MRI is a diagnostic that allows you to get a visual representation of pathological changes in ligaments, cartilage, tendons, neurovascular bundles, bones, and surrounding soft tissues. The construction of detailed images is based on the principle of magnetic resonance and does not imply the effect of ionizing radiation on the body.
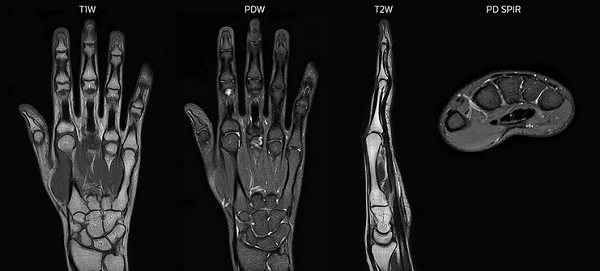
Magnetic resonance scanning can be performed using different modes
MRI of the hands with joint disease shows:
- degree of severity of the inflammatory process;
- areas of ischemia due to insufficient blood circulation;
- nerve compression;
- changes in metabolic disorders (gout);
- consequences of trauma, etc.
The study is carried out if a tumor is suspected. The scans show the interaction of the tumor with neighboring structures, which is important for determining the stage and choosing a treatment method. To improve visualization capabilities, contrast is performed.
The information content of MRI of the hand is comparable to data from arthroscopy - an invasive study with the introduction of instruments into the pathology area through incisions in the skin. Magnetic resonance scanning is considered as an expert diagnosis when obtaining ambiguous results from ultrasound, conventional radiography, and computer scanning.
MRI of the hands for joint disease
Regardless of the genesis of the pathology, clinical manifestations may include:
- pain, dysfunction of the limb;
- visible deformation of one or more joints;
- redness of the skin over the area of inflammation, swelling of surrounding tissues;
- numbness or tingling of the fingers (paresthesia).
If the cause remains unclear and there is no effect of treatment, it is necessary to do an MRI of the hand - the study shows:
- Traumatic injuries.
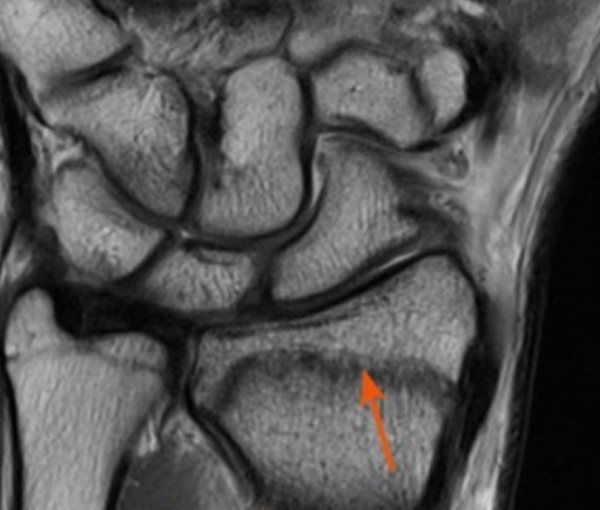
Trabecular fracture without displacement (arrow)
High contrast resolution of soft tissues on MR tomograms makes it possible to study the features of injury. Increased signal intensity indicates abnormal morphology during injury. MRI of the hand is prescribed to differentiate:
- bruises;
- fractures;
- dislocations;
- tendon ruptures, etc.
Magnetic resonance imaging is useful in the evaluation of radiographically occult (occult) fractures. The study is more informative compared to CT, which makes it the gold standard for detecting this pathology.
- Arthropathy.
Damage to the cartilage of the hand and fingers is a common feature of several processes, usually associated with degenerative, inflammatory or infectious factors. Failure to promptly diagnose can lead to irreversible changes and disability.
MRI of the hand has advantages over radiography in the assessment of arthropathy. On radiographs, joint spaces may remain preserved in the presence of synovitis or effusion, which is mistakenly interpreted as normal. MRI allows direct visualization of cartilage and detects small hyperintense subchondral cysts and erosions in the early stages of the disease.
