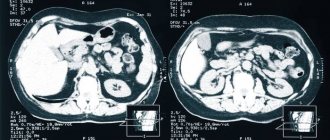
MRI image of the abdominal cavity
Abdominal MRI with contrast is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the abdomen and its organs. The study is carried out to establish the disease, the cause of its occurrence, assess the severity and determine further management tactics. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed when other imaging methods are unclear: ultrasound, radiography and CT. The technology is constantly being improved using various pulse sequences and protocols; the power of modern tomographs can reach 6-7-12 Tesla. Enhanced MRI of the abdomen allows you to obtain images of internal organs, blood vessels, lymphatic ducts and bone structures without exposure to ionizing (X-ray) radiation.
- Prices for MRI of internal organs
Preparing for an abdominal MRI with contrast
Wearing comfortable clothes will allow you to have a magnetic resonance scan with greater comfort.
Preparation for an abdominal MRI with contrast includes the following:
- Choosing comfortable clothes. Metal rivets and parts lead to distortion of images, and given that you will have to lie as still as possible for about an hour in an artificially ventilated space, compression of the abdomen, for example, by tight synthetic trousers will cause discomfort. On the day of the examination, you must choose a loose-fitting set or change into a disposable gown. All metal objects (watches, jewelry, hair clips, coins, keys, pens, cell phones, etc.) must be left outside the examination room. Any of these items can cause injury when exposed to a magnetic field, so check your pockets especially carefully.
- Collecting what you need. A referral from a doctor, hospital discharge notes, results of previous studies, a passport, a compulsory medical insurance/voluntary health insurance policy (if the MRI is paid for by an insurance company) should be taken with you.
How is the procedure done?
On average, the study lasts from 30 to 50 minutes, depending on which organs need to be checked. There is a table inside the device; you need to lie down on it. In order to give the patient's body the desired position and ensure immobility, special bolsters and belts are used.
If the study is carried out with contrast, a solution of the drug is administered intravenously or given to drink.
Sometimes, so that the patient can lie motionless inside the device, light anesthesia - sedation - is used.
While the device takes pictures, the patient must lie still, and the doctor is in the next room and gives commands through a microphone. Periodically, he asks you to hold your breath - this is necessary so that the internal organs do not move during the movements of the diaphragm, and the pictures turn out clearer.
Then the MRI of the abdominal cavity is deciphered. With the result, you need to visit your doctor, he will establish an accurate diagnosis and give further recommendations.
To perform a magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen, it is not necessary to be hospitalized in a hospital; this procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Our doctors will help you
Leave your phone number
Diet before abdominal MRI with contrast

Gentle nutrition will reduce the load on the digestive organs, which will allow you to obtain more reliable MRI results
Switching to a special diet with the exception of gas-forming foods and drinks, eating food prepared using gentle heat treatment allows you to achieve greater image clarity on tomograms. Swollen intestinal loops or dense filling with feces prevent adequate diagnosis. For patients with a tendency to constipation, the doctor may recommend doing an enema or drinking a laxative, taking an antispasmodic, or prescribing activated charcoal a few days before the procedure. Foods that promote flatulence:
- all types of cabbage, raw vegetables, herbs. radishes, turnips;
- fruits, including dried ones;
- legumes;
- corn;
- Rye bread;
- mushrooms and nuts;
- bakery;
- milk, ice cream.
Alcohol (including beer), kvass, sugary compotes, freshly squeezed juices, smoked meats and marinades are not allowed.
If you plan to conduct an MRI with suspected pathology in the pancreas, gall bladder and liver, it is justified to follow a low-carbohydrate diet, which will reduce the load on the organs being examined. Avoid eating cereals, confectionery, baked goods, bananas, grapes, berries, potatoes, pasta, sweet drinks, lemonade, sugar, and honey. This diet is followed for 2-3 days before the diagnostic procedure. Lean varieties of fish, meat, poultry prepared in gentle ways, stewed, baked and boiled vegetables, fermented milk products with a maximum permissible fat content of 2.5% can be eaten during the diet before an MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast. Depending on the area of interest, the patient will be asked to fast 4-6 hours before the scan.
