Each of us has repeatedly encountered laboratory blood tests in our lives.
Blood consists of plasma, the percentage of which is 50-60, and individual cells - red blood cells , platelets (do you know what to do if platelets are low during pregnancy?), leukocytes , and others, the share of which is 50-40 percent. During the study, various components of the blood are determined, or rather, their quantity.
Red blood cells are blood cells whose task is to:
- maintaining acid-base balance;
- removal of various amino acids from plasma;
- isotonic support;
- oxygen saturation;
- removal of carbon dioxide from cells and tissues of the body.
It is quite clear that disturbances in the quantitative content of red blood cells of various etiologies lead to various diseases of the human body as a whole. The main component of a red blood cell is hemoglobin.
Treatment process
During the treatment process, it is important to exclude the influence of the etiological factor that provoked the onset of the disease. If hypoxia is detected in the patient, oxygen treatment is necessary. If the level of red blood cells in the bone marrow has increased, it is necessary to treat with a blood replacement solution and glucose. In case of advanced disease, the patient must be prescribed medications that thin the blood. This will help prevent the formation of blood clots. During the treatment process, it is important to follow the diet prescribed by the attending physician. Physicians often prescribe bloodletting - this will help reduce hemoglobin levels. When using oxygen inhalation, the functioning of oxygen transport into human cells is restored. Specific medications are prescribed by the doctor depending on the identified disease and the general health of the patient.
What do the reduced numbers mean?
Patients often ask what this means: “red blood cell distribution index is reduced.” Since the erythrocyte distribution index cannot be assessed without a volume indicator, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with all the options for underestimated indicators and their relationship:
- RDW is low and MCV is below average - indicating problems with the spleen and liver.
- RDW is lowered, and MCV is higher than the normal level - indicates the presence of oncological pathologies, mainly the development of metastases in the bone marrow.
The fact that the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is reduced, from a biological point of view, cannot, in principle, be observed. For this reason, most often the patient is offered to donate blood again, observing the following conditions:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for 24 hours before blood sampling;
- do not take any medications before the analysis;
- Avoid eating smoked and salty foods the day before.
In the case when the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is indeed reduced, which is necessarily confirmed by deviations from the norm in the MCV indicator, then this indicates the occurrence of certain pathologies. These include:
- Hypochromic microcytic anemia - sometimes also called anemia. A condition in which irregularly shaped red blood cells die because they have no biological value in the body.
- Malignant tumors - usually in this case we are talking about mastopathy, bone marrow and lung cancer.
- Hemolysis of red blood cells is a process during which red blood cells die without reaching their target. As a result, active hemoglobin is released.
Determination of the distribution width of red blood cells
The RDW value shows the heterogeneity (diversity) of red blood cells (Er) in size. Normally, the average erythrocyte volume (MCV) in an adult is from 80 fL to 95-100 fL (μm3). The appearance of small erythrocytes (microcytes) and/or large Er (macrocytes) is noted in blood pathologies.
Various types of anemia and myeloproliferative diseases are accompanied by changes in the size of red blood cells. Transformed Er appears in the blood, the sizes of which are smaller or larger than normal.
The range of Er size values from the smallest microcytes to the largest macrocytes is called the width of the erythrocyte volume distribution.
The following erythrocyte indices have clinical significance and are necessary for diagnosing anemia and bone marrow pathologies:
- RDW-CV is the coefficient of variation (CV) of Er dimensions;
- RDW-SD - means the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume.
What the RDW-CV shows
The RDW-CV index is measured as a percentage and is calculated based on the Er distribution width graph. The coefficient of variation is calculated in the following way:
RDW-CV = SD*100%/MCV.
The calculated distribution of the width of CV erythrocytes depends on the average size of erythrocytes; if RDW- CV is increased, this may mean an increase in the number of macrocytes and an increase in microcytes.
The SD value is the deviation of the Er value from the average value to the greater and lesser sides from the midline on the graph.
- The erythrocyte distribution index is reduced: what does this mean and what to do? Reduced RDW: pathology and norm
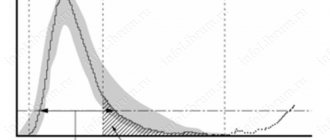
Changes in this index can be monitored using the erythrocyte histogram.
- As the coefficient of variation increases, the shift of the histogram to the right increases when a significant number of macrocytes appear.
- The predominant content of microcytes leads to a shift of the histogram to the left, towards smaller values of erythrocyte cells.
RDW-SD index
The hematology analyzer calculates the RDW-SD indicator automatically and produces a ready-made result based on the red blood cell histogram. This blood index is measured in fl (µm3), and means the difference between the largest and smallest Er.
And if RDW- CV using a formula, then to calculate RDW- SD a red blood cell ( RBC) histogram is needed. On it, along the OX axis the Er values, measured in fl, are indicated, on the OY axis - the total number of erythrocytes in percent.
The RDW-SD value is numerically equal to the length of the straight line segment on the OX axis drawn on the erythrocyte histogram at the 20% level along the OY axis.
RDW standards
Normally, the relative spread width Er RDW-SD is constant and amounts to 37 – 47 fl. A pathological deviation in the size of erythrocytes from the norm or anisocytosis is noted when RDW-SD values are more than 60 fL.
On the histogram, this means that the value of the relative width of the volume distribution is increased if the spread of erythrocytes in the sizes of the smallest and largest Er on a straight line drawn along the OY axis at the level of 20% is greater than 60 fl.
