One of the main features of magnetic resonance imaging is the absence of radiation. There is no radiation exposure - and MRI automatically has an advantage over other imaging methods that use X-rays (computed tomography and radiography).
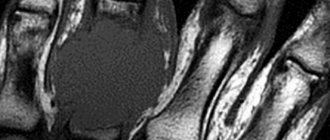
In addition to safety, MRI of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is clearly superior to other diagnostic methods in terms of information content: magnetic resonance imaging has a very high resolution and the greatest contrast of soft tissue structures, which allows detailed visualization and assessment of changes in such fine structures as ligaments and intra-articular meniscus , the cartilaginous plate of the joint, the muscles and fiber surrounding the TMJ.
Anatomy of the temporomandibular joint
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a combined paired joint formed by the heads of the lower jaw and the articular tubercles (pits) located on the temporal bone. In the cavity of the TMJ there are menisci - cartilaginous plates that act as pads and shock absorbers, and also provide articulation function. Thanks to this, the temporomandibular joint is able to withstand significant loads that occur when chewing food. For the same reason, the TMJ has a powerful ligamentous apparatus that strengthens and stabilizes the joint.
The complex structure of the temporomandibular joint and intense loads are the reason why degenerative processes and diseases often occur in the joint. Magnetic resonance imaging, unlike other diagnostic methods, “sees” not only bones, but also cartilage, ligaments and menisci. This is why MRI is the best method for diagnosing diseases of the maxillofacial joints.
Read also
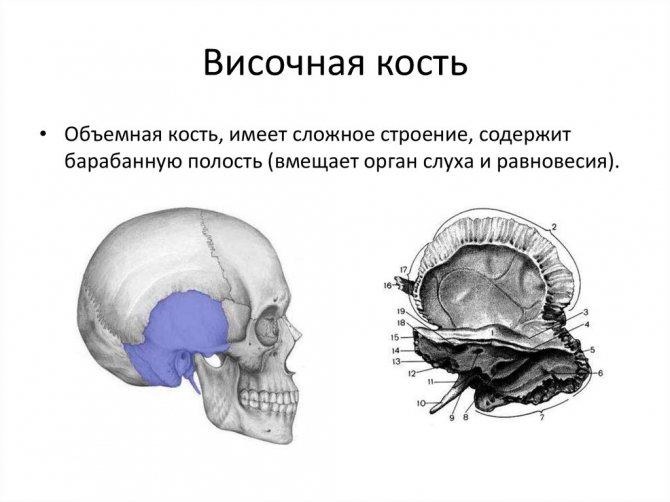
MRI of temporal bones
THE TEMPORAL BONE is one of the most complex bones, as it is the seat of the organ of hearing and balance and the carotid artery and nerves pass through it
.
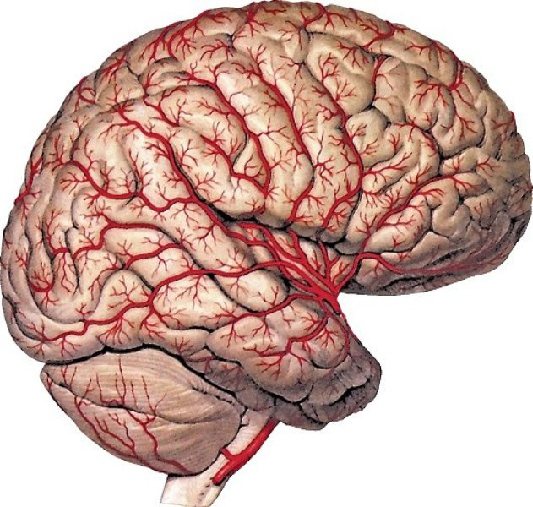
MRI of the brain with blood vessels
The brain is the highest part of the human central nervous system
Read more
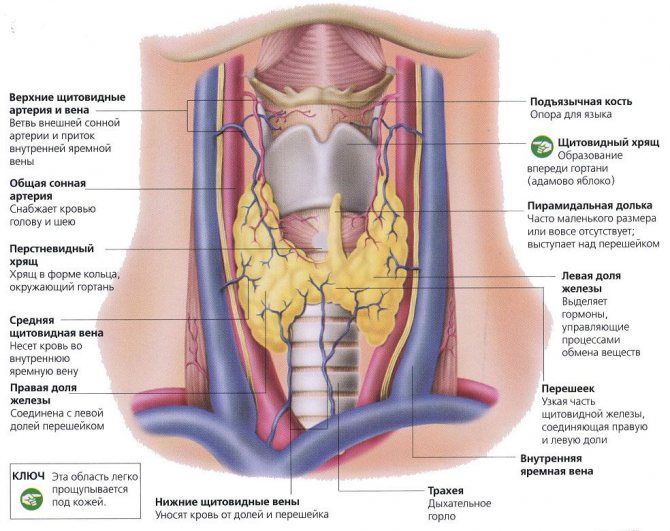
MRI of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is an unpaired organ that secretes thyroid hormones
Read more
Types of MRI
- MRI of the brain
- MRI of the entire spine
- Abdominal MRI
- MRI of the knee joint
- Whole body MRI
- Other types
It is important to know
MRI for children To obtain the best quality images, it is necessary that the child remains absolutely still during the procedure
More details
What is MRI? MRI is a safe, most informative and painless diagnostic method.