MRI with contrast of the abdominal cavity: what does it show?
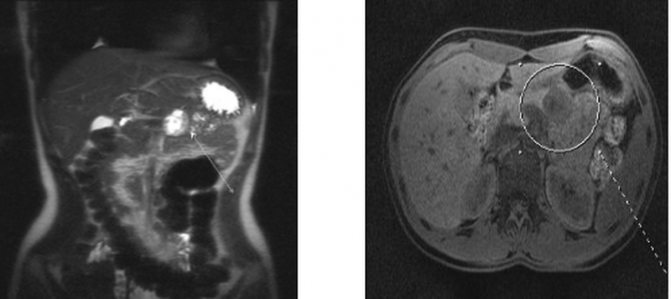
MRI: pancreatic cancer (shown by white arrows)
MRI of the abdominal cavity shows a number of pathological processes and often detects a problem in organs with their normal size and shape, which makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage. Magnetic resonance scanning is used to evaluate the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, kidneys, ureters, adrenal glands, perinephric tissue, etc. It is preferable to examine the intestines and stomach using FGDS and colonoscopy. On tomograms, inflammatory processes of parenchymal organs, consequences of injuries, anomalies and malformations, tumor pathologies, cholelithiasis, infections (echinococcosis, tuberculosis), vascular changes (malformations, atherosclerotic lesions, aneurysms, compression) are distinguishable.
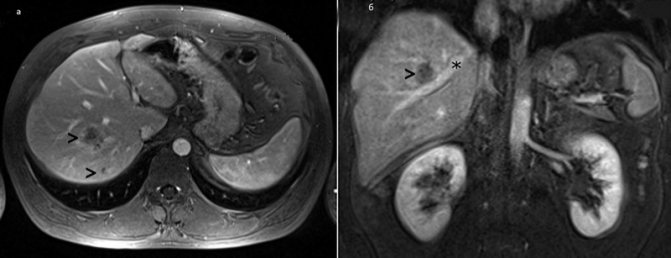
MRI: metastatic liver disease
What does an MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast show? Study:
- pancreas: neoplasms, duct obstruction, fluid accumulation, fistula formation, pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis, abscess;
- gallbladder: cholecystitis and its cause (developmental anomalies, for example, constrictions), thickening of bile, stone formation, tumors of the bile duct or the organ itself;
- spleen: congenital anomalies, accessory tissue, infectious lesions, cysts, infarction, splenomegaly (increase in size), vascular pathologies;
- liver: hepatitis, cirrhosis, metastases, abscess, cysts, hemangioma, primary tumors, hepatic vein thrombosis, fatty infiltration;
- kidneys, ureters, retroperitoneal space: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, benign and malignant neoplasms, hydronephrotic transformation and its potential cause, vascular condition, including the inferior vena cava, nephrolithiasis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, etc. The urinary tract is assessed for abnormalities, determining functional capacity ( magnetic resonance urography);
- adrenal glands: benign and malignant tumors - adenoma, pheochromocytoma, etc., secondary lesions.
- gastrointestinal tract and peritoneum: neoplasms, inflammatory changes in the colon and small intestine, mesenteries, adhesions, primary metastatic lesions, fluid accumulation (ascites), lymphadenopathy.
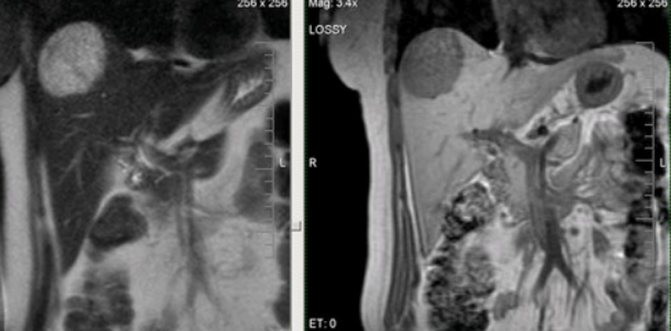
MRI: hepatocellular cancer
MRI is one of the best examinations in diagnosing parenchymal cancer. A contrast study demonstrates the size of the tumor, the degree of its invasion into neighboring organs, regional and distant lymph nodes, and vascular dissemination. The final diagnosis is confirmed by morphological examination.
