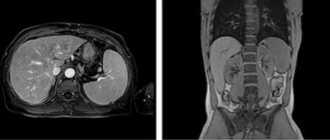
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a popular, painless, safe and highly informative examination of soft tissues and blood vessels. The procedure is carried out both with and without contrast. MRI can be used to diagnose all kinds of pathologies in patients of any age with virtually no restrictions.
The MRI method is based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance. It has been revealed that under the influence of a magnetic field, hydrogen atoms in water molecules begin to emit energy. Hydrogen is one of the most abundant atoms in the human body.
The energy emitted by them is captured by sensors built into the tomograph. The received impulses can be transformed into a three-dimensional image using a special program. Volumetric visualization allows you to:
- examine in detail the area of the body being examined;
- detect anatomical and functional disorders in it;
- identify pathological changes in the relative position of nearby organs and tissues;
- when examining with contrast, highlight an organ or organ system against the background of other tissues.
Magnetic resonance imaging has a number of advantages over other hardware research methods. If we compare it with computed tomography, then the fact that there is no radiation exposure for the patient is indisputable. This allows you to not limit the number of MRI procedures per year.
Compared to ultrasound, MRI provides a clearer image processed by a computer, which increases diagnostic value and reduces the risk of misinterpretation of the study result.
The advantage of MR angiography over X-ray angiography is also obvious. After MRI, a three-dimensional image of the contrasted vascular network is obtained, and an x-ray is taken in one or two projections, as a result of which diagnostic errors may occur (due to the overlapping of shadows of surrounding structures).
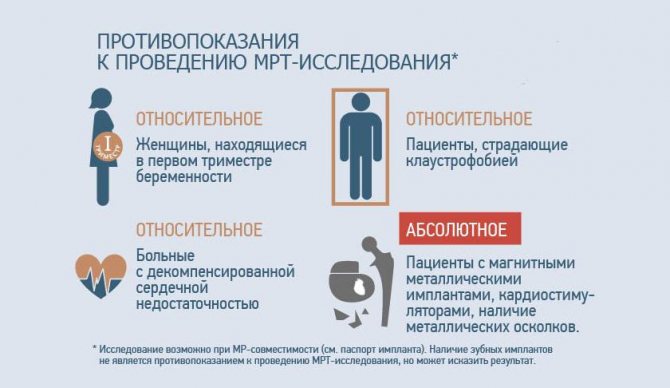
Despite all the advantages, magnetic resonance imaging has a number of contraindications that make it impossible to conduct research in some categories of patients. There are absolute and relative contraindications. Absolute contraindications are those whose presence in a patient precludes examination with an MRI scanner.
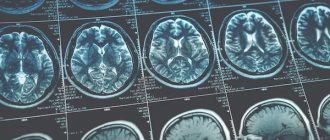
What does a brain MRI show?
Having received 3D images of the brain in different projections, the doctor has the opportunity to examine each area in detail. This allows us to draw conclusions about:
- processes occurring in brain tissue;
- condition of blood vessels;
- the presence, location, shape and size of neoplasms, hematomas or blood clots;
- the presence, stage and localization of other brain pathologies.
If the results are not accurate enough or additional visualization of a specific area is required, an MRI of the brain with contrast may be ordered. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to obtain a more accurate idea of the structure of brain tissue or pathological formation and to clarify its boundaries.
Is it possible to undergo an MRI under the policy?
The MRI procedure is often considered to be exclusively paid, but this is not so. In acute, emergency conditions, when the timing of treatment is extremely important (for example, in oncology), MRI is done without a queue and under the compulsory medical insurance policy. If there is no urgent need for the study, the patient can stand in line for this test. Unfortunately, you have to wait a long time, sometimes several months. Many, unable to bear the wait, prefer to pay for the procedure. Those who do not want to wait in line usually go to a private clinic or medical center. The website https://mrt-v-msk.ru/ will help you choose a diagnostic center in Moscow. Here you can find detailed information about hundreds of clinics and the opportunity to make an appointment at any of them.
