Estradiol is the main female sex hormone of the estrogen group. It is present in both female and male bodies. The result of its influence on the body is a typical feminine figure, which is why it is considered female, although it is formed from male hormones. The FSH hormone converts male hormones into female ones.
Estradiol in women is mainly produced in the ovaries. During pregnancy, it is also secreted by the placenta. The testes, also known as testes, produce estradiol in men. In both sexes, this hormone is produced in small quantities by the adrenal cortex.
The ovaries, under the influence of pituitary hormones, produce sex hormones:
LH, FSH → estradiol
LH → progesterone
Under the influence of pituitary hormones (LH, FSH), estradiol begins to be produced in the ovaries in the first half of the cycle. In the second half of the cycle, after ovulation, luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates the release of progesterone.
Estradiol in women
Under the influence of this hormone in women:
- the waist becomes narrow;
- the timbre of the voice increases;
- subcutaneous fat is formed (due to fat deposition, the hips are rounded and the mammary glands are enlarged);
- the skin becomes thin and smooth;
- a follicle grows on the ovary;
- the inner layer of the uterus prepares for pregnancy;
- the menstrual cycle is normalized.
Estradiol is a beauty hormone. Under its influence, the skin becomes elastic and smooth, the female figure looks truly feminine.
Estradiol in men
Men also produce it, but in much smaller quantities. What does estradiol do in the male body?
- Increases calcium deposition in bone tissue.
- Participates in the processes of sperm production.
- Increases oxygen exchange.
- Regulates the functioning of the nervous system.
- Increases blood clotting.
- Stimulates metabolism.
- Reduces the amount of “bad” cholesterol, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Estradiol: normal in women
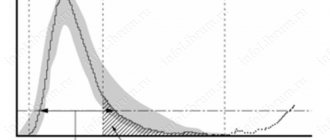
Estradiol constantly fluctuates in the female body: the day of the cycle is of great importance for blood sampling. With the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the hormone begins to be produced. By the middle of the cycle, before ovulation, estradiol levels increase. 24–36 hours after the concentration reaches its maximum, ovulation occurs. After the follicle bursts, estradiol also decreases (cycle day 14–15).
High estradiol after ovulation may mean that a woman has become pregnant.
Low estradiol in the second half of the cycle indicates that conception has not occurred.
If the body produces estradiol in sufficient quantities, the norm in women is:
- follicular phase - 57–227 pg/ml;
- preovulatory phase - 127–476 pg/ml;
- luteinizing phase - 77–227 pg/ml.
Over the years, the amount of estrogen in women's bodies decreases. During menopause, the norm fluctuates at the level of 19.7–82 pg/ml.
Estradiol during pregnancy: normal
During pregnancy, the level of the hormone increases: the closer the birth, the higher its concentration. On the eve of birth, the concentration is highest. 4–5 days after birth, estradiol levels decrease.
During pregnancy, hormone levels fluctuate depending on the period. They prepare the uterus for bearing a fetus.
| Week of pregnancy | Estradiol norm, pg/ml |
| 1st–2nd | 210–400 |
| 3rd–4th | 380–680 |
| 5th–6th | 1060–1480 |
| 7–8th | 1380–1750 |
| 9–10th | 1650–2290 |
| 11–12th | 2280–3120 |
| 13–14th | 2760–6580 |
| 15–16th | 5020–6580 |
| 17th–18th | 4560–7740 |
| 19–20th | 7440–9620 |
| 21st–22nd | 8260–11460 |
| 23–24th | 10570–13650 |
| 25-26th | 10890–14090 |
| 27–28th | 11630–14490 |
| 29–30th | 11120–16220 |
| 31st–32nd | 12170–15960 |
| 33–34th | 13930–18550 |
| 35–36th | 15320–21160 |
| 37–38th | 15080–22850 |
| 39–40th | 13540–26960 |
If your readings do not match the values in the table, consult your doctor. Your normal readings may differ from those listed above. Therefore, interpretation of the analysis must be carried out individually.
The function of estradiol in the female body
The hormone estradiol in women - what is it? The gonads in women produce three types of steroid hormones: androgens, progesterone and estrogens. Estrogens include the following substances:
- estrone (E1);
- estradiol (E2);
- estriol (E3).
