Previous Next
MRI of the hip joints is one of the modern, non-invasive, highly informative and safe diagnostic techniques that can be performed on children of any age, pregnant women, cancer patients and the elderly without harm to health. It does not carry any radiation load and is quite comfortable for the patient. During the scan, the patient's diagnosed area is exposed to a strong magnetic field and electromagnetic pulses, under the influence of which the hydrogen atoms in the cells begin to vibrate. These impulses are captured by the tomograph computer and translated into three-dimensional images of bones, tendons, ligaments, soft tissues and blood vessels. The absence of Rg radiation allows MR examinations to be repeated the required number of times without restrictions, without causing harm to the body.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
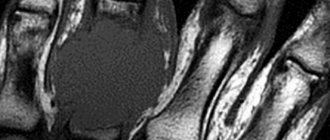
Using an MRI scanner, an image is created in three planes - axial, sagittal, frontal with the required magnification of the area under study. The distance between the sections is so small (2-3 mm) that they make it possible to see minor damage to the joint. Such high-quality images help the treating doctor determine the correct diagnosis with a probability of up to 95%.
What will magnetic resonance imaging of the hip joints show?
For joint disorders, MRI will help identify:
- osteoporosis;
- arthritis and rheumatic lesions, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- congenital and acquired dysplasia of the hip joint;
- spondylitis and ankylosing spondylitis;
- fractures, dislocations;
- pinched tendons and nerves of the joint.
Using MRI scanning, you can obtain information about changes in cartilage tissue and synovial fluid and at the same time abandon painful diagnostic methods in which special needles are used for examination.
Tomography will be mandatory:
- with aseptic necrosis of the femoral head;
- to identify metastases and their spread in the joint in case of cancerous tumors, before and after operations;
- during surgical procedures to control the progress of the operation.
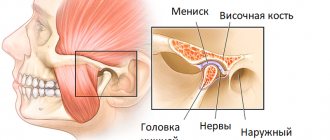
What can be seen on an MRI of the hip joints?
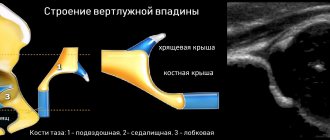
An MRI examination allows you to see and evaluate the condition of all components of the joint, namely: tendons, ligaments, synovial fluid, connective cartilage and muscles, the articular heads of the femurs, their shape, density, size and location. It is important that when scanning, not only the bone tissue of the joints is visible, but also the soft tissue adjacent to it, and how the blood vessels function.
Initial appointment with an ORTHOPEDIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
Hip joint on MRI image
Purpose and contraindications
The doctor recommends an MRI if:
- suspected osteoarthritis;
- the occurrence of rheumatic diseases - lupus erythematosus, ankylosing spondylitis;
- development of infectious arthritis;
- receiving injuries and suspected fractures, cracks, muscle strains;
- dislocation;
- the appearance of painful sensations in the presence of edema, swelling, stiffness of movement;
- development of necrosis of the femoral head;
- cancer tumor, to identify metastases and affected areas.
In addition, it is necessary to examine the pelvic bones in cases of joint diseases such as septic arthritis, tenosynovitis, osteomyelitis and others.
Diagnosis using MRI is contraindicated in several cases: when the patient has a metal device in the body (pacemaker, neurostimulator, electronic or metal implants), women during pregnancy (in the first half) and people with a mental illness that does not allow control of body movements .
Examinations using contrast are prohibited in case of individual intolerance to the substance, as well as in patients with renal failure. In cases where the hip joint needs to be diagnosed, and the person has claustrophobia or the weight of his body does not allow him to be placed in a closed circuit, a procedure in an open chamber is prescribed.
Contraindications
There are both indications and contraindications for this diagnostic procedure. Thus, if there are installed metal components or devices in the body of the subject - vascular clips, pacemakers, neurostimulators, implants, MRI examination may be prohibited. The magnet may interfere with the operation of electronic life support devices. The magnetic field can cause metal structures to move and thereby damage nearby tissue or organ, which in turn will negatively affect the patient’s health. Therefore, before starting a diagnostic study, it is necessary to inform the attending physician about all objects implanted in the body so that the tomography does not cause harm to the body.
Sometimes it is difficult to conduct research for a person who suffers from a lack of control over his movements. These can be various diseases of the nervous system and epilepsy. For high-quality tomography, complete immobility of the pelvic region is required during the entire screening process.
Sometimes claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces) can become a limitation.
The patient’s large weight or dimensions can become an obstacle to the procedure, since the devices have limitations on the table’s load capacity and chamber volume.
