There are a large number of medical techniques that gastroenterologists use to examine patients in order to establish the correct diagnosis for abnormal manifestations.
Each diagnostic technique has advantages and disadvantages. Only your doctor can choose the most suitable procedure for you. Today, magnetic resonance imaging is in great demand - a safe, painless, non-invasive and highly accurate examination of internal structures. The clinical device is capable of visualizing the structure of neoplasms, disruptions in the functioning of development, formed cysts or polyps, the course of inflammatory reactions, ulcerative and erosive manifestations localized in the mucous area. The scan is designed to detect the level of the lesion and the severity of the abnormality.
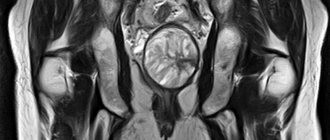
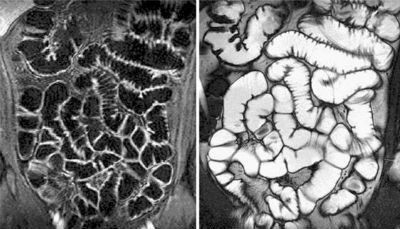
MRI of the intestine ranks first in terms of information content in comparison with other testing options. Colonoscopy is considered a fairly common technology for checking the intestines - an invasive medical examination that involves pronounced discomfort for the patient. It is not prescribed to persons suffering from hernia, hemorrhage, obstruction, or severe pain syndrome. As a result, magnetic assessment of the condition is the most acceptable, since it does not have a toxic effect on the patient, unlike computed tomography or radiography.
When is it recommended to do an MRI of the intestines?
The diagnosis is prescribed by the attending physician, after collecting all the information from the clinical examination and laboratory tests to confirm the conclusion. Magnetic resonance imaging may be performed before or after surgery to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Doctors write a referral if the patient has complaints about:
- Regular pain in the abdominal area.
- Gas formation.
- Difficulty with bowel movements.
- Diarrhea.
- Change in color of stool.
- Nausea.
- Gag reflexes.
- Particles of blood cells in secretions.
Patients with the following indications should undergo the study:
- Determination of the location and shape of the neoplasm with the likelihood of cancer progression.
- Detection of congenital anomalies, developmental disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification of the bleeding factor.
- Presence of sources of inflammatory reaction.
- Obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract of various nature.
Which authorities check?
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to determine pathologies of the structures of the digestive tract. The following internal organs are visualized:
- Pancreas.
- Spleen.
- Liver.
- Stomach.
- Gallbladder.
- Various parts of the intestine.
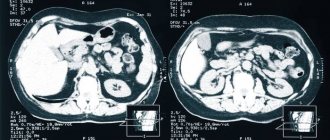
Despite its high information content, tomography allows one to evaluate only the structural features of the digestive tract. The study makes it possible to diagnose the disease or confirm the doctor’s suspicions. However, to obtain more information about the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract structures, additional diagnostics may be required. For example, scintigraphy, studying the functioning of organs after the administration of a radioisotope drug, etc. The choice of examination tactics is decided by the doctor after assessing the situation.
What diseases does MRI of the small intestine detect?
When studying the data obtained after the scan is completed, the following deviations from the norm can be found:
- Formation of benign neoplasms (adenomatous polyps, lipomas, fibromas).
- Formation of tumors of malignant origin (mesothelioma, colloid or undifferentiated cancer).
- The process of metastasis in the gastrointestinal tract, lymph nodes (usually they appear when the ovary, uterus, pancreas are affected).
- Protrusion of the walls of the sigmoid structure.
- Crohn's disease.
- Ulcerative colitis of a nonspecific nature.
- Inflammatory reactions caused by complications of ongoing gastrointestinal abnormalities, abscesses, peritonitis.
- Hemorrhages, formation of ulcers and erosions.
- Damage.
- Presence of foreign objects.
- Thrombosis of large vessels.
- Formation of adhesions.
The most detailed images are obtained when undergoing double contrast during an MRI of the intestine. The cost of such a scan is quite high, but the information obtained is of significant value to doctors. Recorded deformities help establish a diagnosis, understand the stage of the disease, predict possible complications and draw up a tactical pharmacological or surgical treatment plan.
Magnetic resonance method for diagnosing the gastrointestinal tract
The magnetic tomography method is one of the safest diagnostic methods and does not cause side or long-term reactions. The parameters of the magnetic field created during the operation of the tomograph are within acceptable values for humans.
The reasons why an intestinal MRI may not be suitable for a person are cost, expediency in making a diagnosis, as well as contraindications. It is unacceptable to perform tomography on people with foreign metal objects inside the body (fragments, bullets, knitting needles, pins, plates), stimulators and pacemakers (pacemakers, neurostimulators).
What does MRI of the stomach and intestines show?
