Pediatric ENT
Prevention and treatment of ENT diseases in children
is one of the main activities of our clinic. The clinic is adapted to receive the youngest patients; modern medical equipment is equipped with special means for providing medical care to children (for example, special children's attachments for endoscopic equipment, etc.). The clinic's pediatric ENT doctors have extensive experience in treating children of all age categories, have special skills in communicating with children and are able to provide timely and highly qualified medical care, taking into account the age-related characteristics of the diagnosis and treatment of the child.
Symptoms of sinusitis
There are four main symptoms of sinusitis:
- Runny nose (rhinorrhea)
- increasing pain in the upper jaw when tilting the head forward and down;
- prolonged nasal congestion;
- purulent discharge from the nasal cavity
- headache;
- increased fatigue, weakness.
If you suspect you have sinusitis, you should first avoid overheating your sinuses and head (i.e., do not heat your nose, face, head) and make an appointment with a doctor. an ENT doctor can diagnose sinusitis.
, and therefore it is worth contacting him directly if the symptoms do not go away within a week.
Operations in the ear, nose and throat clinic
The clinic performs a wide range of surgical operations, such as adenoid removal, tonsil removal, tympanoplasty, septoplasty, rhinoplasty, vasotomy, etc. We have an operating room and a hospital at our disposal, which are equipped with the most modern medical equipment. The team of surgeons is represented by a wide range of specialists in their field who have extensive experience in performing complex surgical operations using modern technologies for operating and rehabilitating patients.
Causes of sinus inflammation
Sinusitis can develop against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity. They occur with influenza, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections. The mucous membrane can become inflamed under the influence of viruses, bacteria and fungi. Sinusitis is often caused by Pfeiffer bacillus, pneumococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, anaerobes and streptococcus.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of sinusitis:
- oral infections, incl. dental caries;
- medical procedures - probing, intubation or nasal tamponade;
- allergic rhinitis;
- cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disease in which the glands secrete a viscous secretion;
- bronchial asthma;
- immunodeficiency;
- endocrine diseases: hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy;
- tumors of the respiratory system;
- smoking;
- inhalation of chemicals in hazardous industries;
- use of steroid drugs;
- regular hypothermia;
- nasal injuries;
- deformations resulting from unsuccessful surgery;
- congenital anomalies of the ethmoidal labyrinth or nasal structure.
ENT Center in Moscow
The Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic is a modern ENT center in Moscow
, where everyone can count on highly qualified medical care, undergo physiotherapy courses and improve their health.
Physiotherapeutic procedures at the clinic include a whole range of activities:
- laser therapy and magnetic therapy using the Milta device
- tube quartz
- pneumomassage
- electrophoresis
- phonophoresis
- washing the lacunae of the tonsils using the “Tonsillor” apparatus
- salt cave
Physiotherapy is an integral part of complex therapy, allowing you to achieve faster results in the treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. Physiotherapy can also reduce rehabilitation time in the postoperative period.
Development of sinusitis
The maxillary sinuses are located on the right and left sides of the nasal cavity and communicate with it through natural anastomosis. The main cause of sinusitis is a violation of the outflow of mucus from the sinuses against the background of swelling of the nasal mucosa, which manifests itself in congestion. The addition of infection causes inflammation of the mucous membrane and accumulation of pus in the paranasal sinuses. Often the inflammation spreads to other paranasal sinuses. The development of sinusitis is influenced by the following factors:
- prolonged runny nose;
- upper respiratory tract infections;
- diseases of the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw;
- deviated nasal septum;
With incorrect, inadequate treatment, sinusitis becomes chronic. Prolonged sinusitis can lead to serious complications, such as:
- meningitis - inflammation of the lining of the brain;
- meningoencephalitis;
- brain abscess;
- partial or complete loss of smell;
- deterioration or complete loss of vision;
- acute otitis media
Possible complications
The following complications are often diagnosed with sinusitis:
- Meningitis is a lesion of the meninges that occurs in acute ethmoiditis and sphenoiditis.
- An abscess is a purulent inflammation of brain tissue. A complication develops with frontal sinusitis.
- Osteomyelitis is the spread of the inflammatory process deep into the bone tissue.