- Osteoarthritis.
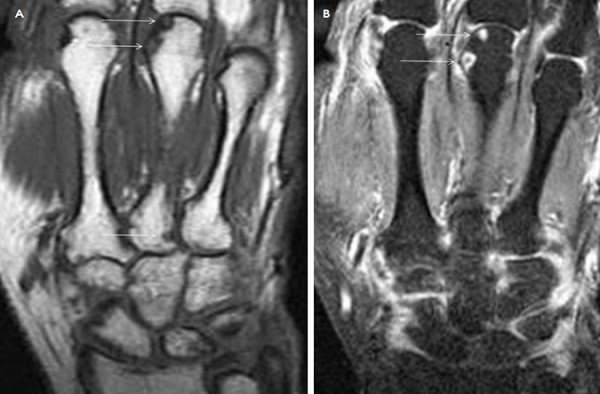
MRI of the hand and wrist with contrast shows increased erosions (arrows)
Osteoarthritis is a common disease of the joints of the hand, the prevalence increases with age. On radiographs, pathology is detected in more than 50% of men and women over 60 years of age. The disease progresses slowly and is characterized by:
- uneven abrasion of articular cartilage;
- development of sclerosis;
- formation of osteophytes and subchondral cysts.
The distal interphalangeal joints and the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb are most often affected. Osteoarthritis and associated synovitis on MRI images indicate a secondary inflammatory response to cartilage damage and the presence of loose particles. Early initiation of preventive treatment helps avoid the development of erosions.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The chronic disease manifests itself as proliferative hypertrophic synovitis, which leads to ulcerative bone defects and cartilage destruction. MRI is ideal for recognizing rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage. The study allows you to accurately detect:
- synovitis;
- tenosynovitis;
- bursitis;
- minor erosion;
- osteitis.
Subcutaneous nodules on visualization of the hand are present in 30-40% of patients.
- Psoriatic arthritis.
The inflammatory process in the joints associated with this dermatosis occurs in 30% of patients. The lesion manifests itself as isolated tenosynovitis, most often involving the flexor tendon sheaths, with associated swelling of the soft tissues of the finger/fingers (dactylitis or polydactylitis). Other systemic inflammatory diseases on MRI of the hand may have similar signs.
- Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis.
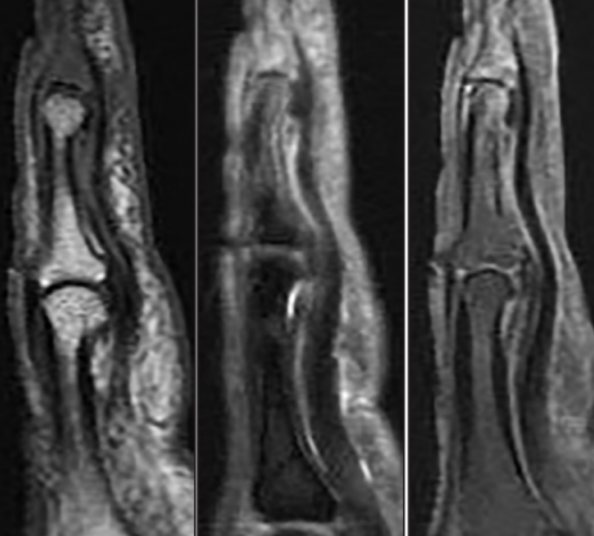
Osteomyelitis of the distal phalanx on MRI after a dog bite
Septic arthritis is caused by infection, and as it progresses, joint destruction develops. Risk factors include:
- bacteremia;
— immunosuppression (HIV, hepatitis B and C, diabetes, etc.);
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Septic inflammation often occurs with the involvement of one joint, accompanied by fever and severe pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to maintain cartilage integrity and prevent irreversible damage and subsequent development of secondary osteoarthritis. Osteomyelitis occurs against the background of a previous injury.
- Tumors.