The generative function of the ovaries is controlled through the interaction of endocrine organs with the corresponding parts of the brain. Under the influence of estrogens in the female body, on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs - the release of an oocyte (egg) from the follicle into the fallopian tube.
The dominant follicle turns into the corpus luteum and begins to synthesize progesterone and estradiol. An increase in their concentration in the body entails loosening of the endometrium, which increases the chances of successful implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall.
The effect of estradiol on pregnancy
Gestation is the period during which estradiol has a significant effect on the functioning of the woman’s reproductive organs and the development of the fetus. From the moment of conception to the birth of the child, its concentration continuously increases from 215 units in the 1st trimester to 27 thousand units at the time of birth.
Until three months of pregnancy, estradiol is synthesized by the ovaries, after which the mature placenta begins to produce this hormone in large doses. Thanks to its presence in the body, the uterus prepares for the birth process; with normal levels of this substance, pregnancy proceeds without complications. If E2 levels decrease during gestation, this may indicate a dysfunction of the placenta and an increased risk of spontaneous abortion.
Low estradiol
In both men and women, estradiol can be reduced for the following reasons:
- smoking;
- vegetarianism;
- great physical activity;
- a diet low in fat and high in carbohydrates;
- sudden weight loss;
- increased prolactin levels;
- malfunction of the pituitary gland;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- endocrine disorders;
- taking medications not prescribed by a doctor (including oral contraceptives);
- disturbances in the production of sex hormones.
Low estradiol in women
Due to decreased hormone levels, women may experience:
- absence of menstruation for more than six months;
- reduction in breast and uterine size;
- dry skin;
- problems with conception.
In women, estradiol may be reduced in early pregnancy. Reduced levels of the hormone in Russian women are less common than increased ones.
Low estradiol in men
A reduced amount of the hormone in men is indicated by:
- osteoporosis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- increased excitability;
- problems with conception.
The cause of low levels of this hormone in men may be chronic prostatitis.
High estradiol in women
With elevated levels of the hormone, women may experience the following symptoms:
- overweight;
- acne;
- cold feet and hands;
- fast fatiguability;
- irregular monthly cycle;
- hair loss;
- swelling;
- stomach upsets;
- breast tenderness;
- increased irritability;
- insomnia;
- convulsions.
If you donate blood for analysis and estradiol is elevated, your doctor may identify diseases associated with:
- increased levels of thyroid hormones;
- development of endometriosis on the ovary;
- ovarian tumors;
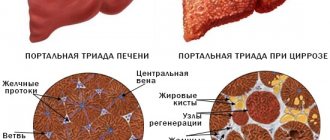
- liver cirrhosis;
- the presence of a follicle that did not burst during ovulation.
In addition to the above, estradiol may be elevated due to taking certain medications.
High estradiol in men
If a man has elevated levels of this hormone, the following changes may occur:
- swelling appears due to water retention in the body;
- muscles are not pumped up;
- a female figure is formed - fat is deposited on the hips, abdomen, buttocks and chest;
- sexual desire decreases;
- the mammary glands become painful;
- the amount of hair on the face and chest decreases.
Causes of elevated estrogen levels in men:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- testicular tumor;
- taking certain medications;
- obesity.
MEDICAL CENTER
The most active estrogenic (female) sex steroid hormone.
In women, it is produced in the ovaries, in the placenta and in the zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone () and prolactin. Estradiol is formed in small quantities during the peripheral conversion of testosterone. In men, estradiol is formed in the testes, in the adrenal cortex, but most of it is formed in peripheral tissues due to the conversion of testosterone.
In women, estradiol ensures the formation of the reproductive system according to the female type, the development of female secondary sexual characteristics during puberty, the formation and regulation of menstrual function, the development of the egg, the growth and development of the uterus during pregnancy; is responsible for the psychophysiological characteristics of sexual behavior. Ensures the formation of subcutaneous fat tissue according to the female type. By reducing the resistance of the uterine vessels, it increases blood flow in it and stimulates endometrial hyperplasia. Ovulation occurs 24 to 36 hours after the occurrence of above-threshold estradiol levels. A necessary condition for the effects of estradiol to occur is the correct relationship with testosterone levels. Estradiol has an anabolic effect, enhances bone turnover and accelerates the maturation of skeletal bones. Promotes sodium and water retention in the body. Reduces cholesterol levels and increases blood clotting activity. Estradiol affects the release of neurotransmitters, contributing to increased nervous tension and irritability.
