Atherogenicity is the ratio of high-density lipoproteins and low- and very low-density lipoproteins in the blood.
The atherogenicity coefficient is reflected in the results of the lipid profile of a biochemical analysis of blood composition and makes it possible to better understand the state of human health.
For specialized specialists, the atherogenicity indicator is important in identifying possible risks of developing vascular pathologies and diseases of the heart organ. It is pathologies of the heart organ and blood flow system that lead in mortality throughout the world.
The reasons for the increase in strokes and heart attacks are:
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Poor nutrition of most people and passion for fast foods;
- Pathology obesity;
- Alcohol addiction, especially drinking large amounts of beer;
- Nicotine addiction;
- Interruption in constant stress;
- Minimum physical stress on the body.
Therefore, in order to prescribe the correct treatment to a patient for the development of systemic and cardiac pathologies, the lipogram indicator and atherogenicity coefficient are very important.
It is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment to the patient
The role of cholesterol
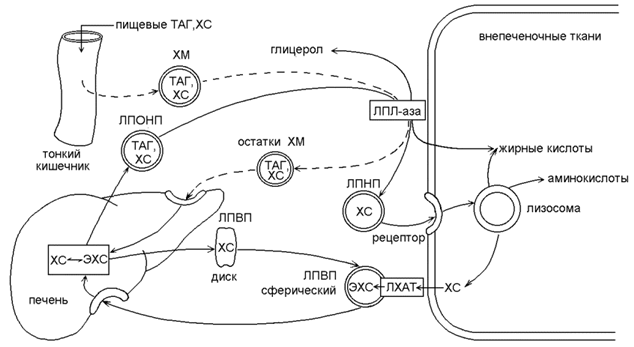
Cholesterol is a fat-containing alcohol that is produced by the body’s own cells - up to 80.0% (50.0% of this indicator is synthesized by liver cells) and 20.0% enters the body with food of animal origin.
Lipid metabolism is responsible for the balance of cholesterol in the body.
The role of cholesterol molecules in the body is very large:
- Cholesterol is found in every cell membrane and gives them elasticity and strength;
- Cholesterol molecules are responsible for the permeability of cell membranes and protect them from the influence of the external environment, increasing immunity to cells and the body;
- Participates in the production of steroid hormones by the adrenal glands;
- Cholesterol promotes the production of vitamin D by liver cells;
- High-density cholesterol molecules ensure normal bile production;
- Cholesterol binds neurons in the brain and spinal cord;
- Cholesterol molecules protect nerve fibers by coating them.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) are molecules that are building blocks of cell membranes. Without molecules of low-density lipoproteins, the vital activity of cells in the human body is impossible.
Low molecular weight (liquid) LDL cholesterol is used in the digestive organs to produce bile acids, and also activates the functioning of the immune system and all brain cells.
Liquid cholesterol takes part in balancing nerve endings.
Liquid cholesterol takes part in balancing nerve endings. It also leads to the restoration of the nervous system during and after overexertion and stress.
All the positive qualities of cholesterol are noted only if low molecular weight lipoproteins do not exceed the norm in the blood.
Then liquid cholesterol is not bad. If its concentration in the blood plasma increases, then low molecular density lipoproteins can harm the bloodstream system, as well as the entire body.
An excess amount of cholesterol in the blood contributes to the formation of cholesterol plaques, which, when growing, lead to the development of systemic atherosclerosis and pathologies of the heart organ.
Cardiac pathologies often result in myocardial infarction, as well as numerous pathologies of the vascular system, leading to cerebral stroke.
Excess cholesterol molecules begin to settle on the inner lining of the arteries, which leads to blockage of the arterial lumen, and can also lead to rupture of the lining and hemorrhage into the affected organ.
High molecular density lipoprotein (HDL) is the good, solid cholesterol that is quite useful in the body.
Its increased content in the blood indicates that the risks of developing pathologies of the vascular system and cardiac organ are minimal and the main lumens are cleared of excess cholesterol molecules.
