Rules for taking tests
How to get tested correctly: recommendations for the patient
- Almost all tests are carried out on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours after the last meal), so you can drink a small amount of water to carry out the tests in the morning. Tea and coffee are not water, please be patient. Taking tests requires quitting smoking an hour before the procedure.
- Strictly on an empty stomach, more than 12 hours after the last meal: complete blood count, biochemical parameters (cholesterol, HDL, LDL, VLDL, triglycerides).
- After 5-6 hours of fasting (the last meal should be light, without high fat content), you can take tests: for hormones (in the morning), antibodies to infections (during the day). Please note that a blood test for antibodies to infections reflects the state of immunity in relation to infection. If the infection is recent, the results may be negative. In doubtful cases, it is recommended to retake the test after 7-10 days.
Analyzes during the day
- Regardless of food intake (not necessarily on an empty stomach): genetic polymorphisms, including polymorphisms of hemostasis genes, vascular tone, polymorphism of cytokine genes, AZF factor, mutations of CYP-21, PCOS, CFTR gene, HLA typing.
- After 3-4 hours of fasting, you can take tests for hCG, antibodies to infections in the blood, tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C, blood type, Rh factor, antibodies to the Rh factor, anti-group antibodies, autoantibodies (from the autoantibody panel ), prenatal screening, tumor markers.
- On the days and hours of operation of the CIR, tests are taken for PCR diagnosis of infections, culture of discharge from the urogenital tract (including cultures for mycoplasma and ureaplasma), microscopy of a smear from the vagina and cervix, microscopy of a smear from the throat, PAP smear, donation of mucus for the Kurzrock-Miller test.
- Laboratory standards are calculated for morning indicators. Only before 11 a.m. are tests taken for TSH, parathyroid hormone, and iron (the values of the indicators change significantly during the day).
- The day before the test, avoid stress, physical activity, changes in daily routine and changes in diet, and drinking alcohol.
- It is advisable that the tests be taken in a calm state. Therefore, if you were in a hurry or worried on the way to the treatment room, it is recommended to sit for 20-30 minutes before donating blood. Attention! Before taking some tests ( ACTH, cortisol, somatotropic hormone or growth hormone ), you need to completely calm down and relax. Please sit in the waiting room for 30-40 minutes.
- A PSA test is carried out no earlier than 7 days after any mechanical effects on the prostate (massage, biopsy, etc.)
- Studies are carried out without taking medications or 11-14 days after their discontinuation (except in cases where this is allowed by the doctor). In the questionnaire, be sure to indicate the names and regimen of medications taken.
- Some tests need to be taken only on those days when prescribed by a doctor (for example, hormones of the female reproductive system, EFORT test, on certain days of the cycle; some - according to the stage of pregnancy). Please indicate in the form the day of your cycle and the duration of your pregnancy.
- Repeated studies are best performed in the same laboratory, since different ones use different research methods and norms of indicators.
Attention! There are procedures with special preparation and method of collecting material :
- General recommendations for testing
- Spermogram and sperm fragmentation
- Smears for infections, gynecological smears, PAP smears, cultures
- Coprogram, advanced stool analysis
- Urine tests
- Dysbacteriosis
- Urine collection using a vacuum system with Stabilur preservative (general urine analysis, urine analysis according to Nechiporenko)
- Cytogenetic study of abortion material
- Obtaining and storing blood plasma
- Obtaining and storing blood serum
- Sampling of material for gene polymorphisms
- Rules for donating blood for hormones
- Urine collection for analysis of trace elements and heavy metals
- Collection of nails for analysis of trace elements and heavy metals
- Hair collection for analysis of trace elements and heavy metals
By following these simple rules, you will get reliable and reliable results. Doing the right tests is the key to correct diagnosis and treatment.
HIV tests. High standards of laboratory research
In Russia, there is an unfavorable epidemiological situation with HIV infection. Therefore, laboratory tests for HIV should be considered as a means of preventing AIDS and reducing the incidence of transmission of infection. Modern laboratory diagnostic methods used in CMD make it possible to detect HIV infection with high diagnostic accuracy.
Anonymous HIV tests
At the Center for Molecular Diagnostics (CMD), you can take an HIV test anonymously.
HIV analysis in CMD is:
- Serological diagnosis: determination of HIV antibodies and capsid antigen of the virus (p24) in the blood by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) with subsequent confirmation of positive results by immunoblotting (IB) in accordance with the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules SP 3.1.5.2826-10 “Prevention of HIV Infection” "(2011);
- along with the serological diagnostic technique - the use of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method: identification of the genetic material of the virus (nucleic acids) in accordance with the “Methodological recommendations for conducting examinations for HIV infection”, approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation on August 6, 2007;
- use of ultrasensitive methods for diagnosing HIV infection;
- guaranteed anonymity;
- efficiency of obtaining results.
