Which method of diagnosing appendicitis in children to choose: MRI, CT, ultrasound
What will an abdominal ultrasound show if appendicitis is suspected?
- Selection method
- Sensitivity - 90%, specificity - 95%
- Longitudinal image demonstrates a tubular structure with thickened walls, sometimes with fluid accumulation in the lumen
- Abnormal non-compressible target sign with axial diameter greater than 6 mm (unreliable sign in patients with cystic fibrosis)
- Significant pain when pressing with the sensor
- Increased echogenicity of adjacent mesenteric fatty tissue (due to edema)
- Free fluid in the immediate vicinity of the appendix (early sign) or in the pouch of Douglas (after perforation)
- Appendiceal stones may be detected
- Enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes
- Signs after perforation may only include the presence of a soft tissue mass with unclear contours.
Pericecal abscess:
- Common locations include the area adjacent to the ascending colon, the ileocecal region, posterior to the bladder, the subhepatic region (Morrison's pouch), the right subdiaphragmatic region, and the interintestinal space.
Why is ultrasound with colorectal dosage performed for inflammation of the vermiform appendix?
- Increased vascularization due to inflammatory hyperperfusion.
What will an abdominal x-ray show?
- Usually not required
- May exclude the presence of free gas in the abdominal cavity
- Left positional bending of the lumbar spine
- If there is an abscess in the lower abdomen, there may be a level of fluid or gas
- Obliteration of the shadow of the right lumbar muscle
- In the presence of peritonitis - signs of paralytic intestinal obstruction.
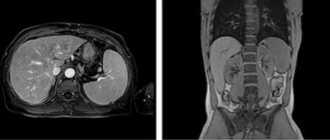
What will CT images of the abdominal cavity show for appendicitis in children?
- Provides assistance if there are doubts when using other research methods
- Intravenous, oral and rectal administration of contrast agent
- Thickening of the wall of the appendix
- Inflammatory damage to the surrounding adipose tissue and adjacent intestinal loops (small intestine and sigmoid colon)
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Visualization of the abscess.
Appendicitis. Ultrasound scanning of the right lower abdominal cavity. A typical sign of a “target” on longitudinal (a) and transverse (b) scanning, including a vermiform appendix filled with fluid and having a thickened wall. Adjacent adipose tissue of the mesentery with signs of inflammatory changes and edema (M). The accumulation of fluid in adjacent tissues indicates the formation of a pericecal abscess
Ultrasound diagnosis of appendicitis
Acute abdominal pain can be caused by various pathological changes in the abdominal cavity. One of them is inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis). Its course is usually transient and therefore immediate diagnosis is indicated. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is considered an effective way to diagnose appendicitis.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix using the ultrasound method
For patients and their relatives, the answer to the question is quite important: is the ultrasound method effective in diagnosing inflammation of the appendix, and will there be a need for additional diagnostic studies? In answer to the question, we note that the diagnostic accuracy when using this technique reaches 90 percent. Moreover, with the ultrasound method, the patient is not exposed to harmful radiation as, for example, with MRI, which is extremely contraindicated for children, pregnant women and women of childbearing age. The area of study includes exactly the area of the abdominal cavity that caused concern to the patient. A true picture of the condition of the organs located in the abdominal cavity is established almost simultaneously with the time of research. We should not forget about the relatively low cost of the ultrasound method compared to others.
Diagnostic procedure
The patient does not need additional preparation for ultrasound when diagnosing inflammation of the appendix. Diagnosis is made by external examination of the abdominal cavity using an abdominal sensor with gentle pressure on the appendix area. Objective signs of inflammation of the appendix are: - an increase in the intestinal walls by a thickness of more than 3 mm; - an increase in the diameter of the appendix by more than 7 mm; — establishment of echogenicity; - inflamed omentum.
To determine the location of the appendix, the doctor uses the ultrasound method to focus on the position of other organs, for example, at the end of the cecum, since the appendix originates from it. The success of using the method for making a diagnosis is directly dependent on the anatomical characteristics of the person and the clinical picture of the organs adjacent to the appendix. It is difficult to diagnose appendicitis using ultrasound in women with ruptured ovarian cysts and ectopic pregnancy. Signs of bloating and excess weight may also affect the test result.
For appendicitis, which is a serious disease, immediate surgery is indicated. It must be preceded by a good medical history and a benign diagnosis. If you experience abdominal pain, you should contact our center as soon as possible. Highly qualified specialists will diagnose appendicitis (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity) and your health will be out of danger.
Clinical manifestations
Typical symptoms:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Nonspecific gastrointestinal symptoms
- Soreness and tension in the right lower abdomen, pain on percussion, pain when released after pressure (Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom)
- Fever
- Leukocytosis
- Increased C-reactive protein levels
- The younger the patient is, the less characteristic symptoms can be identified.
What can appendicitis in children be confused with?
Mesenteric lymphadenitis
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- thickening of the walls of the small intestine with a small amount of free fluid between the intestinal loops and in the pouch of Douglas.
Crohn's disease
- usually a typical medical history;
— clinical course;
- predisposition to development in the final sections of the ileum.
Lymphoma
- may occur as a primary lesion of the intestinal wall (MALT lymphoma);
- enlargement of mesenteric and retroperitoneal lymph nodes.
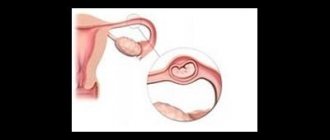
Torsion of ovarian
- hemorrhage and typical sedimentation may occur;
- located next to the uterine appendages;
- The intestines are usually normal.
Intussusception
— typical ultrasound morphology and clinical features.
Inflammation of Meckel's diverticulum
- clinically indistinguishable;
- usually not detected during ultrasound scanning when covered with gas.