A little about cholesterol
Calculation of the indicator
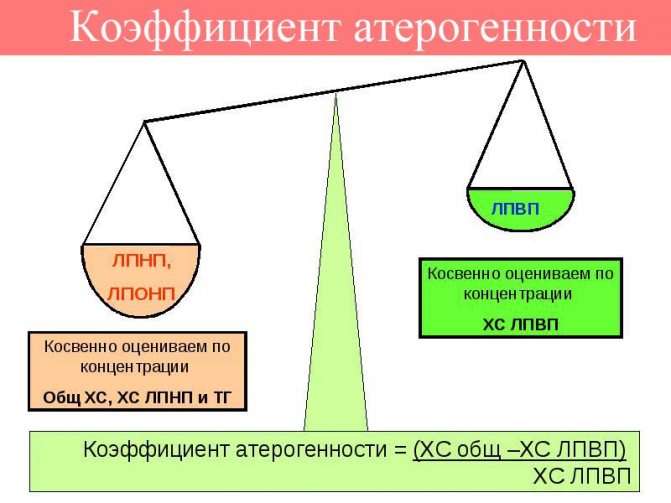
Atherogenicity index is a coefficient that makes it possible to evaluate the metabolic transformations of lipids and their derivatives. Its calculation consists of determining the ratio of “bad” and “good” fractions of cholesterol.
The biochemical blood test, called a lipid profile, contains all the components for calculating the atherogenic coefficient (HDL, LDL, total cholesterol).
There is a special formula to determine the atherogenicity number:
KA = (OX – HDL) : HDL
To calculate the Friewald , it is necessary that the lipid profile be expanded - contain the VLDL value. The formula for calculation is as follows:
KA = (LDL + VLDL): HDL
Such a simple calculation allows you to independently determine the atherogenic coefficient, having in hand a lipid profile with all the necessary components. If the calculation example showed an increase in the atherogenic coefficient, you should undergo additional examinations as prescribed by your doctor.

A high atherogenic coefficient indicates the presence of problems with blood vessels. A reduced rate indicates the absence of problems with fat metabolism.
Online atherogenic index calculator
What does atherogenic coefficient mean?
When diagnosing blood composition using the biochemistry method with a lipid profile, the following indicators are reflected:
- Total blood cholesterol index;
- High molecular density lipoprotein indicator;
- Low molecular density lipoprotein indicator;
- Level of triglyceride molecules.
In order to identify the atherogenicity coefficient, there is a certain formula:
KaT is equal to (total cholesterol index minus HDL) and divided by the HDL index
- CS is an indicator of total cholesterol in the blood;
- HDL is the concentration of high-density cholesterol in the blood.
A good indicator of atherogenicity is a coefficient of 2 or lower.
This atherogenicity coefficient indicates that the bloodstream system is well protected by high molecular weight cholesterol and it copes with the transport of low-density lipid molecules into liver cells, where they are utilized by bile acids.
An atherogenic coefficient higher than 3 units indicates a danger that is in the bloodstream due to a significant excess of low molecular weight lipoprotein fractions in the blood, and high-density cholesterol molecules cannot cope with transporting such a number of LDL molecules for disposal.
This means that the patient may develop cholesterol plugs, the vessels gradually lose their elasticity and become susceptible to diseases.
The atherogenicity coefficient shows how dangerous a person is to develop heart attacks and strokes.
Atherogenic index value
Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels often lead to death
Until recently, general practitioners and cardiologists referred their patients for a general blood test, which can be used to evaluate general lipid parameters. Later, after the positive effects of HDL were identified, it became possible to give a better assessment of lipids. The atherogenicity indicator allows you to get a clear idea of the patient’s diet, the type of fats that predominate in his diet, and the metabolic processes in the body.
A fairly simple formula is used for the calculation: the HDL index is subtracted from the total cholesterol indicator, and the resulting difference is divided by the HDL cholesterol indicator. The result will be the atherogenicity index.
The norm is considered to be an indicator that falls within the range of 2.2 to 3.5, but recently many laboratories have lowered the upper limit to 3.0. Reducing the atherogenicity coefficient for the majority of patients with cardiac pathologies is the main goal they strive for in order to avoid the development of acute complications of atherosclerosis.
How to prepare for biochemistry analysis?