Symptoms of HIV infection
During the first weeks after infection, HIV infection may manifest itself with nonspecific symptoms: weakness, fatigue, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes, intestinal disorders, loss of appetite, and skin rash. The severity of these symptoms decreases, and over time they may completely disappear. A long stage of latent HIV infection begins, which is practically asymptomatic. This period in patients with HIV infection lasts 8-10 years and the disease can only be detected by taking an HIV test (AIDS test).
A timely anonymous HIV test allows you to buy time for the disease, significantly increasing the patient’s chances of effective antiretroviral therapy. This is the best remedy for constant doubts about your own health. You can be tested for HIV and hepatitis at the same time.
Basic measures to prevent HIV infection
The source of HIV infection is people infected with HIV at any stage of the disease, even the earliest.
Since no vaccine has been developed to prevent HIV infection, any person should follow fairly simple rules. The main thing is to prevent HIV infection.
First of all, a healthy lifestyle can already be considered as AIDS prevention. And, of course, abstaining from injecting drug use and casual sex, and using barrier contraception are extremely important measures to prevent HIV infection.
When to get tested for HIV?
If you have the slightest suspicion of possible infection, you should immediately take an HIV test. The Center for Molecular Diagnostics (CMD) conducts HIV tests using various methods: detection of antibodies to HIV and p24 antigen by ELISA, and PCR analysis for HIV. It is also possible to donate blood for HIV and hepatitis.
Where can I get an HIV test?
You can donate blood for HIV testing anonymously at the Center for Molecular Diagnostics (CMD).
By taking a blood test for HIV and hepatitis, you receive a guarantee of complete anonymity and medical confidentiality. The time it takes to perform an HIV test depends on the diagnostic method used. An HIV antibody test is performed within 1 calendar day, PCR testing - from 2 to 7 calendar days.
Doctors named the reasons for errors in HIV testing
The reasons for false-positive HIV testing results are named. The information provided gives rise to complete distrust of these tests. “False-positive results for the immunodeficiency virus are quite common, literally shocking the person donating blood. The thing is that there are a lot of diseases that can provoke a false positive result... The reasons why the result can become a false positive, and it doesn’t matter whether it is anonymous or not, are violations of the rules for donating blood. Ordinary seeds or previously consumed spicy, sour, fried foods, and even mineral carbonated water, especially alkaline water - for example, Borjomi, can provoke a questionable result, no matter how much of them is eaten - a lot or a little... Conditions that can provoke a false positive result:
cross reactions; pregnancy period (risk group - women who have given birth several times); the presence of normal ribonucleoproteins; multiple blood donations; infectious lesions of the respiratory system; influenza and hepatitis virus; recent vaccinations (tetanus, hepatitis B, influenza); very thick blood; primary autoimmune liver diseases; tuberculosis; herpes virus; poor clotting; fever; liver diseases caused by alcohol; arthritis; violation of immunoregulatory processes; damage to small vessels of the body; oncological diseases; different types of sclerosis; organ transplantation; increased bilirubin; increased levels of antibodies; critical days. Some diseases may cause cross-reactions. For example, due to allergies, antigens that are incomprehensible to the body can be produced in the blood, which it recognizes as foreign. Such antigens can cause a false positive result. During pregnancy, a woman experiences a hormonal imbalance, so in some cases there may be a false positive test result. During the menstrual cycle, it is not recommended to donate blood for the immunodeficiency virus. Any infectious, fungal or viral diseases almost always test positive for the presence of the immunodeficiency virus. For this reason, doctors advise undergoing treatment for the disease, and only after 25-30 days undergo an examination. Diseases, oncology, increased bilirubin levels, vaccinations - all these factors affect the result. If a non-standard set of enzymes is present in the blood, then the anonymous analysis will be false positive. For these reasons, doctors do not tell people that they have already been diagnosed with an immunodeficiency virus infection. And having heard that the analysis is positive, a person should first of all think about what could have provoked a positive result. False-positive test results for the human immunodeficiency virus are very common after organ transplantation, especially during the period when the organ is taking root. In this case, unknown antibodies are produced, which, when tested, are encoded as antigens of the immunodeficiency virus. Before taking an anonymous test for HIV or AIDS, you must notify your doctor about whether the disease is present and how long it lasts. This must be done in order to exclude a false-positive test... Even if the test turns out to be positive, there is no need to panic, perhaps it is a false-positive... Such an impressive list of reasons for false-positive reactions in HIV tests, published on the website 101analysis.ru, already gives rise to complete distrust to these tests. And it is worth paying attention to who and how often turns out to be HIV positive.
