What does ALT show in the blood?
Alanine aminotransferase, or ALT for short, is a special endogenous enzyme. It is included in the group of transferases and the subgroup of aminotransferases. The synthesis of this enzyme occurs intracellularly. A limited amount of it enters the blood. Therefore, when a biochemical analysis shows an increased ALT content, this indicates the presence of a number of abnormalities in the body and the development of serious diseases. They are often associated with the destruction of organs, which leads to a sharp release of the enzyme into the blood. As a result, alanine aminotransferase activity also increases. It is difficult to establish the extent of necrosis or the degree of tissue damage by the disease based on this, since the enzyme is not characterized by organ specificity.
Alanine aminotransferase is found in many human organs: kidneys, heart muscle, liver and even skeletal muscles. The main function of the enzyme is to exchange amino acids. It acts as a catalyst for the reversible transfer of alanine from the amino acid to alpha-ketoglutarate. As a result of the transfer of the amino group, glutamic and pyruvic acids are obtained. Alanine is necessary in the tissues of the human body, as it is an amino acid that can quickly be converted into glucose. In this way, it is possible to obtain energy for the functioning of the brain and central nervous system. In addition, among the important functions of alanine are strengthening the body’s immune system, the production of lymphocytes, and regulating the metabolism of acids and sugars.
The highest activity of alanine aminotransferase was detected in the blood serum of men. In women, processes involving the enzyme proceed more slowly. The highest concentrations are noted in the kidneys and liver, followed by skeletal muscles, spleen, pancreas, red blood cells, lungs, and heart.
What is analysis used for?
The largest amount of transferase was found in the liver. This observation is used to detect diseases of a given organ that do not have external symptoms. ALT, unlike many other components considered in a biochemical blood test, has been studied most fully. Therefore, with its help you can identify even minor problems in the body. In some cases, the amount of ALT is compared with the volume of other elements in the blood. This allows us to draw conclusions about the presence of pathologies.
For example, an enzyme such as aspartate aminotransferase or AST is often used. It is also synthesized intracellularly, and a limited amount enters the blood. Deviation from the norm established in medicine for the content of aspartate aminotransferase, as in the case of alanine aminotransferase, is a manifestation of abnormalities in the functioning of certain organs. The most complete understanding of the nature of the pathology can be obtained by correlating the contained amounts of both enzymes. If there is an excess of alanine aminotransferase over aspartate aminotransferase, this indicates the destruction of liver cells. AST levels rise sharply in late stages of disease of this organ, such as cirrhosis. When the level of aspartate aminotransferase exceeds the level of alanine aminotransferase, problems with the heart muscle are observed.
Additional diagnostic methods can confirm the presence of the disease and the extent of organ damage. However, ALT is an accurate indicator; in some cases, it can even be used to establish the stage of the disease and suggest possible options for its development.
When is a test ordered?
An analysis to determine the level of alanine aminotransferase is prescribed when using toxic drugs.
And also if the following symptoms are present:
- fatigue with minimal physical activity;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling of weakness;
- constant presence of nausea;
- vomiting;
- clarified feces;
- yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes;
A yellow tint to the eyes indicates an increase in bilirubin and alanine aminotransferase - dark color of urine;
- pain in the abdominal cavity;
- gas formation in the abdomen;
- yellowing of the skin;
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea or constipation);
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- slight increase in body temperature (up to 38 degrees);
- formation of hematomas for no reason;
- swelling;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- a sharp decrease in body weight (may indicate oncology);
- sleep problems;
- emotional instability – irritability, tearfulness;
- pain in the head;
- increased sweating;
- brittle nails and hair.
In addition to the listed symptoms, an analysis to determine the ALT value is prescribed if the doctor has recommended taking medications. As a result, the effectiveness of therapy can be determined.
When is an ALT test prescribed?
The amount of alanine aminotransferase is determined as part of a general biochemical blood test. Often only one type of examination is prescribed when there is no need to use additional methods. They get tested for ALT. This is due to the selective tissue specialization that the enzyme has.