How to do an MRI of the brain
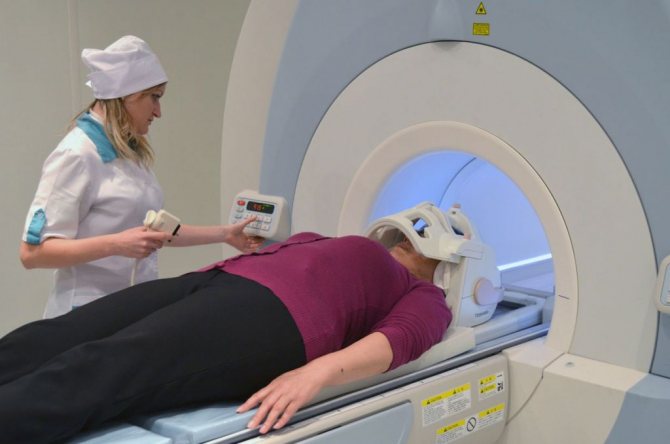
The only requirement is not to wear metal or jewelry, hairpins, or watches when going for an examination (or be prepared to remove them or take them out of your pockets before placing them in the tomograph). Also, during the procedure you cannot have magnetic media (flash drives, bank cards, etc.) with you, since the information stored on them will be destroyed. The diagnosis will take 30–40 minutes. You cannot move your head during the process, but this restriction does not apply to the facial muscles. You can even talk to your doctor while he takes sequential pictures. From time to time, the doctor himself will contact the patient to inquire about his well-being.
If you suffer from claustrophobia, but an MRI of the brain is necessary, you need to say this in advance. Then the doctor will suggest taking a sedative before starting the procedure.
Contraindications for MRI
Absolute:
- applied vascular clips;
- electronic devices in the body (for example, ferromagnetic implants);
- presence of pacemakers.
Relative:
- body weight more than 130 kg;
- claustrophobia;
- metal fragments in the body;
- metal-ceramic dentures;
- severe forms of heart failure;
- conditions that do not allow the patient to remain immobile for a long time, etc.
Who needs to undergo an MRI of the brain?
Most often, a neurologist refers you to magnetic resonance imaging. Indications for research may include:
- regular dizziness and headaches of unspecified nature;
- decreased hearing or vision in the absence of an explanation from an ENT or ophthalmologist;
- frequent fainting;
- head injuries;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- stenosis (narrowing of blood vessels);
- aneurysms (dilation of blood vessels);
- epilepsy;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- other neurological diseases.
Although brain tomography is a completely safe procedure, there are still contraindications. First of all, they are due to the presence of metal elements that cannot be removed during the procedure:
- braces;
- pacemakers;
- prostheses;
- staples on vessels;
- foreign objects;
- implants.
If there are fixed metal parts and devices, MRI cannot be performed.
Overweight patients may be limited by the diameter of the tomograph capsule.
It is not recommended to undergo an MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy, however, if there are medical indications, the diagnosis will be carried out. At a later date, the examination will not harm either the mother or the child. Breastfeeding women also do not have to worry: magnetic waves do not affect either lactation or the quality of milk.
Is magnetic resonance imaging harmful to health?
MRI and CT (computed tomography) provide approximately the same images of the areas of the human body being examined. The information content of such images is also approximately similar. The methods differ in what physical phenomena are used as the basis for obtaining images.
In computed tomography these are x-rays. The magnetic resonance imaging method involves the use of a magnetic field that is created by powerful magnets. Under the influence of electromagnetic pulses, hydrogen atoms contained in tissues begin to resonate. This resonance is detected by tomograph sensors and converted into an image using a special program. Areas of different shades of gray correspond to tissues and organs of the human body, which differ from each other by different contents of hydrogen atoms.
