Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out only if there are preliminary results of determining glucose on an empty stomach, without load. The glucose content in blood plasma is determined on an empty stomach and 2 hours after a glucose load. It is necessary to follow a normal diet (with carbohydrate content > 125-150 g per day) and adhere to the usual physical activity for three days before the study. The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach after an overnight fast for 10-14 hours (during this time you should not smoke or drink alcohol). During the study, the patient should lie or sit quietly, not smoke, not be overcooled, and not engage in physical activity. It is not recommended to conduct research after and during stress, after operations and childbirth, during inflammatory processes, alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis, during menstruation, and in gastrointestinal diseases with impaired glucose absorption. Before the test, it is necessary to exclude medical procedures and medications (adrenaline, glucocorticoids, contraceptives, caffeine, thiazide diuretics, psychotropic drugs and antidepressants).
Indicators of a comprehensive general blood test:
- hemoglobin level (normal m 130-172 g/l, w 120-160 g/l);
- number of red blood cells (normal m 4.2-5.8x10¹², w 120-160x10¹² per liter);
- hematocrit (percentage of formed elements in blood plasma) (normal m 39-51%, w 34-47%);
- the number of leukocytes (normal 4.5-11x109 per liter), indicating the relative content of granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes;
- platelet count (normal 150-400x109 per liter);
- MCV - average erythrocyte volume (normal 80-10 fl);
- MCH - average amount of hemoglobin in one red blood cell (normal 27-35 pg);
- MCHC - average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes (normal 310-360 g/l);
- RDW – relative width of distribution of erythrocytes by volume (in absolute and relative values) (normal 11.5-14.5%);
- MPV – average platelet volume (normal 9.1-11.9 fL);
- PDW - relative width of platelet distribution by volume (normal 9.9-15.4%).
A particularly striking change in the morphology of erythrocytes occurs with iron deficiency, which also happens with normal hemoglobin levels (latent iron deficiency), with a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid (vitamin B9), leading to disruption of the process of cell division.
The average volume indicates the activity of mature platelets, the ratio of young and old cells, and if deviated, signals the risk of thrombosis or bleeding.
Normally, platelets are represented by anucleated plates of different sizes. The width of platelet distribution makes it clear how many micro- and macroplatelet cells are contained in the blood. If the indicator goes beyond the norm, the doctor will suspect a problem (anemia, oncology, blood loss, inflammation).
Leukocyte formula
the CBC demonstrates the quantitative composition of white blood cells (leukocytes) in absolute numbers and percentages:
- neutrophils (normal 47-72%, 2.5-7.5x109 per liter);
- eosinophils (normal 1-5%, 0.04-0.44x109 per liter);
- basophils (normal 0-1%, 0.01-0.1x109 per liter);
- lymphocytes (normal 19-37%, 1.5-3.5x109 per liter);
- monocytes (normal 3-11%, 0.2-0.8x109 per liter).
Changes in the number and ratio of leukocytes occur with a large number of diseases: acute and chronic inflammatory processes, incl. infectious, diseases of the immune system (autoimmune, immunodeficiency), allergies, oncopathology, bone marrow lesions.
Hormones
Blood for hormonal studies must be donated on an empty stomach in the morning. If this is not possible, blood can be donated for some hormones 4-5 hours after the last meal in the daytime and evening (except for those studies for which blood must be donated strictly in the morning).
1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from the diet; the last meal should not be large. 1 day before the study, psycho-emotional and physical comfort (calm state without overheating and hypothermia) is necessary.
• Thyroid hormones
When initially checking thyroid hormone levels, discontinue medications that affect thyroid function 2-4 weeks before the test. When monitoring treatment, exclude taking medications on the day of the study and be sure to note this on the referral form (also note information about taking other medications - aspirin, tranquilizers, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives).
• Sex hormones
In women of reproductive age, the results of hormonal studies are influenced by physiological factors associated with the stage of the menstrual cycle. During the examination for sex hormones, the phase of the menstrual cycle should be indicated. Hormones of the reproductive system must be taken strictly on the days of the cycle:
- LH, FSH - 3-5 days of the cycle;
- Estradiol - 5-7 or 21-23 days of the cycle;
- Progesterone - days 21-23 of the cycle.
- 17-OH-progesterone, DHA - sulfate, testosterone - days 7-9 of the cycle.
- Prolactin - donate blood in the morning at rest; before the study, exclude palpation of the mammary glands.
When should you take a clinical blood test?
Since childhood, we have all become accustomed to undergoing a medical examination at least once a year, and we know that during this procedure we need to undergo a general (clinical) blood test and a general urine test. Thus, if over the past year there has been some kind of disorder in our body, then by taking a clinical blood test and a general urine test once a year, we can, with the help of our attending physician, timely identify certain disorders in the body and eliminate them as soon as possible. early stage, with little bloodshed, so to speak. In general, clinical examination is carried out precisely in order to identify not a disease, but a functional disorder in the organs and tissues of the body, which, if preventive measures are taken in a timely manner, should not turn into a chronic disease. This is the first one.
Secondly, if you are already sick, then you have two options: the first is to treat yourself with folk remedies, the second is to consult a doctor. The doctor also has two options: the first is to treat you “as is”, having first carried out only a physical, that is, a general examination (palpation, percussion, auscultation), on the basis of which he will establish a preliminary diagnosis and can already prescribe treatment. And the doctor’s second option is to still send the patient to at least the first, screening stage of laboratory tests, which primarily means a clinical blood test and a general urine test. This is what a competent doctor should do so that by the time you come for a follow-up examination, he would already have the results of the primary laboratory diagnosis, and with them, an understanding of how far your illness has progressed. And the tactics of your further treatment will depend on this.