More details
Best MRI Exam There are a few key factors to consider
More details
About the site
- About the site
- Authors of articles
- Add address
- Feedback
- Search
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of use
- Site Map
Indications for MRI of the maxillofacial (temporomandibular) joints
The temporomandibular joint, like any other joint in the human body, is susceptible to rheumatic and degenerative diseases. The outcome of these pathologies depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. In severe cases, the disease can cause complete loss of TMJ function, leading to the inability to eat solid foods and other negative consequences.
In complex and controversial cases, MRI of the TMJ can be performed with contrast. To do this, a special contrast agent is injected into the patient’s ulnar vein, which is absorbed by diseased tissues, facilitating diagnosis. The contrast is safe and only occasionally can cause mild allergic reactions in the form of a rash or itching on the skin.
TMJ diseases that can be seen on MRI images:
- Inflammatory diseases (arthritis);
- Degenerative-dystrophic pathologies (arthrosis, deforming osteoarthritis);
- Ankylosis (fusion) of the TMJ;
- Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- TMJ dislocations and other injuries;
- Neoplasms;
- Aseptic necrosis, bone osteomyelitis;
- Congenital anomalies of the TMJ.
Alarming symptoms, in the presence of which it is recommended to do an MRI of the TMJ:
- Pain in the area of the maxillofacial joint, intensifying with movement of the lower jaw (when chewing) and radiating to the face and temple;
- Swelling and redness of the maxillofacial joints;
- Nodules, dense or soft formations, bumps that are identified in the TMJ area visually or by palpation;
- Impaired mobility of the TMJ, stiffness, limited mouth opening;
- Spasm of the masticatory muscles;
- Clicking in the joints that occurs when chewing and moving the lower jaw;
- Discomfort that occurs when the mouth is opened wide (it is difficult for the patient to close the mouth, which may cause clicking and pain in the TMJ area).
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the jaw
This examination is prescribed in the following cases.
- Jaw injury.
- Pain, clicking or cracking in the jaw joints when opening and closing the mouth.
- Painful sensations when touching the area of the temples, ears, chin.
- Difficulty and pain while chewing.
- The appearance of swelling on one side of the face.
- Limitation of muscle movements when opening the mouth.
- Preparation for prosthetics and dental implantation.
- Tomography of the upper jaw is also prescribed to clarify the condition of the maxillary sinuses.
However, MRI is contraindicated for patients with metal or electronic implants, pacemakers, or ferromagnetic Ilizarov devices. The procedure is also not recommended for pregnant women and people with heart failure.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging of the maxillofacial joint is contraindicated:
- Patients with pacemakers, neurostimulators, cochlear hearing prosthetic systems, defibrillators implanted in the patient’s body (magnetic fields used for MRI can disable the devices);
- Patients who have metal foreign bodies in their bodies (steel or iron shavings in the eyes, vascular clips on the main arteries, fragments and fragments of ammunition);
- Children under 5 years old;
- Pregnant women up to 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- Persons with excess weight of more than 130 kg and body girth of more than 150 cm (there is no physical ability to place the patient in the tomograph).
Preparing for MRI of the temporomandibular joint
The procedure does not require any preparation. The study is carried out at any time convenient for the patient, is not accompanied by pain and does not require complex medical procedures. All that is required of the patient is to remain motionless until the examination is completed.