Daily fluctuations in the concentration of estradiol in the serum are associated with the rhythm of LH (luteinizing hormone) secretion: the maximum occurs from 15 to 18 hours, and the minimum between 24 and 2 hours. In men, the level of estradiol progressively increases, in boys the increase occurs to a lesser extent.
In women of childbearing age, the level of estradiol in blood serum and plasma depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. At the beginning of the cycle, the concentration of estradiol slowly increases. The highest levels of estradiol are observed in the late follicular phase. After ovulation, the hormone level decreases, and a second, smaller amplitude, rise occurs. Then there is a decline in the concentration of the hormone, which continues until the end of the luteal phase. During pregnancy, the concentration of estradiol in serum and plasma increases at the time of delivery, and after delivery it returns to normal on the 4th day. With age, women experience a decrease in estradiol concentrations. During postmenopause, the concentration of estradiol decreases to the level observed in men. Limits of detection: 37.0 pmol/l -40370 pmol/l
Estradiol in medications
Most combined oral contraceptives are based on the “beauty hormone”. Under no circumstances should you “prescribe” hormonal contraception to yourself. Self-medication with “female hormone” can cause unpleasant consequences:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- sudden mood swings;
- disturbances in liver function;
- the appearance of gallstones;
- overweight;
- vaginal bleeding.
Estradiol is a hormone that is used in the treatment of:
- insufficient development of the genital organs;
- absence of menstruation for more than 6 months;
- osteoporosis;
- increased sweating (due to hormonal imbalances).
The doctor should prescribe treatment with hormonal drugs only after tests. For liver diseases, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, such drugs are not prescribed.
Decreased hormone levels and possible complications
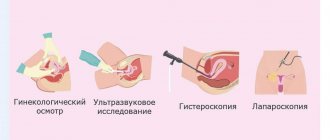
Before engaging in treatment, the doctor is obliged to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient. First, a clinical blood test is performed to determine the content of estradiol in a woman’s body. It is required for:
- assessment of the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system (in particular, the ovaries);
- finding out the reasons for the long absence of menstruation or shifts in the menstrual cycle;
- preventive monitoring of the follicle development process as part of in vitro fertilization;
- determining the causes of delays in puberty in adolescent girls;
- finding out the reasons for the early onset of menopause.
We recommend reading: EPINEPHRINE: instructions, reviews, analogues, price in pharmacies
Only if the reasons why women have elevated estradiol are accurately determined will the doctor be able to give specific recommendations regarding further treatment.
Features of therapy
Hormonal disorders are the responsibility of an endocrinologist. But since in this case we are talking about high estradiol in women, which is a sex hormone and therefore directly affects the reproductive system, you can also turn to a gynecologist for help.
First, the cause of the hormonal imbalance is eliminated, and only then, if necessary, additional treatment is carried out aimed at normalizing the hormone level. So, how to lower estradiol in women? For this purpose, you first need to:
- improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- direct efforts to get rid of extra pounds;
- take a course of vitamin therapy;
- completely cure acute liver diseases, or transfer chronic pathologies into a phase of long-term remission.
There are other, no less effective, ways to reduce estradiol in women. These include:
- following a gentle low-carbohydrate diet with a predominance of Omega-3 fatty acids;
- complete abstinence from drinking beer;
- adequate distribution of time for rest and physical activity;
- sufficient consumption of foods containing macro- and microelements, antioxidants.
Possible consequences of deviation
Hormonal imbalance is dangerous in any case, and it does not matter in which direction the deviation from the norm is observed. If estradiol is higher than normal, this can lead to the following health problems in women:
- serious disturbances in the psycho-emotional state, including prolonged depression;
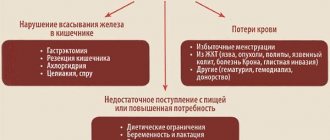
- intense bleeding that can cause the development of iron deficiency anemia;
- increasing the likelihood of developing oncological processes in ovarian tissues;
- reproductive function disorders up to the development of secondary infertility.
Based on the above complications of hyperestrogenism, we can draw an unambiguous conclusion: such a deviation requires mandatory treatment. It is especially dangerous if it occurs against the background of pathological processes. Ignoring their signs can sometimes be fraught with dangerous consequences not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life!