If it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis in controversial cases, an MRI of the intestine is performed to assess the condition of the organs before surgery, monitor the treatment provided, as well as the ineffectiveness of other research options. Moscow has a wide network of clinics where you can undergo this examination.
What can be seen in tomography images:
- Features of the shape and size of the gastric organs.
- Signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Anomalies in the development of the esophagus, partial narrowing of the lumen, obstruction of patency.
- Foreign bodies, injuries, bleeding, acute appendicitis, proctitis, gastritis.
- Benign neoplasms (lipoma, hemangioma, fibroma, neurogenic mediastinal tumors, leiomyoma).
- Malignant neoplasms (lymphoma, carcinoid, gastrointestinal tumors).
- Localization and prevalence of metastases of cancer processes.
- Condition of large vessels, including the veins of the esophagus, disorders of the blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract (ischemia), lymph nodes.
- Crohn's disease, celiac disease, infectious lesions, abscesses, polyps, hematomas, diverticulitis.
What to choose: MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy
It is impossible to say for sure which is better: MRI of the intestines or colonoscopy. Each method has its own advantages in diagnosis depending on individual tasks.
Unlike tomography, colonoscopy is an invasive method associated with side effects: the possibility of organ damage, bleeding, and gastrointestinal infection. At the same time, colonoscopy is performed using a fiber colonoscope equipped with a video camera, with the ability to take material for a biopsy or perform minor operations (removal of polyps, cauterization of the walls).
Magnetic resonance diagnostics in this case acts solely as a visualization method, after which a colonoscopy can be prescribed, which combines the functions of accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The choice of examination option (MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy) is made by the attending physician, based on the clinical picture, contraindications and missing information in making a diagnosis.
Contraindications to an MRI examination of the intestine
An MRI of the intestine in Moscow is possible only if there are no restrictions. During testing, the patient's body begins to interact with a powerful level of magnetic vibrations, which affect products made of metal alloys and electronic devices. They begin to gradually heat up, move and, as a result, lose the ability to function stably. Doctors categorically prohibit people with metal structures inside their bodies from undergoing scanning: pacemakers, bullets, shrapnel, insulin pumps, etc. Immediately before undergoing the examination, you will need to consult with your doctor to clarify what the implanted item consists of (information can be found in the certificate). Sometimes, such inserts contain different materials that do not affect the magnetic tomograph in any way.
Relative restrictions include:
- Carrying a child in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Pronounced signs of claustrophobia.
- Age contraindication: children under 7 years of age.
- Obesity - the patient's body weight exceeds 120 kg.
The final decision rests with the medical professional, who relies on the available evidence. In cases where the final results will play a significant role in setting the conclusion and drawing up therapeutic manipulations, a magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed even if there is a specific risk. However, the contrast agent is not administered to patients with renal or liver failure, pregnant or nursing mothers.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast
- Installed pacemakers and other electronic devices whose operation may be disrupted during the procedure.
- The presence of metal prostheses in the body, except titanium.
- Pregnancy. Since contrast agents can cross the placenta, their use during this period is undesirable.
- Allergic reaction to contrast.
- Severe kidney damage. Gadolinium salts are excreted through the urinary system, so the study is not carried out in case of serious renal damage. Minor abnormalities in kidney function are not contraindications.
There are also relative contraindications, in which the possibility of performing the procedure is determined by the doctor depending on the area of study and other factors:
- The presence of non-magnetic implants, braces, tattoos with metal-containing inks, permanent piercings.
- The patient’s serious condition, in which it is difficult for him to remain motionless for a long time, mental illness, claustrophobia - fear of closed spaces. In this case, the procedure is carried out after the use of sedatives or sleeping pills.
Preparing for MRI of the small and large intestine
Detailed and highly accurate images can be obtained if the rules are followed. The patient will need to adhere to dietary restrictions for several days before the scheduled session. Before starting to introduce an additional amplifier, there should be no accumulations in the gastrointestinal tract. This indication helps prevent the appearance of interference that would significantly interfere with the study. In case of incorrect preparatory measures, the diagnostician prescribes a repeat test. Preparation consists of the following procedures:
- Following a low-carbohydrate diet a couple of days before the start of the diagnosis.
- Elimination of products that cause increased gas formation.
- In the evening before taking it, you will need to cleanse the body using an enema or pharmacological drugs with a laxative effect.
- It is recommended to use activated carbon to bind and remove remaining gases from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is mandatory.
- A visit to the doctor should be on an empty stomach.
- Half an hour before the procedure, you need to take a medicinal substance (antispasmodic) to relax the walls and ensure immobility.
- Once in the office with the device installed, you will need to remove all metal accessories (it is advised not to use makeup products).
- The patient undergoes examination in a medical gown, which is supplied to them by the staff of the medical center.
