General blood tests
10/27/201801/25/2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 1536 Views platelets
Platelets are produced in the red bone marrow and their main function is to stop bleeding by forming a blood clot. The lifespan of the cells does not exceed 12 days, after which they are destroyed in the spleen or liver.
When visiting a pediatrician with a child, the doctor must prescribe a set of laboratory tests. The set of standard indicators in a general blood test necessarily includes determining the number of platelets. The fundamental importance of the criterion is due to vital functions, and its deviation from normal values indicates a number of serious pathologies.
- 1 Normal platelet counts in children by age in the table
- 2 Deviations 2.1 Exceeding the norm
- 2.2 Platelets below normal
You need to understand how to properly prepare a child for analysis, what indicator norms exist for children of different ages, and also what their deviation from the norm indicates.
general information
Platelets are elevated in a child, which means thrombocytosis is occurring. This phenomenon contributes to increased thrombus formation.
Based on what exactly provoked the increase in the number of platelets, they distinguish:
- the primary form is the result of abnormalities in the production of blood platelets, for example, when bone marrow tumors grow;
- secondary - thrombocytosis is a sign indicating a certain disease.
Why does it occur

The growth of blood platelets is influenced by the following factors:
- presence of erythremia;
- inhibition of the process of platelet destruction;
- unequal distribution of blood platelets - typical in the presence of overvoltage.
Thrombocytosis can occur in children of any age. We can talk about such a diagnosis when there is a significant increase in platelets. Much more common is a slight excess of the upper limits of the norm.
Secondary thrombocytosis develops against the background of such pathologies:
- ulcerative colitis;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatism (active form);
- osteomyelitis;
- infections, acute and chronic;
- anemia;
- result of spleen removal;
- fractures of bones, in particular tubular bones;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- severe blood loss;
- multiple surgical interventions;
- oncology;
- amyloidosis.
In addition to diseases, the use of certain medications, namely the side effects of these drugs, for example, epinephrine, adrenaline, and corticosteroids, can affect the growth of this indicator.
Why does deviation occur?
Causes of an increased number of platelets in the blood include:
- changes in the rate of production of blood cells by bone marrow tissue;
- slowing platelet breakdown (occurs after removal of the spleen);
- uneven distribution of colorless blood cells during increased physical or emotional stress.
Thrombocytosis can occur in children of any age. A similar diagnosis is made when there is a pronounced change in the number of blood cells. A slight deviation from the norm is more common. Depending on the nature of the provoking factor, the following forms of thrombocytosis are distinguished:
- Clonal. In this case, a defect in the stem cells present in the bone marrow is detected, which means that there is a malignant tumor. Tissues do not respond to endocrine stimulation, which is why the process of maturation of blood platelets gets out of control.
- Primary. Associated with an increase in the volume of certain areas of the red bone marrow. This leads to a change in the number of maturing platelets. The reasons for the increase in the rate are genetic diseases or malignant neoplasms. Deviations can have different degrees of severity - from minor to severe. The properties of blood cells also change. The blood sample contains platelet platelets of large size and atypical shape.
- Secondary. Most often, changes in blood composition are detected after or during an illness.
The causes of secondary thrombocytosis include:
- Splenectomy. After surgery, the process of destruction of old platelets slows down, and new ones continue to arrive at the same speed. In addition, the spleen produces antibodies and humoral factors that inhibit the maturation of colorless blood cells.
- Inflammatory processes. In such diseases, the level of thrombopoietin increases. This indicates an increase in the rate of maturation of cells that help the body fight inflammation. Active compounds with anti-inflammatory effects accelerate platelet production.
- Tumors of the respiratory, lymphatic and excretory systems. A lot of platelets in a child’s blood are found in pulmonary sarcoidosis, lymphogranulomatosis, and nephroma.
- Frequent blood loss. A change in the number of certain blood cells will indicate hidden intestinal and gastric bleeding.