The following consequences may develop:
- arachnoiditis - inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain;
- inflammation of the optic nerve or eye socket;
- thrombosis of the cavernous sinus of the dura mater.
In chronic frontal sinusitis, bone structures are affected, resulting in the formation of fistulas and dead areas. Long-term progression of sphenoiditis causes progressive deterioration of vision. Advanced sinusitis with intracranial complications can lead to a sad outcome.
Indications for the use of video endoscopic examination
Endoscopy of the nasal cavity is the most informative and reliable method of examining the nasal cavity for various pathologies:
- nasal breathing problems,
- prolonged nasal discharge,
- impaired sense of smell,
- nosebleeds,
- headache of unknown origin,
- nasal liquorrhea,
- for tumors of the nasal cavity,
- to clarify the source of metastases,
- if necessary, biopsy
- for postoperative control, etc.
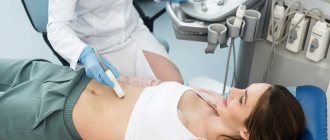
Ultrasound examination of the maxillary sinuses
Expert:
Natalya Valerievna Nikitina, rheumatologist, Ph.D.,
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor at the VitaNova clinic
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. It is unlikely that anyone will dispute this truth. Modern medicine has a number of methods for studying the paranasal sinuses, among which the maxillary sinuses are perhaps the most accessible to the doctor. And if establishing a diagnosis of acute purulent sinusitis does not require any examination methods other than a routine examination by an otolaryngologist, then monitoring the condition of the paranasal sinuses during treatment causes significant difficulties.
The more effective the treatment, the faster the purulent process disappears, the more difficult it is for the doctor to determine without special research methods when to stop antibiotic treatment and whether to prescribe any additional measures, for example, rinsing the paranasal sinuses or physiotherapy. Meanwhile, the adequacy of the treatment directly determines whether sinusitis will go away forever, or whether a relapse of the disease should be expected in the near future.
The most informative diagnostic methods are x-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses and computed tomography. However, an x-ray examination always involves radiation, so pictures can be taken once every six months.
Meanwhile, there is an absolutely safe method for examining the paranasal sinuses, which will tell a specialist no less than computed tomography, although special training is required to correctly interpret the study results. We are talking about ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses. This method is easy to perform, it is safe and painless. If necessary, such an examination can be carried out on the patient daily, without any harm to health. Often, ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses is performed at an initial consultation with an otolaryngologist.
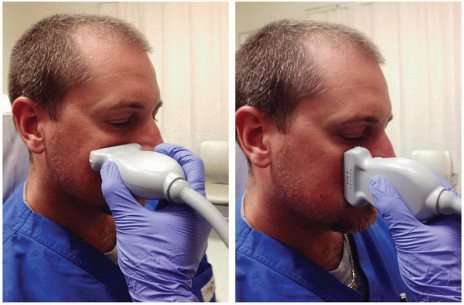
Thus, the initial examination when dealing with problems of the paranasal sinuses (for example, sinusitis) involves, firstly, an x-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses in rare cases, and almost always an ultrasound examination. This approach allows not only to avoid possible relapses of the disease, but also to optimize the course of treatment.
Ultrasound determines the presence of secretion (fluid) and swelling of the mucous membrane in the sinuses. Swelling and fluid are characteristic signs of sinusitis (sinusitis). In addition, ultrasound may suspect the presence of cysts (except for those localized on the posterior wall of the sinus), polyps inside the sinuses and other space-occupying processes (tumors).
The method belongs to the category of reliable, fast, simple, safe and relatively inexpensive research methods. However, this method also has difficulties and disadvantages that to some extent reduce its diagnostic value. Ultrasound of the sinuses should be performed in the “sitting” position so that the fluid inside the sinus is concentrated in the area of the bottom of the sinus. If the patient's head is tilted strongly backward, the secretion moves to the posterior sections of the sinus, and a “layer” of air forms between it and the anterior wall of the sinus. As a result, the ultrasound beam does not reach the posterior wall of the sinus, being reflected at the tissue-air interface. Therefore, dynamic ultrasound technique should be used.
A false negative result may also be caused by the presence of a small amount of secretion inside the sinus. The scanty secretion does not delimit the anterior and posterior walls of the sinus, so ultrasound does not pass to the posterior wall, giving a picture of a healthy sinus. A similar error is possible in 3.1% of cases.