The amount of alanine aminotransferase in case of liver problems helps to identify them even before the appearance of the most characteristic symptom - jaundice. Therefore, a doctor most often prescribes an ALT test to check for damage to this important organ as a result of taking medications or any other substances that are toxic to the body. The study is also carried out if hepatitis is suspected. An ALT test is required if the patient has symptoms such as fatigue and weakness. He loses his appetite and often feels nausea, turning into vomiting. Yellow spots on the skin, abdominal pain and discomfort, yellowing of the whites of the eyes, light-colored stool and dark urine can all be signs of liver disease. In such cases, this analysis is required.
ALT can be compared with AST to provide additional information about the causes of liver damage. This is done if the amount of enzymes significantly exceeds the norm. The ratio of AST to ALT is known in medicine as the de Ritis ratio. Its normal value ranges from 0.91 to 1.75. If this indicator becomes more than 2, then damage to the heart muscle is diagnosed, which occurs with the destruction of cardiomycytes. Myocardial infarction is also possible. A de Ritis coefficient not exceeding 1 indicates liver disease. Moreover, the lower the value of the indicator, the greater the risk of an unfavorable outcome.
ALT analysis can be used not only as a diagnostic method, but also during treatment. This allows you to determine the dynamics of the disease and identify improvements or deteriorations in the patient’s condition. ALT testing is necessary if factors contributing to liver disease are present. These include abuse of alcoholic beverages or drugs that destroy organ cells. If the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood exceeds the normal level, other medications are prescribed. It is imperative to check the amount of ALT if the patient has been in contact with people with hepatitis or has recently had it, has diabetes and is overweight. Some people are predisposed to liver disease. They are also shown an ALT test.
It uses either venous or capillary blood. To obtain reliable results, certain requirements must be met. Firstly, do not eat 12 hours before the test and do not drink alcohol for a week. Even a small amount of food can make a significant difference in your results. Secondly, for half an hour before the analysis, stop smoking, don’t worry, and avoid mental and physical stress. The results are usually ready a day after the test.
Complexes with this research
For those who are at risk of COVID-19 Diagnosis of diseases complicating the course of coronavirus infection 2,590 RUR Composition
Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause Extended monitoring of age-related changes during the postmenopausal period 20,420 RUR Composition
Female infertility Analysis of women's reproductive health 9,790 RUR Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 7,380
- Men's check-up No. 1 11,280 RUR
- Biochemistry of blood. 13 indicators 2,260 RUR
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 20,100
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 3,880 R
Normal ALT levels in the blood of men and women
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, or ALT) is a marker enzyme for the liver.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, or AST) is a marker enzyme for the myocardium.
The amount of alanine aminotransferase enzyme in the blood is measured in units per liter.
ALT (AlAT) in children
ALT in children varies depending on age:
- In newborns up to 5 days: ALT should not exceed 49 U/l. (AST up to 149 U/l.)
- For children under six months this figure is higher – 56 U/l.
- At the age of six months to a year, the amount of ALT in the blood can reach 54 U/l
- From one to three years – 33 U/l, but gradually the normal amount of enzyme in the blood decreases
- In children from 3 to 6 years old, its upper limit is 29 U/l.
- At 12 years of age, alanine aminotransferase levels should be less than 39 U/l
In children, minor deviations from the norm are allowed. This is due to uneven growth. Over time, the amount of enzyme in the blood should stabilize and approach normal.
ALT (AlAT) in adults
| Enzyme | Norm for men | Norm for women | In mmol/l |
| ALT (AlAT) | up to 45 U/l. (0.5 – 2 µmol) | up to 34 U/l. (0.5 – 1.5 µmol) | 28 – 190 mmol/l (0.12-0.88) |
| AST (AST) | up to 41 U/l | up to 31 U/l | 28 – 125 mmol/l (0.18-0.78) |
Degrees of enzyme enhancement
| Degrees of enzyme enhancement | In what diseases does AST and ALT increase? |
|
|
But the results of the ALT analysis are often far from the established norms. This may be due not only to the presence of inflammatory processes in the body, but also to other factors. Elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase can be caused by taking aspirin, warfarin, paracetamol and oral contraceptives in women. Therefore, the doctor should be aware of the use of such drugs before taking an ALT test. Medicines based on valerian and echinacea have a similar effect. Unreliable test results may be caused by increased physical activity or intramuscular injections.
Rules for preparing and submitting analysis
To obtain objective results, a biochemistry analysis should be done after simple preliminary preparation. The patient must comply with the following conditions:
- for 5–7 days, avoid drinking alcohol-containing drinks, because toxic metabolites of ethanol disrupt the synthesis of proteins and enzymes in the liver.