Elevated platelets in the blood of a child over 2 years of age may occur against the background of reactive thrombocythemia. The following reasons contribute to the development of the pathological process:
- infections caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- various forms of anemia (if a child’s blood composition changes, this may indicate a deficiency of iron or vitamin B12);
- acute form of rheumatism;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes of the large intestine;
- osteomyelitis;
- viral and bacterial infections in acute or chronic form;
- fungal and parasitic diseases;
- postoperative complications;
- acute one-time blood loss;
- inflammation of liver tissue;
- amyloidosis;
- oncological diseases;
- long bone fractures.
Secondary thrombocythemia is characterized by a mild excess of the norm. In rare cases, the indicator increases by more than 5 times. The structure and functions of colorless blood elements are not affected.

An increase in platelets may be due to the presence of ulcerative colitis
The growth of blood platelets is influenced by the following factors:
- presence of erythremia;
- inhibition of the process of platelet destruction;
- unequal distribution of blood platelets - typical in the presence of overvoltage.
Thrombocytosis can occur in children of any age. We can talk about such a diagnosis when there is a significant increase in platelets. Much more common is a slight excess of the upper limits of the norm.
Secondary thrombocytosis develops against the background of such pathologies:
- ulcerative colitis;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatism (active form);
- osteomyelitis;
- infections, acute and chronic;
- anemia;
- result of spleen removal;
- fractures of bones, in particular tubular bones;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- severe blood loss;
- multiple surgical interventions;
- oncology;
- amyloidosis.
Characteristic manifestations

The following signs may indicate that a child has thrombocytosis:
- heaviness in the legs, their swelling;
- general weakness;
- cyanosis of lips and limbs;
- dizziness;
- itching;
- painful sensations in the fingers;
- cold extremities.
Diagnostics
If a deviation exceeding the normal limits has been detected for the first time, it is advisable to conduct an additional examination.
- Ultrasound;
- identification of c-reactive protein content;
- determination of ferritin and serum iron levels;
- study of the coagulation system;
- consultation with a hematologist, if necessary;
- If a specialist suspects any pathologies of the circulatory system, he will refer you for a bone marrow test.
What is the danger
- As a result of excess platelets in the blood, the clotting process accelerates.
- Platelet agglutination and vascular blockage are observed. This leads to the formation of blood clots.
- It is necessary to understand that this phenomenon has a serious impact on the functioning of organs. This condition will be especially dangerous if there is blockage of blood vessels leading to the brain or heart. The likelihood of developing a stroke or heart attack increases.
Treatment

- Therapy is determined taking into account the disease, which entailed changes in the quantitative composition of platelets. Then the basis of treatment will be aimed specifically at getting rid of a specific disease.
- If changes in the bone marrow are to blame, medications are prescribed that inhibit the production of new platelets.
- Along with this, blood thinning medications are also prescribed.
Diet food

In a situation where there is a slight increase in platelets, the use of medications is not justified. The doctor will recommend changes to the child's feeding process.
The following foods should be included in the diet:
- fortified with calcium, in particular dairy products;
- high in iodine, such as seafood and seaweed;
- high in iron, such as liver and green apples;
- that affect the blood thinning process, for example, cranberries or ginger.
The following should be excluded from the diet:
- nuts;
- lentils;
- banana;
- grenades.
It is important to consume a sufficient amount of fluid appropriate for the baby's age.
Preventive measures

Before preventing platelet growth, you need to follow certain recommendations.
- You need to consume a sufficient amount of foods containing vitamins and microelements.
- Take enough fluids appropriate for the child's age.
- It is important to maintain a daily routine.
- It is necessary for the child to be outside every day; walks in the fresh air are necessary.
- Great importance should be given to playing sports.
- It is necessary to identify and treat diseases in a timely manner and not allow them to reach an advanced state.
Now you know how to behave if the platelets in your child’s blood are elevated. It is worth understanding that changes in this indicator can affect the baby’s well-being. It is very important to diagnose abnormalities in a timely manner and begin appropriate treatment.
Every conscientious parent cares about the health of their child. The desire to learn more about the results of blood tests and their interpretation is not forbidden, but you need to know when to stop. Below we will discuss the moments when elevated platelets are detected in a child’s blood.