But first of all, you need to pay attention to the fact that the HIV/AIDS theory itself was initially built on the unproven hypothesis that it is the HIV virus, which supposedly causes immunodeficiency, that is, accordingly, the root cause of the development of AIDS-associated diseases in HIV-positive people. Therefore, if a patient has developed such a disease, and when tested for HIV, he turns out to be HIV-positive, then, in accordance with this theory and with instructions, speedologists simply automatically diagnose such a patient with HIV infection, and already at the stage of AIDS, that is, the development of AIDS- associated disease. And if a patient has symptoms or diseases from the list below, then for speedologists they are not a signal that if they are present, the HIV test may be false positive - quite the opposite! - for them they are just a direct and legal reason for testing such a patient for HIV, and one of the “evidence” of his “infection”. LIST OF INDICATIONS FOR TESTING FOR HIV/AIDS IN ORDER TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF DIAGNOSIS OF HIV INFECTION. 1. Patients according to clinical indications: - feverish for more than 1 month; - having enlarged lymph nodes of two or more groups for more than 1 month; - with diarrhea lasting more than 1 month; - with an unexplained loss of body weight of 10 percent or more; - with prolonged and recurrent pneumonia or pneumonia that is not amenable to conventional therapy; - with prolonged and recurrent purulent-bacterial, parasitic diseases, sepsis; — with subacute encephalitis and dementia in previously healthy individuals; - with villous leukoplakia of the tongue; - with recurrent pyoderma; - women with chronic inflammatory diseases of the female reproductive system of unknown etiology; 2. Patients with a suspected or confirmed diagnosis: - drug addiction (with parenteral drug administration); - sexually transmitted diseases; - Kaposi's sarcoma; — brain lymphomas; — T-cell leukemia; — pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis; — hepatitis B, Hbs antigen carriage (at diagnosis and after 6 months); - disease caused by cytomegalovirus; - generalized or chronic form of infection caused by the herpes simplex virus; - recurrent herpes zoster in persons under 60 years of age; — mononucleosis (3 months after the onset of the disease); - pneumocystosis (pneumonia); — toxoplasmosis (central nervous system); — cryptococcosis (extrapulmonary); — cryptosporidiosis; - isosporosis; - histoplasmosis; — strongyloidiasis; - candidiasis of the esophagus, bronchi, trachea or lungs; — deep mycoses; — atypical microbacteriosis; — progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; - anemia of various origins.
Compare the list of reasons for false-positive reactions with the list of clinical indications for HIV testing (and in fact, AIDS-associated diseases and symptoms attributed to HIV infection), and you will find that some items are the same, such as fever, tuberculosis, herpes, hepatitis, and other infections and oncological diseases. Thus, it turns out that on the one hand, according to the HIV/AIDS theory, the development of all these diseases and symptoms in HIV-positive people is explained by the progression of HIV infection, as if it were their root cause, and if they are present, one can literally diagnose HIV/AIDS automatically, but on the other hand, almost the exact opposite is stated - all these factors themselves can cause a false-positive reaction when testing for HIV, and therefore, if they are present, this testing cannot be considered reliable. The contradiction between these approaches, as you see, is fundamental, and one might say insoluble in the sense that the HIV/AIDS theory itself was initially built on the fact that HIV leads to the development of AIDS-associated diseases, in particular infectious diseases, since they are accompanied by a decrease in immunity, and within the framework of this theory, the very discussion that the presence of such diseases in itself can be the reason for a positive reaction in HIV tests is, to put it mildly, unacceptable, since it completely contradicts this theory and casts great doubt on it. Judge for yourself: if the diagnosis of HIV infection itself is made precisely by the presence of clinical signs, that is, the presence of AIDS-associated diseases and symptoms, and this is enshrined in theory and practice, then abandon all this and actually stop testing for HIV according to clinical indications - for the AIDS industry, this can be said to be an act of suicide, an admission of the complete failure of the HIV/AIDS theory. After all, it will immediately lose all meaning if HIV testing is canceled for clinical indications, recognizing these very indications as nothing more than the reasons that cause false-positive results of HIV tests. And what have we come to?