- Eliminate fatty foods and fried foods from your diet in 2–3 days so as not to create additional stress on the liver and pancreas;
- temporarily stop using medications;
- fast before the procedure for at least 8–12 hours.
Why do you need to take the test on an empty stomach? This is due to the fact that any food changes the composition of the blood, and fats make the plasma cloudy. Test results performed on a full stomach will be inaccurate.
ALT is elevated in the blood
The amount of alanine aminotransferase in the blood is considered elevated if it exceeds the established norm, especially tens, and in some cases hundreds of times. Depending on this, the presence of the disease is determined. When the ALT level increases by 5 times, myocardial infarction can be diagnosed; if it reaches 10-15 times, we can talk about the deterioration of the patient’s condition after the attack. The value of the de Ritis coefficient also changes upward.
Hepatitis provokes an increase in ALT in the blood by 20-50 times, muscular dystrophy and dermatomyositis - by 8. Gangrene and acute pancreatitis are indicated by exceeding the upper limit of the indicator by 3-5 times.
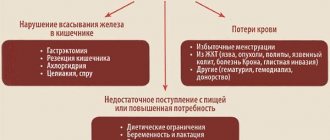
It is possible not only to increase the content of alanine aminotransferase in the blood. Its too low amount is associated with a lack of vitamin B6, which is part of this enzyme, or with complex inflammatory processes in the liver.
What does an increase in ALT indicate?
An increase in ALT indicates the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the body. They can be caused by the following diseases:
- Hepatitis. This inflammatory liver disease can come in several forms. For chronic or viral hepatitis, the excess level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood is insignificant. For hepatitis A, ALT analysis makes it possible to detect infection in advance. The amount of enzyme in the blood increases a week before the first external manifestations of the disease appear in the form of jaundice. Viral or alcoholic hepatitis is accompanied by a pronounced increase in ALT levels.
- Liver cancer. This malignant tumor often forms in patients with hepatitis. ALT analysis in this case is necessary both for diagnosing the disease and for making operational decisions. When alanine aminotransferase levels are significantly higher than normal, surgery may not be possible, as there is a high risk of various complications.
- Pancreatitis. The presence of this disease is also indicated by the level of ALT. Its increased amount indicates an exacerbation of pancreatitis. Patients with this diagnosis will have to undergo ALT testing periodically throughout their lives. This will help avoid attacks of the disease and monitor the progress of treatment.
- Myocarditis. It manifests itself in lesions of the heart muscle. Its main symptoms are shortness of breath, rapid fatigue of the patient and increased ALT levels in the blood. To diagnose this disease, the AST level is determined, and then the de Ritis coefficient is calculated.
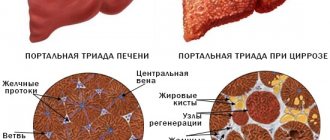
- Cirrhosis. This disease is dangerous because it may not have pronounced symptoms for a long time. Patients quickly get tired and feel tired. Pain in the liver area occurs less frequently. In this case, cirrhosis can be determined by the increased level of ALT in the blood. The amount of enzyme in the blood can exceed the norm by 5 times.
- Myocardial infarction. This disease is a consequence of impaired blood flow, resulting in necrosis of cardiac muscle tissue. In the case of an uncomplicated heart attack, the level of ALT increases slightly compared to AST, however, it can be used to determine the attack.
Reasons for increased ALT
- Taking a number of medicinal or herbal preparations – barbiturates, statins, antibiotics;
- frequent consumption of fast food before taking an ALT test;
- muscle damage;
- drinking alcohol less than a week before blood sampling;
- non-compliance with the basic rules for taking the test, including the sterility of the procedure;
- increased emotional or physical stress;
- Carrying out cardiac catheterization or other surgical intervention shortly before analysis;
- steatosis - a disease manifested in the accumulation of fat cells in the liver area, most often found in overweight people;
- necrosis of a malignant tumor;
- carrying out chemotherapy;
- taking narcotic substances;
- lead poisoning of the body;
- psychological shock;
- mononucleosis is an infectious disease that manifests itself in changes in blood composition, damage to the liver and spleen;
- hepatitis.