Low platelets in a child: causes
If there are few platelets in a child’s blood, this may be caused by the following factors:
- Decreased platelet production due to problems with bone marrow function (mumps virus, blood cancer, drugs used to suppress tumor growth, radiation therapy).
- Excessive destruction of platelets due to the fact that the body produces antibodies to them, considering them foreign cells. This disease is called idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. You should know that idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura can also occur in adults.
- An enlarged spleen , part of the body's immune system, can lead to low platelets in a child. This usually occurs with pathologies such as liver cirrhosis and hepatitis.
PLATELETS IN A CHILD ARE LOW DOWN
What are platelets
Before you begin deciphering the analysis, it is worth understanding what platelets are. Platelets are blood platelets, the smallest formed elements of blood.
The functions of platelets are very diverse, but their role in the body is to control the performance of blood vessels by releasing various biological substances. The well-known function of platelets is their participation in the blood clotting process. In this case, platelet levels are associated with the formation of bleeding and blood clots.
Conditions in which platelets are elevated in a child
An increased number of platelets in the blood is called thrombocytosis.
The reasons for their increased level may be:
- enhanced hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow , which leads to a high concentration of platelets in the blood and other formed elements;
- high platelet consumption , resulting in a compensatory increase in their number;
- infectious process (tuberculosis);
- taking medications and others.
If platelets are elevated in a child, what does this mean?
Deciphering the analysis results should be done exclusively by a specialist. Independent interpretation of results and prescription of treatment is strictly unacceptable.
It is important to understand that since changes in platelet levels can be caused by many reasons, a diagnosis cannot be made based on just one test.
A physiological increase in platelet levels may occur if the patient:
- ate a heavy meal before taking blood;
- Haven't consumed enough fluids in the last few days;
- afraid of injections, doctors, etc. (against the background of acute emotional stress, an increase in the level of platelet cells in the blood is possible).
In this regard, if an elevated platelet level is detected, a repeat test is carried out to exclude false results.
The results of the study should be interpreted in conjunction with other test results and clinical symptoms. In patients with acute infectious diseases, high platelets in the blood will be combined with high ESR, leukocytosis or lymphocytosis.
In dehydrated patients, a high platelet count will be associated with an increase in red blood cell count, an increase in hematocrit, an increase in total protein, a decrease in urine output, etc.
It should also be noted that errors are possible when automatically determining platelet cell levels. Therefore, if a deviation from the norm is detected, a repeat study is required with manual counting of the number of platelet cells (microscopy of stained smears with counting of platelet cells using the Fonio method).
Low platelet count
A few words should be said about low platelet levels. Low platelet count in the blood – thrombocytopenia. Due to the fact that platelets take part in blood clotting processes, a lack of them in the blood can lead to bleeding.
The reason for a low platelet count in the blood may be, for example, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis as a result of radiotherapy or if there are factors leading to their destruction in the blood. The latter may include autoimmune diseases. There are cases when thrombocytopenia is hereditary, for example, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Bernard-Soulier syndrome .
How to normalize platelet levels in the blood
If the excess or deficiency of platelets is not caused by critical reasons requiring urgent medical intervention, then the balance of these blood cells can be restored at home. The most effective method is to create the right diet.
If there is a lack of platelets, foods rich in vitamins B, K and A, iron, folic acid and taurine will be useful. The list of the daily children's menu must include:
- buckwheat porridge;
- red meat and fish, prepared in any way;
- beef liver;
- hard cheese;
- legumes;
- eggs, especially yolks;
- apples;
- bananas;
- walnuts;
- vegetables and greens, especially white cabbage, spinach, dill and asparagus.
Juices of chokeberry and pomegranate, decoctions of rosehip and nettle will be extremely useful for thrombocytopenia.
Products that thin the blood are contraindicated in case of platelet deficiency. This list includes:
- olive oil;
- some berries, in particular blueberries, raspberries;
- ginger;
- chocolate.
For thrombocytopenia, it is recommended to avoid aspirin.
