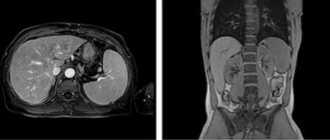
MRI of the coccyx is a separate targeted examination of the last part of the spine. It should not be confused with MRI of the lumbosacral spine, which covers the sacrum but not the coccyx. The coccygeal bone, or coccyx, is located at the very bottom of the spinal column. If you carefully examine the coccyx, you will find that it consists of 4-5 rudimentary vertebrae that have fused together. Its main task is to attach ligaments and muscles that ensure the normal functioning of the intestines, as well as the human reproductive system. In addition, it is the tailbone that helps to extend and bend the leg at the femur.
Most often, the reason to do a magnetic resonance imaging of the coccyx is discomfort in the coccyx. As a rule, pain in this area occurs in young mothers, professional athletes, office workers, and people who are engaged in constant physical labor.
MRI of the thoracic spine
MRI of the lumbosacral region
MRI of the cervical spine
MRI of the craniovertebral junction
MRI of the sacroiliac joints
MRI of the sacrococcygeal area
MRI of the entire spine
MRI of 3 parts of the spine
What is MRI of the coccyx
During the examination, the tomograph creates a magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses around the patient. Under this influence, hydrogen protons line up in tissue cells for some time parallel to the field, and then return to their original position. During this change, a small amount of energy is released. It is captured by the device’s computer, digitized and recorded as a three-dimensional image on the monitor screen.
The advantages of MRI are:
- Obtaining data not only about the coccyx, but also about neighboring tissues;
- Determination of damage, neoplasms, inflammatory processes;
- The high quality of the images makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis in one examination;
- During surgery, tomography data can reduce injury to neighboring areas;
- The absence of harmful radiation and safety allow the frequent use of MRI.
Indications
A patient may receive a referral for examination of the coccyx using a tomograph in the following cases:
- Anomalies in the coccygeal region;
- Possible displacement, fracture;
- Suspected tumor, metastases;
- Suspicion of cauda equina syndrome;
- Pain syndrome;
- To confirm previous studies;
- To identify the dynamics of treatment.
Previous Next
For what diseases is an MRI of the coccyx performed?
During the examination, pathological phenomena in the area of the coccyx and sacrum are considered simultaneously, since they are functionally connected. The connection of the above structures forms a syndesmosis. Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to identify pathologies of bone and soft tissues. A doctor prescribing an MRI suspects the following diseases:
- fracture of the coccyx, cracks, displacement of the vertebrae;
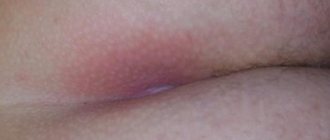
- coccydynia (inflammatory reaction and deformation of the appendix);
- neoplasms of bone or soft tissue (benign and malignant), metastases;
- compression of nerve roots (cauda equina syndrome);
- infectious pathologies, including the formation of fistulas;
- spondylolisthesis (vertebral displacement);
- vascular disorders;
- spinal canal stenosis (narrowing);
- tuberculosis of bone structures;
- autoimmune and congenital pathological changes.
Coccydynia on MRI
Diseases of the coccyx have a direct impact on the functioning of the pelvic organs and hip joints. When moving, part of the load from the upper vertebrae is distributed onto the process. Delay in going to the clinic can significantly worsen the condition and lead to irreversible changes in the structure of the lumbosacral region.
What will a tomography of the coccyx show?
During an MRI examination, you can obtain accurate information on the condition of the coccygeal region and:
- Identify congenital or acquired anomalies;
- Detect tissue destruction in the coccygeal region;
- Identify possible post-traumatic changes;
- Find out the condition of the coccyx. When healthy, it represents an inverted pyramid;
- Find out the number of vertebrae that form the coccygeal bone;
- Determine the position of the coccyx, the presence of injuries, fractures, displacements;
- Consider the condition of the vessels that are located in the pericoccygeal region;
- Determine the presence of fistulas, abscesses, as well as tumors and cysts;
- Examine the articulation of the patient’s coccygeal bone and the sacrum;
- Note changes in connective tissue or bones;
- See the presence of degenerative changes.