Whether HIV causes AIDS-associated diseases and symptoms, or whether these diseases and symptoms themselves are the cause of a positive reaction in HIV tests - this is a question that has long required research and resolution in the form of an unambiguous answer. AIDS orthodox, of course, adhere to their position - HIV tests are quite reliable, and by definition they detect nothing more than antibodies to HIV (ELISA and IB tests), or its genetic material (during PCR testing). And in principle they never admit that all these tests can give a false positive result for some other reason. Judge for yourself: if they admitted this, it would again mean that HIV tests are in fact completely unreliable and unsuitable, and then what about the millions of previously diagnosed HIV infections? For the AIDS industry, any move towards discussing the fallibility of HIV tests is tantamount to suicide. But if we start from an alternative point of view, or HIV denial, then the picture with these tests turns out to be exactly such that they do not work positively for the mythical HIV virus, but obviously and by definition are unreliable, fake, and all their positive results are everything! - are false positive. And in the light of this opinion, the list of reasons for these false positive reactions is quite relevant and deserves attention, research and proper objective assessment. Do HIV tests really work positively for the reasons stated in it? Why not? If, on the basis of these tests, a diagnosis of HIV infection is made to certain categories of test subjects, with very specific diseases, symptoms, conditions, then it is a very logical and reasonable assumption, and even a statement, that the positive results of these tests are directly and directly related to these causes and factors. Let's take one example for clarity. The most common AIDS-associated disease in Russia is tuberculosis. And almost all patients are tested for HIV. Of these, about 10% are HIV positive. Official medicine makes no mention at all that tuberculosis caused a positive reaction to HIV tests. A diagnosis of HIV + tuberculosis is immediately made, and all that remains is to sympathize with such patients if, in addition to anti-tuberculosis treatment, they are prescribed antiretroviral therapy, since their chances of recovery are greatly reduced, but their chances of joining the sad statistics of those dying from AIDS increase. And what is very remarkable and curious in this regard. According to the HIV/AIDS theory, AIDS in HIV-positive people develops within 10-20 years from the moment of “infection”. That is, if a patient has already developed tuberculosis, and as HIV-positive he was identified precisely during testing based on clinical signs, then speedologists, without blinking an eye, claim that this patient has been living with HIV for a long time, it’s just that it was not previously detected, and you yourself know did not know that he was infected. And note, again, there is no talk that tuberculosis can be the cause of a positive test for HIV, and it is, in principle, impossible and unacceptable within the framework of the HIV/AIDS theory. But this very statement that the patient has been infected for a long time, was simply not previously identified, and he himself did not know anything - this statement is absolutely unfounded and unprovable. After all, it is absolutely impossible to go back in time with a time machine and take blood from this patient for analysis before he developed the disease and check whether he was HIV-positive or not. Moreover, the very formulation “he’s been infected for a long time, he just didn’t know it and realized it too late” provokes us to ask a simple question: why does it happen that such cases turn out to be the rule and not the exception? Why does every patient find out about their HIV-positive status only when they are admitted to the hospital? Is there any statistics on such patients whose HIV-positive status was known for a long time, and they developed AIDS-associated diseases within 10-20 years? There are simply no such statistics. There is only an absolutely unfounded formulation by speedologists: “they have been infected for a long time, they just didn’t know about it.” And go and check them, and prove that it was not HIV that led to the disease, but the disease itself is the reason for the positive reaction of HIV tests. I hope that the essence of the fundamental contradiction between the unproven HIV/AIDS hypothesis and the statement that HIV tests work positively for a number of reasons, among which it is worth highlighting AIDS-associated diseases, or clinical signs of HIV infection, is quite clear. The first point of view dogmatically asserts that HIV tests are infallible, and if the patient is HIV-positive and has an AIDS-defining disease, then there is no doubt and cannot be - he is HIV-infected, and for a long time, even if he just found out about HIV status. The second point of view is almost exactly the opposite: patients cannot be tested for HIV for a number of reasons that are likely to cause a false-positive result, and in particular, patients cannot be tested for HIV precisely for all the notorious clinical signs of HIV infection. A compromise between these approaches is in no way possible, since any step in this direction will lead to the complete collapse of the AIDS system... Who and how often is diagnosed with HIV infection in Russia? Some statistics. In 2013, 28,327,314 people were tested for HIV antibodies in Russia. A positive result in ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) was obtained in 271,408 of all those examined. A positive result in IB (immune blotting) was obtained in 103,168 of the previous ones. Only in 38% of cases a positive result in ELISA is confirmed by a positive result in IB. That is, in the remaining 62% of cases, a positive ELISA result is a false positive. And there were 168,240 such false-positive ELISA results in 2013. What does this mean? And this suggests that ELISA tests for HIV are completely nonspecific due to the fact that in almost 2/3 of cases they erroneously give a positive result. And of course, the sensitivity of 99% or higher indicated in the description of these tests is nothing more than a blatant deception