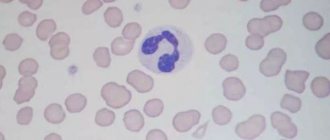
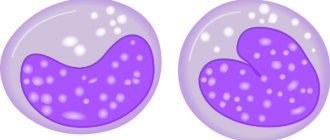
Normal in blood
Neutrophils are the most numerous cells of all types of leukocytes: their share is from 50% to 70% of all white blood cells.
If you look at the test form, you can see their different designations due to the fact that when counting, neutrophils are divided into band (not fully mature) and segmented (fully mature). The norm of segmented leukocytes in the blood of women is the same as that of men, and is 1500 – 8000 units/mm3. The determination of low segmented neutrophils in the blood of a child differs from the norm in an adult. The lower norm for children aged 2 weeks to 1 year is 1000 units/mm3. But after a year, this norm becomes like that of an adult.
It should be noted that the count of leukocytes strongly depends on the type of equipment (ie hematology automatic analyzers) on which the count is carried out. Therefore, segmented neutrophils, the norm of which is measured on different equipment and in different laboratories, should always be compared only with those values that are printed on tests in the laboratory.
Reticulocytes
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells. Their normal amount in the bloodstream is no more than 1% of the total number of red blood cells. The efficiency of these cells in transporting oxygen is lower than that of mature red blood cells, so their excess affects the quality of cellular respiration. This indicator is designated in analyzes by the corresponding Russian name.
An excess of reticulocytes indicates hypoxia of the body: immature cells appear in large numbers during tissue oxygen starvation. The kidneys produce the hormone erythropoietin, which stimulates the formation of new blood cells in the bone marrow. The release of numerous immature reticulocyte cells occurs when red blood cells are lost (bleeding, hemolytic anemia, etc.).
Low reticulocyte counts occur in diseases of the red bone marrow and often appear during chemotherapy. A deficiency of iron, folic acid, and erythropoietin leads to a decrease in their number. These anomalies may indicate poor nutrition or disease of the internal organs (gastrointestinal tract and kidneys). A decrease in the level of reticulocytes causes doctors to suspect certain types of anemia (aplastic, malignant).
Important information: What is toxogenic granularity of neutrophils in a child’s blood test?
Segmented neutrophils are increased
If neutrophils in the blood are elevated, what does this mean and what is the reason – doctors cannot immediately answer for sure. The only correct statement is the presence of an infection, a pathology complicated by the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the body. In order to accurately establish a reliable cause, a thorough, comprehensive examination of the entire body is required.
However, in most cases, increased segmented neutrophils in the blood are recorded when:
- development of bacterial infection;
- the appearance of a fungal infection;
- mild inflammatory process.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - reasons
An increase in segmented neutrophils is always a reason to examine the body. In such cases, they speak of a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right.
Among the common situations accompanied by this symptomatology, it is necessary to highlight:
- Not related to pathology: physical activity, food intake.
- Pathological: purulent abscesses, burns, trophic ulcers, leukemia, acute inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis, sepsis, peritonitis), the formation of malignant or benign tumors.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - what to do?
The main task in this case is to determine the reason why increased segmented neutrophils are detected.
The patient is indicated for additional examination, including consultations with the following specialists:
- therapist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist.
The patient must strictly follow the doctor's instructions and prescriptions. If neutrophilia is caused by a certain pathology, therapy is aimed at its complete cure.
- Reduced neutrophils in the blood
To help your body recover faster, doctors recommend following the following rules:
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Healthy eating.
- Seasonal therapy using multivitamins.
If segmented neutrophils are increased
The growth of cells of the neutrophil species is called neutrophilosis. The level of segmented neutrophils exceeds 75%.
Both segmented and rod cells increase.
Sometimes earlier forms appear in a blood test - myelocytes, but segmented ones do not change. In the leukocyte formula, this looks like a shift to the left (according to the location of cells in the list of leukocyte forms). At the same time, granularity is detected in neutrophils.
The causes of neutrophilia can be:
- infection with acute bacterial, fungal infection, spirochetes;
- exacerbation of the inflammatory process in rheumatism, pancreatitis, polyarthritis;
- the presence of a dead area in the body, for example, in acute myocardial infarction;
- recent vaccination;
- severe alcohol intoxication;
- disintegrating tumor;
- damage to the kidney tissue, especially with diabetic nephropathy;
- treatment with steroid hormones, heparin.
