Causes
Most often, anisocytosis occurs with iron deficiency anemia, sideroblastic anemia, B12-folate deficiency anemia, hypovitaminosis A, massive blood loss, blood transfusion, damage to the red bone marrow with changes in pluripotent stem cells, cancer, chronic liver diseases, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and some acute intoxications.
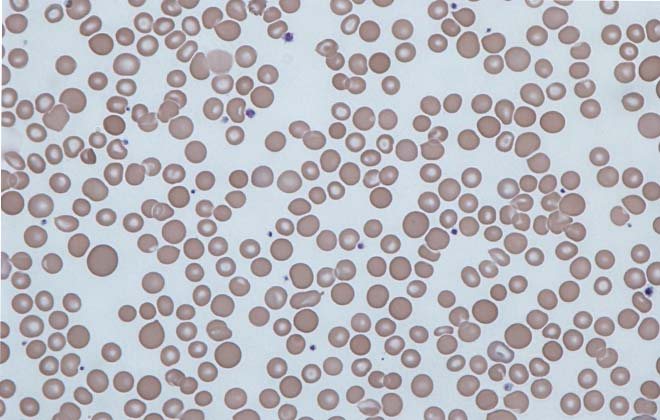
Normally, a human erythrocyte is a nuclear-free, biconcave, round cell with a diameter of 6.8 to 7.7 microns. The maximum permissible percentage of altered red blood cells should not exceed 30%.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing RDW
Anisocytosis is an early sign of anemia, the severity of which is determined by its degree. The main reasons for increased RDW in both adults and children are as follows:
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Megaloblastic anemia (deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid).
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Metastases to the liver.
- Blood transfusions.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Alcohol addiction.
In addition, RDW can be increased in Alzheimer's disease, hemoglobinopathy, lead poisoning, microspherocytosis, bone marrow metaplasia, and cardiovascular diseases.
During treatment of iron deficiency anemia, the anisodide index increases. This is explained by the appearance in the blood of a large number of young red blood cells, which differ in diameter from mature ones. With effective treatment, RWD returns to normal, but after other indices.
A change in the diameter of red blood cells is considered a diagnostic marker that informs about the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
RDW is almost never low. If you receive such a result, you most likely should retake the analysis. If the indicator is slightly reduced and there are no other changes in blood tests, this result should be considered normal. A reduced RDW has no diagnostic value.
In some pathologies, RDW does not change; the indicator remains normal. This includes the following conditions:
- anemia accompanying chronic diseases;
- β-thalassemia;
- spherocytosis;
- acute aplastic and hemorrhagic anemia;
- sickle cell anemia.
The essence of the problem
The problem of kidney hydrocalycosis: what it is, causes, symptoms and treatment in adults and children
Before you panic at the sight of an incomprehensible name on a laboratory form with the phrase “anisocytosis”, it is important to understand what it is, since the situation does not always indicate critical problems in the body. In medicine, under this name it is customary to identify a precedent in which processes occur in the body of the subject, under the influence of internal and external factors, that provoke modification of blood components
Ideally, blood cells have a standard size and specific appearance. Situations when blood cells of a certain type differ in configuration, indicate the presence of a certain kind of pathology in the body, are identified in the results form with the phrase “anisocytosis”, and with the specification “anisocytosis of erythrocytes” or “anisocytosis of platelets”, depending on the criterion, which components biomaterials do not meet the standard. Often, such precedents are diagnosed in children, mainly in newborns, as well as in pregnant women, which does not indicate the presence of critical problems; they arise against the background of restructuring of the body to a new life status and normalize over time. Defective sizes or appearance of these cells in the blood of adults require further diagnosis, since such development can have diverse prerequisites, from simple incorrect nutrition, all the way to oncology.
Anisocytosis - causes
PDA (patent ductus arteriosus) in newborns, children and adults: symptoms, treatment and life prognosis
Any change in the blood has a basis that needs to be clarified in order to find the root of the problem. The causes of anisocytosis vary in nature, often as follows:
- poor nutrition, which results in a lack of iron, vitamins B12 (predominance of megakaryocytes), A, which are responsible for the creation of red blood cells;
- oncology;
- blood transfusion - the donor material must be checked for the presence of this disease, because it is transmitted to another person;
- myelodysplastic syndrome – provokes a change in the size of blood cells.
Anisocytosis in a general blood test can occur due to the following reasons:
- Poor nutrition. No pronounced changes in blood cell parameters were observed. However, eating a poor diet or eating certain foods can cause vitamin and iron deficiencies. Anemia develops especially often in children with decreased appetite. Eating meat and fish products, fresh vegetables and fruits helps normalize the indicators. Vitamin B12 increases the number of red blood cells, vitamin A restores normal cell size.
- Blood transfusion. Before the procedure, the donor material must be checked for the presence of non-standard shaped elements. Otherwise, the recipient may receive a blood transfusion with larger or smaller cells. The immune system cannot eliminate these elements immediately; this takes several days. Over time, all blood cells acquire normal sizes.