A biochemical blood test for cholesterol is recommended for everyone over 35 years of age for prevention.
If, as a result of a lipogram, the atherogenic coefficient is increased, then it is necessary to correct cholesterol using an anti-cholesterol diet and periodically monitor the indicators of all cholesterol fractions using the lipid spectrum method.
There is a category of people at risk for whom cholesterol biochemistry must be done regularly.
This category includes:
- Age over 50 years;
- Patients with obesity pathology;
- People with arterial hypertension;
- Patients suffering from type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- Patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction, or by all indicators are in a pre-infarction state;
- People who have a history of a hereditary factor for the development of atherosclerosis and heart pathologies;
- In the post-infarction and post-stroke period.

In order for the indicators in the lipogram to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary to prepare to donate blood for a detailed biochemical analysis:
- The last meal should be from 8 to 12 hours before the blood sampling procedure;
- Do not fast for more than 12 hours, because the lipogram results will be distorted;
- Dinner should be light with as many vegetables as possible;
- Do not eat fried and smoked foods for dinner, and do not eat salty or sweet foods;
- One to two days before the blood sampling procedure, do not drink alcohol, even beer;
- Do not smoke a couple of hours before the procedure;
- Donate blood in a calm state;
- If the patient plays sports, stop sports training the day before donating blood for cholesterol;
- You should not radically change your lifestyle on the eve of the test. Under no circumstances should you start playing sports;
- On the eve of the blood donation procedure, avoid nervous tension and stressful situations;
- Inform your doctor about taking any medications;
- Take the test on an empty stomach; you can drink a small amount of clean water without gas;
- If the patient climbed the stairs to the clinic, you need to sit relaxed for 10 minutes before the procedure for donating blood for the lipid spectrum.
Cholesterol test
Norms for men and women
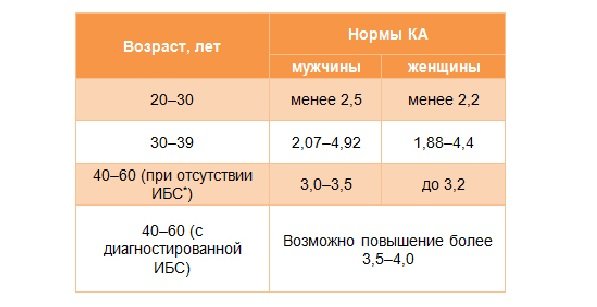
First of all, the norm of KA depends not only on gender, but also on the age of the person. Therefore, scientists have only recently been able to identify normal values at which a person has the lowest risk of developing atherosclerosis and its consequences.
| Age, years | Atherogenic coefficient norms | |
| Men | Women | |
| 20-30 | less than 2.5 | less than 2.2 |
| 30-39 | 2,07-4,52 | 1,88-4,20 |
| 40-60 (without coronary heart disease clinic) | 3,0-3,5 | up to 3.2 |
| 40-60 (with coronary heart disease clinic) | Possibly more than 3.5-4.0 | |
- The absolute norm at almost any age is within 2-3 (with the exception of people over 40 years old, in whom KA can reach 3.2-3.5). Patients with KA values within these values should not worry about the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Values in the region of 3-4 are acceptable only at the age of 30-40 years. In other cases, they mean that the blood composition is not entirely natural and the need for adjustment, that is, lowering cholesterol levels. As a rule, in order to slightly reduce the atherogenicity coefficient, it is enough to adjust your diet.
- Values above 4-4.5 in both men and women of any age indicate a high risk of developing atherosclerosis or its presence. Often this condition requires immediate treatment. If progressive atherosclerosis is detected, in addition to a well-designed diet, doctors also prescribe a number of drugs that reduce the production of cholesterol by the liver - fibrates and statins.
Separately, it is worth noting the situation when the atherogenic coefficient is reduced. Often, low KA indicates a minimal risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, which occurs only in people who follow a balanced diet, regularly exercise and do not have bad habits.
However, extremely low values, below 1.9-2, may be the result of a prolonged diet. In this case, this is not a good sign and can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences, which we will discuss in the appropriate paragraph.