Lymphoma of the fourth proximal phalanx on magnetic resonance scan
MRI in the diagnosis of benign and malignant neoplasms of the hand and fingers allows us to obtain detailed characteristics of the painful focus, including:
— localization;
- dimensions;
— degree of invasion;
— origin.
Magnetic resonance angiography is sometimes ordered to detect vascular disease. Research involves contrasting.
Benign neoplasms are detected more often: MRI of the hand shows enchondromas consisting of hyaline cartilage, giant cell tumor of the bone.
Based on the images, one can assume the malignant nature of the pathology in chondrosarcoma, lymphoma, metastatic lesions of the distal parts of the upper extremities, etc.
Who is prescribed MRI of soft tissues?
MRI of superficial structures and muscles may be recommended for diseases and conditions such as:
- severe pain;
- edema, swelling of tissues;
- vascular disorders;
- traumatic damage to muscles, tendons, subcutaneous fat, etc.;
- pinched nerve fibers;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms;
- suspicion of inflammatory or infectious processes;
- preoperative or postoperative examination;
- atrophic, dystrophic and other degenerative changes, etc.
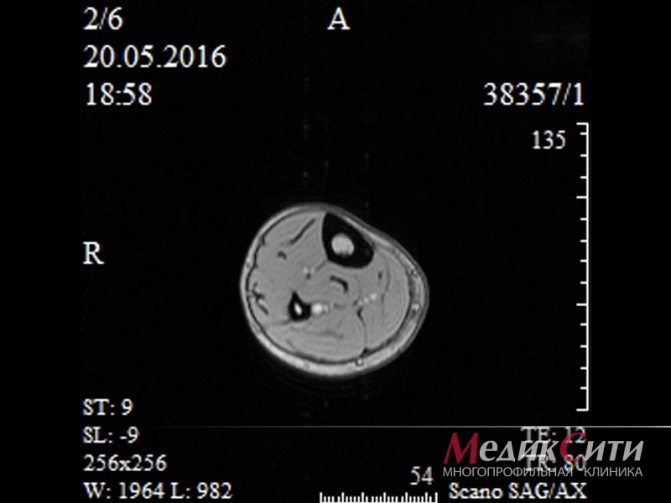
1 MRI of muscles
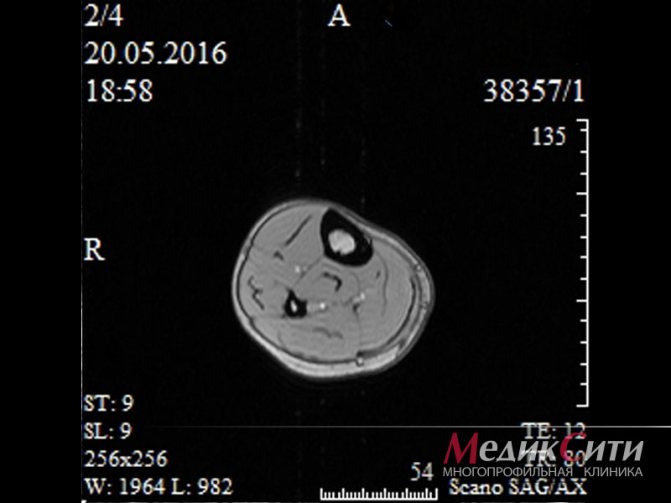
2 MRI muscles
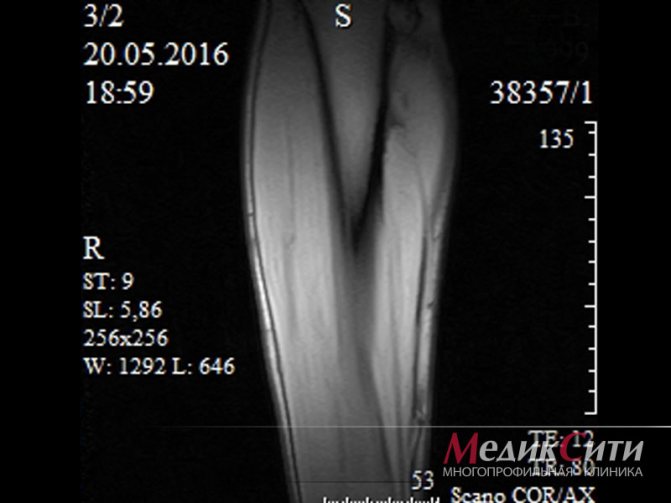
3 Muscle MRI
Tomography for wrist fracture
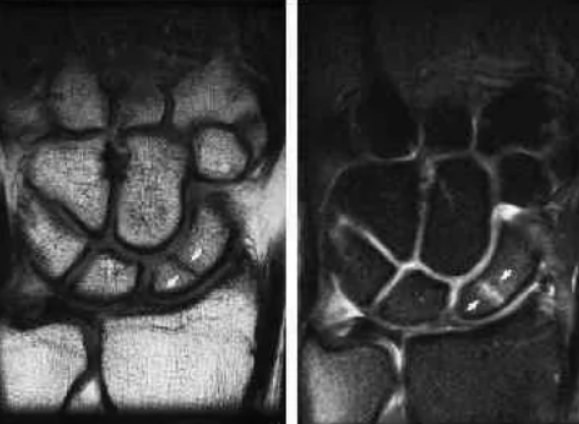
Scaphoid fracture on MRI
Traumatologists often prescribe diagnostics for fractures of the hard structures of the hand. A fall or direct blow can lead to partial or complete disruption of the integrity of the scaphoid, lunate, pisiform and other bones. Symptoms include:
- acute pain;
- increasing swelling;
- pathological bone mobility;
- hemorrhage/hematoma due to vascular damage;
- wrist deformity;
- limitation of movements in the hand;
- crepitation (characteristic crunching), etc.
In an open wrist fracture, bone fragments are visible. A cold limb with a bluish tint is suspicious for insufficient blood circulation due to a violation of the anatomy.
In an emergency, the victim will undergo a CT scan. The results of the CT examination will be ready almost immediately. Often the patient is transferred from the diagnostic room to the operating room.