- Oncological diseases. Atypical cells often invade the bone marrow, which promotes the production of altered blood cells.
- Liver diseases, including cancerous tumors that metastasize to this organ. In this case, macrocytosis is most often detected.
- Thyroid diseases. Anisocytosis can be provoked by autoimmune thyroiditis, nodular goiter and malignant neoplasms.
- Disruption of hemoglobin production processes.
- Syndromes accompanied by a violation of the normal ratio of maturing and dying blood cells. Anisocytosis of a similar origin is detected in elderly and senile people.
- Long-term systematic use of alcohol.
- Infectious diseases, helminthic infestations.
Anisocytosis of platelets and leukocytes is not an independent disease. The diameter, color and shape of blood cells change due to various disorders in humans.
More article:Distribution of red blood cells by volume
- errors in nutrition. A slight disturbance in the level of blood cells may indicate poor nutrition or insufficient intake of certain components into the body. Of course, this factor cannot provoke a strong deviation from the norm, but it cannot be ignored;
- lack of iron, vitamins A and B12. These elements are necessary for the normal formation of red blood cells. Vitamin A ensures the maintenance of normal cell diameter. If iron and vitamin B12 deficiency occurs, the percentage of blood elements is disrupted, which can cause anisocytosis;
- blood transfusion. Often, after a blood transfusion from a donor who has an abnormality in the form of anisocytosis, the person who received the blood will also develop this condition. This is explained by the inability of the immune system to quickly normalize these indicators. If a person is healthy, after some time his anisocytosis will disappear on its own;
- oncology. Bone marrow neoplasms always entail a disturbance in the composition of the blood;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, liver.
A common cause of anisocytosis is a lack of vitamins and iron deficiency in the blood.
With a long course of infectious diseases and severe intoxication of the body, transient compensatory anisocytosis is observed. This condition is characterized by a change in the cell structure of lymphocytes and leukocytes.
Macrocytosis is more often found in anemia, leukemia, liver and pancreas diseases. Often in combination with this, the patient is diagnosed with hypochromia - a decrease in hemoglobin production.
Etiological reasons
What reasons can lead to deviations of this kind:
- These include nutritional disorders - most often this is a lack of vitamins and minerals, leading to a lack of iron content in the body, as well as vitamins B12 and A. Since vitamin B12 and iron are involved in the formation of red blood cells, therefore, their deficiency leads to the development of anemic paintings. Vitamin A supports the process of stabilizing the size of blood cells.
- Blood transfusions - before blood transfusion, a thorough examination is necessary to determine its size. The donor's body will not be able to immediately cope with a sudden large number of abnormally sized blood cells - this will be stressful for it.
In the presence of tumors, especially those localized in the bone marrow, the process of changing cell sizes begins. The presence of a myelodysplastic process causes the formation of blood cells of different sizes.
This is anisocytosis. We figured out what it is.
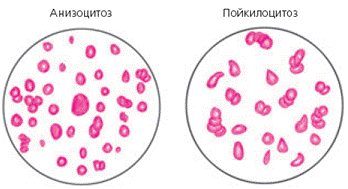
Poikilocytosis
Catarrhal rhinitis: causes, symptoms and treatment for adults and children
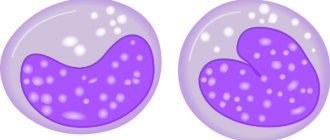
Poikilocytosis is a pathological modification of red blood cells. In this case, cellular deformation and improper functioning occur.
The presence of cells means the presence in the body of one or another type of anemia, which in most cases has a moderate or severe stage.
To detect poikilocytosis of red blood cells, a general blood test is performed. If the result indicates the presence of “anisocytosis” or “poikilocytosis” on the form, further verification will be required.
At the first concept, possible initial stage anemia. that the patient suffers from mild anemia. Poikilocytosis may indicate a moderate to severe stage.
Diagnosis of hemolytic disease
Preparation is as important as the test itself
Poikilocytosis is the main indicator of disorders in the body. When the parameters or color of blood cells change, a pathological condition develops in the internal organs. Diagnostic measures are carried out exclusively in the laboratory through blood sampling. Additional studies are rarely prescribed.
To obtain the correct interpretation of the analysis, the patient is recommended to prepare:
- Blood sampling is carried out only on an empty stomach - it is forbidden to eat, if necessary, it is permissible to drink a little water without gas;
- dinner the day before should be light - it is not recommended to eat heavily, exclude fried foods, pickles, and smoked foods from the menu;
- the day before blood sampling, it is not recommended to play sports, visit the pool, sauna, or have sex - all physical activity must be limited. Moreover, alcohol is also contraindicated before taking the test;
- Before donating blood, all medications must be stopped. If it is impossible to do without the medicine, it is better to warn the laboratory assistant about this;
- if repeated analysis is necessary, the study should be carried out at the same time of day. Before taking blood, you should catch your breath and relax.