MRI of the TMJ is a safe procedure, provided that safety regulations are followed. It is prohibited to carry metal objects, accessories, jewelry, wearable electronics and gadgets on the body or in pockets or on clothing. Magnetic fields can cause metal to heat up, causing burns. Massive metal objects attracted to the scanner's magnet can cause injury or equipment failure. Any excess can be left in the storage room.
How to do an MRI of the temporomandibular joint
There are special installations for carrying out MR tomography - MR tomographs. They look like a large cylindrical block, weighing several thousand kilograms, in which a superconducting magnet is located, generating a magnetic field, receivers and transmitters of radio waves. In the center of the tomograph there is a tunnel, about 60 cm long and wide. A narrow movable table passes through the tunnel, on which the patient lies during the examination.
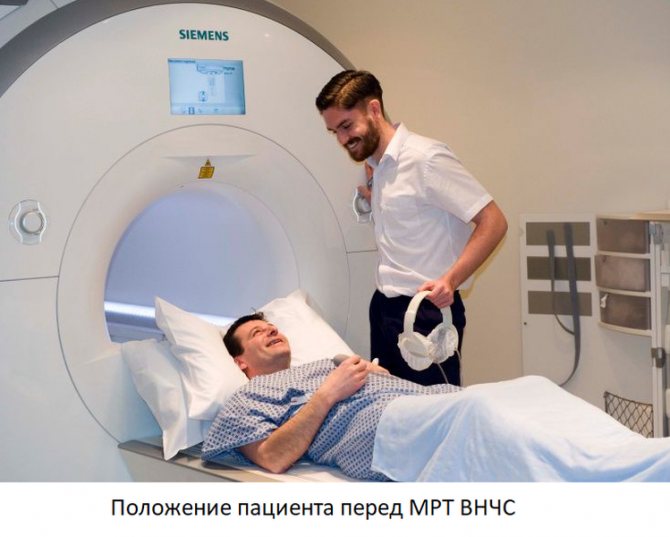
The procedure begins with placing the patient on the table. After the patient is laid down, he is asked to put on headphones - they muffle the noise that comes from the equipment and are used to communicate with the operator and even listen to music. The table is then moved so that the patient's head is in the center of the installation tunnel. This is why some patients who suffer from claustrophobia may experience discomfort during the examination.
During the procedure, you must follow all the operator’s recommendations, remain calm and still. The noise the equipment makes may sound like banging, whistling, or trumpet sounds. It is not a sign of a breakdown and indicates normal operation of the tomograph. After completing the procedure, the patient needs to wait a little - 15-30 minutes until the decoding of the images is completed. For storage, they are recorded on a CD (free of charge), or, at the patient’s request, on a flash drive, or printed on film (for a fee). After completing the examination, the radiologist talks in detail about the results of the study.
What will magnetic resonance imaging of the maxillofacial joint show?
MRI, unlike CT, perfectly “sees” tissues of all types. Computed tomography, unlike magnetic resonance imaging, is not capable of providing clear and legible images of cartilage, ligaments and tendons, but is better suited for examining bones. Therefore, to diagnose TMJ diseases, it is better to do an MRI.
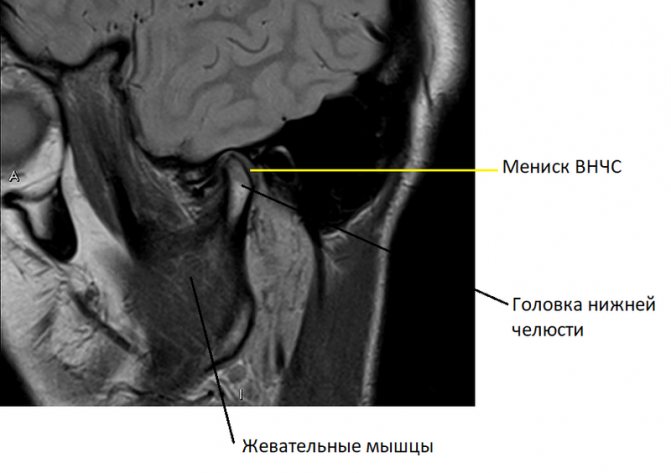
In a series of such images, taken layer by layer in the form of thin sections in several planes, it is easy to recognize the articular cartilages covering the heads of the lower jaw and the articular tubercle, forming the temporomandibular joint, the TMJ meniscus. Individual ligaments and tendons and masticatory muscles are visible. Any possible pathological change, such as joint inflammation or neoplasm, will immediately be visible on the MRI.