ALT is elevated during pregnancy
In women, the amount of alanine aminotransferase is limited to 31 U/l. However, in the first trimester of pregnancy, a slight excess of this value is possible. This is not considered a deviation and does not indicate the development of any disease. In general, ALT and AST levels should be stable throughout pregnancy.
A slight increase in the number of enzymes of this group is observed during gestosis. In this case, they are mild or moderate in severity. Preeclampsia is a complication that occurs in late pregnancy. Women experience weakness, dizziness and nausea. Their blood pressure rises. The greater the deviation of ALT from the norm, the more severe the gestosis. This is the result of too much stress on the liver that it cannot handle.
Elevated alanine aminotransferase
The highest increase in alanine aminotransferase level, when the indicator is 20 or even 100 times higher than the specified norm, can occur in acute types of hepatitis, for example, in viral and toxic hepatitis. When hepatitis A occurs, an increase in alanine aminotransferase begins several weeks before the detection of jaundice. Alanine aminotransferase returns to normal after three to three and a half weeks. With hepatitis B and C, the level of alanine aminotransferase may increase unpredictably or, on the contrary, decrease, however, returning to normal after a sharp jump or drop.
Obstructive or obstructive jaundice may also increase alanine aminotransferase levels. These jumps can be completely different: both small and significant, with a rapid and noticeable increase of up to six hundred units per liter with a further decrease over the course of a couple of days. This phenomenon is considered a feature of this type of jaundice.
When metastases develop in the liver, small changes in alanine aminotransferase levels can be observed, whereas in primary-grade tumors there are no changes at all.
Alanine aminotransferase can increase two to three times in a disease such as liver steatosis. Liver cirrhosis has approximately the same effect on a jump in alanine aminotransferase levels.
Other causes are alcoholic hepatitis and shock, severe burns, infectious mononucleosis and lymphoblastic leukemia. You can also distinguish myocardial infarction and myocarditis, heart failure and acute pancreatitis. Alanine aminotransferase can often increase in the second trimester of pregnancy.
At the same time, infections in the genitals and bladder can reduce the level of alanine aminotransferase; tumors and pyridoxal phosphate deficiency, which can manifest itself in poor nutrition and frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Some medications can increase pyridoxal phosphate levels, including the following:
- Cholestatics and anabolic steroids
- Estrogens and oral contraception, nicotinic acids
- Excess ethanol and iron salts
- Mercaptopurine and metohifuoran
- Methyldopa and methotrexate
- Sulfonamide substances
As you can see, not only various diseases can change the level of alanine aminotransferase in our body; incorrectly selected drugs, or drugs the use of which was not thought out together with the attending physician, can have a similar effect. For this reason, treatment for elevated alanine aminotransferase levels, as well as for low levels, should be based on the characteristics of the individual, and not selected on the basis of general opinion about the drug or the disease.
- Diseases starting with the letter A - vitamin deficiency
- angina
- anemia
- appendicitis
- arterial pressure
- arthrosis
- Graves' disease
- varicose veins
- gardnerellosis
- dermatitis
- cholelithiasis
- candidiasis
- leukoplakia
- mastopathy
- runny nose
- oliguria
- gout
- lungs' cancer
- salmonellosis
- tonsillitis
- ureaplasmosis
- pharyngitis
chlamydia
cervicitis
_
- lump on foot
- eczema
- Blood analysis
- Analysis of urine
- Pain, numbness, injury, swelling
- Letter A
Allergy - Letter B
- Letter G
- Letter K
- IN
- D
- Advances in medicine
- Z
- Eye diseases
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Diseases of the genitourinary system
Genitourinary system - Respiratory diseases
Cough - Diseases during pregnancy
- Diseases of the heart and circulatory system
- Diseases in children
- Women's health
- Men's health
- Interesting Facts
- Infectious diseases
- Skin diseases
- beauty
- L
- Medicinal plants
- ENT diseases
- M
- Neurology
- Medical news
- P
- Parasites and humans
- R Miscellaneous_1
- Cancer
Miscellaneous_2
➤
How to lower ALT in the blood?
It is possible to reduce the level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood by eliminating the cause of this phenomenon. Since the most common factor in increasing ALT is liver and heart disease, it is necessary to start with their treatment. After a course of procedures and taking appropriate medications, a biochemical blood test is repeated. With proper treatment, ALT levels should return to normal.