Analysis on RDW
This analysis is carried out using analyzers. They help to accurately count red blood cells of all sizes and shapes in 1 μl of blood. The sampling is carried out on an empty stomach. The material for the study is taken from a vein.
The average capacity of an erythrocyte is determined automatically, and the deviation in the number of normocytes in relation to macro- and microcytes is calculated. The data is displayed in the form of a histogram. If the percentage of RDW falls within the normal range, then the result is recorded as negative.
If the norm is exceeded, a positive result is indicated. For such cases, the procedure is duplicated in order to identify the causes of abnormal indicators.
Sometimes a false positive result occurs, especially if there are a large number of macrocytes in the blood. These results often occur after surgery or blood transfusion. The redistribution or change in the type of cells itself can change frequently, and in a short time.
Therefore, it may be necessary to process the data using a statistical analysis method. The standard deviation value is calculated using a number of formulas. Previously, the results were obtained manually, but this is an extremely labor-intensive process, and therefore today it has been practically abandoned in favor of computer data analysis.
Signs
With mild and moderate anisocytosis, the patient's condition slightly worsens. Signs appear that are not typical for this pathology. With severe anisocytosis, the following symptoms are observed:
- muscle weakness that does not disappear even after a long rest or night's sleep;
- decreased physical and mental performance;
- moderate pain localized in the parietal or occipital part of the head;
- daytime sleepiness;
- tremor of the limbs observed after waking up.
With prolonged absence of treatment, the pathology worsens, and more dangerous manifestations, such as cardiac syndrome, are added to the above symptoms. The main signs of severe and critical anisocytosis include:
- increased heart rate;
- increased heart rate;
- breathing problems (shortness of breath, attacks of asphyxia);
- a feeling of shortness of breath that occurs at any time of the day and does not depend on physical activity;
- pallor of the skin, lips and mucous membranes of the oral cavity (in severe forms of anisocytosis, the tissues acquire a bluish tint).
Slight anisocytosis with a predominance of microcytes and macrocytes is often found in pregnant women. This is due to the development of anemia or hypovitaminosis caused by non-compliance with recommendations for proper nutrition and taking nutritional supplements. The clinical picture may include the following signs:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dizziness;
- general weakness, apathy;
- decreased appetite;
- deterioration of hair and nails.
In children
Anisocytosis can be detected in a blood test in a child of any age. In most cases, the cause of this phenomenon is a previous infection or vaccination. Weakening of the body contributes to the development of iron or vitamin B12 deficiency, due to which cell sizes deviate slightly from normal. You should consult a doctor if the pathological condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- brittle hair and splitting nails;
- dry skin;
- indigestion, in which constipation is replaced by diarrhea;
- frequent occurrence of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- increased fatigue, irritability;
- deterioration of dental condition, change in taste perception;
- increased heart rate.
General definition
Anisochromia in a general blood test is a condition in which there is uneven coloration of red blood cells. This is due to the hemoglobin content in them. The more of it there is in red blood cells, the brighter their color. Those red blood cells that contain insufficient hemoglobin look paler. In a blood test, this indicator is determined as color.
The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues. The more hemoglobin these blood cells contain, the faster the body is saturated with oxygen. But there must be moderation in everything. Therefore, experts have identified the optimal hemoglobin content in red blood cells, which allows for the most efficient functioning of the entire body. Deviation from normal values may indicate the presence of pathological processes.
Platelet anisocytosis
The protective function of preventing acute blood loss is performed by blood particles called platelets. They are very important for the human body and are responsible for the ability of blood clotting. In the analysis, the normal indicator of the number of particles of changed sizes should be from 14 to 18%. With platelet anisocytosis, the numbers are different. When examined in the analysis, the platelet index is designated as PDW.
This pathology has its origins and is explained by the presence of various diseases, since it is only an accompanying symptom. The patient feels a physiological change. His health is deteriorating. Changes in the size of platelet cells are provoked by hemorrhoids (anal fissures) and heavy menstruation. Other possible reasons:
- myeloneoplastic processes;
- leukemia;
- liver failure;
- viral infection;
- radiation sickness;
- aplastic anemia;
- lack of biologically active substances;
- DIC syndrome.
Treatment
Therapy begins with the elimination of the underlying disease, which was the source of the development of the qualitative characteristics of blood cells.
The basis of treatment for this pathology is etiopathogenetic therapy. So, if the cause of anisocytosis is folate deficiency or iron deficiency anemia, then it is necessary to treat these diseases first, that is, those diseases that led to this pathological process
It doesn’t matter whether erythrocyte anisocytosis is low or high
Treatment in this case should include a balanced and rational diet, enriched with either iron (for iron deficiency anemia) or B vitamins. These are legumes, veal, prunes, dried apricots, however, it must be remembered that certain foods cannot be combined, since in these In some cases, some vitamins may not be absorbed. For example, tannins contained in strong tea suppress iron absorption. Medicines for IDA are products containing iron (Ferrum-Lek), and in case of folate deficiency anemia, folic acid (Cyanocobolamin at a dosage of 500 milligrams intramuscularly).