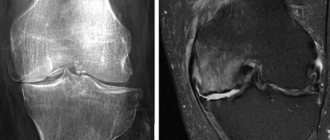
Coccyx on MRI image
| MRI of the coccyx | MRI of the coccyx with coccydynia |
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
How to prepare for a tomography of the coccyx and sacrum
No special preparation is required to study the coccygeal region. A person may not change his eating habits and lifestyle. Special instructions can be set by the doctor only if contrast is administered to the patient. As a rule, restrictions include refusing food 2 hours before the procedure.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
How is an MRI examination of the coccygeal area performed?
When a doctor recommends undergoing an MRI examination, a person immediately has thoughts about how the procedure will go and whether it will be painful. You can immediately calm down - this method is absolutely painless and safe.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the coccygeal area takes place in several stages:
The first step is to remove all metal objects from the body. All chains, rings, belts will need to be removed during the procedure, and all electronic devices - phones, tablets, watches - should be left in the preparation room.
Next, the patient takes a comfortable position on a special table, which slides into the MRI machine. You will have to lie on your back or stomach.
The tomographic scanner will begin its work. It is worth noting that the device sometimes makes specific noises. While the scanner is taking pictures, the patient will hear noises and tapping sounds. To rid yourself of these sounds, you can use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones.
The entire diagnosis usually lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. When the table with the subject leaves the MRI machine, the diagnostic procedure is considered complete.
You can find out the results of the study in about 1 hour. Occasionally this time can be increased to 2 days.
Questions about diagnostics
Dress code
You can enter the MRI room in any clothing that does not contain metal. When going to the clinic, it is best to wear loose, non-restrictive clothing without metal elements (zippers, rivets, hooks), in which you can lie comfortably. For women, we recommend bringing a T-shirt or not wearing a bra with metal wires or hooks.
Preparation
This tomography does not require any preparatory steps from the patient.
Is MRI harmful to health?
MRI is a completely harmless diagnostic method for the human body. This method of examination can be carried out at any age and for any disease an unlimited number of times, unless you have contraindications.
Contraindications
Some pacemakers and foreign objects in the body may pose serious limitations to tomography. In particular, cochlear implants, vascular clips, stents, heart valves and insulin pumps, pacemakers, neurostimulators, steel screws, staples, pins, plates, joint endoprostheses may be a contraindication to diagnosis. The patient must notify the radiologist about all implanted objects in the body. The diagnostician will be able, based on information about the composition and model of the implant, to assess the possibility of conducting diagnostics.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, be sure to report any allergies to medications or kidney problems. It is also necessary to inform the radiologist about a possible pregnancy.
Is it possible to do an MRI with braces and dental implants?
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic field does not have any negative effect on them. Fixed brace systems can produce artifacts on tomograms during MRI of the head. If the light effect is too strong, the doctor will stop the study and offer the patient alternative diagnostic methods.
Is the device noisy?
Any MRI machine in working condition makes noises reminiscent of tapping. The open tomograph is one of the quietest installations. The noise from its operation is significantly lower compared to closed tomographs. If the sounds of the operating unit cause you anxiety, you will definitely be offered special noise-canceling headphones.
What should I do if I have claustrophobia?
An open tomograph is the optimal solution for patients suffering from panic attacks in a closed space. It is open on the sides on three sides and does not create a claustrophobic feeling.
Can I take sedatives before an MRI?
If you are a little nervous, before the tomography you can take mild sedatives, for example, valerian, motherwort infusion or afobazole. Taking sedatives does not have a negative impact on the quality of MRI.
Why is it important not to move during the test?
Any movement during the examination reduces the quality of the resulting images. Multiple motion artifacts may appear on the images, and the MRI results will be uninformative.
Can I do the research with an accompanying person?
Absolutely yes. You can invite any accompanying person from among your family and friends to the MRI room. It is important that your companion does not have metal implants or artificial pacemakers in his body.
Computed tomography (CT)
This method is based on measuring the attenuation of X-ray radiation passing through the human body in various projections. A CT tomograph allows you to obtain layer-by-layer thin-section images, eliminating their overlap. Its sensitivity to small changes is at least 10 times higher than that of an X-ray machine. Computed tomography is quick and painless, but it is often not recommended, since X-ray radiation can negatively affect the patient’s body.
However, CT is the leading method for diagnosing diseases of the chest organs (lungs and mediastinum), retroperitoneum, and adrenal glands. CT is better than other methods in identifying stones in the urinary system and assessing destructive changes in bone tumors of any location.