In case of thrombocytosis, that is, an excess of platelets, you should pay attention to foods rich in antioxidants, iodine and vitamin C, which, on the contrary, contribute to better blood thinning and prevent blood clots. So, on the dining table, at which a child with a high platelet count in the blood sits, there should be:
- tomatoes;
- olive or linseed oil;
- ginger;
- onion and garlic;
- figs;
- citrus;
- chocolate.
Drinks that will be useful are sea buckthorn and orange juices, green tea, and cocoa. In general, if there is an excess of platelets, it is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible - this will help reduce the thickness of the blood.
You should be wary of:
- from fruits and berries - chokeberry, mango, pomegranate, bananas;
- from everyday food - carbohydrate and fatty foods, as well as animal fats.
Do not drink carbonated drinks under any circumstances.
Remember that proper nutrition is not a panacea if the cause of an imbalance of platelets in the child’s blood is due to some serious illness. You should not neglect the consultation and recommendations of your doctor. As for preventive measures, fresh air and physical exercise are what a child should become familiar with in order to have the maximum chance of healthy blood.
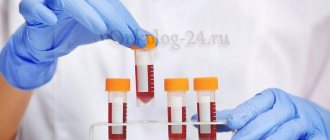
Test to determine the level of platelets in the blood
What tests can be prescribed, including counting platelet levels in the blood? One of these tests is a general clinical blood test. This is a study of the level of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets together. Depending on the equipment the laboratory is equipped with, other blood parameters may be determined.
Sometimes, if the indicators are inadequate or questionable and do not correspond to the clinical picture, a separate study of platelet levels may be prescribed. It is carried out manually, and in this case it is more reliable, as it helps to avoid erroneous readings from the device.
Low platelets in a child's blood: treatment
The decrease in platelets in the blood in children is adjusted based on the causes of the disease. If low platelets in a child are caused by other diseases, then appropriate treatment is prescribed.
For primary thrombocytopenia, bed rest and chilled food are recommended. Treatment methods include:
- Administration of immunoglobulins.
- The use of hormonal drugs with corticosteroids.
- Transfusion of the platelet portion of blood from a donor (consequences of platelet donation).
- Surgeries to remove the spleen (if conservative treatment is ineffective).
In mild stages of the disease, the child may be left outside the hospital.
PLATELETS IN A CHILD ARE LOW DOWN
The basis of treatment in this case is proper nutrition. If a child’s platelets are below normal, then it is necessary to eat foods with a high content of hemoglobin and iron (buckwheat, apples, homemade meat, beets), vitamins A and C, as well as fresh vegetables and fruits.
You should include in your diet:
- Carrot.
- Spinach.
- Parsley.
- Fish.
- Bell pepper.
- Nuts.
How to prepare properly
One of the important components when preparing for a general blood test is the emotional calm of mother and child. Drawing blood is stressful and can lead to fluctuations in your readings, so it’s best to be mentally prepared for it.
Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. But in infants this is difficult to comply with, so it is allowed to donate the material between feedings.
Also, the child’s hands should not be cold. At low temperatures, the capillaries spasm, blood flow slows down, and the procedure may be delayed.
It is important to sit or lay the child down so that he is comfortable.
How much does platelet determination cost in Moscow laboratories?
Determining the number of platelets during a general clinical blood test in laboratories in Moscow will cost you 250-400 rubles; in addition, you may be required to pay money for taking blood. To avoid being deceived, visit the website of a specific medical center. There is almost always a price list there.
You can also additionally request a manual method of platelet counting (according to Fonio). It will cost you somewhere around 200-300 rubles. Some medical centers do not separately conduct manual platelet level testing, only as an additional method. Therefore, you need to be prepared for this.
How to get tested
The level of platelet concentration is determined using a clinical blood test. In childhood, the sample is taken from the finger and vein, in newborns - from the heel. The analysis is carried out routinely once a year. If pathological symptoms are detected in a child, the frequency of testing increases.
The reasons for prescribing an analysis are:
- Bleeding gums;
- Frequent bruising at the slightest blow;
- Nosebleeds;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Pain in the limbs;
- Tumor growth;
- Infections of a viral, bacterial nature;
- Systemic pathologies.