Complications

If treatment for anisochromia is not started in a timely manner or is completely absent, more serious pathological conditions may develop. These include:
- Decreased immunity.
- Enlarged liver.
- Decreased quality of life due to unpleasant manifestations of the pathological condition.
- Growth retardation in children.
- Mental and mental retardation in a child.
- Chronic anemia.
It is important to note that if the reason for the detection of anisochromia in a general blood test is tumor processes, hepatitis and other dangerous diseases, the lack of treatment can lead to the development of serious complications.
Anisocytosis of red blood cells
In the body of a healthy person, the norm of erythrocytes is 70%, micro- and macrocytes - 11.5-14.5% (or 10-20 fl). For a child under 6 months of age, the rate is higher – from 15% to 18.8%. During pregnancy it may increase. If the result exceeds or does not reach the norm, this means that a pathological process is developing. Microcytosis also occurs - a decrease in the permissible diameter. The following indicators of cell diameter are distinguished:
- normocytes reach 7-8 μm (erythrocyte anisocytosis was not detected);
- macrocytes – above 8 µm;
- megalocytes – above 12 µm.
This pathology can be caused by an insufficient amount of vitamins A and B in the body, cancer with metastases to the bone marrow. Liver disease and thyroid dysfunction should not be ruled out. Another possible reason is donor blood transfusion. In order to prevent the disease in time, it is necessary to regularly monitor the composition and parameters of the blood.
The rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis is higher than normal
An increased test result is common in patients with iron or vitamin deficiencies. If a blood test reveals an indicator of erythrocyte anisocytosis above normal, this is a signal that pathology is developing. Depending on the stage, the doctor will make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment. Often the cause of such changes is anemia of any type.
The disease is classified according to the degree of intensity. There are only 4 of them and they are distributed according to the system of advantages:
- The first degree is characterized by a slight increase, when macrocytes and microcytes fill 30-50% (+).
- The second is moderate, 50-70% (++).
- The third is pronounced, more than 70% (+++).
- The fourth is pronounced, almost all red cells are of a pathological size (++++).
RBC anisocytosis rate is below normal
It is extremely rare that the RDW index is lowered; in such cases, it is recommended to take a new blood test. If the rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis is below normal, and there are no other significant changes, such an analysis is considered satisfactory and is not required to be retaken. Sometimes, if certain diseases are present, the RDW result does not change. A reduced result has no diagnostic value.
Classification of anisocytosis
Pathology comes in two variants:
- Anisocytosis of erythrocytes.
- Anisocytosis of platelets.
It can also manifest itself in two forms:
- Anisocytosis observed during pregnancy.
- Anisocytosis in children.
Let's try to figure out what it is - anisocytosis of erythrocytes.
There are four degrees:
- first (minor anisocytosis) – microcytes and macrocytes make up 30-50%;
- second (moderate) – 50-70%;
- third (pronounced) – above 70%;
- fourth (sharply expressed) - almost all red cells have a size different from the normal value.
Depending on the increase in the number of certain forms of red blood cells, there are:
- microcytosis - an increase in the number of small cells;
- macrocytosis – increase in the number of macrocytes;
- mixed - an increase in the number of both small and large cells.
Microcytosis is usually observed in the following conditions:
- iron deficiency anemia;
- in case of lead poisoning;
- thalassemia;
- sideroblastic anemia;
- with anemia associated with chronic bleeding;
- for some malignant diseases.
Macrocytosis can be a normal variant or pathological. In the first case, we are talking about anisocytosis of newborns in the first two weeks of life; by two months the condition is normalized. Pathological macrocytosis is due to the following reasons:
- impaired DNA synthesis, which may be associated with the use of certain medications, myelodysplasia, erythroleukemia, folic acid and cobalamin deficiency.
- pathology of red blood cell membrane lipids in liver diseases, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, after removal of the spleen.
In mixed anisocytosis, both microcytes and macrocytes can predominate. In the first case, as a rule, hypochromic anemia occurs. If macrocytes predominate, then the possibility of B12 deficiency or pernicious anemia cannot be excluded.
Anisocytosis: what is it?
Platelets in the bloodstream
Anisocytosis is a change in the size of blood cells. This is an indicator of pathology that can tell about various diseases or disorders in the circulatory system. The predominance of large platelets provokes the risk of blood clots and is a marker of a number of unnatural changes in the body; the presence of predominantly small sizes indicates a disorder in hematopoiesis and carries the risk of bleeding.
Platelets are miniature blood cells that perform important functions in preventing bleeding and tissue regeneration. Their lifespan is about 10 days, during which they change their size from larger to smaller. It is mature cells that perform their tasks optimally; the presence of a large number of abnormal sizes means the inability of platelets to fulfill their natural purpose.
To determine anisocytosis, the following indicators are required:
- MPV (Mean Platelet Volume) - the average volume of a platelet, allows you to assess which platelet sizes predominate in the blood.