How is the intestine diagnosed using MRI?
An MRI of the intestine, the cost of which can be found on the search portal mrt-v-msk-ru, takes place in a room with an installed tomograph. The diagnostician controls the analysis and operates the device through a glass barrier. The subject is accompanied by an assistant and helps him take a comfortable horizontal position on a mobile couch. If necessary, a contrast agent is administered intravenously. The average diagnostic time is 40 minutes. In the device tunnel, the patient can hear noise that accompanies the operation of the tomograph, or feel a surge of heat in the area affected by the magnetic field. If questions or discomfort arise, the patient will be able to contact the doctor via two-way communication pre-installed in the equipment. There is a ventilation system inside.
Hydro-MRI of the small and large intestine
To obtain a highly accurate image, tomography is performed using double contrast. Before an MRI of the intestine in Moscow, the addresses of the centers can be found on the website mrt-v-msk.ru. Half an hour before testing, the subject is asked to take about one and a half liters of a solution containing active components. The substance is able to reach the necessary sections, fill their lumens, straighten the folds of the mucous membrane, which increases the detail of the body structure. Immediately before the scan begins, a second amplifier is administered to the patient. A special role is played by complete immobility during diagnosis and correct implementation of all instructions of the diagnostician. All pharmacological agents used do not pose a health hazard and are eliminated from the body within 48 hours.
What does the examination reveal?
MRI of the small intestine reveals:
- internal bleeding;
- areas of irritation and swelling;
- abscesses, which are pus-filled pockets in the intestinal wall;
- blockages.
MRI enterography allows for a detailed examination and detection of diseases, anomalies and defects in the early stages. The image can be viewed on a computer monitor. Images can also be recorded onto the patient's digital media or sent by email.
MRI results of the small intestine
The price of an MRI of the intestine in Moscow usually depends on the form in which the person receives the final information. The most accessible way is to transfer pictures by email or dump data onto a portable drive. It will cost more to print an image on wide-format film or dump information onto a USB flash drive. All results are provided 24 hours after the end of the study. The area is checked layer by layer, obtaining thin-section images that help model the model in three-dimensional projection. The images show the thickness of the walls, the presence of swelling, injuries to the mucous area, determine the extent of the spread of the affected areas, the depth of penetration of the disorder and the level of involvement of nearby areas. You can find out the addresses and prices of intestinal MRI in Moscow on the search service mrt-v-msk.ru. The portal contains more than a hundred offers from medical centers located in different areas of the capital. After receiving the report, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist to decipher the answer.
Where to get an MRI of the intestines?
You can select a clinic based on the patient’s capabilities and needs, the level of the tomograph and the qualifications of the organization’s employees. On the site you will find information with current promotional offers and discount coupons to make an MRI of the intestine profitable. We have fixed discounts that are provided to university students, people of retirement age, people with disabilities, and temporary promotions that can be found on the portal. For patients weighing more than 120 kilograms, our managers will select medical centers equipped with open-type tomographs or that can withstand a load of up to 180 kg. To fill out an online application for an appointment at a capital clinic: fill out a short form, provide contact information, select the desired time of day and day of the week for diagnostics.
The text was checked by the doctor Mikhail Mikhailovich Motov
Therapist
Indications for the procedure
A specialist of almost any profile can prescribe a diagnostic procedure, since the procedure helps make a diagnosis for many pathologies. There are the following indications for diagnostics using MRI:
- Brain diseases: if a stroke is suspected; neoplasms and their relapses; assessment of the condition after surgery; demyelinating disorders (multiple sclerosis); inflammatory processes; congenital features of the development of the craniovertebral zone; convulsive readiness and epilepsy; DEP (dyscirculatory encephalopathy); hypertension of unknown origin; metastatic foci; traumatic brain injury (if the injury is not recent).
- Cervical vessels and cerebral vessels: anomalies in the development of the vascular bundle; aneurysms; signs of vertebrobasilar insufficiency due to cervical osteochondrosis; vascular stenosis (narrowing); migraine pain.
- Diseases of the temporal and jaw joints, their discs; preparation for dental prosthetics.
- Problems with the eye orbits and extraocular muscles.
- Diseases and inflammation of the lacrimal glands.
- Problems with the paranasal sinuses: cysts, sinusitis, preparation for surgery.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland (including oncology).
- Spinal column and spinal cord: osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, injuries, etc.
- Osteoarticular system: rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory, traumatic lesions, conditions after surgery.
- Organs of the thoracic cavity: lung tumors, mediastinum, myocardial infarction, coronary angiography, pleurisy.
- Organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space: problems with the liver, pancreas, gall bladder, intestines, spleen, kidneys.
- Pelvic organs: diseases of the bladder, prostate gland, ureters, uterus, etc.