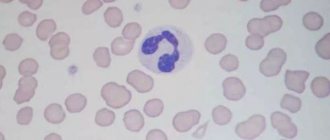
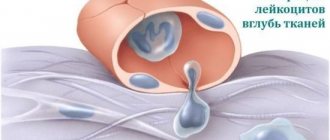
Basophils, large granulocytes that form in the bone marrow and enter the blood. They are responsible for the development of an allergic reaction in the body.
In a healthy person, basophils are contained in small quantities; an increase or decrease in their level indicates the development of the disease.
Basophils: sequence of formation in the body
Leukocyte production occurs in the bone marrow. After this, the formed elements migrate into the bloodstream. Then several hours are found in the peripheral blood. But basophils perform their main functions in tissues, where they remain for 8-12 days.
Basophilic bodies are an indicator of allergies. They contribute to the development of an allergic reaction in the body after the introduction of foreign particles. Most often, the inflammatory response is manifested by bronchial asthma, urticaria, respiratory symptoms, and anaphylactic shock.
Allergies can be caused by parasites (helminthic infestation), dust, medications, wool, etc. As soon as an irritant enters the human body, the BAS shell opens and releases granules contained in the cytoplasm into the bloodstream. And they contain biological active substances that block the enemy particle. The main components of the basophil cell are histamines, serotonins, prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
In medicine, leukocytes of this type are called scouts, because they are the ones who detect the irritant and do everything possible to get rid of it. A pronounced allergic reaction to the introduction of an allergen indicates increased activity of BAS. The body tries with all its might to eliminate the pest and cleanse the tissues.
What functions do basophils perform?
In addition to the fact that leukocyte bodies take part in the formation of inflammatory reactions and allergies, they also take care of maintaining other physiological processes:
- Ensure proper blood circulation in the capillaries, which leads to normal nutrition of all tissues;
- Promote the growth of new small vessels;
- Help other types of leukocytes migrate throughout the body;
- Participate in phagocytosis and detoxification;
- Activate platelet aggregation for proper blood clotting.
Basophils can inhibit the effects of toxic substances, including those of animal origin (snake venom). In fact, they react very quickly to irritating particles or substances, protecting the body from their spread and negative effects.
Despite the fact that basophilic formed elements are found in the blood in small quantities and do not directly participate in the formation of immunity, their large size makes it possible to utilize allergens and parasites that enter through the respiratory or digestive tract, as well as damaged skin.
What are basophils
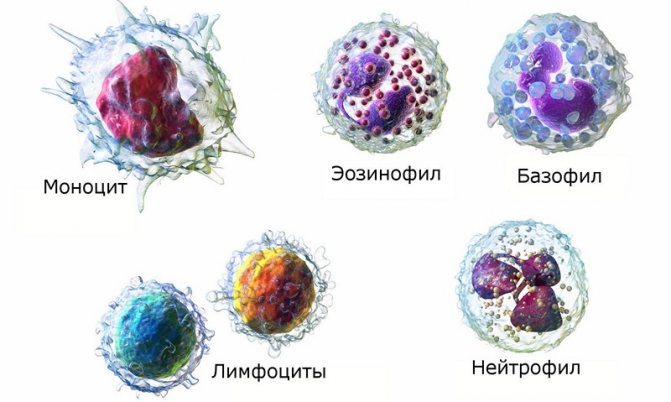
There are fewer basophils than other cells of the immune system, but they are everywhere - in the skin, connective tissue, serous membranes. If necessary, their level in the body can increase. Basophil cells or white cells (leukocytes) are formed in the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream when fully mature.
They are divided into two types: agranulocytes and granulocytes - cells that are granules that contain serotonin, prostaglandin, histamine and heparin.
Basophils live very short lives; once they enter the bloodstream for a short period of time, they almost immediately penetrate the tissues and settle there for 10–14 days. You can often find another name - histiocytes or “mast cells”. These cells themselves do not fight the threat; they only attract attention and give rise to further diagnostics.
https://youtu.be/o94ikVJc6L0
The mechanism of action of these cells can be schematically explained as follows:
- A foreign agent enters the child's body.
- Receptors signal this to basophils and histiocytes.
- Blood cells become activated and begin to release the contents of their granules at the site of infection.
- Vessels and capillaries at the site of inflammation expand. Wall permeability increases and blood flow increases
- Fluid accumulates in the tissues around the site of infection.
- The remaining cells of the immune system are sent to the site of inflammation.
The main function of basophils is protective or signaling. Also they:
- nourish cells and support tissue vital activity;
- participate in tissue repair;
- normalize trophic processes;
- create new capillaries - small blood vessels;
- improve blood flow in the riverbed;
- protect the gastrointestinal tract;
- participate in blood clotting;
- support immunity;
- absorb toxins, harmful microorganisms and foreign substances;
- take part in phagocytosis;
- participate in maintaining colloidal water balance in the body.
Both the child and the adult basophil perform the same functions.
Reduced basophils: when does the level deviate from the norm?
If the levels of basophilic bodies fall, this means that the body is not able to fully respond to the introduction of foreign particles. Accordingly, allergic reactions are disrupted and protective functions are reduced.