Sometimes special drugs are used to reduce it, such as hefitol, heptral, duphalac. They must be prescribed by a doctor, and the appointment is carried out under his supervision. Most drugs have contraindications that must be taken into account before starting treatment. However, such remedies do not eliminate the main cause of the increase in ALT. Some time after taking the drugs, the enzyme level may change again. Therefore, it is necessary to contact a qualified specialist who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
How the biomaterial is collected
There is nothing complicated about collecting biomaterial. Venous blood is often used for analysis because the accuracy of the result increases. But sometimes they take capillary blood from a finger, this often happens in clinics. The method of collecting biomaterial is indicated in the table.
| Type of blood | Collection method |
| Capillary | Mechanism for drawing blood from a finger: 1. The person is asked to sit opposite the qualified professional.
2. Disinfect the intended puncture site with an alcohol wipe. 3. Using a disposable needle, make a puncture in the pad of the ring finger. 4. Remove the first drop of blood with cotton wool. 5. Take material from your finger using a glass adapter. 6. Place the biomaterial in a test tube. 7. Sign the container with blood (full name, date of birth). 8. Treat the damaged area on the finger with an alcohol wipe. 9. They ask you to hold the cotton wool and hold it until the bleeding stops completely. 10. Send the test tube to the laboratory |
| Venous | Taking venous blood differs from taking capillary blood. To do this, the nurse uses the following action plan: 1. The person is asked to sit on a chair. 2. A vein is selected from which the biomaterial will be taken. 3. A tourniquet is applied to the shoulder. 4. The health care worker asks the person to clench and unclench their fist several times. This is required so that the veins become more filled with blood and can be palpated. 5. Using alcohol wipes, disinfect the intended site for collecting biomaterial. 6. Insert the needle into the vein. In modern laboratories, vacuum tubes are used - vacutainers. The needle goes into a plastic cap. The tube is inserted into the cap and filled with blood. 7. Loosen the tourniquet. 8. Fill the test tube. 9. The needle is removed and the damaged area is treated with alcohol wipes.
10. A person needs to bend his arm at the elbow and firmly press the cotton wool onto the damaged area so that there is no bruising. In modern laboratories, a medical worker bandages the injury site with an elastic disposable bandage, which is removed after 30–40 minutes. 11. Sign the tube with the biomaterial (full name, date of birth) and send it to the laboratory |
Why are liver enzymes below normal?
A decrease in ALT and AST signals possible liver cirrhosis. Enzymes are found in organ cells. When cells are destroyed during cirrhosis, they cannot produce transaminases.
General exhaustion, in which the level of vitamin B6 in the blood decreases, treatment with antibiotics and intestinal dysbiosis is another reason for the lack of enzymes. By restoring the intestinal microflora, taking vitamins and probiotics, a man can normalize the level of ALT and AST.
The cause of a decrease in ALT can be urinary tract infections in men and various cancers.
Decrease in values (in dynamics)
It is possible to predict a favorable outcome of the disease against the background of treatment by determining, albeit slowly (over several weeks), but a decrease in ALT levels to normal values. If the ALT concentration decreases too quickly, and at the same time there is still an increase in blood bilirubin (hyperbilirubinemia), then the prognosis for the patient is unfavorable.
In women, alanine aminotransferase activity is slightly lower than in men. During pregnancy, ALT decreases without damaging parenchymal cells - the condition is due to the functional “restructuring” of the body of the expectant mother.
Sources:
- Marc S Orlewicz, MD. Alanine Aminotransferase. — English-language database of current medical data Medscape.
- Data from the independent laboratory Invitro.
- Data from Helix laboratory.
- A.A. Kishkun, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Guide to laboratory diagnostic methods, - GEOTAR-Media, 2007.
What could affect the validity of the study?
Alanine aminotransferase is increased or decreased - this is a condition that may not always be accurate. Sometimes a specialist sees that the value deviates from the norm, but there is no reason for this. Then it is recommended to take the test again. The fact is that sometimes a person does not follow the preparatory rules, so the result may be distorted.
Additionally, the following factors influence the reliability of the study:
- taking medications or dietary supplements (dietary supplements);
- pregnancy;
- allergic reaction;
- recent surgery;
- carrying out chemotherapy.
