Article on the topic
Food supplements: Dietary supplements do not cure obesity, but help control weight
My daughter was only a month old when lack of sleep, worries and numerous worries made themselves felt: I had a terrible headache. I bravely endured the whole day, remembering that taking medications and breastfeeding are incompatible things. When the headache did not go away by the end of the second day, I called a doctor I knew. It turned out that the pain I endured was much more harmful than the consequences of taking the pill.
It's possible, just be careful
In Soviet times, when asked whether a nursing mother could take medication, the answer was categorical: either you are breastfeeding or you are sick. But at the end of the last century, WHO revised its position and, after a series of studies, decided that it is possible for a mother to take medications during breastfeeding. But be careful...
Yes, most medications pass into breast milk, but in small quantities - we are talking about only tenths. The drug reaches its peak concentration in breast milk 2–3 hours after administration. And then it is gradually eliminated from the body. So sometimes it’s enough just to separate the time between taking the pill and the next feeding - and everything will be fine.
Moreover, even the notorious ARVI is not an obstacle to breastfeeding. After all, along with mother’s milk, the baby receives not only viruses, but also antibodies to them. That is, a kind of vaccination occurs.
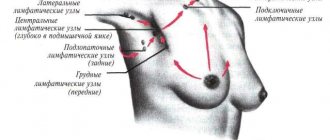
Personal hygiene products
Such medications, although they are not taken orally, can enter the baby’s body through feeding. These are products for treating nipples and areas around them after feeding, to prevent cracks and inflammation. Most often, widely used drugs are prescribed - for example, Vinilin (Shostakovsky balm). It does its job quite well - preventing cracks, infection and moisturizing. But before each feeding, it must be washed off the breast (or washed with a damp sanitary napkin), since the chemical compounds included in its composition should not enter the baby’s body.
But the product for the prevention (and treatment) of superficial cracks in the nipples, Purelan, consists of medical lanolin, without additives or preservatives. This is a hypoallergenic cream, tasteless and odorless. It effectively moisturizes the nipples, and, what is especially convenient, it does not need to be washed off before feeding. In addition, the cream can be used to moisturize the baby's lips (this may be necessary if the breasts are very sensitive). There are other products recommended to prevent cracked nipples, but they need to be washed off before feeding.
What to be afraid of
Forget about analgesics . Penetrating into breast milk, they depress the baby’s central nervous system and cause hematopoiesis and kidney dysfunction.
You should not abuse acetylsalicylic acid. If necessary, the drug can be taken once. Large doses cause an increased concentration of acid in mother's milk and can lead to metabolic disorders in the baby.
Anti-poisoning agents should be taken with great caution. The most harmless drug for indigestion is activated charcoal. But laxatives taken by the mother will not harm the baby.
Antihistamines also do not interfere with breastfeeding. But if necessary, choose means of only one action.
If you have an acute bacterial infection, then, contrary to popular belief, you can take antibiotics and continue breastfeeding. The exception is sulfonamide drugs. And do not self-medicate; only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics!
Any antidepressants should be taken only after consulting with a competent specialist. Almost all drugs in this group pass into breast milk and remain in high concentrations there for a long time. Many popular pharmaceutical herbal preparations contain alcohol, so they are not an option for you either. For irritability and nervousness, it is better to drink soothing herbal teas.
Prohibited medications while breastfeeding
There is a list of medications prohibited during breastfeeding, these include:
- narcotic analgesics depress breathing in infants, especially newborns;
- phenobarbital (hypnotic and anticonvulsant); Long-term use of phenobarbital by a nursing woman, despite its low content in milk, disrupts the function of the child’s liver enzymes;
- lithium preparations (can be prescribed for postpartum psychosis) disrupt the functioning of the heart and kidneys, causing a decrease in muscle tone and temperature;
- chloramphenicol causes a decrease in the hematopoietic function of the bone marrow; with individual intolerance, an infant may experience vomiting, convulsions, jaundice, and difficulty breathing;
sibazone, diazepam, seduxen (sedative and anticonvulsant effect) when taken by the mother for a long time accumulate in the child’s body, leading to neurological disorders, drowsiness, loss of appetite, short-term respiratory arrest;- metronidazole (Trichopolum) causes vomiting, diarrhea, and suppression of bone marrow function;
- antithyroid drugs (mercazolyl, methylthiouracil) cause the formation of goiter in a child, suppression of thyroid function, and impaired hematopoiesis;
- ergotal, ergotamine (drugs that contract the uterus) inhibit lactation; may cause vomiting, diarrhea, weak pulse, and convulsions in a child.
It should be remembered that ergotamine is part of bellataminal and bellaspon, which are used for irritability, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and neurodermatitis.
Pay special attention to chloramphenicol, which is undeservedly loved by the people and taken uncontrollably for any reason (from a runny nose to diarrhea).
Its side effects and complications are so dangerous that it can be used strictly according to indications and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Reception tactics
The very first and most important rule is to consult a doctor about any medicine. A competent specialist must demonstrate to you not just knowledge of the instructions for use, but also the nuances: how much the drug penetrates into milk, how long it remains there, what harm is possible for the child.
Before starting medication treatment, consult your doctor: maybe they can be replaced by folk remedies? After all, instead of buying an antitussive, you can drink milk with honey. Raspberries or cranberries will help bring down the temperature. However, you should be careful with medicinal plants. For example, mint and sage help reduce lactation.
If medication is necessary, take it immediately after feeding so that the maximum concentration of the drug occurs during the break.
Paradoxically, the more often you need to take the medicine, the better it is for the baby. Give preference to those drugs that are taken not 1-2, but 3-4 times a day. The latter have a short-term effect and are eliminated more quickly from mother's milk.
What sedative can you use while breastfeeding?
Resorting to sedatives during lactation, even herbal ones, should only be used as a last resort, when all possible relaxation methods have been tried. Almost all drugs have not been studied for safety for children. In medical practice, doctors prescribe any sedatives to nursing mothers and, thus, over a long period of time, the positive or negative effect of the medicine is determined by trial and error.
You should know that emotional instability occurs not only with worries and fatigue, but can also be the cause of a malfunction of the thyroid gland or a lack of vitamins. Therefore, before choosing a sedative, you need to pass the entire range of tests (blood, urine, feces). If there is no suspicion of serious illness, then seek help from a psychotherapist.