Basophils are measured as a percentage relative to other types of white blood cells. Their blood levels in a child will differ from those in adults. Doctors always look at a patient's white blood cell count result to see why abnormalities may have occurred.
The absolute content of basophils is 0.4-1%. This is an average value and corresponds to the norm. In order to find out normal indicators in patients of different ages, you need to consider the tabular data.
| Newborn babies | 0,75 |
| Children under one year old | 0,6 |
| Child over 2 years old | 0,7 |
| Adult men and women | 0,5-1 |
Reduced basophilic bodies are numbers that fall below 0.4%. Sometimes people have a zero index of white formed elements.
It is worth noting that women experience fluctuations in test results, especially during the period of ovulation, menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Therefore, if the patient donated blood and her numbers turned out to be low, then the analysis should be repeated after a few days or a week to make sure that they are stable.
Also, the BAS level deviates after taking medications with hormonal components. Women using oral contraceptives experience changes in their leukocyte count.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
The level of basophils in the blood is a kind of indicator of the presence of allergic or inflammatory processes in the human body. This indicator is not decisive in making a diagnosis, but in most situations it is necessary for the doctor to understand the complete picture that determines the functional activity of leukocytes. With its help, it is possible to track the reaction of white blood cells in response to the action of various pathogens.
Basophil levels are increased
The absolute content of these cells is not a constant value. It can be influenced by many endogenous and exogenous factors. At the same time, a significant increase in basophils (over 0.2 * 109 g/l) is observed extremely rarely, but a less pronounced increase is a common phenomenon. In adults, the most common causes of increased basophils in the blood are the following:
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs (hemolytic anemia);
- diabetes mellitus, intoxications of various etiologies, chicken pox;
- myxedema – insufficiency of pancreatic function;
- acute and chronic diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, ulcerative colitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers);
- allergic reactions: damage to the respiratory organs, itching, urticaria, dermatitis, eczema and others;
- neoplasms in the lungs and bronchi in the initial stages.
Also, the cause of increased basophils can be the use of corticosteroid drugs, estrogens or hormones prescribed for thyroid dysfunction. Allergic reactions and blood pathologies are a group of the most common conditions when an excess of these cells is noted in the blood test of adults. In a child, such manifestations are caused by similar reasons, but to them it is also worth adding poisoning with toxic substances and helminthic infestations.
Blood pathologies leading to basophilocytosis include a list of diseases such as acute and chronic leukemia (malignant pathology of the hematopoietic system), Hodgkin's disease or lymphogranulomatosis (pathology of the lymphatic system, which is malignant), polycythemia vera (benign damage to the hematopoietic system). Each of the listed pathologies can cause an increase in the number of any leukocyte groups, not excluding basophilic granulocytes.
Important! Slightly elevated basophils may be evidence of the development of an acute or chronic inflammatory process in both adults and children.
Processes that perform the body’s protective function from adverse influences can occur in the respiratory, urinary, and digestive systems. The negative influence of factors gives a signal to trigger an immune response, as a result of which hormones and enzymes that are found in basophil granules become necessary.
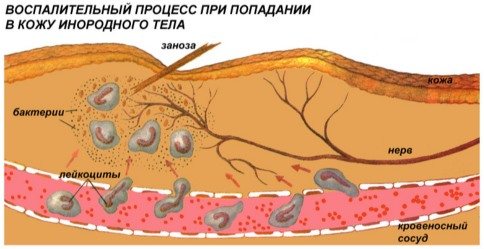
The process of releasing basophil cell granules into tissue
The breakdown of basophilic granulocytes leads to the release of prostaglandin, histamine and other elements, which is the impetus for launching a protective tissue reaction to the antigen that has entered the body. In addition, there are several more non-pathological situations in which basophils can also be elevated. Such reasons in women include the condition preceding the onset of the menstrual cycle and the period of ovulation, but, as a rule, with them the increase in level is observed to be low.
It is also worth mentioning that iron deficiency in the body often leads to an increase in the number of basophils. From all of the above, it follows that if a general blood test indicates an increase in the content of these cells, then what such an increase means can only be understood by a specialist. Self-diagnosis in such situations will not bring the desired result, and delaying a visit to the doctor will only worsen the development of the disease.
Approach to eliminating basophilocytosis
In most cases, when choosing the right treatment strategy to rid the patient of the underlying disease, and its timely administration, the number of basophils returns to normal. If the cause of basophilocytosis lies in prolonged use of hormonal drugs, then medications are canceled or analogues are selected that do not cause such side effects.
To normalize the blood count after treatment for infectious and inflammatory diseases, patients are prescribed an additional course of vitamins, as well as a diet that includes foods that contain a lot of B12. This approach has a beneficial effect on hematopoietic function, which affects the general condition of a person. A constantly observed increase in basophil levels is a high probability of a chronic disease that needs to be diagnosed and eliminated.
Low indicators: reasons for suppression of the protective function
Most often, people have an increased or normal percentage of large white cells according to the KLA. Reduced basophils are rare, in some cases they can even be a variant of the normal functioning of the body.