- PDW (Platelet distribution width) - platelet index, indicates the degree of distribution of abnormal sizes.
Diagnostics
The main way to diagnose pathology is a blood test for anisocytosis. The diagnosis is made if the resulting material contains cells of uncharacteristic sizes. When taking the analysis, you must follow the following rules:
- biomaterial is handed over in the morning;
- You cannot eat on the day of visiting the laboratory; fried and spicy foods are avoided the evening before;
- 2 days before donating blood, avoid heavy physical activity;
- 3 days before the examination, stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
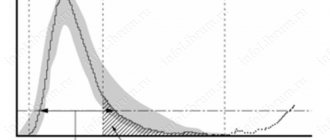
When taking a test after a previous infection, the results may be distorted. Sometimes additional diagnostic procedures, such as a histogram, are required. Normally, the erythrocytometric curve has the shape of a regular triangle with a high apex. Cells with a diameter of 6-8 mm predominate.
With microcytosis, the curve shifts to the left and takes on an asymmetrical shape. A shift to the right indicates the presence of macrocytosis.
What does elevated blood levels mean, what should I do?
An increase in RDW levels is the norm only for children under 6 months of age, which is due to the peculiarities of their hematopoietic system. Also, a slight excess of the established norms for the concentration of altered red blood cells is allowed in people who have recently undergone surgery or a blood transfusion.
In all other cases, an increase in RDW indicates the possible development of the following diseases and pathological conditions of the body:
- aplastic anemia;
- internal bleeding;
- megaloblastic anemia;
- hemoglobinopathy;
- cancer of the bone marrow;
- homozygous thalassemia;
- hyperglycemia;
- anemia caused by too little nutrition, or the presence of chronic diseases of the internal organs.
The percentage of changed blood cells is just one of the general indicators of a clinical blood test. In order to establish the cause of the pathology, the attending physician examines all points of the laboratory report. An individual treatment regimen is developed only after a final diagnosis has been made.
Treatment of microcytosis

Diet as a method of prevention and treatment
Microcytosis is an indication for a thorough examination of the patient, since the causes of the pathology can be completely diverse
For effective treatment of pathology, it is important to identify and influence the causative factor of its development.
Microcytosis caused by the growth of a malignant tumor in the body requires adequate treatment through surgery or radio/chemotherapy. Microcytic anemia caused by a chronic inflammatory process requires anti-inflammatory, antiviral therapy.
If the cause of microcytosis is insufficient iron content, then correction of the diet is necessary (consume more cod liver, beef, veal, natural pomegranate juice, buckwheat porridge, spinach and other products).
If the causative factor in the development of microcytosis cannot be eliminated, the patient must be treated symptomatically: given tablets or injections of iron, detoxification therapy, and enriched the diet with the above products.
Preventing the development of microcytic anemia is much easier than treating it
Therefore, it is important to adhere to the rules of a healthy diet, lead an active lifestyle with moderate and regular physical activity, monitor your health (undergo annual preventive examinations in medical institutions), try to isolate yourself from stressful situations
Attention! Timely detection and prescription of adequate therapy for microcytosis is the key to success and good health.
Causes
Most often, anisocytosis occurs with iron deficiency anemia, sideroblastic anemia, B12-folate deficiency anemia, hypovitaminosis A, massive blood loss, blood transfusion, damage to the red bone marrow with changes in pluripotent stem cells, cancer, chronic liver diseases, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and some acute intoxications.
Normally, a human erythrocyte is a nuclear-free, biconcave, round cell with a diameter of 6.8 to 7.7 microns. The maximum permissible percentage of altered red blood cells should not exceed 30%.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
Anisocytosis of red blood cells is detected by a complete blood count and occurs as a result of a number of diseases. In adults, the state of microcytosis is caused by various pathologies:
- Violation of the synthesis of red blood cells in the bone marrow due to hereditary diseases.
- Development of malignant tumors.
- Poisoning with lead and other toxic substances.
- Sideroblastic anemia.
- Anemia caused by chronic bleeding.
- Malnutrition and lack of vitamins B12 and A.
Pathological macrocytosis occurs for the following reasons:
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Absence of spleen.
- The effect of certain medications.
- Lack of cobalamin and folic acid in the body.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Alzheimer's syndrome.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Alcoholism.
The mixed type of anisocytosis manifests itself as a result of hypochromic anemia.
The RDW index is extremely rarely lowered. Most often, the analysis will need to be repeated. In the case of a repeated result confirming that erythrocyte anisocytosis is reduced, such a result is not considered a pathology in the absence of serious changes in other parameters in blood tests.
The process of collecting material for examination occurs mainly in the morning. Before this, it is not recommended to expose yourself to serious physical activity and stress; you should not eat before the procedure.
Sampling of material to detect anisocytosis
When interpreting the results, the attending physician draws conclusions about the person’s health status, based, in addition to RDW data, on other indicators. In rare cases, the anisocytosis index may not exceed the normative limits, but the presence of altered red blood cells can still signal pathological processes in the body.