There is no arguing with appendicitis. How not to miss the first symptoms of the disease
120 symptoms
“Acute appendicitis is an insidious disease,” says Alexey Prikhodko .
– Start with the same clinical picture. A third of cases do not correspond to canonical ideas about the development of the disease. The pain can radiate to the right hypochondrium, lower back, and the symptoms resemble renal colic, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis. Even a specialized examination does not guarantee an accurate diagnosis. For example, a general blood test will reveal a large number of leukocytes. But growth is characteristic of other inflammatory diseases. And ultrasound is not always informative. The pathology of the appendix is noticeable only in already destructive forms of acute appendicitis - infiltrate, abscess or peritonitis.”
— I once read that surgeons described a total of 120 symptoms of appendicitis. - And the list is open. I will not exaggerate if I say: any surgeon, if he wanted, could apply for a patent by describing a symptom from his practice. Appendicitis in its manifestations is actually diverse.
— And how do doctors deal with the situation in practice?
“There is a catchphrase: “In the right iliac fossa - this is the location of the appendix - more than one outstanding professor has been lost.” As they say, there is some truth in every joke. This is why you should never try to diagnose yourself. If you suspect acute appendicitis, you should call an ambulance. You don't even need to go to the clinic. Because the clinic surgeon, no matter how highly qualified a specialist he is, I think, does not see appendicitis on the fly. And experience is extremely important here.
There is no such thing as without a scar
— Classic surgery to remove the appendix leaves a characteristic scar in the lower abdomen. But can medicine offer a modern option for appendectomy?
— Do you mean laparoscopy ? Yes, this is a minimally invasive intervention. But also an operation! And there is still no consensus on laparoscopy. Although it is considered a low-traumatic technique, it is also associated with general anesthesia and penetration into the abdominal cavity. During laparoscopy, one way or another, two, usually even three, instruments are inserted. And these are three cuts of 1.5 cm each. If you add them into a common line, you get almost 5 cm.
But there is no clear conclusion that laparoscopic surgery is more gentle than conventional surgery. There is another strict rule: any case of diagnosed acute appendicitis must be operated on. Because there is no conservative way to treat this disease. By the way, according to statistics, every year the incidence of acute appendicitis is 4–5 people per thousand of the population.
“But scars can be small and neat, but they can be large and ugly.” Does it depend on the professionalism of the surgeon?
— If appendicitis proceeds typically, if the patient seeks help on time , a small incision is sufficient, from which an adequate operation can be performed. But the appearance of the incision is not even a matter of length or suture technique. This is, if you like, a minor point. Whether the scar will be small and invisible depends on the person, on the reactivity of his immune system, and his ability to regenerate.
There are patients in whom a 2–3 cm incision forms into a rough, dense, protruding scar. And there's nothing you can do about it. This is a feature of fabrics. Even plastic is powerless. The grinding technique and creams will not lead to anything drastic.
shutterstock.com
Prevention is harmful
- Or perhaps this: the surgeon cuts the abdominal cavity, but does not detect inflammation of the appendix. He sews it up so that the appendix remains.
— By default, it is assumed that if the incision is made, the operation must take place. Imagine a situation where, hypothetically, a person’s appendix was not cut out, but he has a characteristic scar, and forgot about the nuances of the operation. The doctor sees the scar and rules out appendicitis, but... In short, “cut - not remove - and sew up” - there is no such option in our arsenal.
- It's clear. But the vermiform appendix is still not superfluous in the human body?
— Many millions of years ago, our ancestors were content with plant foods. Over the long years of evolution, human nutrition has changed greatly; Although the appendix is part of the gastrointestinal tract, it has not taken part in the digestion process for a long time. From this point of view, the process was included in the rudimentary organ.
By the way, at the beginning of the twentieth century, scientists in one fell swoop condemned about 180 organs and anatomical structures as useless. Including - tonsils , spleen , thymus gland . The “innovators” went into such a frenzy, if I may say so, that at the beginning of the last century, when the cause-and-effect relationship between the appendix and acute purulent inflammation was proven, in the USA and Germany they performed universal appendectomies in one-month-old children. For prevention purposes. But this did not lead to anything good. Life showed: after the operation, the babies were unable to digest mother's milk, grew up with weakened immunity, and a high predisposition to colds. They were lagging behind in development – physical and intellectual. The experiment was over. Prevention has stopped.
You are not doomed
— Because there is nothing superfluous in nature?
— The vermiform appendix consists of lymphoid tissue. The organs of the human immune system consist of such tissue. The appendix is an incubator, a farm, a depot where beneficial microorganisms multiply and are stored. When conditionally pathogenic microflora is activated, the number of beneficial bacteria decreases sharply. But in the autonomously located appendix they remain and, if something happens, they rush together to move to the intestines. They work no worse than any Linux.
But this does not mean that people without appendicitis are doomed. Under no circumstances should you wring your hands: “Oh God, how can I live! I’ve been without an appendix for ten years and that’s why I’m constantly sick!” I have never seen statistics from significant studies that talk about such a relationship.
— Who is at risk?
— According to monitoring data, among the sick there are more young people from 20 to 40 years old. Women get sick more often than men . But this does not mean that a person overcomes some age limit and sighs with relief: “Well, it’s gone!”
In fact, each of us can get sick. Statistics show up in big numbers. The causes of acute appendix have not been established. There are versions, theories, assumptions. And no more. Therefore, one piece of advice can be given: lead a healthy lifestyle.
How to avoid appendicitis:
- do not trigger inflammatory processes in the body;
- You should not take medications, especially antibiotics, without a doctor’s prescription;
- physical activity is important for normal blood circulation in the abdominal organs;
- reduce the consumption of fatty and fried foods, smoked meats, nuts, seeds, especially with skins;
- Get regular medical checkups.