Since MRI does not use X-rays or ionizing radiation (radiation), the examination does not harm the human body. It is possible to examine several areas at once, and, if necessary, the entire human body in one procedure. There are no restrictions on the number and frequency of procedures performed.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that the examination will be safe only if all contraindications for MRI have been taken into account.
Diseases and conditions that may be contraindications for MR imaging
MRI can cause harm if the patient is silent about his contraindications. The simplest things, missed due to ignorance, negligence or malicious intent, can create a serious problem.
- Metal foreign bodies found in the human body . In a working tomograph, metal objects begin to be attracted to magnets located around the tunnel of the device. Depending on the size and location of metallic foreign bodies, they can cause a variety of tissue damage. Small objects become hot and can cause localized tissue burns. Displacement of foreign bodies is also possible. For example, vascular clips that neurosurgeons leave in the cranial cavity to stop bleeding can become dislodged during an MRI procedure, which can cause the formation of a hematoma in the cranial cavity. Large metal fragments can become dislodged and seriously injure surrounding tissue. Also, any metal objects located inside the tomograph create interference, so images may not be clear. The exception is medical products made of titanium. The presence of a foreign body in one or another part of the human body can be confirmed using an x-ray examination. Piercing earrings, if they are not made of titanium, will also have to be removed to avoid problems during the procedure. If the possibility that the piercing earring will not be able to be inserted into the skin after it is removed for an MRI procedure is a concern for the patient, then it is better to leave everything as is and get a referral from the doctor for a CT scan.
- Various electronic devices that are implanted into the human body . The magnetic field of the tomograph can disrupt the operation of any electronic devices located in the immediate vicinity of a working installation. This applies to both a mobile phone, which a patient may have in his pocket, and a pacemaker, which is implanted in a person’s chest. During the consultation, it is necessary to warn the doctor about the presence of any implanted devices that are in the body. Not every such device is an absolute contraindication for MRI. In each specific case, the doctor will make the decision. For example, ferromagnetic or electronic middle ear implants, a pacemaker, or an Ilizarov apparatus are an absolute contraindication for the examination. Relative contraindications include prosthetic heart valves, nerve stimulators, etc.
- Diseases.
The list of diseases and conditions for which MRI is undesirable is small. This includes :
- claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces);
- epilepsy;
- any conditions in which the patient behaves inappropriately (alcohol or drug intoxication, mental illness, etc.);
- severe condition of the patient, when constant connection of a cardiac monitor or ventilator is necessary;
- decompensated heart failure.
Contraindications for contrast-enhanced MRI are::
- chronic renal failure;
- pregnancy;
- intolerance to gadolinium-based drugs.
The significance of certain contraindications listed above is largely determined by the severity of the patient’s symptoms of the disease. For example, for most patients suffering from claustrophobia, undergoing the examination procedure does not present any particular problem, since taking sedatives a day or two before the procedure allows them to reduce anxiety and other manifestations of fear of closed spaces to an acceptable level. In some patients with epilepsy, anticonvulsant therapy can completely relieve the person from seizures. Accordingly, doctors have no reason to refuse to perform an MRI procedure on such patients.
Preparing for an MRI of the spine

A light breakfast will help you not feel hungry, and will reduce nausea and drooling during the administration of contrast during MRI.
Preparatory activities rather concern the collection of necessary documents: you need to take with you a referral from a doctor, a passport, a medical insurance policy (if insurance covers the cost of an MRI of the spine), the results of previous studies and discharge from the hospital.
There should be no metal parts on clothing that could cause defects on the films. Women should choose a bralette.
Depending on the area of interest, an enema may be required (if a pathological process in the pelvic organs is suspected, for example, a tumor with potential metastasis to the skeletal bones). It is necessary to clarify in advance whether to cleanse the intestines before the diagnostic procedure. A light snack 40 minutes before contrasting will help reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions from the autonomic nervous system: drooling, dizziness, metallic taste in the mouth, etc. Cell phones, plastic magnetic cards, jewelry, and keys are deposited before the MRI scan.