Interpretation of MRI results of the coccyx
An example of MRI decoding of the coccyx
Area of study: MRI of the coccygeal spine In a series of MR images weighted by T1 and T2 in the sagittal and axial planes, the structure of the coccygeal vertebral bodies is quite homogeneous, the intensity of the MR signal from the bone marrow of the coccygeal vertebral bodies is moderately increased on T2 and T1-weighted account of fatty degeneration.
Location of the coccygeal vertebrae according to type 1. There were no signs of bone marrow edema of the vertebral bodies. Direct MRI signs of post-traumatic changes are not determined. Presacral fatty tissue is not changed. Conclusion: Initial degenerative-dystrophic changes in the coccygeal spine. It is difficult for an ordinary person to independently understand and interpret the results that, after an MRI, will be given to him on a digital medium. Therefore, with the conclusion of the radiologist and the photographs, he should go for a consultation with the attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis based on the summary data of the examination, medical history and tomography data. In our clinic , after an MRI, you can have a free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist . Doctor
- will answer all questions based on the results of the research and the conclusion received
- Helps explain tomography results without using complex radiological terminology
- will conduct an examination and, if necessary, offer treatment.
“Second independent opinion” service Medicine is an area where we want to be 100% sure . Therefore, at your request, we will be happy to offer you the service of a second independent opinion from the leading consultant of our clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences , a doctor of the highest category with 18 years of experience in the field of tomography and radiology N.V. Marchenko.
Indications for MRI of the spine
As a rule, clinicians (neurologists, neurosurgeons, therapists, traumatologists) recommend undergoing an MRI for back pain, regardless of what nature it is. It should be noted that often problems with the spine can manifest themselves not only in the form of pain, but also be accompanied by impaired sensitivity (numbness) of the fingers, weakness in the arm or leg, atrophy of the muscles of the limb, dizziness, pain in the heart, urinary retention and other complaints.
MRI of the spine is indicated for:
- DDSD (degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine), the most common of which is osteochondrosis. MRI reveals not only the disease itself, but also its complications (protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs, spinal canal stenosis, spondyloarthrosis of the facet joints, etc.). Based on the data obtained, the attending physician selects the most optimal method of conservative (non-surgical) therapy, or resorts to surgical (surgical) treatment;
- inflammatory diseases of the spine (spondylodiscitis, tuberculous spondylitis), spinal cord (transverse myelitis) and roots (arachnoiditis);
- vascular diseases of the spinal cord (cavernous angioma);
- congenital anomalies of the spinal cord (myelocele and myelomeningocele, hydromyelia, syringomyelia, diastematomyelia (spinal cord splitting);
- suspected tumor: of the spinal cord, its roots or spine;
- traumatic injuries of the spine and spinal cord;
- demyelinating diseases of the brain, to search for intramedullary (localized in the spinal cord) foci of demyelination, as well as to assess the dynamics or determine the activity of the process of previously identified foci;
- assessing postoperative complications (pseudomeningocele), determining the degree of resectability, excluding or identifying continued tumor growth in operated patients.
What determines the price of tomography of the coccyx?
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the brain | 3300 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of cerebral vessels (arteries) / MR angiography of cerebral vessels | 3300 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the brain and cerebral vessels | 6600 rub. | 5180 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland (without contrast) | 3500 rub. | 2590 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast | from 6500 rub. | not implemented | from 6900 rub. |
| MRI of the pituitary gland and brain | 7800 rub. | 5180 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral region) | 13200 rub. | 9290 rub. | 10790 rub. |
| Comprehensive head diagnostics (MRI of the brain, MRI of cerebral vessels, ultrasound of neck vessels, consultation with a neurologist) | 10900 rub. | 7500 rub. | |
| Contrast administration (based on patient weight) | from 4000 to 6000 rub. | from 4000 to 6000 rub. |
What determines the cost of tomography?
![]()
Tomograph power
![]()
Applying Contrast
Personnel qualifications
![]()
Promotions and discounts
Medical centers engaged in diagnostics set their own prices for procedures. The cost depends on various factors. The most important of them is the tomograph model. The higher its inductive power, the more expensive the service. In diagnostic centers of St. Petersburg, MRI of the coccyx can be done most cheaply using open-type devices, and the best quality is possible using ultra-high-field tomographs of the latest generation 3 Tesla.