Specific diseases cause a drop in blood levels. This condition is called basopenia. It occurs almost unnoticed in adult patients and is more pronounced in childhood. Typically, basopenia in a child is caused by serious dysfunction of the bone marrow or endocrine system.
What pathological changes can reduce basophils:
- Acute infection (pneumonia, etc.);
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- Hyperthyroidism (increased production of hormones);
- Allergy;
- Adrenal diseases;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- Prolonged exposure to stress;
- Treatment of tumor with chemotherapy.
Basopenia can also be present in healthy people with certain physiological changes. For example, the period of pregnancy or ovulation is a common cause of a drop in the BAS percentage, but is not pathological.
But treatment of cancer and metastases with the help of toxic and hormonal drugs leads to the complete absence of white cells.
Basopenia
Indicators of relative basophils reflect the proportion of these granulocytes from the total number of leukocytes. The population of these cells is small. And normally for adults the percentage of basophils is allowed from 0% to 1%.
If the test form indicates BA 0%, this means that there were no basophils in the sample taken for the test.
The term “basopenia” is not entirely correct, since 0% of relative basophils, even in the complete absence of absolute BAS, is not considered as a mandatory indicator of the disease. A value of 0% in a general blood test in an adult is within normal limits.
This result only indicates a significant, almost to 0, decrease in the number of this population of cells, but not their complete disappearance from the body.
How to increase the level of white blood cells in adults?

In order to overcome basopenia, it is first necessary to establish the exact cause of the development of disorders in the hematopoietic system. Diagnostics allows us to identify pathology and prescribe effective therapy. After completing the course of treatment, a repeat blood test is taken to see whether basophils have increased to normal.
All doctors advise, even before starting therapy in adults, to reduce the impact of stressful situations on the body. This is the first rule that every patient should know. After all, it is the emotional and mental stress that greatly depresses all systems, including the hematopoietic one. It is also recommended to reduce physical activity.
Often a calm lifestyle together with an adjusted healthy diet in an adult, even without medications, increases the level of basophilic cells. The patient feels better, relaxes and his indicators return to normal.
If deviations in the tests were caused by taking hormonal drugs or chemotherapy, then stopping treatment eliminates basopenia after some time.
And in case of disruption of the endocrine system, therapy is prescribed by an endocrinologist. This is the most dangerous pathology, which requires careful selection of medications and adjustment of their dose during treatment.
If the diagnosis did not help to identify any serious disorders in the body, then perhaps the reason lies in a weakened immune system. Then the solution to the problem depends on the immunologist. He will be able to prescribe immunomodulatory drugs to boost immunity and restore normal blood counts.
Reasons for the decrease in basophils
Basophils are reduced to 0 in adults with a decrease in the barrier function of the immune system and speak of conditions such as:
- acute phase of the immune response;
- infectious diseases;
- anemia B12-deficiency, B9-deficiency;
- mental disorders;
- agranulocytosis;
- stress;
- pregnancy;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- physical stress;
- treatment with hormonal agents - prednisolone, progesterone;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- Cushing's syndrome.
A decrease in BAS to 0% indicates general exhaustion during fasting or impaired absorption of beneficial nutrients in the digestive tract. Basophils are reduced to 0 in the first days of infection with infectious diseases.
The acute onset of an allergic reaction or infection is accompanied by active migration of basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes to the site of inflammation. The outflow of leukocytes from the bloodstream causes a temporary decrease in the content of all white blood cells to 0.
Such a decrease is a normal physiological reaction of the adult immune system and indicates its capacity and high reactivity.
Treatment of basopenia in a child: how is it carried out?
Most often, in children, a drop in BAS in the blood is not a consequence of serious illnesses. Typically, indicators decrease due to stressful situations or infection. But there are also cases of basopenia caused by endocrine disorders and chemotherapy for diseases of the bone marrow or other organs.
But usually changes in the leukocyte formula do not frighten doctors and are a variant of the norm even with a zero percentage ratio. It is important to note that in a child any pathology always provokes jumps in several types of formed elements. For example, pictures are simultaneously observed when both eosinophils and basophils are reduced.
Cushing's disease is most often diagnosed in children. This is a neuroendocrine disorder that provokes increased activity and production of glucocorticoid hormones, reducing the level of basophilic bodies. At an early age, the disease leads to growth retardation. As women mature, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and men develop potency.
Treatment of Cushing's disease is carried out using different methods, depending on the severity of its course:
Light shape;
Radiation therapy aimed at the hypothalamic-pituitary region is sufficient. It is combined with medications.
Moderate severity;
Radiation therapy is combined with the prescription of drugs that suppress the functions of the pituitary gland and adrenal cortex. Sometimes unilateral adrenalectomy is used.
Severe course;
Bilateral adrenalectomy is recommended, which makes it possible to quickly reduce hormone production. After this, hormone replacement therapy is selected for life.
This is just one of the treatment options for basopenia in children with the development of serious disorders. It must be remembered that in case of severe pathologies, you should follow the doctor’s instructions and not self-medicate. Neglected conditions lead to complications.