Abdominal MRI with contrast: indications and contraindications
Before performing an MRI, the doctor weighs the pros and cons
Indications for MRI of internal organs:
- preoperative assessment of neoplasms and anatomical features;
- the need to clarify/finally establish the diagnosis, dissatisfaction with the results of the primary diagnosis;
- dynamic monitoring of the pathological process after surgery and conservative therapy.
Symptoms that warrant an MRI of the abdominal organs:
- unexplained pain in any part of the abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, unstable stool, bloody stool, tarry appearance;
- icterus of the skin, sclera;
- palpable tumor formation in the abdominal cavity, epigastrium, unexplained weight loss, severe weakness;
- attacks of renal colic, frequent recurrent urinary tract infections, accompanied by pain in the lower back, fever, and blood in the urine. To assess nephrolithiasis, it is better to do a CT scan, which shows the density of the stone and the prospect of spontaneous passage or dissolution.
- high blood pressure resistant to therapy, etc.
Contraindications for MRI

The main contraindication to MRI is metal components in the body
There are few contraindications to the diagnostic procedure. The main thing is the presence of any metal components in the body: orthopedic structures, pacemakers, prosthetic heart valves, hearing aids, etc. This category of people undergoes computed tomography. The study is not carried out for technical reasons for people weighing more than 120 kg. The first trimester of pregnancy is a contraindication for MRI of internal organs with contrast, although the damaging effect of a magnetic field or radio pulses on a developing fetus has not yet been proven.
The introduction of an amplifier is unacceptable in case of a burdened allergic history, if a generalized reaction such as Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock to the use of a paramagnetic drug has previously been noted, or there is chronic renal failure with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 ml/minute. Claustrophobia and diseases in which it is impossible to lie still for a long time also serve as an obstacle to magnetic scanning; in these cases, sedation is considered.
Contraindications
For the procedure, absolute contraindications are the patient’s excess weight, over 120 kg, and the use of a pacemaker and insulin pump. Metal prostheses and implants can interact with a magnet, so if they are present in the body, tomography is not performed.
Breastfeeding women and people with severe kidney pathologies will not be able to undergo MRI with contrast.
The diagnostic center in Moscow offers services for examination of retroperitoneal internal organs using modern equipment and under the supervision of highly qualified specialists.
How is an MRI done with contrast in the abdomen?
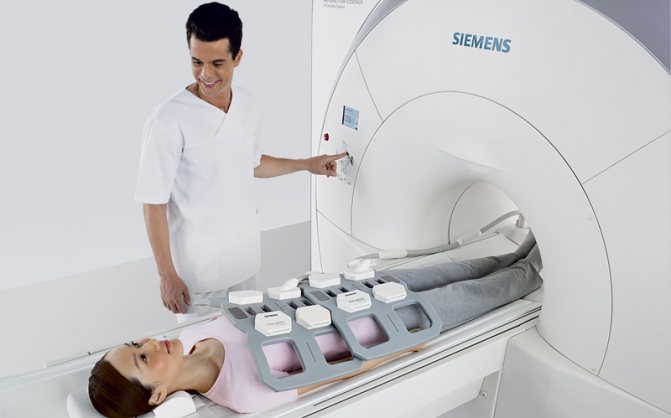
Maximum immobility during the entire diagnostic procedure is necessary so that there are no blurs on the films.
The CT scanner table slides into the central tunnel, on which the patient is fixed using special belts and bolsters. This allows you to maintain maximum stillness and correct position while shooting. Devices containing coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves are placed near the area of the body being examined.