Before the ultrasound, dentures should be removed so that the sensor can be placed on the cheek in the area of the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus. Before starting the study, it is necessary to check the configuration of the alveolar process (especially for adult patients), because the location of the sensor outward from the alveolar process inevitably leads to the propagation of ultrasound waves lateral to the bone structures, while the cheek muscles cause the appearance of a false positive echo signal.
The most common mistake leading to negative ultrasound results is insufficient amount of contact gel applied to the skin. If the skin is dry, a small amount of air will form between the transducer and the skin, preventing ultrasound from passing through the tissue. If there is too much gel, the skin becomes slippery. At the slightest turn of the patient's head, the sensor may change its position. In this case, the echo signal can pass above the orbit, laterally (through the soft tissues of the cheek) or medially (through the nasal cavity). Therefore, the doctor should always be sure that the sensor is on the anterior wall of the sinus.
It should also be taken into account that ultrasound of the ethmoid sinus is possible only in the presence of a pathological process in the “large” sinuses (sinusitis or sinusitis), since the ultrasound wave, when passing through the air sinuses, is reflected and does not reach the ethmoid.
There are also anatomical reasons that complicate ultrasound of the maxillary sinuses:
- pseudocyst in the sinus, simulating free secretion;
- absence of the maxillary or frontal sinus, or their hypoplasia;
- the anterior wall of the sinus is too thick, so when the ultrasonic wave penetrates into the sinus, its power is significantly weakened;
- the sinus is too deep, so the posterior wall of the sinus is located at a great distance from the ultrasound sensor, which leads to an increased effect of ultrasound scattering and absorption by tissues
- polyps, jelly-like exudate and soft tissue neoplasms give similar echograms. In such cases, scanning should be performed in different positions of the patient's head.
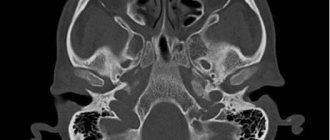
CT scan of the upper jaw with contrast
Native CT examination of the upper jaw accurately diagnoses pathologies in the sinuses, lacrimal ducts and anastomoses with the nasal cavity. With the addition of contrast to the procedure, adjacent soft tissues are clearly visualized.
Most often, CT with contrast is prescribed when malignant processes are suspected. Intravenous administration of iodine-based drugs improves the visibility of the circulatory system: tumors have their own network of vessels, which is clearly visible after contrast. By identifying additional foci of blood supply, computed tomography can detect tumors at an early stage.
Examination of sinuses without enhancement does not require special preparation. It is enough to bring with you a referral from your attending physician, an extract from the outpatient card and the results of previous diagnostic measures. Before a CT scan of the upper jaw and maxillary sinuses with contrast, it is necessary to do a blood test for creatinine. If creatinine levels increase, the use of contrast is prohibited, since there is a high risk of problems with removing the medication from the body.
Other contraindications:
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
The patient may develop reactions to iodine - dermatological (skin redness, rash, itching) or systemic (facial swelling, difficulty breathing, bronchospasm, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock). Similar phenomena during CT scanning of the upper jaw with contrast cannot be excluded in people with any serious allergies.
- Taking metformin in patients with diabetes mellitus.
This medication reduces the glomerular filtration rate of the kidneys, which increases the damaging effect of the contrast agent. In combination with iodine-containing drugs, metformin can provoke the accumulation of lactic acid in the body (lactic acidosis). This condition is life-threatening. For patients taking metformin, it is important that two days before a CT scan of the upper jaw with contrast, the endocrinologist either discontinues the drug or replaces it with another medicine.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
Iodine-based substances accumulate in the tissues of the thyroid gland, which can significantly worsen the patient’s condition. In this situation, the possibility of examination with contrast appears only after preventive preparatory treatment. In any case, CT scanning of the upper jaw and maxillary sinuses using iodine-containing preparations should not be done without consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Age up to 12 years.
It is difficult for young children to get into a vein, and it is also difficult for children to explain the need and sequence of the manipulations performed.
Lactation is not a contraindication to CT scanning of the maxilla with contrast. But since the dye used partially penetrates into breast milk, a woman should take care of the baby’s nutrition in advance. After the procedure, you must skip two feedings in a row, expressing and pouring out the milk.