If, when the test is repeated, the indicator again deviates from the norm, then the doctor recommends undergoing a full examination of the body.
It includes the following procedures:
- blood test;
- taking a urine test;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- X-ray;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ways to normalize ALT levels
Alanine aminotransferase can be elevated in any person, but this is a condition that requires treatment. The doctor interviews and examines the patient, studies the examination results. Then he makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. Often the therapy is complex, that is, it includes several methods.
Namely:
- medications;
- traditional therapy;
- proper nutrition.
Drugs
Medicines help bring the ALT level back to normal. Commonly used medications are listed in the table.

| Group of drugs | Action | Medicines |
| Hepatoprotectors | Protect the liver from the effects of toxic substances, restore its structure |
|
| Antibacterial | Prescribed for infectious lesions. Drugs destroy bacteria | Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav |
| Antiviral | Reduce the number of viruses | Acyclovir, Anaferon, Ingavirin |
| Chemotherapy | A group of medications is prescribed in case of oncology | Methazolamide, Mitomycin |
| Choleretic | Accelerate the excretion of bile | Allohol, Holenzim |
| Digestive enzymes | Improve digestion | Mezim, Festal, Creon |
| Immunostimulants | Stimulates the immune system | Immunal |
| Vitamin complexes | Replenishes the lack of nutrients | Vitrum, Complivit, Multi – Tabs |
Folk remedies
Alternative therapy can be used to reduce alanine aminotransferase levels. Compared to medications, herbal remedies have a low likelihood of causing side effects.
Popular recipes for traditional therapy:
- Milk thistle infusion. To prepare the recipe, you need to take 1 tsp. crushed plant seeds, as well as 1 glass of hot water. Close the container with the solution tightly and leave for 20 minutes. Filter, take 30 minutes before. before meals 2 times a day. The indicated quantity is calculated for 1 application. Course of use – 3 weeks. The solution should be drunk slowly, like tea.
- Herb tea. For preparation, you need to take St. John's wort, immortelle, and celandine in a ratio of 2:2:1. Grind the raw materials thoroughly, mix everything, pour 1 liter of hot water. Close the container with the liquid tightly and leave for 12 hours. Next, cook over low heat for 10 minutes. Filter, take 100 ml 4 times a day. The course of therapy is up to 14 days.

- Dandelion infusion. To prepare the recipe, take 200 g of crushed dandelions and 100 ml of vodka. For a better effect, it is recommended to add 30 ml of glycerin, which can be purchased at the pharmacy chain. Mix everything and leave the solution in a cool place for 24 hours. Take 2 tbsp. 3 times a day. The course of therapy is from 2 to 3 weeks.
Diet therapy
To reduce ALT levels, it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition.
Diet principles:
- Eat 5 – 6 times a day with breaks between meals of 3 – 4 hours. Portions should be 200 - 300 g.
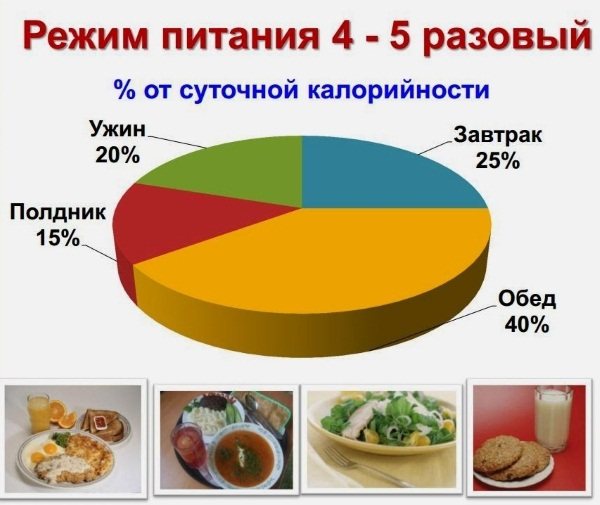
- It is forbidden to eat fatty, fried, salty foods.
- You should not eat sweets, flour, or smoked foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt, as it retains water in the body.
- It is better to steam, boil or bake food in the oven.
- Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
- Replace high-fat products with low-calorie ones.