To avoid using sedatives, mom needs more rest
Valerian
The raw materials for the manufacture of tablets are the roots of the valerian officinalis plant. The official instructions for use indicate possible use during lactation as prescribed by a doctor, if the benefit for the mother is greater than the risk for the child. In practice, the drug is prescribed to nursing women to correct sleep and relieve irritability.
Valerian has the ability to accumulate in the body, so the therapeutic effect does not appear immediately. The maximum duration of therapy is 4 weeks.
The tablets have a sedative, antispasmodic, and choleretic effect.
The price of Valerian depends on the manufacturer and composition of the drug. Forms enriched with vitamins B and C are available for sale. Valerian extract is also included in other multicomponent sedatives and herbal preparations.
The cost of the medicine varies from 20 to 200 rubles.
Some annotations indicate pregnancy and the lactation period among contraindications.
Adverse reactions in the form of depression, lethargy, drowsiness, and decreased concentration may occur when taken in high doses. If you take Valerian for a long time, there is a risk of developing constipation.
Valerian is the most popular drug for neuroses, which is prescribed to nursing mothers, although there is still no scientific data on the safety of the drug’s effect on the baby’s body
Persen
Persen is a combined herbal preparation that contains valerian, lemon balm and mint. It has a sedative and antispasmodic effect.
The instructions for use do not recommend taking the drug for longer than 1.5–2 months.
The product is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to lack of research. Persen can provoke allergic reactions and bronchospasm. When taken for a long time, the drug can cause constipation.

The combination drug Persen is best taken under medical supervision.
Novo-Passit
The drug Novo-Passit consists of seven herbs:
- valerian;
- lemon balm;
- St. John's wort;
- hawthorn;
- passion flowers;
- hops;
- elderberries.
Manufacturers produce Novo-Passit in the form of tablets and solution. Thanks to specially selected herbs, the drug has an anti-anxiety and sedative effect. If there is an urgent need to take the drug during lactation, then you need to stop feeding the baby.
The official annotation for the drug indicates hypersensitivity, myasthenia gravis (a severe chronic disease that manifests itself as abnormal muscle weakness), children under 12 years of age, and pregnancy as contraindications.
Manufacturers note very rare allergic reactions, fatigue, drowsiness, and stomach upsets as side effects.
The price of Novo-Passit depends on the form of release and the number of tablets in the package. The cost of the drug ranges from 150 to 1100 rubles.