In addition, the price increases when a contrast agent is used. If, according to the doctor’s recommendation, the diagnosis should be carried out with contrast, and the patient underwent tomography without it, then the diagnosis may be made incorrectly.
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
What does an MRI of the lumbosacral region show?
Many patients are interested in what an MRI of the lumbosacral region shows. The high detail of images obtained using MRI diagnostics makes it possible to accurately identify the following diseases localized in the lumbar spine:
- protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs;
- degenerative diseases: osteochondrosis, spondylosis;
- consequences of previous injuries, such as compression fractures, subluxations and vertebral displacements;
- multiple sclerosis;
- neoplasms of primary and metastatic origin;
- osteomyelitis;
- myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord).
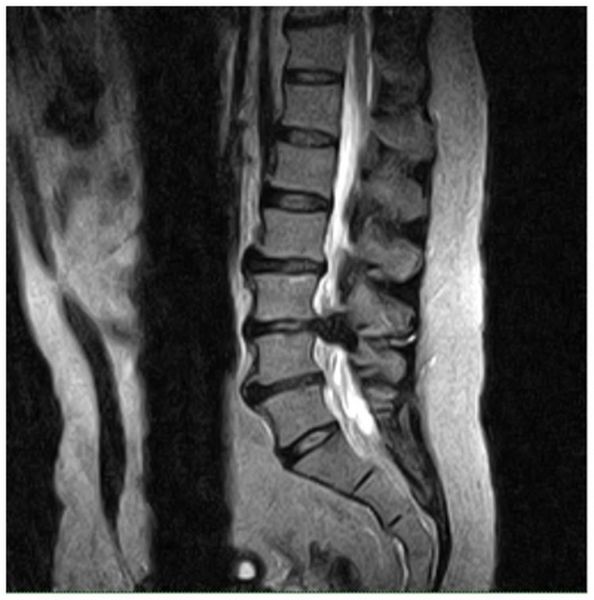
Intervertebral hernia
On MRI you can clearly see:
- thickness and density of intervertebral discs;
- dystrophic changes in the vertebral body;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- the condition of the soft tissues in the area under study.
Based on these data, it is possible to draw a clear picture of the course of diseases of the lumbosacral spine.
The most common indication for an MRI examination of the lumbosacral region is suspicion of osteochondrosis, protrusion and herniated intervertebral discs.
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease in which deformation of the vertebral bodies occurs, erasure and flattening of the intervertebral discs.
Typical manifestations of lumbar osteochondrosis are periodic aching and nagging pain, numbness and loss of mobility. People who lead a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle are at risk for the incidence of osteochondrosis.
Timely detection of the disease makes it possible to stop degenerative processes and the occurrence of complications. Diagnosis using MR scanning will give an idea of the stage of the disease and the extent of the affected area.
Protrusion is a bulging of the intervertebral disc without rupture of the surrounding fibrous ring.
The disease occurs when degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the lumbar region are advanced. The appearance of protrusions can also be preceded by sudden movement or heavy lifting.
A common symptom of the disease is lower back pain of varying intensity, numbness in the legs and groin area.
MRI of the lumbar region helps to identify even small protrusions in the early stages of occurrence. Further treatment of the disease is usually conservative. The patient is prescribed painkillers, physiotherapy and massage. An important factor in preventing protrusions is physical activity adequate for age and health status.
A herniated disc occurs when the annulus fibrosus ruptures and the disc moves into the spinal canal, compressing the spinal cord.
The disease is characterized by severe pain, which may subside over time and return again. Depending on the location of the hernia and possible compression of the spinal cord roots in a certain area, the patient may experience shooting pains in various areas of the lower extremities, urinary incontinence and severe pain in the lower back, buttocks and thighs.
Timely diagnosis of hernias helps relieve the patient from discomfort and pain. MRI gives a detailed picture of the course of the disease. In the pictures you can see the location of the hernia, its size and the degree of compression of the spinal cord, and determine the inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
Treatment of hernias can be conservative and include therapeutic blockade, avoidance of excessive tension and stress, physical therapy and yoga, and massage. In severe cases of the disease and when the pain syndrome does not subside over time, surgical intervention is performed.