Vaccination of the adult population is carried out according to epidemic indications.
A shift to the right is detected when a high level of segmented forms predominates over younger band forms. It's possible:
- Segmented neutrophils are increased in the child’s blood and nasal smear. Reasons what to do
- after acute blood loss;
- as a reaction to blood transfusion;
- for some types of anemia.
The cause of a temporary increase in neutrophils may be:
- condition before menstruation in women;
- long-term stress associated with increased workload;
- physical stress.
Pregnancy causes a general increase in white blood cells by 20%. This is the protection of the mother and fetus from unwanted influences. During pregnancy, the absolute number of segmented neutrophils is increased (more than 6 x 109/l), and their relative level in the formula remains unchanged.
To determine the severity of the disease, neutrophilia is divided into forms:
- moderate - the number of cells is not higher than 10 x 109/l;
- pronounced - absolute content from 10 to 20 x 109/l;
- severe - cell count above 20 x 109/l.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the main part of the blood cell that carries oxygen to the tissues of the body. This is a protein compound that is able to bind oxygen molecules and then release them to cells. Hemoglobin contains iron compounds, which have a reddish tint. Due to the hemoglobin content, red blood cells are colored red.
The content, or concentration, of hemoglobin in the analysis can be read opposite the designation Hb or Hgb. It is also measured in grams per 1 liter of whole blood.
Important information: What is RBC in a blood test (decoding norms and deviations)
The normal concentrations of protein that is important for health are:
- in men 130-160 g/l;
- in women 120-140g/l;
- newborns - about 240 g/l;
- after 1 month the norm ranges from 110-145 g/l.
Blood protein concentrations decrease slightly in pregnant women. In this state, 110-130 g/l is considered normal. The reason is an increase in total blood volume. After childbirth, a drop in concentration is observed, which is associated with blood loss. These fluctuations are not regarded as pathology. The norm is restored a few months after childbirth if the woman adheres to a balanced diet.
Deviation from the norm towards lower values is considered a sign of anemia. Reduced hemoglobin concentration is caused by:
- poor nutrition and a decrease in the amount of iron entering the blood with food;
- impaired absorption of the mineral in the intestine (due to pathologies of the small part);
- constant minor blood loss (nasal, gastric, hemorrhoidal bleeding);
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs (spleen, red bone marrow);
- gynecological tumors in women;
- oncological diseases.
An increased hemoglobin content does not always indicate pathology. Most often it occurs due to dehydration of the body.
Normal indicators
There is a leukocyte formula that allows you to assess the condition of the blood and the body as a whole.
The table shows the indicators of a healthy person:
| Index | Normal values |
| % | x10 9 /l | |
| Band neutrophils | 42887 | 0,04-0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 45-72 | 2-5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5-5 | 0,02-0,3 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | 0-0,065 |
| Monocytes | 43042 | 0,09-0,6 |
| Lymphocytes | 19-37 | 1,2-3 |
What are segmented neutrophils responsible for? For the immune response during a bacterial infection.
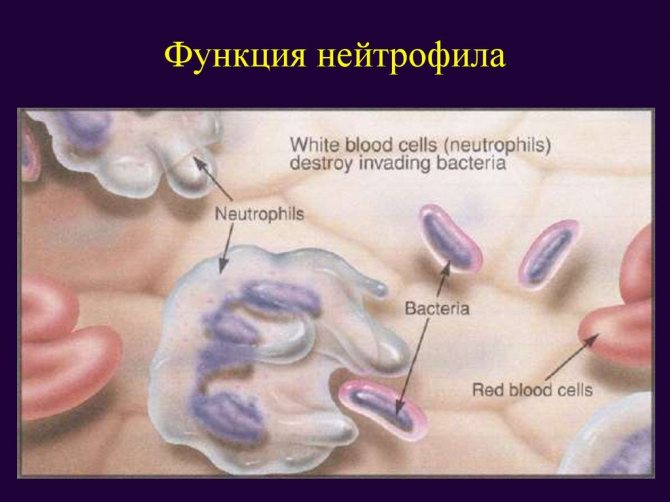
Of the total number of neutrophils in the blood, 45-72% are cells with segments in the nucleus. This is an indicator of the norm.