Norms for the coefficient of variation of erythrocytes RDW-CV - volume distribution width, table.
| Age categories | RDW-CV (percentage) |
| children up to ½ year old | 14.9 to 18.7 |
| children over ½ year old | 11.6 to 14.8 |
| adults | 11.5 to 14.5 |
The normal distribution width of erythrocyte cells changes during pregnancy and is by trimester:
- in the first – 11.7 – 14.9%;
- in the second – 12.3 – 14.7%;
- in the third – 11.4 – 16.6%.
The RDW-SD indicator is characterized by increased sensitivity to the appearance of microcytes. RDW-CV exhibits particular sensitivity to anisocytosis, the occurrence of deviations in the size of Er blood.
The level of anisocytosis of a blood sample reflects the heterogeneity (variability) of red blood cells in size.
There are different degrees of anisocytosis:
- The first – 30 – 50% Er deviate in size from the norm.
- The second – 50 – 70% of transformed cells.
- Third – more than 70% of Er deviate from the standard.
Analysis transcript
Red blood cell RDW indices obtained when processing a sample with hematological automatic analyzers are necessary for early diagnosis:
- deficiency of Fe, folate, vitamin B12;
- types of anemia;
- morphology of erythrocytes - structural features and sizes;
- myeloproliferative diseases affecting the bone marrow.
Decoding of the analysis data is carried out taking into account all erythrocyte indices. When interpreting the distribution width Er, the MCV value is of particular importance.
Raising RDW
The index of erythrocyte volume distribution is increased in anemia caused by B12 deficiency, and this means that the number of macroerythrocytes in the blood is increased, and the histogram is shifted to the right.
If the volume distribution width is increased, but the erythrocyte index such as MCV is increased, we can assume:
- hemolytic anemia;
- B12 deficiency;
- cold agglutination is a disease associated with the appearance in the blood of antibodies that glue red blood cells to each other in response to the action of cold.
Increased RDW (wide distribution of erythrocytes) and increased MCV in liver diseases, anemia caused by lack of vitamin B9.
An increase in the distribution width with a reduced index of average erythrocyte volume is observed in diseases:
- thalassemia;
- iron deficiency.
An increase in the Er spread width with normal MCV values may indicate:
- for a lack of vitamins B9 and B12;
- on the development of iron deficiency.
With increased values of the distribution width in the blood, accelerated destruction of red blood cells occurs, which is why the liver and spleen work at the limit of their capabilities. This leads to disruption of their functions, which manifests itself:
- the appearance of excess bilirubin;
- high Fe content;
- enlarged spleen.
Lower RDW
A decrease in the volume distribution width of Er means that there are cells of similar sizes in the blood. The boundaries of the spread of the RDW-CV value are narrowed in the following cases:
- oncological diseases - myeloma, leukemia;
- hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells;
- injuries with significant blood loss;
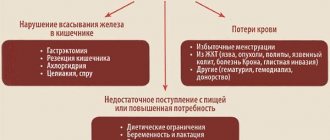
- deficiency of iron, B vitamins.
RDW- CV decreases In these forms of the disease, red blood cells are predominantly increased or decreased in size compared to the norm.
Microcytic anemias include iron deficiency, iron saturation, and iron redistribution. Macrocytic anemia develops with hypothyroidism, pregnancy, liver disease, hematopoietic disorders in the bone marrow, lack of copper, vitamins B12, and folic acid.
Reduced RDW: norm and pathology
A person in good health has red blood cells of the same shape, density and color. In case of deviation, especially in the presence of autoimmune diseases or oncology, the failure occurs at the level of microcells, when young cells do not receive a certain number of components, which, in fact, inhibits their performance. Thus, anemia occurs - a pathology during which the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, in other words, the metabolic function in red blood cells is disrupted.
Red cells
Red blood cells are blood cells that give it a characteristic color. In healthy people they are the same in volume and shape. Red cells perform the following tasks:
- ensuring a normal acid-base environment;
- oxygen saturation;
- isotonic support;
- removal of carbon dioxide from tissues.
The proper functioning of red cells depends on their volume in the blood.
A disturbance in the level of red blood cells is caused by the development of some pathology in the body.
- Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is increased
The main component of red cells is hemoglobin.
HCT (Ht, Hematocrit) – hematocrit
Design parameter
In modern hematology analyzers, the hematocrit indicator is most often a calculated (secondary) parameter and is derived from the number of red blood cells and their volume. The coefficient of variation for the automatic method does not exceed 1%, since when analyzing on the device there is no problem of “residual” plasma.
False indicators
| A false increase in hematocrit is observed when: |
|
Clinical and diagnostic value
| Increased hematocrit value |
|
| Conditions of decreased circulating plasma volume |
|
| Decrease in hematocrit value |
|
| Conditions of increased circulating plasma volume |
|
Why measure RDW in a blood test?
RDW is usually assessed to diagnose anemia of various origins, conditions in which red blood cells cannot carry enough oxygen throughout the body.
RDW is also used to diagnose thalassemia, diabetes, liver disease and cancer.
In addition, the reasons for prescribing a blood test with erythrocyte indices may be:
- health control for insufficient intake of iron and vitamins
- presence of symptoms of anemia (weakness, pale skin, dizziness, etc.)
- significant blood loss
- chronic diseases affecting red blood cells
In recent years, many clinical studies have proven that changes in RDW levels may be associated with many cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). RDW plays a significant role in assessing the severity and progression of CVD. However, the mechanisms of the relationship between RDW and CVD prognosis remain unclear.