Where to do
Our website contains a catalog of clinics by city where you can get an MRI.
We tried to compile a catalog of all cities in the CIS and Baltic countries.
To go to the list of clinics in your city, go to the “Addresses” page and click on the city name.
If your city is not on the list, then select the one closest to you.
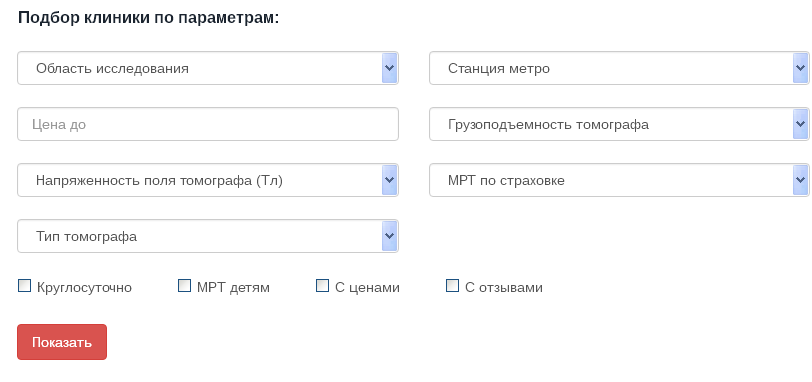
On the page for the list of clinics in the city, you will see a form for selecting clinics by parameters. This form is shown for most cities in the catalog, but not all. Some filter fields are present in the form, others may be absent, for example, not all cities have a metro and not all cities have the “Metro station” field.
|
| This is what the form for selecting clinics looks like based on parameters using the example of the city of Moscow |
The following filter fields are available:
- Field of study.
- Price up to.
- Tomograph field strength (T).
- Type of tomograph.
- Metro station.
- Load capacity.
- Insurance MRI.
- Around the clock.
- MRI for children.
- With prices.
- With reviews.
You can use the form and filter the list, or you can go straight to the list of clinics.
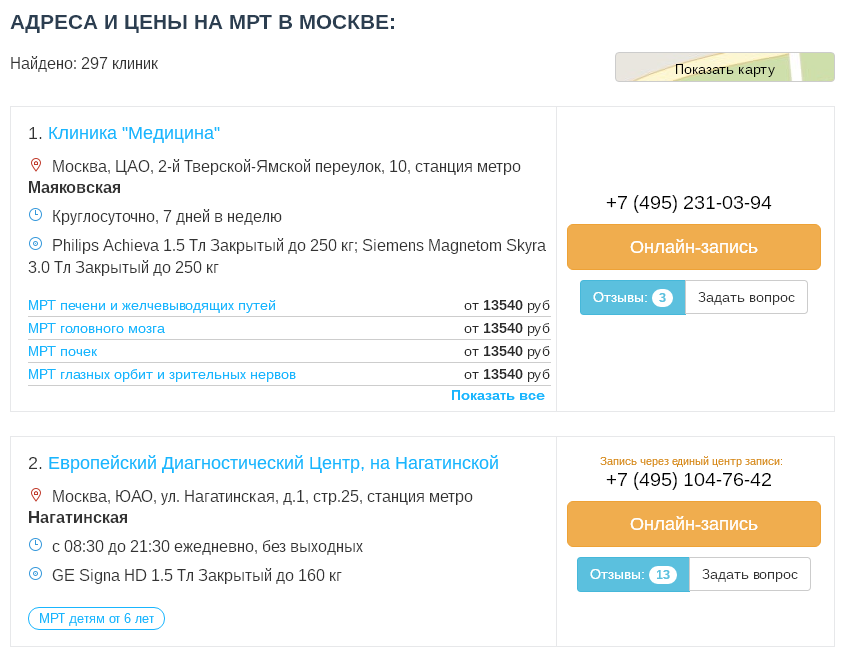
|
| This is what the list of clinics looks like using the city of Moscow as an example |
To sign up for an MRI, select one or more clinics that suit you based on various parameters and call them at the specified phone numbers. Ask questions that interest you, after which you will already decide where you want to go. Call this clinic and schedule a visit.
We wish you good health!
Publication date
30.12.2020
Author
Popov Pavel Alexandrovich
Share