It varies depending on several factors:
- Segmented neutrophils are reduced
- The age of the person. In newborns, the indicator may be at its maximum level. During the first month of life, a decrease occurs down to a minimum percentage of immature cells. When a child reaches 6-7 years of age, the number of segmented neutrophils stabilizes. The immune system is strengthened. After 7 years, the norm of mature elements in a child coincides with the indicators of an adult.
- Absolute indicator. In some cases, a value is taken into account, which is calculated by the number of mature cells per microliter of blood. The norm for an adult is 1800-6500 neutrophils.
- Temporary factors. Mostly, deviations occur in children. A decrease and increase occurs after vaccination, during teething.
In other cases, deviations from the norm are a sign of an inflammatory process.
Hematocrit
The hematocrit number is the volume of blood cells (i.e., its different cells). The bulk of these bodies are erythrocytes (up to 99%). The result of the study can be found under the designation Ht. The indicator is calculated as the ratio of the volume of cellular elements to the total volume of blood and 1 liter is taken as a unit. The hematocrit number is expressed as a percentage (%) or expressed as liter per liter (l/l). See decreased hematocrit.
The normal ratio of cellular elements to the total volume is:
- in men 0.40-0.48 l/l or 40-48%;
- in women 0.36-0.46 l/l (36-46%);
- in a newborn, the hematocrit is approximately 20% higher than in adults (up to 55% or 0.55 l/l);
- in children older than 1 month, the indicator decreases and exceeds the adult norm by only 10%, and by 13-15 years it acquires average normative values depending on gender.
An increase in hematocrit indicates a decrease in the volume of the liquid part of the blood (plasma). This occurs with severe dehydration due to vomiting, diarrhea and burns or peritonitis.
An increased hematocrit may also indicate the presence of pathologies in the body:
- leukemia;
- kidney diseases (hydronephrosis, polycystic disease);
- erythremia;
- neoplasms in the kidneys.
Important information: What does it mean to have an increased hematocrit in a child’s blood?
The number of red blood cells decreases with anemia. Hematocrit can be reduced in pregnant women, and gradually decreases in newborns over the course of 1 month of life. It can also be caused by an increase in total blood volume with excess fluid in the body.
Neutrophils - what are they?
Neutrophils play a very important role in human immunity, removing and destroying microorganisms, unnecessary metabolic products, foreign substances, damaged and malfunctioning cells. Neutrophils perform these functions by the method of phagocytosis, that is, by the method of absorbing and eating these substances.
Neutrophils also participate in a very necessary process for the body called proteolysis, which breaks down proteins into their component parts . This is done by adding water to protein molecules. It is worth noting that proteins are very complex substances that consist mainly of amino acids necessary for the renewal and functioning of the human body.
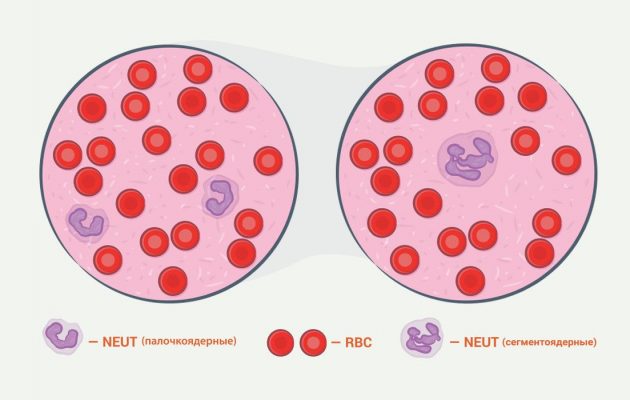
Neutrophils are produced primarily in the bone marrow, which fills cavities in the bones. Once the white blood cells are sufficiently formed, they leave the bone tissue and travel through the blood circulation. Here they are usually divided into two types - segmented and band leukocytes. When they say that a neutrophil is mature, this means that its development has reached its greatest point. This cell goes through several stages in its development:
What does a general blood test show during pregnancy? 34528
- Myeloblast.
- Promyelocyte.
- Myelocyte.
- Metamyelocyte.
- Band forms.
- Segmented, mature form.
The main characteristic of a mature neutrophil is that its nucleus (central structure) is divided into 3-5 sections called nuclei, which do not exist separately, but are connected together by thin threads called chromatin. Under the magnification of a strong microscope, these nuclei are clearly visible.