Gadolinium chelate contrast agent is administered intravenously through an injector during the required phases of the study, or a paramagnetic agent is administered by a nurse after the initial series of scans. The amount of indicator depends on the body weight of the subject. Additional pictures will be taken after the injection. Communication with the patient occurs through a speakerphone. At the command of the X-ray technician, you will need to hold your breath. The duration of the procedure is 45-60 minutes; upon completion, the catheter is removed from the vein and a bandage is applied. To prevent subcutaneous hematoma, the arm should be kept bent for some time. If sedation is not performed, there is no obstacle to daily activities.
A radiologist will interpret the results and you can ask him questions.
What contrast is used for abdominal MRI?
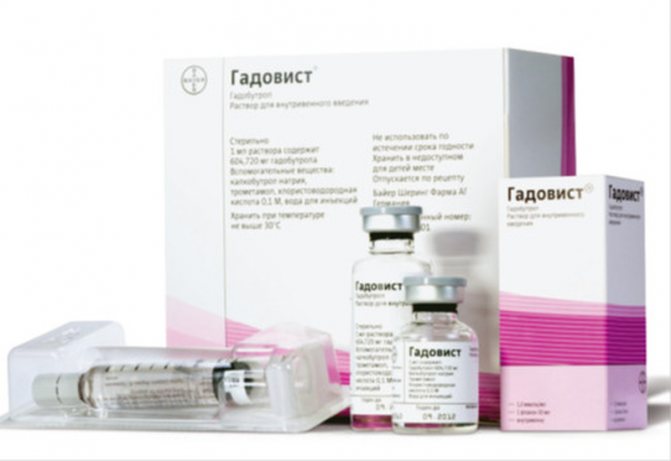
Modern radiologists more often use a paramagnetic agent based on gadolinium chelates for MRI. Each manufacturer has its own name for the drug: Gadovist, Dotarem, Magnevist, Omniscan, etc.
Gadolinium is a rare earth metal, a lanthanide, used in dissolved form for contrast in MRI. The action is based on its more intense accumulation in pathological foci and a change in relaxation times in target tissues, which provides better visualization, for example, after enhancement, the tumor boundaries are better visible. Side effects develop less frequently than with the use of iodine-containing contrasts, and include allergic manifestations such as urticaria, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Nephrogenic contrast-induced fibrosis is a casuistic complication that occurs in less than 1% of patients, but the risk of encountering pathology is higher in people with advanced stages of chronic renal failure.
MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast can be standard, when a paramagnetic agent is administered intravenously by a nurse at the rate of 0.2 mg/kg of the subject’s weight, or bolus, in which contrast is dosed at certain minutes of the diagnostic procedure, which allows assessing the functional abilities of organs in real time ( dynamic MRI).
All indicators based on gadolinium chelate complexes used for enhancement are safer than their analogues or radiopharmaceuticals. After the study is completed, it is recommended to increase the drinking regime, since in this case the contrast agent is eliminated from the body by the kidneys faster.
Indications
Despite its harmlessness, the procedure should not be carried out without a doctor’s prescription. In most cases, a referral for an MRI with contrast is given when cancer is suspected.
The cavity CT procedure does not require special preparation. The patient does not need to adhere to a diet or give up his usual lifestyle. If you are taking medications, you should inform the doctor who writes the prescription. The doctor will decide whether to stop taking the medication or not.
MRI of the retroperitoneal space with contrast can cause exacerbation in allergy sufferers, so before prescribing the procedure, the doctor talks in detail with the patient to identify all possible complications.
The contrast agent, which is gadolinium, is administered intravenously. Gadolinium is safer than iodinated contrast used in computed tomography, but may cause side effects such as shortness of breath, hives, and itchy eyes in some patients.
The tomograph is a large tube, and scanning is carried out using a magnet. Before the procedure, you must remove all jewelry, hairpins, watches and other metal objects.