An MRI of the hand is done a little later to assess the consequences of the injury: a computer scan does not always demonstrate damage to soft tissue structures.
Indications for diagnosing wrist joints using MRI
Your attending physician may recommend an MRI in the following cases:
- for preoperative diagnostics,
- to monitor the rehabilitation process after surgical treatment,
- with difficulty in movement and pain,
- if there is a suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome,
- in the presence of various developmental anomalies,
- after being injured,
- for arthritis and arthrosis.
The cost of services we have established will help everyone undergo highly effective diagnostics at optimal material costs. Choose favorable prices while guaranteeing the reliability of the survey results provided.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the hand
Unexplained long-term pain in the arm is a reason for advanced diagnostics
It is justified to do magnetic resonance imaging in case of:
- lack of effect of therapy, resumption of symptoms after treatment;
- complaints unexplained by other methods of examination, receiving ambiguous results from ultrasound, radiography, CT;
- negative dynamics, manifested by:
- increasing swelling;
- paresthesias;
- decreased range of motion;
- persistent pain syndrome, etc.;
- suspected involvement of soft tissue structures, blocking of the wrist joint, development of tumor pathology, complications of the inflammatory process (osteomyelitis, necrosis), etc.;
- the need for dynamic observation, differentiation, etc.
Contraindications to MRI of the hand include:
- the presence of metal components in the body - vascular clips, endoprostheses, fragments, etc.;
- functioning devices - heart pacemaker, drug pump, cochlear implant, myo- and neurostimulator;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- neonatal period up to a month;
- patient weight over 150 kg (limit for closed-type devices);
- conditions requiring resuscitation (traumatic shock, acute heart attack, stroke);
- inability to remain still (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, etc.).