Blood test for infections
Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach (or in the afternoon and evening, 4-5 hours after the last meal). 1-2 days before the test, exclude high-fat foods from your diet. Before donating blood for viral hepatitis, 2 days before the test, it is advisable to exclude citrus fruits, orange fruits and vegetables from the diet.
The results of tests for the presence of infections depend on the period of infection and the state of the immune system, so a negative result does not completely rule out infection. At an early stage of the disease, seroconversion occurs (absence of antibodies during the acute period of the disease). In doubtful cases, it is advisable to re-test after 3-5 days. A blood test for the presence of IgM class antibodies to infectious agents should be carried out no earlier than 5-7 days from the moment of illness, and IgG and IgA class antibodies no earlier than 10-14 days. This is due to the timing of the production of antibodies by the immune system and their appearance in the blood in the diagnostic titer.
Seal
Preparation for a general blood test and donation procedure
You need to take a general test on an empty stomach; usually blood is drawn in all clinics in the morning. In case of emergency indications, the study is carried out no earlier than 3.5-4 hours after eating. Such restrictions were introduced because after eating, the number of leukocytes in the blood increases, and fats entering the bloodstream can interfere with diagnostics.
Half an hour before the test, you can drink clean water, but smoking is prohibited. It is not recommended to donate blood for research if the patient underwent radiography or physical therapy courses that day. If you are taking antibiotics or other pharmacological agents, you must notify your doctor.
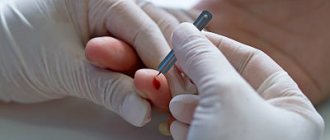
A general blood test is taken from a finger, and the skin is pierced with a Frank needle or other specialized instrument. The procedure is virtually painless; only a few drops of blood are taken for testing. To eliminate the possibility of infections, the finger is treated with alcohol, and after drawing blood, a cotton swab soaked in an alcohol solution is applied to the puncture site.
How often should you get tested?
Instrumental studies
Regular medical examination includes the following studies:
1. Fluorography
Fluorography evaluates the condition of the lungs. It allows you to identify tuberculosis at an early stage, gives an idea of pleural diseases and the presence of malignant neoplasms. Every year it is necessary to do fluorography
2. Electrocardiogram
Such diagnostics are undertaken to determine the functioning of the heart.
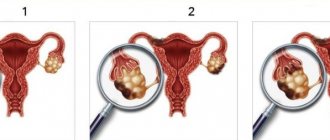
3. Ultrasound of the peritoneum and pelvis
An examination of the peritoneal cavity allows one to assess the condition of many internal organs: liver, spleen, pancreas, gall bladder, kidneys.
Ultrasound determines the structure, shape, presence of tumors, stones, cysts, and the location of organs. Pelvic ultrasound diagnoses pathologies of the reproductive system: ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes in women and prostate in men. In addition, the examination shows the condition of the rectum, ureters and bladder.
Additional diagnostics
The list of mandatory studies may include some additional tests and examinations. The appropriateness of such a diagnosis is dictated by the patient’s age, place of residence, and lifestyle.
Your doctor may recommend:
1. Study of thyroid hormone levels
This blood test must be taken by all people who live in areas depleted of natural iodine. The study evaluates the functioning of the gland and the level of hormones produced. Timely therapy eliminates the risk of developing severe complications.
Test for thyroid hormones
How often should I do a blood test for hormones? If the thyroid gland is functioning correctly, then once a year is enough. If pathologies are present, the doctor prescribes a test regimen.
2. Blood for markers of hepatitis B, C, HIV
These studies are recommended for patients who frequently visit the dentist, who have undergone extensive surgery, and who like tattoos. A blood test should be taken for people changing sexual partners. The frequency of the study depends on the patient. It is usually recommended to undergo diagnostics once every 6–12 months.
3. Coprogram
If gastrointestinal pathology is suspected, the patient will be advised to undergo a stool test. It characterizes disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, liver, pancreas, and improper absorption of substances in the small and duodenal intestines. The coprogram identifies inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract and colitis of various natures.
4. Gastroscopy
Such instrumental research is prescribed for people who have crossed the 45-year mark. Gastroscopy is performed using a special probe and allows you to assess the condition of the esophagus, stomach, and identify pathologies of the duodenum. The study identifies ulcers, tumors, bleeding.
5. Colonoscopy
This diagnosis is also recommended for people over 45. It is intended to assess the condition of the intestines. The study reveals the presence of tumors, polyps, ulcers, detects stenosis (narrowing), tuberculosis, diverticula in the intestines.
Diagnosis according to gender
The above are studies that are recommended for both men and women. However, it is necessary to monitor not only general health, but also the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Therefore, depending on gender, the doctor will prescribe several more studies.
Do I need to take a clinical blood test and a general urine test before vaccinations?
In addition to medical examination and acute illness, the third reason for taking a clinical blood test and a general urine test is the upcoming vaccination. If you or your child last had blood and urine tests a year ago and everything was fine, this is not a reason to refuse them.
Vaccination is a rather serious intervention in the body, requiring 100% confidence that the patient is healthy. This is why I always recommend that my patients preparing for vaccinations take a clinical blood test and a general urine test at least 30 days before vaccination, but the closer, of course, the better.