Which is better - MRI or ultrasound of the pelvis
The attending physician should also give a clear answer to this question. However, we note that ultrasound is a more accessible and cheaper method and has no contraindications (can be performed in the presence of a pacemaker, ferromagnetic objects in the body, claustrophobia, etc.). Using ultrasound, the anatomical state of the pelvic organs is assessed and pathological formations are determined, while very minor lesions may not be visualized. However, for final conclusions about the nature of the process, its possible malignancy, assessment of the size, and the degree of development of the pathology, clarification is required using the MRI method, which is characterized by greater information content and reliability.
In addition, ultrasound is a subjective technique, and the results directly depend on the qualifications of the doctor. MRI data is recorded on disk or printed on film and can be provided to any doctor for independent interpretation.
MRI is also performed if ultrasound cannot be performed due to the patient's obesity, since ultrasound does not penetrate dense tissue.
Preparation
In many ways, preparation for magnetic resonance imaging of a pair of hip joints depends on the need to use a contrast agent. If a patient is scheduled for an MRI of the hip joints with contrast and suffers from renal failure, it is recommended to undergo blood tests for creatinine.
When undergoing a procedure with contrast, you will need to refrain from eating 2 hours before the examination.
If there are medications that are taken on an ongoing basis, you must inform the radiologist about this.
All jewelry, watches, cell phones and other items and gadgets are not allowed into the MRI room. Therefore, it is better to leave unnecessary accessories at home. If you feel nervous being in a confined space, you can take a sedative in advance or invite a loved one with you to the study to be nearby and support you.
MRI of the pelvic bones: preparation
The duration of the scan is 25-30 minutes; maximum immobility is required during the procedure.
No special measures are required to study this anatomical area: you must leave all objects containing metal outside the diagnostic room and choose comfortable, loose clothing without zippers, rivets, jewelry, etc.
Pain in the pelvis can be caused by a pathological process of internal structures (irradiation to the bones or joints). Therefore, to be able to evaluate parts of the reproductive, urinary and intestinal tract in the area of interest, 2-3 days before the scan, gas-forming foods and drinks should be excluded from the diet: peas, beans, cabbage, black bread, milk, kvass, beer, etc. For examination You should come after a 4-6 hour fast.
To prevent vegetative reactions to the administration of the drug, it is recommended to have a light snack 20-30 minutes before diagnosis with contrast. Eating a small amount before the procedure will not interfere with visualization.
MRI of the pelvic bones and vital organs of a given anatomical region is technically carried out in different ways: to study a specific structure, they use variable sequences and modes, wait a certain period of time to achieve contrast, etc. The doctor, with a preliminary assessment of the images and a clear suspicion of a disease of any organ may change the diagnostic algorithm. Proper preparation for an MRI will allow you to get better images. All identified changes will be described in the conclusion.
Take with you the results of previous diagnostics: X-ray and ultrasonography, CT, MRI, PET, hospital discharge. To conduct the study, you need a passport, a referral, and a Compulsory Medical Insurance/VHI policy (if the MRI is paid for by an insurance company).
How to do an MRI of the hip joints
During tomography, it is always necessary to examine a pair of hip joints, since degenerative processes and inflammation most often affect both joints at the same time. The examination itself is absolutely painless, and the person does not need subsequent recovery. It can be done using open and closed tomographs.
The procedure for MRI of the hip joints on a closed machine is quite simple: before the procedure, you need to put on disposable medical clothing, suggested by the diagnostician, and lie down on a table-couch. If tomography is prescribed with contrast, then the patient is injected with the drug into a vein in the elbow before scanning, and then the movable table-couch is inserted into the cylinder of the device. The task of the person being diagnosed is to remain motionless during the entire diagnosis, since this is an important point, which is the main factor determining the quality of the obtained tomograms.
The closed chamber of the tomograph is equipped with lighting devices and ventilation. A microphone is used to establish a permanent connection with the doctor. During the procedure, the patient hears crackling and tapping sounds, which change throughout the study depending on the scanning program. If they are annoying, you can always ask to wear noise-cancelling headphones. The patient does not experience any other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes slight heating of tissue in the scanning area may occur.
The examination can last from 15 to 20 minutes, and with the use of contrast, the examination time increases to 30-40 minutes.
MRI of the hip joints using an open tomograph does not require the patient to be immersed inside a cylindrical chamber. During scanning, the subject is located under a magnet in the form of a canopy, which is open on three sides.
Tomography with an open device can last from 30 to 40 minutes, and with the use of contrast, the examination time increases to an hour.
| OPEN TYPE MRI | SEMI-OPEN MRI | CLOSED MRI |
Contraindications to diagnostic procedures
There are a number of contraindications to any diagnostic method. Let us first consider the general contraindications to CT and MRI:
- inappropriate behavior of the patient;
- large body weight (CT allows a weight of 150 kg, MRI - 110 kg).