Contrast is not available if:
- an allergic reaction to gadolinium has been reported;
- renal failure was diagnosed with a decrease in glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 ml/min - in the terminal stage;
- the patient is pregnant.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist joint
Magnetic resonance imaging uses a powerful magnetic field and a computer to obtain a high-quality and complete image of the tissues, tendons, muscles, and nerves inside the wrist joint. Thanks to MRI, you can see the detailed structure of a person’s internal organs without the use of invasive methods.
During the examination, the human body is exposed only to a magnetic field; ionizing radiation is completely absent. A detailed image of the area under study, obtained using magnetic waves, is displayed on a monitor for analysis by a doctor. If necessary, all information can be written to disk or printed.
Why do you need an MRI of the wrist joint? MRI of the wrist joint makes it possible to: – detect bone fractures, causes of pain, as well as decreased motor functions or joint blocking; – identify space-occupying formations; – investigate the effects of sports injuries, injuries resulting from lifting heavy objects or prolonged exposure to vibrating hand tools; And also find out the causes of pain, bruising, swelling in the area of the wrist joint, etc. If necessary, the doctor can inject the patient with a special contrast agent to visualize the structure of the area under study in more detail. Using MRI, it is possible to determine in a patient: – Kienböck’s disease (impaired blood supply to the lunate bone); – Dupuytren’s contracture (palmar fibromatosis); – tendonitis; – bursitis of the wrist; – ganglion cysts in the wrist; – abscess; – infections; – all kinds of damage to muscles, tissues, tendons, nerves; – tumors; – osteonecrosis;
How to prepare for an MRI of the wrist joint During an MRI, the patient must wear underwear or, with the doctor's permission, wear his own clothing, but it must be loose, not tight, and in no case contain metal objects. Examination of the wrist joint has nothing to do with the digestive organs, so eating before the procedure is not prohibited. However, if the patient is planned to be injected with a contrast agent, it is still not recommended to eat, since the injection of the drug may cause vomiting or nausea. In addition, the doctor must make sure that the patient is not allergic to gadolinium (the metal contained in the contrast agent). Also, given that examination in MRI machines involves placing the patient in a closed space, people suffering from claustrophobia may experience unpleasant sensations, which can be avoided with the help of mild sedatives. Examination of children is possible only with the use of anesthesia or sedatives, since it is necessary to remain motionless during the process. Adults must be present during the procedure. It is prohibited to conduct an MRI of a patient with the following items: – jewelry; – piercing; – knives, glasses, watches, pins and other items containing metal or which lose their properties under the influence of a magnetic field (credit cards, mobile phones). In addition, MRI cannot be performed on patients with: – ear implants; – some types of clips used for cerebral aneurysms; – some types of metal stents installed in blood vessels; – pacemakers; – metal joints, pins, plates, stents, etc. in the area under study; - infusion pumps. A patient who has electronic or metal elements inside the body must warn the doctor about this. Most implanted devices have instructions that describe in detail all the indications for their use; it is better to take it with you to the examination. MRI procedure of the wrist joint Before an MRI examination, it is recommended to undergo an x-ray to determine the presence of metal particles in the body. Indeed, in addition to implants, human tissue may contain metal fragments from bullets, shells, etc. They will move under the influence of a strong magnetic field and damage the tissue. During the procedure, the patient remains motionless. Sometimes the patient may feel warmth in the area being examined, but this is a normal reaction of the body to the action of the magnetic field. There is no pain during the examination. The actual MRI procedure of the wrist joint takes 20-30 minutes; more time will be needed if the examination must be performed with contrast.
Advantages of MRI : 1) the study is completely painless and does not use ionizing radiation; 2) makes it possible to study the examined area in detail due to its high-quality visualization; 3) determines the need for surgical intervention; 4) accurately detects bone fractures that were not detected using x-rays or other diagnostic methods; 5) allows you to diagnose anomalies that were not noticed using other diagnostic methods; 6) the contrast used during MRI causes fewer allergic reactions than other drugs used during CT or X-ray examinations. However, with the help of medications, severe allergic reactions can be avoided.