The indicator of anisocytosis of erythrocytes serves rather as an auxiliary sign when studying the results of the analysis. An increased RDW index most often indicates anemia and acts as an early symptom of the disease. In rare cases, this indicator may remain unchanged even with serious illnesses.
Reasons for the development of anisocytosis
Isolated anisocytosis of red blood cells may be present in mild stages of anemia. It can develop in a woman during her period, especially if for one reason or another it is somewhat delayed. There can be many reasons for this condition, both minor and quite serious.
The most common symptom of anisocytosis is:
- Anemia, hypochromia, chlorosis, post-hemorrhagic anemia, hyperchromic anemia and so on,
- Lack of vitamin B12,
- Iron deficiency
- Lack of vitamin A,
- Lead poisoning
- Malignant neoplasms,
- Received blood transfusion.
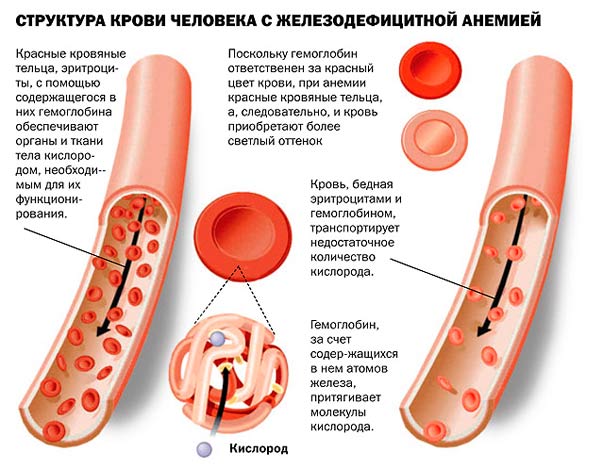
Iron deficiency
In the case of the last point, we can say that this is a passing anisocytosis, which will eliminate itself as soon as the body gets used to the “new” blood and replaces the diseased cells with healthy ones. So in this case, you just need to wait time and, if necessary, replenish internal reserves with vitamins, minerals and other useful substances.
Often the state of platelets changes in parallel with pathological changes in erythrocytes.
Causes of microcytosis
An increased content of microcytes is typical for different groups of people at different periods of life. Microcytosis can often be observed after an infectious disease in a child. If the level of such red cells is slightly increased, then it can be easily corrected with the right lifestyle and nutrition.
This is a common condition in infants, since the systems are just returning to normal. Therefore, such conditions can go away on their own without treatment. Also, women often suffer from microanisocytosis during pregnancy and lactation due to hormonal changes in the body and high consumption of nutrients .
In other cases, anisocytosis of this type can be caused by:
- Iron deficiency or microcytic anemia,
- Microspherocytosis,
- Cooley's syndrome or thalassemia,
- Chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases,
- Heavy bleeding
- Lack of foods with iron in the diet,
- Oncological lesions.
It is important to remember that some diagnoses require not only clarification and lifestyle adjustments, but also serious treatment. Oncological diseases can develop very quickly, and therefore one should not delay diagnosis.
The deterioration of cell characteristics can lead to the deterioration of red blood cell function.
Causes of macrocytosis
Macrocytosis may also indicate the development of anemia. Third-party factors may also influence this sign. Even a lack of nutrients and vitamins in the diet can significantly change blood composition.
But often an increase in the number of macrocytes is caused by such conditions as:
- Heavy bleeding
- Various types of anemia
- Bone marrow pathologies,
- Oncological lesions, most often blood,
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Chronic alcoholism,
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs,
- Taking certain medications.
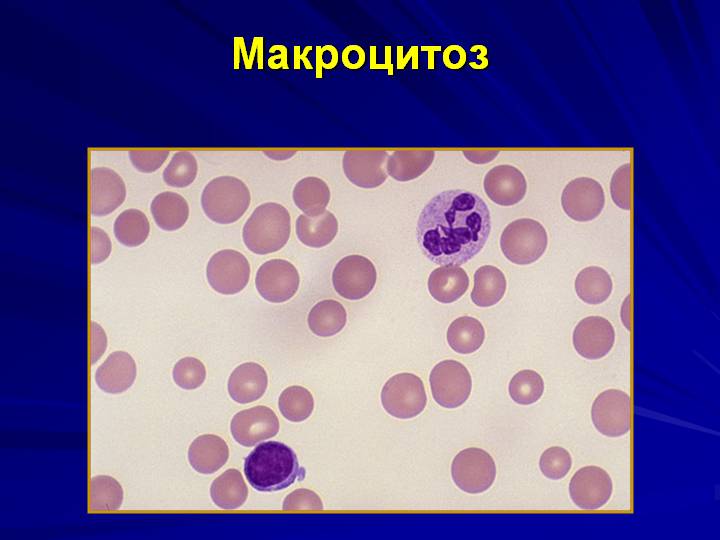
Macrocytosis
Some diseases are quite serious and require immediate intervention. Often, some pathologies end in death in the absence of adequate therapy.