The list of permitted and prohibited products is shown in the table:
| Authorized products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
De Ritis coefficient as an indicator of enzyme levels: how to calculate it and determine the disease
Early diagnosis of any disease is the key to successful treatment. However, trying to identify all possible diseases in oneself, a person will stop leaving medical offices and research laboratories, eventually earning a nervous breakdown.
There are a number of biochemical blood tests that can detect abnormalities in the body and set the direction for further examination.
These include the determination in the blood of the quantitative composition of the enzymes ALT, AST and their ratio, called the de Ritis coefficient.
It was named in honor of the Italian scientist who showed its diagnostic significance in blood tests and introduced it into widespread medical practice.
De Ritis coefficient
How to calculate?
In order to calculate the de Ritis coefficient, it is necessary to know the concentrations of AST and ALT. The measurement of these values is included in the blood chemistry results. Screening is carried out in the laboratory with blood taken from the antecubital vein. To obtain the correct concentration of enzymes, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid shocks to the body that threaten the functioning of the nervous system.
- Do not smoke at least 2 hours before donating blood.
- Blood collection must be done on an empty stomach.
- Do not drink alcohol-containing drinks at least 7 days before the test.
The ALT and AST results help determine whether a ratio needs to be calculated. When the levels of these substances in a person’s blood do not deviate from the norm, it is not advisable to calculate the de Ritis coefficient. Enzyme concentration standards:
The analysis is carried out if liver disease is suspected.
Due to the fact that AST and ALT are produced by the building blocks of the liver and heart, respectively, the coefficient is used when there is a risk of damage to these two organs. Indications for calculating the ratio:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- viral, chronic hepatitis;
- pancreatitis;
- liver cancer;
- alcohol poisoning;
- myocardial infarction;
- pregnancy;
- poisoning with mercury and other metals;
- drug overdose;
- jaundice;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
The above diseases occur with a number of pronounced symptoms:
- darkening or lightening of urine/stool;
- yellowness of the skin, sclera of the eyes;
- deterioration in performance;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Who should get tested?
Testing for alanine aminotransferase (ALT, AlAt) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AsAt) is necessary for men over 40 years of age and those who have worked in hazardous industries for a long time and have the following diseases:
- viral hepatitis, mononucleosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer;
- pancreatitis;
- myocardial infarction and other heart diseases;
- hypothyroidism;
- inflammatory processes of muscles (myositis, myopathy);
- pulmonary infarction;
- hemolytic anemia;
- hypoxia;
- burns, injuries.
Men are more prone to bad habits than women.

The norm of ALaT and ASaT indicators depends only on the method by which this analysis is carried out. To avoid making a mistake and mistaking the norm for a pathology, it is better to ask a doctor or laboratory assistant.
Smoking, relieving stress with alcohol, eating fast food, heavy physical activity and muscle injuries have a detrimental effect on health and blood counts. The ALT analysis in these men is higher than normal.
What is the de Ritis ratio?

The coefficient is important in diagnosing liver and kidney pathologies
The coefficient is the ratio of AST and ALT. This indicator is determined if there are deviations from the norm in one or two of its components. It is important for diagnosing a number of pathologies.
This is due to the organ-specific nature of the enzymes, which means they are related to the proper functioning of the liver, heart, pancreas and, to some extent, the kidneys.
If a deviation from the norm is detected, a full examination is required to determine what pathology is occurring.
Ratio norms
For the indicator, the normal limits are determined, within which it is found in the absence of pathologies in a person. This value ranges from 1 to 1.75 U/l, regardless of the age and gender of the patient.
When AST increases in the body, the coefficient also increases. If the volume of ALT increases, then the coefficient decreases. This feature allows you to more accurately and efficiently diagnose liver and kidney diseases.
Thus, it is known that with a de Ritis index of less than 1, the patient is most likely to have chronic liver pathologies, and with a value of 2 or more and an increased volume of albumin, severe liver disorders are most likely.
A value of 2 with normal albumin indicates heart disease and primarily myocardial infarction.
How is the de Ritis coefficient calculated?

The coefficient is the result of calculating indicators
The indicator is calculated using a formula. For its use in blood biochemistry, AST and ALT indicators are determined. Next, the AST level is divided by the ALT level. The resulting number will be an indicator of the de Ritis coefficient. The coefficient is determined only if the patient’s blood test shows a deviation from the norm in AST and ALT.
If they are normal (neither increased nor decreased), then their ratio is not of interest.