It is worth noting that the quality of the image depends on the patient’s immobility during the session, which is very difficult to ensure in case of severe pain. In addition, the presence of metal objects in the body can distort the image. By the way, the large size of the patient will not allow him to fit in the device, which the patient must also take into account. MRI of the wrist joint is recommended to be performed on high-field machines, since low-field machines will not be able to provide a high-quality image of the examined area. The exception is contraindications for a patient to undergo MRI on high-field machines.
Preparing for MRI of the hand
For native magnetic resonance scanning, no special measures are required. It is enough to choose comfortable clothes without metal parts. In response to the administration of contrast, some patients may experience drooling, nausea, dizziness, etc. Unpleasant reactions from the autonomic nervous system can be prevented by having a light snack 20-30 minutes before the examination.
Take with you:
- identification document (passport);
- compulsory medical insurance/voluntary medical insurance policy (if the research will be paid for by the fund);
- doctor's referral indicating the scanning area, preliminary diagnosis, and the need to use contrast;
- results of previous diagnostics regarding diseases of the wrist joint, hand, etc.;
- discharge from the hospital.
Contraindications to the procedure
MRI of the vessels of the upper extremities has the only drawback - not everyone can scan. The following are not allowed for examination:
- pregnant women;
- patients with cardiac and neurostimulators;
- patients with electronic and metal devices installed in the body;
- people with metal prosthetics, shrapnel and bullets in their bodies;
- children under 6 years old;
- patients with neurological diseases (sometimes, so that such patients can undergo a scan, the doctor prescribes sedatives);
- patients with allergies to the drug.
How is an MRI of the wrist done?
The procedure can be carried out using a closed-circuit tomograph with a power of 1.5 Tesla and an open low-floor unit. The first option is more preferable, since the diagnostic value of the images is higher. Low-floor equipment is more often used in routine practice when examining athletes.
The diagnostic algorithm is standard:
- The patient arrives at the clinic 15 minutes before the start of the MRI scan.
- After identifying contraindications and filling out a medical record, the radiographer places the patient on the tomograph table and explains the rules of behavior.
- A special coil is installed above the area of interest to enhance the magnetic field.
- During the scheduled contrast procedure, the nurse inserts a catheter into the vein and connects an injector: during certain phases of the study, chelated gadolinium will be released into the body automatically.
- Once the scan is complete, the guidewire is removed and a dressing is applied.
The medical staff continuously monitors the patient’s condition through the window of the next room; for unforeseen situations, the patient has a panic button at hand. Communication takes place via speakerphone. The duration of an MRI of the wrist joint is 20 minutes, with contrast - a little more than half an hour. There is no pain, the noise from the operating equipment can be neutralized using headphones.
The result will be ready in 30-50 minutes.
How is MRI of the extremities performed?
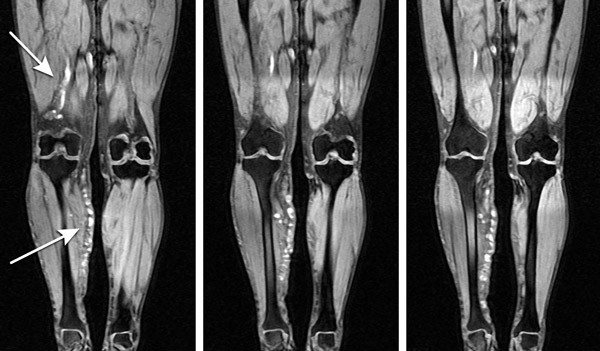
An MRI machine is a cylindrical tube with a magnet embedded in a circle. The person lies down on a table and enters a tunnel where individual images of the limbs are taken. The resulting images are processed by a computer connected to the equipment. The results are displayed on an LCD monitor, so the doctor and patient can clearly see the images.
Expert opinion
Accurate diagnosis using modern magnetic equipment allows the doctor to make accurate conclusions regarding the condition of the vessels and tissues of the extremities. Based on these results, the specialist can prescribe individual treatment.