Mixed type
The mixed type of anisocytosis is manifested by the dominance of macrocytes and microcytes over normocytes. Combined pathology with a predominance of macrocytes is characterized by the presence of an impressive number of abnormally large red blood cells. They are detected in blood smears and have a hyperchromatic structure without clearing in the center. The cells look like ovals with a diameter of about 11-12 microns.
Detected when:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency,
- Folic acid deficiency,
- Hypochromic anemia,
- Pernicious anemia,
- For anemia during pregnancy,
- With dyserythropoiesis,
- With helminthic infestation.
This deviation quite often develops when affected by worms, and therefore it is necessary to identify their presence, as well as determine the type of disease. Only in this case will it be possible to recover from pathogenic organisms.
Anisocytosis rate higher than normal can even be due to a simple change in the environment, due to moving.
Anisocytosis during pregnancy
When carrying a child or breastfeeding, a state of moderate anisocytosis of red cells quite often appears, which can easily be corrected by dietary nutrition, vitamins and the use of medications.
Often, a pregnant woman develops iron deficiency anemia and the microcyte count increases. The reason is a lack of iron, which is caused by the formation of the embryo.
It is important to monitor blood test results and, if there are deviations from the norm, immediately follow all doctor’s instructions to eliminate them. Ignoring this fact leads to:
- fetal hypoxia;
- swelling, improper formation of the child;
- danger of losing a child;
- premature birth.
If anisocytosis is diagnosed during pregnancy planning, then in combination with poikilocytosis, the pathology indicates a direct contraindication to IVF, requiring the necessary treatment.
RDW standard
A normal body produces red blood cells that are almost identical in volume. Moreover, in a healthy adult, normocytes make up about 70% of the total volume of red cells. With anisocytosis, red cells have different shapes and volumes.
RDW analysis allows us to determine the degree of distribution of red blood cells by volume, that is, their heterogeneity. As a person ages, these cells gradually begin to decrease in volume. The same changes occur with anemia.
The following approximate indicators are considered the RDW norm:
- 13% for adults,
- 16.8% for children under six months,
- 13.2% for children six months and older.
Indicators can vary between 1.5-1.9%. If the transcript shows a deviation from the norm, then it is necessary to examine the patient followed by therapy.

RDW standard
Symptoms of anisocytosis
Anisocytosis in almost all cases is accompanied by a decrease in the number of blood cells, so the clinical manifestations of this condition cannot be considered specific, characterizing this pathology.
Almost all patients in whom anisocytosis is detected during additional examination note changes in their own health in the form of progressive weakness, inability to perform usual physical activity, rapid heartbeat, observed against the background of complete well-being. With a long course, anisocytosis, combined with anemia and thrombocytopenia, provokes the development of respiratory disorders in the patient, manifested in increasing shortness of breath of the inspiratory type. Upon objective examination of the patient, pronounced pallor of the mucous membranes and skin may be observed, up to the development of acrocyanosis. Due to the fact that the above symptoms are not specific and may accompany the development of cardiac diseases, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient using not only laboratory, but also instrumental imaging methods.
The severity and specificity of clinical manifestations directly depend on the pathomorphological type of anisocytosis, therefore, when changes in the metric parameters of blood cells are detected, the “anisocytosis index” and “anisocytosis index” are necessarily calculated. In a situation where a patient has exclusively a decrease or increase in the size of blood cells, the medical laboratory technician uses the terms “microcytosis” or “macrocytosis”, but in some situations both conditions can be observed in the same person, so the term “mixed anisocytosis” should be used.
In addition to detecting the presence of anisocytosis, for a specialist in the field of hematology, the severity of the detected changes is of great importance, therefore, to divide anisocytosis into degrees, there is a generally accepted gradation, represented by four degrees of severity. Minor anisocytosis is designated in laboratory analysis as “+” and is used when the content of blood cells changed in size is within 25% of their total concentration. Moderate anisocytosis or “++” occurs when the content of altered blood cells increases to 50%. A pronounced degree of anisocytosis “+++” is accompanied by severe clinical manifestations, since the number of altered blood cells prevails over the content of “healthy cellular composition” (up to 75%). Critical anisocytosis or “++++” is extremely rare and is accompanied by a complete replacement of normal blood cells with altered ones.
Types and degrees of anisocytosis
Anisocytosis is classified depending on what types of blood cells are changed. Pathology has the following classification:
- anisocytosis of mixed type. Here, the material under study contains up to 50% macro- and microcytes;
- microcytosis - the diameter of blood cells is less than 6.7 microns;
- macrocytosis - a condition with a predominance of macrocells, their diameter is more than 7.8 microns;
- megalocytosis – cell size exceeds 12 microns.