CT is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy;
- in the presence of intolerance to contrast agents containing iodine.
MRI has many contraindications:
- pregnancy (1st, 3rd trimester);
- presence of pacemakers;
- claustrophobia;
- metal foreign bodies (postoperative structures, clips, implants, stents);
- middle and inner ear implants.
A pelvic ultrasound can be done in almost all cases. There are no strict contraindications to this procedure. Due to its safety, it is used to diagnose pathologies in infants and pregnant women.
Decoding
The doctor deciphers the images obtained during the tomography and issues a research protocol, which will indicate all joint parameters: tissue thickness, its shape and structure, location and size. Along with the protocol, the radiologist transfers to the patient all the images recorded on digital media. If desired, they can be obtained in printed form. The time required to compile a protocol can take about an hour on average, and in complex cases about 2 days.
Thus, the cycle from the start of the procedure to the receipt of results can be 2 hours. If the patient does not want to wait for the transcript results in the clinic, he can receive the data by email or come for an x-ray report the next day.
With the results of magnetic resonance imaging, you should contact your attending physician or a specialist who, based on the radiologist’s report, will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
- If you have rheumatoid arthritis, you should consult a rheumatologist.
- A neurologist can help treat pinched tendons and the sciatic nerve.
- For complex joint injuries, arthritis and arthrosis, you need to make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist.
- If a tumor is detected, you need to go to an oncologist.
It is worth remembering that the radiologist does not make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. This should be done by the attending physician based on the diagnosis.
It is difficult for an ordinary person to independently understand and interpret the results that, after an MRI, will be given to him on a digital medium. Therefore, with the conclusion of the radiologist and the photographs, he should go for a consultation with the attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis based on the summary data of the examination, medical history and tomography data. In our clinic , after an MRI, you can have a free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist . Doctor
- will answer all questions based on the results of the research and the conclusion received
- Helps explain tomography results without using complex radiological terminology
- will conduct an examination and, if necessary, offer treatment.
An example of decoding an MRI of the hip joints
On a series of MRIs of the hip joints, the relationships in the joints were not disturbed.
Free intra-articular fluid is not detected. The synovial membrane is not differentiated in native sections. No traumatic bone changes were detected according to the MRI examination. The bony contour of the articular surface of the femoral heads is not deformed, the heads are spherical in shape, centered within the articular sockets, and the arches of the acetabulum are formed correctly. Areas of increased MR signal on T1-weighted images from the bone marrow in the area of the proximal femurs and pelvic bones due to fatty degeneration. There are areas of unevenly expressed subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces of the acetabulum. The articular fibrocartilaginous lip has a homogeneous structure on both sides, without signs of rupture. The joint spaces are uniformly and moderately narrowed, the signal of the cartilaginous component of the joint is unevenly reduced, and the articular hyaline cartilage is moderately and uniformly thinned. There is an increase in signal intensity on Stir IP (swelling) in the area of the greater trochanter at the level of attachment of the tendons of the gluteus medius muscle on both sides, the structure of the tendons at this level is heterogeneous due to areas of increased signal, their integrity is not compromised. Conclusion: MRI signs of grade 1 deforming arthrosis of the hip joints. MRI signs of enthesopathy of the gluteus medius tendons on both sides. Author: Usenko Nikita Sergeevich
Orthopedist-traumatologist with 8 years of experience
What affects the cost and quality of MRI of the hip joints
The cost of a hip MRI may vary from hospital to hospital. Most often this depends on the equipment installed in clinics. Research using high-field tomographs is 1.5-2 times more expensive than medium- and low-field ones. If it is necessary to identify mechanical, gross damage to the joint surfaces, arthritis, arthrosis, then open-type tomographs can easily cope with this task, and in this case there is no need to overpay. But if there is a suspicion of tumor changes or systemic disorders, then a closed high-voltage (1.5 T and higher) tomograph is indispensable.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the hip joints | 5000 rub. | 2990 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
Computed tomography (CT)
The operating principle of CT is based on the effect of X-rays on the human body, which, passing through certain structures of the body, are more or less retained in them and thereby produce a three-dimensional image of the body tissues. CT is most informative in the following cases:
- Pathologies and injuries of bones, skull, teeth (including tumor lesions of bones)
- Pathologies of the spine (bone component)
- Diseases of internal organs: stomach, intestines, genitourinary system and others
- Vascular diseases, atherosclerosis and others
In general, CT is most often used to examine internal organs and detect bone injuries and bleeding. Despite the high effectiveness of this method, remember the dangers of CT X-ray radiation. Do not resort to this examination too often!
MRI in our center
Power 1.5 Tesla
High image quality
Study for patients up to 250 kg
Burn to disc for free