The role of the coefficient in the diagnosis of liver diseases
When diagnosing liver diseases and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, the coefficient is of great importance. The activity of the ALT enzyme in blood serum during hepatitis increases significantly - up to 8-10 times. At the same time, the AST indicator rises only 2-4 times.
In this case, the de Ritis coefficient drops to 0.6. If the decrease in value turns out to be even greater, then this is regarded as an unfavorable indicator of the development of the disease.
In the event of necrotic changes in the liver tissue, the coefficient increases due to the fact that AST and ALT are released into the blood in increased quantities.
What analysis allows you to calculate the coefficient
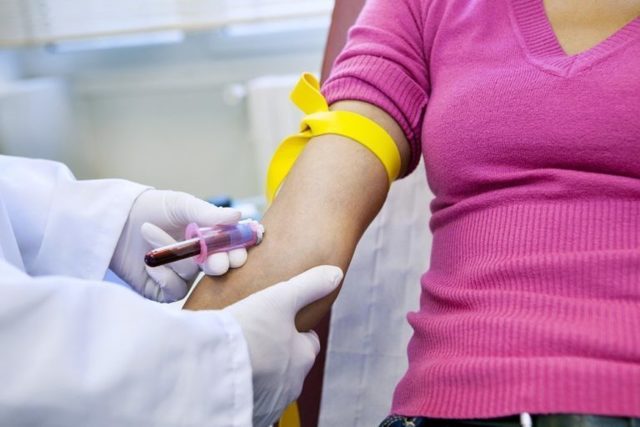
To calculate the coefficient, a biochemical study is required
To identify the de Ritis coefficient, it is necessary to identify the AST and ALT indicators. To do this, a biochemical blood test is carried out, during which its other parameters are also determined.
Such an analysis most fully shows the general condition of the body, allowing one to assess the correct functioning of most systems and organs.
The values of only aspartaminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase are rarely determined, since in diseases for diagnostic purposes it is important to obtain a complete blood picture.
There are no differences in the study for children and adults. It requires venous blood, which is donated on an empty stomach. Afterwards, in the laboratory, it is placed in a centrifuge and serum is obtained, in which enzymes are determined.
Indications and preparation for analysis
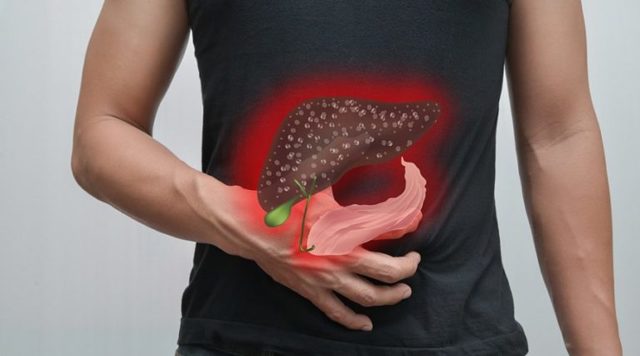
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract - indication for analysis
Indications for a blood test, which will determine the coefficient, are conditions that cause changes in the levels of AST and ALT. These are the following diseases:
- hepatitis of various nature;
- malignant neoplasms of the liver, primary or secondary;
- liver cirrhosis and suspicions of its presence;
- pancreatitis;
- severe poisoning that can lead to liver damage;
- infectious form of mononucleosis;
- myocardial infarction.
Also, a biochemical blood test is performed during routine examinations in pregnant women. In this case, the coefficient is determined only if there are deviations in AST and ALT.

Preparation is required for reliable results.
To obtain reliable analysis results, proper preparation is required. Its basic rules are:
- avoiding fatty and spicy foods 3 days before donating blood;
- abstinence from alcohol 2 days before donating blood;
- the fasting period before collecting material is 12 hours;
- drink water for the last time before the study no later than 4 hours;
- reducing stress and physical activity on the eve of the analysis.
If you are taking medications, you must inform your doctor about this. If necessary, he will inform you how long before donating blood you need to refuse them.
Decoding the analysis results

The test results are interpreted by the doctor
The result of the study is deciphered by the doctor who gave the referral. At the same time, the data cannot be independently regarded as the final diagnosis, since a complete examination of the patient is necessary to determine the pathology that caused the violation of the de Ritis coefficient.