Before taking the test, the child must be prepared to eliminate the risk of unreliable interpretation of the results.
The day before the test and immediately before the test, you should avoid physical and emotional stress, otherwise there will be an increase in the concentration of cells in the blood. A similar effect often occurs when a mother and baby are in a hurry to explore. Upon arrival at the laboratory, it is best to rest for about 15 minutes and calm down.
Some foods also affect platelet concentration: fish, cereals, tomatoes, beets - reduce it, and cabbage, apples, nuts - increase it. Tell the doctor if your child is taking any medications or undergoing physical therapy.
Why are platelets needed?
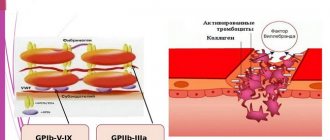
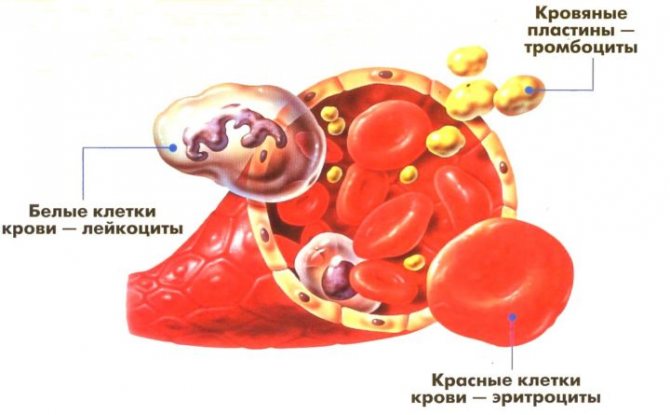
Platelets are the smallest blood cells that are synthesized in the bone marrow and, after maturation, are released into the blood . During the day, their number is not subject to sudden changes, but increases sharply when any tissues of the body are damaged. As soon as the integrity of the vessels is disrupted, they spasm, and a stream of platelets rushes to the site of the breakthrough, which stick to the injured tissues and to each other, after which they adhere tightly, preventing blood from leaving the vessel.
Then the adherent platelets begin to secrete hormones, under the influence of which vasoconstriction accelerates, and the enzyme thrombin is activated. Under its influence, fibrinogen is converted into an insoluble protein, fibrin, the structure of which resembles a network of thin threads with cells that trap nearby red and white blood cells, which leads to the formation of a blood clot.
After some time, the platelets begin to stick together, which leads to a decrease in the blood clot and tightening of the wound. The wound is healing, the clot is dissolving.
Considering that platelet activity is associated with damage to body tissue, an increase or decrease in platelets in the blood of children for no obvious reason is a very alarming bell. Therefore, it is very important to detect the problem in time and find out the cause, for which it is necessary to undergo regular tests (doctors recommend doing this at least once a year, and if possible, more often).
About the normal platelet count in a child’s blood
The number of platelets in the body is constantly changing - these blood cells live only 7-10 days, then they are destroyed in the internal organs (mainly in the spleen and liver), and new ones are produced to replace them. The production of platelets is a constant and continuous process. Some cells are destroyed, new ones appear. Even within one day, the amount of these elements may change, but the difference will be no more than 10%.
The following indicators are the norm:
| Child's age | Blood platelet volume |
| 1-9 days | 100-420x10 to the 9th degree l |
| 10 days | 150-400x10 to the 9th degree l |
| 1 month | 160-400x10 to 9 degrees l |
| 6 months | 180-400x10 to 9 degrees l |
| 1 year | 180-400x10 to 9 degrees l |
| 2-4 years | 180-400x10 to 9 degrees l |
Minor deviations from the norm are possible, but since the permissible range is quite wide, if you go beyond its limits, you should still pay increased attention to the child’s health.
If the baby is in good health and rarely communicates with doctors, for control it is enough to take a CBC test to check the number of platelets in the blood once every six months.