on the part of their manufacturers. And the most amazing thing is that this fact of blatant deception has long been self-evident based on well-known statistical data, and yet no one pays attention to it at all, and still all doctors, like zombies, blissfully believe that the specificity of ELISA is tests for antibodies to HIV is 99%. And you might think that all the cases of erroneous, false-positive results listed above in the above article constitute only 1%. But in reality they make up 62%!!! ELISA tests for HIV antibodies are absolutely nonspecific and unreliable! On the part of their manufacturers, this is a blatant fraud, and on the part of consumers, either complicity in this fraud, or complete ignorance of the complete unsuitability of these tests, and the waste of billions of money is not just wasted, but also to the detriment of those who become victims of this completely unreliable and erroneous testing . Moreover, here we theoretically accepted IB as the standard and gold standard, and in comparison with it, ELISA turned out to be an absolutely unsuitable test. But we are talking about the unsuitability of all HIV tests in general, including IB. But in essence, these are similar tests, they have the same principle, and of course the same shortcomings... According to data for 2013, a positive result for HIV antibodies in IB was obtained in 0.364% of all 28 million examined. This is essentially the average value of a positive reaction in information security according to these data. 3,837,983 people were routinely examined (medical examination). Of these, 1,288 received a positive result in the IB. This is 0.034%. 10 times less than average. 3,382,246 donors were examined. Positive IB was obtained from 1111 of them. This is 0.033%. Almost the same as among those examined as planned, that is, relatively few. 455,737 doctors working with HIV-positive people or with contaminated materials were examined. Of these, 177 received a positive result in information security. This is 0.039%. Slightly more than among those examined as planned and among donors. That is, also relatively little. 238,885 patients with drug addiction were examined. Of these, 11,337 received a positive result in the IB. This is 4.75%. 13 times more often than the average value. 140 times more often than among those examined as planned and among donors. The difference is colossal. What explains it? Is it really the HIV virus? Of course no. 886,168 patients with STDs were examined for antibodies to HIV. Of these, 4,798 received a positive result in information security. This is 0.54%. One and a half times more often than average. 398,807 people were examined in places of detention. 10,791 of them tested positive in the IB. This is 2.7%. 7 times more than average. 2 times less than for drug addicts. A prison is not a sanatorium. And in general... 5,914,421 people were examined for clinical indications. The list of these indications includes all AIDS-associated diseases and symptoms attributed to HIV infection, as well as drug addiction and pregnancy. But here it is important to simply understand that in this case this category consists of patients with diseases such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, toxoplasmosis, cytomegaly, Kaposi's sarcoma and everything else from the list of AIDS-associated diseases.
Please note right away that in 2013 alone, almost 6 million people in Russia actually had clinical signs of HIV infection, and that is why they were tested for HIV. And of these, 27,229 people received a positive result in information security. This is 0.46%. Just 1.26 times more than average. The category is quite numerous, so this is not surprising. But what is very, very surprising and remarkable is precisely the fact that clinical signs of HIV infection are detected annually in almost 6 million Russians, and less than 0.5% of them turn out to be HIV-positive. If you check the statistics of HIV diagnoses made this year, it is even less, and significantly. And what does it mean? This means that for every HIV-positive patient who shows clinical signs of HIV infection, there are at least 200 patients with the same clinical signs of HIV infection, but when tested for HIV, they all turn out to be HIV-negative. And from here a self-evident medical fact directly follows: it is absolutely impossible to diagnose HIV infection based on the presence of these notorious clinical signs, because they are 200 times more likely to be found in HIV-negative people. Not only are HIV tests themselves profanation and fraud, but in addition to this, the notorious clinical signs of HIV can be attributed to millions of HIV-negative patients. And this means that these signs have absolutely no diagnostic reliability for the presence of HIV infection. 5,223,644 pregnant women were examined, including cases of termination of pregnancy. Of these, 8,136 received a positive ELISA result. This is 0.16%. Twice less than average. But 5 times more than among those examined routinely and among donors. In the Other category, 10,147,879 people were examined. A positive result in the information security was obtained from 26,363 of them. This is 0.26%. Less than the average, but nevertheless this is a quarter of all positive information security results. These include military personnel entering military service and military educational institutions, as well as those examined at their own request. The latter are the most “gifted”, to put it mildly, they are still idiots. During epidemiological investigations, 176,092 people were tested. A positive result in the IB was obtained from 10,549 of them. This is 6%. At first glance, this category has a record number of HIV-positive people, although it is the smallest of those already listed. But the fact of the matter is that during the epidemiological investigation, so-called contacts are tested for HIV, that is, children of HIV-positive mothers, sexual partners of HIV-positive people, participants in the sharing of equipment for injecting drugs. That is, this category should not only be the leader in the percentage of obtaining a positive result in information security, but it should be a very high percentage. In this case it is only 6%. What does this mean? Let me explain clearly.