The combined drug Novo-Passit with a complex composition may have an undesirable effect on infants
Notta
Manufacturers produce the homeopathic remedy Notta in the form of drops and tablets.
Active ingredients of the drug:
- oats;
- phosphorus;
- chamomile;
- a coffee tree;
- zinc valerate.
The drug in the form of drops contains ethyl alcohol, so it is not advisable for nursing mothers to use the product.
Notta has a tranquilizing effect, improves tolerance to emotional stress, and normalizes sleep.
The official instructions list only hypersensitivity as contraindications. Manufacturers do not recommend taking the drug during lactation, since there is insufficient clinical data on the use of the drug during this period. In practical medicine, doctors prescribe Notta to nursing mothers in severe mental conditions.
To date, no side effects have been reported after taking Notta. The cost of the drug, depending on the form of release, ranges from 170 to 500 rubles.
Notta is a fairly safe drug; theoretically it is not recommended for lactation, but in practical medicine doctors prescribe the drug to nursing mothers
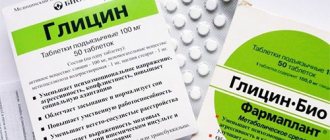
Glycine
Glycine is considered a safe sedative for nursing mothers. The product helps eliminate fatigue and irritability, relieves insomnia and stress. Glycine can be given even to infants to normalize sleep.
The active component of the drug is an amino acid that stimulates the process of brain metabolism, promotes the saturation of nerve cells with oxygen and prevents overexcitation.
Thanks to Glycine:
- metabolism is normalized;
- overwork and nervousness are eliminated;
- excitability decreases;
- brain function is stimulated;
- memory and concentration improves;
- sleep is stabilized;
- the risk of developing vegetative-vascular pathologies is reduced.
The drug must be taken in a course. The drug is allowed during lactation, but in a certain dosage, which must be selected by the doctor.
Possible side effects include:
- allergic manifestations (rash, itching and redness of the skin) in mother and baby;
- lethargy and drowsiness in mother and child;
- baby's refusal to breastfeed;
- excessive excitability of the newborn.
It is not recommended to take the drug if you have low blood pressure or individual intolerance.
Teas
The safest remedies in the fight against frayed nerves are considered to be herbal decoctions: valerian, motherwort, mint, lemon balm, passionflower, fennel and others. Soothing teas have a gentle effect on the body. The effectiveness is noticeable in mild disorders of the nervous system. The dosage and duration of administration are prescribed by the doctor. As a rule, the course of treatment lasts up to 1 month.
It is necessary to take into account some features of herbs. For example, mint reduces milk production, and lemon balm helps increase lactation.
Herbal decoctions are well tolerated by the body. Individual sensitivity is a contraindication. Side effects may include allergic reactions.
The price of herbal teas varies from 30 to 150 rubles.

Fennel not only has a mild sedative effect, but also increases mother's milk production
Which sedative is better and safer?
It is best for a nursing mother to avoid taking any medications if possible. If the negative state persists for a long time, and possible methods of calming do not work, then the doctor will prescribe a herbal drug. Proven, natural remedies will help relieve the first symptoms of depression: Valerian and Motherwort.
All other drugs should be used with caution, since their safety has not been scientifically proven. During lactation, it is better to brew herbal teas or use tablets. All alcohol tinctures are strictly prohibited for mothers.
You should not evaluate the effectiveness of the drug based on the advice of friends or acquaintances. One remedy can have the opposite effect on different people. You need to consult with professionals, and not just one, but preferably several.
Recommendations for taking medications
Depending on the severity of the woman’s condition and the age of the child, the doctor may prescribe a suitable drug. The older the baby, the more products are available for use. The dosage regimen must be agreed with a specialist. It is better to start with a minimum dose and monitor the baby’s reaction. If no undesirable manifestations are noticed, you are allowed to continue taking the medicine.
The most compatible with breastfeeding are sedatives. But this does not mean that you can drink tea in unlimited quantities. The maximum dose for a nursing woman is no more than two glasses of light decoction per day. To begin with, it is better to choose one herb. If you drink tea from several plants at once, it is difficult to determine which of them the baby reacted to. Multicomponent and homeopathic preparations pose a potential risk for the child in the form of the development of allergic reactions and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. The younger the baby, the more harm the medicine can cause.
The mother is allowed to use herbal teas for children: lemon balm, chamomile, fennel, valerian.
In addition to ingestion, you can take baths with decoctions of soothing herbs. Moreover, such a procedure will be useful for both mother and baby.

Taking a relaxing bath will help you find emotional balance and put you in a great mood.
Example and life
Natalia, 35 years old, Krasnogorsk:
My daughter was six months old when my hands became covered with eczema. I was prescribed hormonal ointments and injections. And the dermatologist strictly told me to stop breastfeeding.
When my son was born 5 years later, history repeated itself. But either during this time something changed in our medicine, or I just happened to have a conscientious doctor, but I was prescribed modern hormonal creams and... allowed to continue breastfeeding the baby. Then I repeated the course of treatment with these creams a couple of times. And she successfully fed the boy for more than a year.