Increased platelet count - thrombocytosis
This phenomenon requires treatment, adjustment of the body’s functioning in order to reduce platelets. Otherwise, the colorless bodies will aggregate into large clots, which slows down the blood flow and also leads to the formation of blood clots. And although blood clots in newborns break off extremely rarely, it is better to try to eliminate the likelihood of this process.
Children are most susceptible to thrombocytosis during periods of active growth and stressful situations.
Obvious symptoms of the disease are:
- A bluish tint to the body.
- Pain in the limbs.
- Bleeding gums.
- Enlarged spleen.
Of course, these symptoms may not be related to thrombocytosis, but if at least one of them is present, it is a priori necessary to take a blood test. There are two types of the disease.
Primary thrombocytosis
Increased platelet counts in infants can be caused by dysfunction of the bone marrow, namely, increased division of the primary (parent) platelet cell. This can be caused by heredity or the degeneration of the parent cell from a platelet into a tumor substance. This phenomenon occurs in the following diseases:
- lymphoma;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- myeloid leukemia;
- erythermia.
Secondary thrombocytosis
Appears when the production of thrombopoietin, an activator of cell division, increases. Or when there has been significant blood loss - in this way the body tries to make up for the platelet deficiency. Secondary thrombocytosis occurs in the following cases:
- infection of the body;
- autoimmune disease;
- injury;
- prolonged bleeding;
- undergone surgery;
- splenectomy;
- chronic kidney disease;
- osteomyelitis;
- tuberculosis;
- anemia (lack of iron in the body);
- hemolysis (excessive breakdown of red blood cells).
Elevated platelets in an infant without an obvious reason require additional research to understand why their number has increased and what this can lead to. It is necessary to treat not only the consequence (which is thrombocytosis), but also the root cause - otherwise the effect on the body will not be effective.
Treatment of thrombocytosis is complex. It consists of taking medications that stabilize hematopoiesis, as well as a balanced diet dominated by dairy products, red meat, red fruits and vegetables, and sea fish. Nuts and seafood are also recommended for adults, but such components are not recommended on the menu for children in their first year of life due to increased allergenicity. It is also necessary to take multivitamin complexes, in which B vitamins predominate.
Why is deviation dangerous?
The platelet rate in an infant's blood differs from that of babies over one year of age. Therefore, the number of blood platelets in a healthy child is:
- up to 10 days: from 100 to 420 x 10 9 cells per liter of blood;
- up to 1 year: from 150 to 350 x 10 9 cells per liter of blood
- from 1 year and older: from 180 to 320 x 10 9 cells per liter of blood.
If there are too many platelets in the blood of children, they collide with each other, other cells, and the walls of blood vessels, which leads to activation of the blood clotting process. As a result, blood clots form inside the vessels, which can clog large or small arteries, veins, and capillaries. If this happens, there is a blockage in the flow of blood to the tissues in the area that feeds the vessel, which leads to tissue necrosis and can even cause death (fortunately, this type of event occurs much less frequently in children than in adults).
Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the symptoms characteristic of high platelet counts and consult a doctor. These include:
- bleeding without obvious reasons of various types: from the nose, gums, etc.;
- streaks of blood may be observed in the stool;
- itching, puffiness, bluishness of the skin, bruising;
- dizziness;
- the baby becomes lethargic and mentions feeling weak;
- The child complains of numbness in the feet, hands, and pain in the fingertips.
A platelet level below normal is no less dangerous, since it causes wounds to take a long time to heal and bleed, which is very dangerous for both external and internal bleeding. With a low platelet count in children, bleeding is also observed, and bruises or red subcutaneous spots often appear on the skin. Urine becomes red, brown or pink, stool becomes black and sometimes bloody. The child is vomiting and his vision is deteriorating.
Often, when platelet counts are low or high in children, only some of these signs are observed. That is why you should not wait for all the symptoms characteristic of platelet level deviations from the norm to appear, since this may indicate a very advanced case, and consult a doctor if at least one of them appears.
Normal platelet count in children's blood
The normal platelet count in children varies depending on age, lifestyle, heredity and environmental risk factors. Parents need to carefully monitor the indicators and periodically visit the diagnostic room for a general blood test.