100 people have already turned out to be HIV-positive based on testing results. During the epidemiological investigation, their sexual partners are tested for HIV. And among all the examined sexual partners of these 100 HIV-positive people, only 6 HIV-positive ones were found, and in the remaining 94 cases all partners turned out to be HIV-negative. The source of infection has not been found. That is, epidemiological investigation in the vast majority of cases is a complete fiasco and is a pointless waste of effort, resources and time. And therefore it turns out that among sexual couples with HIV, the vast majority are those in which only one of the partners has this diagnosis. And this fact alone shatters the myth about sexual transmission of HIV and the HIV virus in general! Let us present the obtained figures again. Positive IB for HIV antibodies was obtained during epidemiological investigations - in 6% of cases (a shamefully low percentage for the HIV/AIDS theory!); among drug addicts - in 4.75% of cases; among prisoners - 2.7%; in patients with STDs - in 0.54%; in patients with clinical signs of HIV infection - 0.46% (shamefully low percentage for the HIV/AIDS theory!); in the Other category - 0.26%; in pregnant women - 0.16%; among those examined as planned and among donors - 0.033-0.034%. And these are actually all the main and mass categories, that is, almost all those examined for HIV. It is these categories that are tested for HIV, and accordingly they make up the lion's share of all cases of HIV infection diagnosis, namely drug addicts, prisoners with clinical signs of HIV infection, pregnant women, patients with STDs, and another quarter of all cases are examined in the Other category. On the one hand, all this can really be regarded as direct evidence that HIV tests give false positive results when using drugs, during pregnancy, for a number of different diseases, and much less often (10 times or more) generally give a positive result when testing completely healthy people, the same donors, health workers undergoing preventive medical examinations. On the other hand, taking into account the fact that even in such categories as drug addicts, those with clinical signs of HIV infection, and pregnant women, the percentages of HIV-positive people among all surveyed are approximately 5%, 0.5%, 0.16%, respectively. , that is, very small, it is absolutely impossible to categorically state that HIV tests give a false-positive result in precisely these categories of subjects, precisely in connection with diseases or other indicated reasons. Millions of such people are examined, and a fraction of a percent of them turn out to be HIV-positive, a few people out of a thousand tested. Therefore, it is absolutely impossible to say, for example, that “any infectious, fungal and viral diseases almost always give a positive result for the presence of the immunodeficiency virus.” Yes, they almost always don’t give it, and if they do, it’s quite rare. Well, of course, the HIV/AIDS scam could not have been so cleverly introduced into life, and the false HIV/AIDS theory into official science and into the consciousness of the population, if its false premises were self-evident from the beginning. For example, if HIV tests gave a positive result in almost all drug addicts, or in all patients with AIDS-related diseases, or in a relatively large number of pregnant women. But this is not the case. Even among these categories, the number of HIV-positive people is very low, the figures are shown above. And year after year, as a result of HIV testing, tens of thousands of people in Russia alone are diagnosed with HIV infection, and the general picture of the epidemic seems to be quite plausible, at least for complete laymen in this problem. But. If not only HIV deniers say that HIV tests react positively to antibodies that have nothing to do with the HIV virus, but doctors who adhere to the orthodox theory of HIV/AIDS also report this, then we must think a question mark over HIV testing is becoming more and more widespread, and perhaps HIV testing itself will soon cause more doubts and mistrust than blind faith in it and in the HIV virus itself. After all, previously it has always been stated: HIV tests are absolutely reliable, there can be no mistakes, there are errors, but they are completely excluded by additional double checks, etc., etc. Now it seems to be recognized that a positive result can still be caused by a number of known reasons, and therefore they should be taken into account and excluded when diagnosing HIV infection. But in this case, let me ask right away: are all the reasons for the false positive reaction of HIV tests known and voiced? Maybe there are some others that are still unknown, and which are precisely the most significant? Who can responsibly assert that the existence of such causes is completely excluded? P.S.: Personally, I share the opinion of HIV deniers, the essence of which is that HIV is pure commercial and political fiction, from which big money is made and with which the “surplus” population is cynically exterminated. And today it turns out that the mystery of HIV tests is gradually ceasing to be a mystery and is beginning to be revealed. And if yesterday they were officially considered absolutely reliable, and today they are considered to have serious shortcomings, then perhaps tomorrow they will finally be recognized as completely unsuitable and fake, which they obviously are. All that remains is to find out for certain the real reasons for their positive reaction, and then there will no longer be a bold question mark above them, but a