Reasons for the downgrade
A reduced atherogenicity rate is quite rare.
The main reasons why the lipogram result was below normal:
- The patient has been taking statin drugs for a long period of time , which are often prescribed to reduce low molecular weight cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood;
- The patient began to play sports . This is a fairly rare occurrence, but obese patients sometimes begin to sharply load their body with loads, which leads to a deterioration in their health;
- Long-term anti-cholesterol diet is also a reason to reduce atherogenicity;
- Low atherogenic index when taking estrogen hormones , as well as when taking antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
Reasons for decline in women
In a healthy woman, when donating blood for a biochemical analysis on an empty stomach, the CAT index should be within normal limits.
If the atherogenic coefficient is reduced, this indicates that the woman’s body is at the stage of exhaustion.
This depletion can occur for several reasons:
- A woman has been on a diet with a minimum amount of fatty foods for quite a long time. This is quite common among young girls who have chosen a diet from the Internet and, without consulting a doctor, deplete the body and disrupt lipid metabolism;
- CAT is reduced in women involved in heavy sports and who do a lot of hard training;
- There is also a reduced atherogenicity index in those patients who independently prescribed estrogen hormonal therapy. With uncontrolled intake of hormones, lipid metabolism is disrupted and the body is depleted.
If a woman systematically takes contraceptives with hormones, then the lipogram result will be inconclusive and it is prohibited to use it as a basis for treatment.
It is necessary not to take birth control pills for 2 weeks and re-test your cholesterol and lipid profile.
With uncontrolled intake of hormones, lipid metabolism is disrupted and the body is depleted
Reduced rate in men
Today, it is very rare for men to have a reduced atherogenicity coefficient, because many men have stopped leading an active lifestyle and prefer to sit at the computer for days.
High-calorie foods, as well as fast foods with the maximum amount of trans fats, do not help reduce the rate of atherogenicity in the body.
If atherogenicity in the male body is below the normal level, then it is necessary to find out the reason for this decrease.
The reasons may be:
- The cholesterol test was carried out after exercise or a morning run;
- If there was no morning load on the body, and CAT is reduced , then there is the option that the man does not consume foods containing animal fat for a long period of time;
- Reduces CAT and treatment with Erythromycin . A repeat test must be taken 2 weeks after finishing the course of Erythromycin.
Erythromycin
In children
A reduced coefficient of atherogenicity in children is a reason to examine the child. A high index of bad cholesterol does not threaten the child’s body, but a decrease in atherogenicity may indicate that the child does not have enough nutrients in his growing body.
If a child’s body is deficient in cholesterol for a long period of time, then a disturbance in metabolic processes occurs and a number of pathologies develop. Very often, reduced atherogenicity occurs from poor nutrition of the child.
It is necessary to focus the attention of parents on this aspect and seek recommendations from a nutritionist.
Complexes with this research
The nutritionist recommends an assessment of the state of metabolism 7,570 RUR Composition
Stress complex Assessment of the state of the body during stress 4,310 RUR Composition
Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics Advanced monitoring of key indicators in men aged 40+ RUR 33,710 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Metabolic profile RUB 5,900
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 12,070
- Male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 13,300
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 29,230
- Healthy interest 4,250 RUR
Power supply at reduced level
The atherogenicity coefficient is reduced most often as a result of a long-term diet unbalanced in nutrients. Therefore, patients are offered to supplement the menu with products containing animal fats.
These include:
- fatty meats and fish;
- butter;
- dairy products with medium and high fat content;
- chicken and quail eggs.

Nutritionists insist on the gradual introduction of this food into the diet. This will avoid creating a significant load on the digestive organs and will not cause disruptions in the functioning of the liver and pancreas. After bringing the indicators back to normal, you need to adjust your diet in such a way as to prevent them from fluctuating upward or downward.
The best option for this is to consult a professional nutritionist. Simultaneously with the change in diet, the intensity of physical activity should be adjusted. This is especially true for professional athletes who work to achieve high results and experience enormous mental and physical stress.
To maintain the health of their players, coaches are required to develop optimal training schedules and special diets. Only in this way can the KA be kept within acceptable physiological norms.