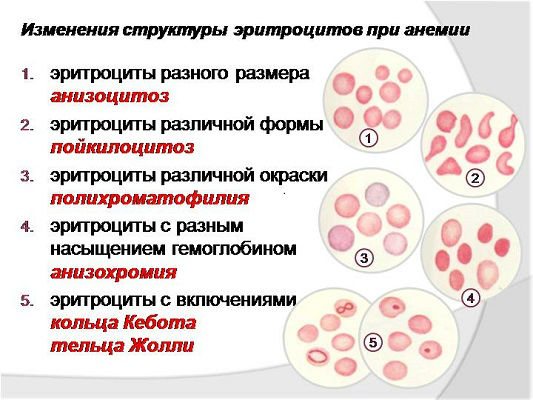
Under various conditions, the shape and size of blood cells change
In addition, the blood rdw indicator is distinguished depending on the degree:
- +(I) – the number of altered erythrocytes is not more than 25% – micro anisocytosis is insignificant;
- ++(II) – the number of altered cells from 25% to 50% – moderate, that is, the number of blood cells with irregular shapes is moderately increased;
- +++(III) – the number of red blood cells having irregular size or shape ranges from 50% to 75% – pronounced;
- ++++(IV) – all red blood cells have a changed shape – pronounced anisocytosis.
Taking into account this classification, the doctor can give a conclusion, for example, mixed-type anisocytosis is moderate, which means that the blood contains macro- and microparticles of altered size, and their total number is no more than 50%.
Important! Severe anisocytosis almost always indicates the development of severe pathologies in the body.
Mixed anisocytosis
In this pathology, the level of the overall content of increased and decreased cell sizes decreases. To correctly determine the percentage during the survey, the Price-Jones method is used.
Price-Jones curve: click to enlarge
This type of anisocytosis indicates the predominance of macrocytes. The source of the changes is a lack of vitamin A, B12, which suggests the formation of anemia.
The problem may also relate to kidney failure. If macrocytosis is detected above the established norm, this means iron deficiency.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of anisocytosis involves eliminating its cause. If the pathology is a consequence of iron deficiency anemia, you will need to change your diet and take medications that increase the hemoglobin level.
When diagnosing mild anemia, therapy is based on following a diet that involves consuming foods with a high iron content. This approach helps normalize hemoglobin levels. But a severe form of anemia requires drug treatment.
In the case when anisocytosis develops as a result of the formation and development of a malignant tumor, the result of therapy depends on its removal.
If the cause of anisocytosis was not a serious illness, but the use of medications that affect this indicator, a lack of minerals or vitamin complexes in the body, or an incorrect lifestyle, then the patient will receive the following recommendations from a specialist:
Replenishing mineral and vitamin deficiencies by taking multivitamins containing B12, A and iron. Improving the quality of nutrition, it is recommended to pay special attention to red foods (beef, liver, apples, tomatoes). Maintaining a good daily routine with enough time to sleep.
In exceptional cases, restoring the balance of blood cells requires surgical intervention.
Moderate anisocytosis is a fairly common phenomenon in women during pregnancy and lactation. Typically, this condition does not require serious intervention and is corrected by prescribing vitamin-mineral complexes and a special diet. Intrauterine development of a child sometimes causes iron deficiency in the body of a pregnant woman. In this case, the content of microcytes increases. For this reason, during such an important period, you need to periodically take a general blood test and carefully monitor its results.
If there is a serious deviation in the RDW indicator, ignoring the problem can lead to complications:
- various types of embryo development abnormalities;
- fetal hypoxia;
- risk of premature onset of labor.
Detection of anisocytosis during pregnancy planning, in combination with some other pathologies, may become a basis for a ban on IVF. The solution to the problem remains with the doctor, whose competent approach will help get rid of the pathology and avoid the risk of complications.
Specifics of the course of the disease in pregnant women and children
For the pediatric category of patients and women in an “interesting” situation, the doctors’ verdict “Anisocytosis of erythrocytes” is a fairly common phenomenon, and often it does not have any underlying pathological support. In most cases, in newborn babies, the diagnosis under discussion does not require specific treatment; the morphological composition of the biomaterial is normalized in a period of time from two weeks to two months. In older children, such a precedent often indicates an anemic condition that has arisen against the background of an infectious or viral disease of simple etiology, which is mainly eliminated by adjusting the child’s diet, with the possible parallel intake of vitamin complexes or drugs to restore immunity. In pregnant women, a precedent with the presence of modified cells also indicates the development of anemia, which is typical when carrying a child against the background of hormonal changes in the body and a deficiency of vitamin B. As in children, the precedent does not require complex adjustments and is eliminated by taking special preparations of the vitamin group, with parallel changing your diet.
Anisochromia in children

Diagnosing anisochromia in a general blood test in children in most cases indicates the development of anemia. This is a fairly common pathology in childhood, which occurs due to intensive growth of the body against the background of an underdeveloped hematopoietic system. This can also be contributed to by poor nutrition and various pathological processes occurring in the body.
Manifestations of pathology include pale skin, some developmental delay, lethargy, apathy, the appearance of cracks in the corners of the lips, prolonged and frequent colds.
Parents should monitor their children more closely and consult a doctor at the first suspicious signs.