bold cross. And it is possible that the answer has long been known and voiced many times, and is that these tests give a positive result with a generally elevated level of antibodies in the blood sample being tested. That is, to be HIV-positive, it is not enough to use drugs, or have some kind of disease, or be pregnant, or get vaccinated, or for some other reason. As we have just seen, all these reasons are associated with HIV-positive status in almost isolated cases. In particular, out of 200 patients with clinical signs of HIV infection, only one is HIV positive. Why? Why is his case so different and stands out? Moreover, the diagnosis of HIV infection is often made to completely healthy people, and such people have been living with this diagnosis for 30 years, without any treatment. Remember about those who receive a diagnosis of HIV infection during medical examinations, donations, enlistment in military service, due to their own stupidity. How are these people different from the rest? What's so special about them? Maybe the whole point is really just that HIV tests react positively to a given threshold of total antibody levels in the blood? And if their concentration exceeds this threshold, then the person is declared HIV-positive? And further, in accordance with the theory, just sit and test for HIV drug addicts, patients with AIDS-associated diseases and STDs, as well as everyone who can be fearlessly declared HIV-infected - and among those tested, of course, there will be those who have obviously false, programmed known test result will give a positive result. And you don’t even need to prove anything. Drug addict? Test positive for HIV? Everything is clear, HIV-infected. The epidemic... In general, we can rightfully say that the greatest effort and investment in promoting the HIV/AIDS scam was due to its promotion in the media of disinformation. The very same whipping up of AIDS hysteria, fear and panic in front of mortal danger and extinction of humanity, a new plague and the end of the world. Well, and, accordingly, sucking out of thin air all the “discoveries” related to HIV/AIDS, and their introduction into official science and practical medicine, and, if necessary, into the empty heads of billions of naive humanoid bipedal bioorganisms. This is what was most difficult and costly. And then everything went as if on a well-worn track. And here you have the day of the fight against AIDS, and the day of remembrance of those who died from AIDS, and all sorts of actions and months, and the fooled population is now so mired in this deception and self-deception that the very idea that the whole fight against AIDS is just a deception , many are simply horrified, and they are simply unable to accept the truth. And even if they themselves become victims of the AIDS industry, and it would seem that their eyes should open, even then their brain is not able to turn on and earn money, and find the truth and make an independent decision. They follow the lead of the speedologists, and thoughtlessly and doomfully follow their recommendations, in particular the chemotherapy against HIV prescribed to them, which, of course, does not bring them the slightest benefit, but on the contrary only cripples and kills the naive imaginary HIV-infected people who take it... Because what are the real reasons for positive HIV test results? You know that? Or do you simply believe everything that swindlers from science and medicine have told you for their own financial gain? And until you find the most complete and comprehensive answer to this question, I would very strongly advise you to refuse HIV testing. Because you are as much a layman in it as I am, and perhaps even 10 times more ignorant and naive.
The mystery of the two stripes. How do HIV tests work?
After the release of the famous film Dudya, most HIV service NGOs were overwhelmed by a wave of people wanting to get tested. Including AIDS.CENTER - the flow of clients almost tripled, and people came for testing who had never visited the open space of the foundation at Artplay before.
However, Dud himself was tested in the premises of our foundation, this footage is in the film. He runs a white spatula with a plastic handle over the gums, then presents the result - one strip. “Healthy!”
Due to the great interest of the public, including clients who came to our loft on Nizhnyaya Syromyatnicheskaya, today we are telling you how these and other HIV tests work. Why do stripes appear on the tester’s pen, how reliable and reliable is such testing, and most importantly, what alternatives exist to it.
Everything you wanted to know about HIV testing technology is in one material.
All HIV tests are designed to either look for parts of the virus or to record the body's response to its presence. Therefore, to understand how HIV tests work, you need to have a rough idea of how the virus works and how it behaves once inside a cell.
The HIV virus is a member of the retroviridae family. Representatives of this family look like tiny round particles that have a shell dotted with special proteins. With the help of these proteins, the virus recognizes the victim cell and attaches to it.
Then the membranes of the cell and the virus merge, and the contents of the virus - the nucleocapsid - enter the cell. A nucleocapsid is a protein capsule containing genetic information about the structure of the virus - two copies of double-stranded RNA - and a set of enzymes that “turn on” the RNA once it enters the cell. After the virus merges with the cell, the nucleocapsid opens, RNA and viral enzymes get inside, and the virus itself begins its dirty work.
