscope is inserted. For a high-quality inspection, gas is pumped inside, straightening the walls of the cavity. In a certain order, all the walls are examined and the image is recorded on a disk; a biopsy is taken from places suspicious for pathology.
The hysteroscope is removed and RDV is started, collecting the mucous membrane of the cervix and cavity in different jars.
RDV - what is it and the technique of implementation, how is it done with and without hysteroscopy
Diagnostic dilation (widening of the cervical canal) and curettage (cleaning of the uterus) were originally intended to identify intrauterine pathology of the endometrium and help with abnormal uterine bleeding. Now new methods have emerged for assessing the uterine cavity and diagnosing endometrial pathologies. For example, pipel or aspiration biopsy. But dilation and curettage still plays an important role in medical centers where advanced technology and equipment are not available, or when other diagnostic methods are unsuccessful.
Traditionally, cervical dilatation and curettage of the walls of the uterine cavity are performed blindly. Diagnosis can be done under ultrasound guidance or in combination with hysteroscope imaging.

Back to contents
Recovery period
A woman can leave the hospital in the evening if there are no contraindications from other organs. For prophylaxis, antibiotics and pain relief with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed.

For several days, there is discharge from the genital tract, initially blood-colored, becoming lighter every day. Their volume is individual, but not comparable to menstruation. If a smell appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A woman needs to give up sex for at least a week, avoid douching, and limit physical activity.
Preparing a woman for the Russian Far East
With planned curettage, the operation is performed before the onset of menstruation. Before the operation begins, the patient must undergo some tests. First of all, this is a general blood test, cardiogram, test for the presence/absence of HIV infection, test for various types of hepatitis, as well as a test for blood clotting. The patient must undergo complete depilation of pubic hair and also purchase sanitary pads. It is recommended not to eat before surgery. You should also bring a clean T-shirt, hospital gown, warm socks and slippers.
Possible complications
An unpleasant consequence is that the lifting forceps coming off the “flaccid” neck can injure it. The tears are small and do not hurt, but later the neck may become deformed with scars.
The introduction of gas into the uterine cavity can cause short-term arrhythmia due to its absorption and changes in the gas balance of the blood.
Excessive scraping of the mucosa, which removes the endometrial growth zone, as well as bleeding from a damaged vessel, can subsequently lead to scars and synechiae.
The most dangerous thing is a breakthrough through the uterine wall into the abdominal cavity and damage to the nearby pelvic organs.
Rehabilitation after RDV
In the future, in order to avoid the development of inflammatory processes, the woman is prescribed medication. Although immediately after the operation you can return to your normal lifestyle. Just during the recovery period, you should not expose yourself to excessive physical exertion, which can lead to complications. Scanty vaginal discharge or minor pain in the genital area is not considered a pathology.
Can complications occur after RDV of the uterine cavity and cervical canal?
In general, in skillful hands, curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal is rarely accompanied by complications, but they still occur. These include:
- Perforation of the uterus. You can perforate an organ with any instrument, but most often this happens with a dilator or probe. If the perforation is minor, it heals itself, otherwise it has to be sutured.
- Cervical tear. Most often this happens when the forceps holding it fall off the cervix.
- Inflammation of the uterus. It occurs if separate curettage was performed during inflammation or in violation of septic and antiseptic requirements.
- Damage to the mucous membrane. It occurs when excessive scraping occurs when the germinal layer of the membrane is damaged.
- Hematometra. If cervical spasm occurs after curettage, the blood that should flow out accumulates, becomes infected and can cause pain.
In general, complications can be avoided if this operation is performed carefully and correctly.
Complications of curettage also include those situations when, after the procedure, a pathological formation or part of it remains in place. As a rule, this happens when curettage is performed without hysteroscopy, that is, when it is impossible to evaluate the result at the end of the operation. In this case, curettage must be repeated, since the pathological neoplasm cannot be left in the uterine cavity.
Biological tissue samples obtained during RDV of the uterus are sent for testing to the laboratory. These data allow the gynecologist to confirm the preliminary diagnosis and choose methods and directions of treatment. This is especially important to confirm suspicions of the formation of a malignant tumor.
Alternative methods
Today there is nothing to replace diagnostic hysteroscopy with RDV, but treatment without RDV is possible and has advantages for some pathological conditions of the uterine mucosa.
Modern hysteroscopes allow the use of laser and electric current to remove large amounts of tissue; the disadvantage is that nothing remains for analyzing the cell structure under a microscope, because the entire pathological substrate is “burned out”.
With electrical destruction, the likelihood of bleeding is higher, with laser ablation it is lower than with conventional RDV. Laser ablation virtually eliminates perforation of the uterine wall.
In terms of the stages of manipulation, hysteroscopy using modern alternative technologies is no different from the standard RDV.
Our clinic conducts a full range of gynecological examinations; we will choose the most optimal and informative for you, making your stay within the walls of our clinic not only healthy, but also enjoyable.
Book a consultation around the clock +7+7+78
Hysteroscopy with RDV: pre-registration and price in Moscow
Where can I have curettage performed under hysteroscopy control in Moscow? At the Miracle Doctor clinic you can receive qualified medical care. Our gynecological department employs doctors of the highest category with many years of experience.
Using first-class diagnostic and medical equipment, the capital's leading gynecologists conduct examinations. We have our own histological laboratory, where we can analyze the obtained material for malignant tumors. Find out the price for diagnostic curettage in Moscow and make a preliminary appointment on the clinic’s website.
Treatment after the procedure
Therapeutic measures after the procedure:
- To prevent the development of an infectious process, antibiotics are prescribed.
- To prevent clots from accumulating, in the first few days you can take No-shpu (one tablet twice a day).
- In the first few hours, you can take a pain reliever to reduce pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
The results of the histological test are usually obtained on the tenth day after cleaning. It is important to see a doctor at the specified time to discuss further treatment tactics.