Platelets perform three main functions in the human body: they promote blood clotting, strengthen the walls of blood vessels with nutrients, and are a criterion for the resistance of the immune system to external irritants.
The rate of platelets in a child’s blood varies depending on various factors, among which heredity and the course of pregnancy take priority.
Table of platelet norms in children.
| Age | Normal, 10^9/l |
| Infant (up to 10 days) | 100-420 |
| Children under 1 year | 150-350 |
| Children from 1 year to 12 years | 160-300 |
| Teens and adults | 180-320 |
A reduced level indicates the initial stage of development of hemophilia, the consequences of which are dangerous for the child’s health due to uncontrolled hemorrhages and bleeding. The symptoms of a disorder in the body are extremely simple.
If bruises or bruises appear on the baby’s body after the slightest touch, the capillary network is clearly visible and poor blood clotting is observed after a small cut, you should immediately seek help from your doctor.
He will prescribe intensive therapy using the pharmacological drug immunoglobulin and identify the cause of the disease through a series of studies and appropriate procedures.
The causes of the pathology are the following factors:
- Abuse of incompatible pharmacological drugs: analgesics, histamines or antibiotics.
- Congenital pathology caused by placental abruption during childbirth or the unhealthy lifestyle of the mother during pregnancy.
- Unbalanced diet, lack of the vitamin and mineral complex necessary for health, which is included in vegetables and fruits.
- Chronic allergies to external irritants and untimely treatment.
- Infectious diseases that suppress the immune system in the body, which are provoked by various strains of viruses. Their untimely treatment.
Platelets serve as a kind of barrier that prevents external or internal bleeding. In addition, they “feed” the walls of blood vessels with nutrients, which helps strengthen them and ensures constant blood circulation throughout the circulatory system. Platelets are renewed after 7-10 days. Any changes may lead to irreversible consequences. Also, a low level of blood platelets is more often characteristic of premature or post-term babies who were born with extremely low birth weight.
Elevated platelets in a child’s blood can cause blockage of blood vessels and interfere with blood circulation in the body, which causes blood clots that cause swelling of the extremities, narrowing of blood vessels, coronary heart disease and heart attacks.
Blood clots block the circulatory system and veins of internal organs. In addition, an increased concentration of platelets can be detected with the rapid development of myelogenous leukemia.
Reasons for the increased level:
- consequences of meningitis, pneumonia, hepatitis of various categories, viral infections, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stressful situations that provoke physiological changes and the formation of pathological conditions;
- previous operations;
- lack of iron in the blood.
The rate of platelets in the blood of children depends on factors that are divided into two groups: primary (congenital thrombocytosis) and secondary (acquired thrombocytosis). Primary risk factors include heredity, pathology during fetal development or childbirth, and secondary risk factors are caused by past diseases.
An increased concentration of blood platelets causes blockage of blood vessels, and a deficiency causes hemorrhage or bleeding of internal organs and the development of hemophilia.
1 Comment
Causes and importance of treatment
The following reasons can affect the increase in the number of platelets in the blood of children:
- external or internal trauma;
- fracture of tubular bones;
- surgery;
- splenectomy;
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs, primarily the hematopoietic system;
- liver diseases;
- hepatitis;
- tuberculosis, pneumonia;
- abscess;
- rheumatism;
- treatment with corticosteroids;
- leukemia
A platelet level below normal is observed in infants if their growth at birth was 35% below normal. A low number of blood platelets can occur if the mother and child have an incompatibility regarding the Rh factor (the mother is negative), which is why antibodies from the mother’s body pass into the baby’s blood. The reason why there is a decrease in platelets may be anemia, allergies, infectious or viral diseases and other factors.

Thus, deviations of platelets from the norm in children can provoke diseases of a very different nature, from a common infection to tuberculosis and blood cancer. Therefore, it is very important to determine the cause in time and prescribe treatment aimed at curing the underlying disease. Otherwise, the number of platelets in the blood will not be reduced or raised. To do this, the doctor, based on the blood tests obtained and the symptoms accompanying the disease, prescribes additional examinations.