HIV virion. Reconstruction. Proteins with which the virus attaches to the cell are shown in red.
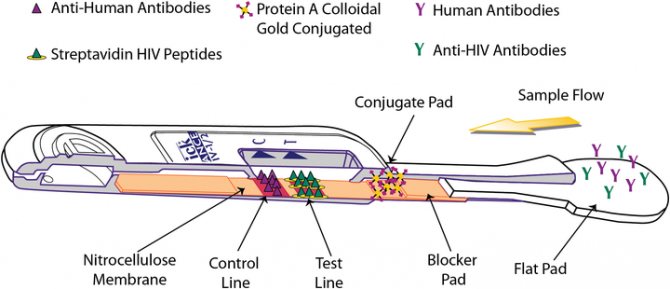
There are a lot of tests for HIV, but they can be divided into several large types. Those rapid tests that most HIV service NGOs use are based on the principle of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, or ELISA.
Their task is to determine the antibodies to HIV that the body produces in response to the penetration of the virus into it.
How it works? When the HIV virus enters the body, the human immune system does not sit idle. It begins to produce antibodies - immune proteins that help the body fight infection. These proteins can be found in many biological fluids.
There are many ways to detect such antibodies. But the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is considered the most popular. Abroad, this test is called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, abbreviated as ELISA.
The principle of ELISA is based on the antigen-antibody reaction. Blood or fluid from the gums (this is not quite saliva) is taken from the person, which may contain antibodies to the HIV virus.
Then a reagent with HIV virus proteins, or rather, antigens, not simple ones, but “modified” ones, is added to it. The antigen used in the reaction differs from a regular viral protein in that a chemical tag is “attached” to it.
While the “labeled” antigens float in the reagent on their own, nothing happens. But if there are antibodies to HIV in the biological fluid, they will combine with “labeled” antigens and give a signal that can be detected by a laboratory assistant or a rapid test. If there are no antibodies to HIV, there will be no signal.
Let us remind you: antibodies are particles that the body produces in response to the presence of a virus in it. Antigens are particles of the virus itself. In this case, modified.
In rapid tests, which are used by the AIDS.CENTER Foundation and many of our other colleagues for free and anonymous testing, antibodies are applied in a thin line to a special surface hidden under the plastic body of the tester.
First, the client dabs away the gingival fluid using a spatula mounted on the end of the tester. And as soon as the liquid is collected, the laboratory assistant lowers the spatula into the reagent, which rises through the tester within 15 minutes, eventually reaching the strip with antigens.
If there were antibodies in the gingival fluid mixed with the reagent, the strip turns red.
As a rule, there is a second stripe on the tester’s handle - a control stripe, it is always painted red. So, as a rule, a negative result (there is no virus in the body) is marked with one strip on the handle of the tester, and a positive result (there is a virus in the body) is marked with two.
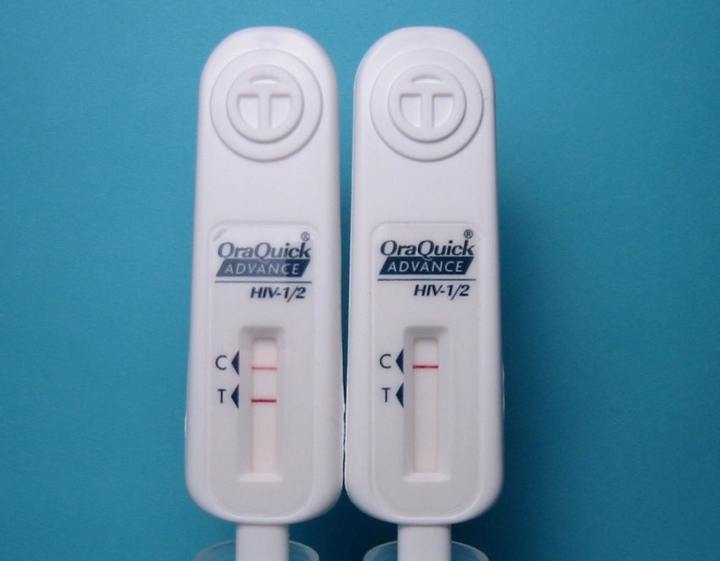
Express HIV testers. On the left is a positive (two stripes), on the right is a negative (one) result.
Two lines on the tester are a sure sign that a person received HIV infection some time ago. Therefore, the client urgently needs to see a doctor for therapy - at a regional or city AIDS center. There he will be given confirmatory tests and prescribed antiretroviral therapy.
Exactly the same test (ELISA), only laboratory, can be done in many commercial clinics - but for money. Its technology generally looks the same, but the accuracy differs slightly.