In addition to taking medication, you need to pay attention to the child’s nutrition: the diet should include greens, vegetables, fruits, juices, compotes, and herbal tea. You should reduce your baby’s intake of high-calorie foods, sugar, and fats. Seafood will be useful; it is better to season salads with vegetable oil.
You should also pay attention to the child’s lifestyle, especially if he doesn’t move much. You need to take him for walks in the fresh air more often, play outdoor games, if your health allows, and take time to exercise. This will strengthen the immune system and normalize blood flow.
Normal platelet count in a child’s blood: table by age
11.08.2018
Good day, dear readers. Today we will talk about what the normal platelet count is in children. You will find out when diagnostic tests may be ordered. Find out how to prepare for the analysis and how the result is assessed. Let's talk about the normal indicators depending on the baby's age and about deviations from it.
general information
Platelets are also called platelets of blood. These cells occupy up to 75% of the bloodstream. Fluctuations in platelets are possible throughout the day, but they should not exceed 10%. If the deviation is stronger, then it is likely that there is a pathological process in the body, deviations in the functioning of internal organs.
The function performed by platelets is the formation of blood clots during wounds in order to prevent blood loss, as well as participation in coagulation processes. The main functions include:
- participation in the process of cell division;
- ensuring contraction of vessel walls;
- adhesion;
- production of proteins necessary for coagulation and blood clot formation;
- transfer of immune complexes, attachment to the cell membrane;
- restoration of damaged blood vessels.
Platelets are produced continuously. Cells of different ages can be present in the bloodstream at the same time. Most of the functions come to the share of mature platelets.
If the baby has no complaints, then this study may be planned. An unscheduled test is prescribed if the child has:
- nosebleeds occur occasionally;
- bleeding gums occur;
- after a cut, the blood does not clot for a long time;
- bruises often appear;
- painful sensations in the limbs;
- constant fatigue.
The child will definitely be sent for a blood test to determine his platelet level if he:
- enlarged spleen;
- a systemic disease has been diagnosed;
- leukemia;
- viral infection;
- anemia.
Preparation before analysis
The study may be influenced by certain circumstances
Therefore, it is important to know what rules need to be followed before taking a general blood test.
The test must be taken on an empty stomach. For children over seven years old, you need to refrain from eating for 12 hours, for children under seven - for eight hours.
An infant is allowed to go two hours without food. It is important that there is no physical or emotional stress before the actual test. Properly selected clothing is of particular importance so that the baby does not become overcooled. It is not recommended to go for testing immediately after the child enters the clinic; he must first rest, calm his breathing and heart rate. If the baby is taking any medications or has already been prescribed a certain treatment, then before taking the test it is necessary to inform about this, since some medications can affect the platelet count. The biomaterial should be taken in the morning, two hours or an hour after waking up. It is not recommended to eat or drink before the test. Very young children are allowed to drink some regular drinking water. A couple of days before the test, you need to limit your baby’s physical activity.
If the child is already attending school, then he must be exempted from physical education for this period.
Evaluating the result
It must be taken into account that there are circumstances that can affect the number of blood platelets in the blood:
- the age of the baby, newborns have the highest number of platelets in the blood, in infants this figure is higher than in children of the second year of life and older;
- from taking medications;
- the presence of certain diseases;
- the platelet count deviates from the norm with a certain type of diet - some foods can affect the increase or decrease in the level of platelet cells;
- time of year and day - platelet deviation can vary within 10%.
Deviation from the norm
- develops when there are disturbances in the synthesis of new platelets;
- is the result of various infections, tumors, chronic diseases and excessive physical activity.
How to normalize platelet levels
- different types of nuts;
- vegetables, especially beets, various types of cabbage and carrots;
- dog-rose fruit;
- boiled fish;
- grenades;
- liver;
- bananas;
- boiled meat;
- buckwheat porridge.
- garlic;
- lemon;
- onion;
- sea buckthorn;
- tomatoes;
- flaxseed or olive oil;
- ginger.