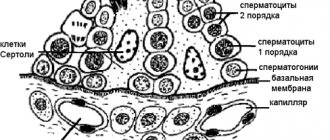
Women's health is a fragile system that depends on many internal and external factors. Penetration of a pathogenic pathogen into the body always poses a threat, but latent infections, which in women occur without pronounced symptoms, are especially dangerous.
Against the background of satisfactory health, a severe infectious and inflammatory process develops in the patient’s body. Complications of latent sexually transmitted infections in women can lead to infertility, disruption of internal organs and even death.
You can get tested for hidden infections in women in St. Petersburg at the modern Diana Medical Center on Zanevsky Prospekt.
Where do hidden infections in women come from?
The content of the article
Most infectious diseases that are asymptomatic are sexually transmitted (STDs). The main risk of such diseases is a long period of imaginary well-being. After infection, the patient has no idea about the disease and becomes an active source of further spread of pathogens.
STDs can be of different nature. They are called:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- fungi;
- parasites;
- representatives of opportunistic microflora.
Everyone has a risk of contracting an STD, but representatives of the following risk groups are especially likely to encounter such diseases:
- people who are promiscuous without barrier contraception (condoms);
- representatives of sexual minorities;
- injection drug addicts;
- immunocompromised patients;
- people living in unsanitary conditions who do not observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Even one unprotected sexual contact can lead to the development of a dangerous disease. Less commonly, infection occurs through household contact.
How do hidden infections manifest themselves in women?
The symptoms of such diseases are always vague. The patient may not notice any changes in the body until severe complications develop. In this case, preventive examinations by a gynecologist help make a diagnosis in a timely manner.
It is important to know the first symptoms of latent infections in women in order to pay attention to warning signs in time. These include:
- pathological discharge from the vagina and urethra (purulent, mucous, bloody);
- redness, irritation, rashes in the genital area;
- itching, burning, pain, discomfort in the genitals;
- pain, discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin;
- the appearance of impurities in the urine, change in the color of urine;
- menstrual irregularities;
- general weakening of the body, increased body temperature;
- frequent, painful urination;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the perineum;
- swelling of the vulva;
- infertility.
When these symptoms appear, a woman needs to make an appointment with a gynecologist and get tested for hidden infections.
Methods for diagnosing infectious diseases
Depending on the diseases diagnosed, the methods of their research may differ.
Bacteriological culture
The material to be tested is taken from the patient (blood, genital and urethral secretions) and placed in a sterile tube, after which it is inoculated onto a nutrient medium in the laboratory.
After the period required for the growth of microorganisms (from two days to several weeks), the result is obtained - the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
In this way, all bacterial and fungal pathogens can be identified. These are the causative agents of gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis and other aerobic infections.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
When a pathogen appears in the body, the body begins to fight it, forming antibodies aimed at destroying the foreign protein. They can be detected using enzyme immunoassay.
This type of research allows not only to detect the presence of the causative agent of the disease, but also to determine at what stage the disease is - acute or chronic.
PCR diagnostics>
This analysis makes it possible to determine the presence of both viral and bacterial infection in the material under study, even in a very small concentration.
Urine analysis for sexually transmitted infections
Makes it possible to determine the presence of aerobic and facultative aerobic bacteria, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas and identify the severity of the inflammatory process.
What are hidden infections in women?
The list of hidden infections in women is very long. Their asymptomatic course leads to late diagnosis and difficulties in treatment.
The following types of STDs are very dangerous:
- Chlamydia.
The causative agent of this disease is chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis). They penetrate into the cells of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. Only in 15-20% of cases does chlamydia cause any unpleasant symptoms. Most patients live with the disease without even knowing they are infected. The incubation period lasts on average 10-14 days. In women, chlamydia causes pathologies of the cervical canal, cervical erosion, dryness and discomfort in the vagina. In addition, the disease makes it difficult to conceive, plan and carry a pregnancy. Advanced chlamydia is fraught with female infertility. - Mycoplasmosis.
Mycoplasmas are the smallest free-living microorganisms. Penetrating into the body, they can exist for a long time without causing pathologies. However, with minimal weakening of the immune system, women develop severe inflammation of the pelvic organs. This can lead to damage to the tissues of the reproductive organs and the formation of adhesions in the pelvis. The result of advanced mycoplasmosis is infertility. If an infected patient still manages to become pregnant, there is a high risk of intrauterine infection, placental abruption, and spontaneous miscarriage. - Gardnerellosis.
Latent gardnerella infection in women of reproductive age is very common. Normally, the causative agent of this disease is part of the healthy microflora of the vagina in small quantities. If the number of gardnerella increases, pathologies develop. Gardnerellosis is practically asymptomatic, causing low-grade inflammation of the vaginal mucous membranes. At the same time, the woman feels slight discomfort during sexual intercourse and notes copious vaginal discharge. Leucorrhoea has a specific fishy smell. The disease is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since the infection increases the risk of fetal pathologies. - Ureaplasmosis.
Latent infection of ureaplasma in women is most often manifested by disturbances in the urination process. The patient feels itching and burning in the genitals, pain when emptying the bladder, and notes pathological discharge from the vagina. Advanced ureaplasmosis causes inflammation of the uterine appendages - the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This can lead to infertility. If pregnancy has occurred, the risk of miscarriage is very high. - Papillomavirus.
For women, this type of STI is especially dangerous, since the papilloma virus can penetrate cells, disrupting their division processes. It has been proven that it is the papillomavirus that causes a life-threatening oncological process - cervical cancer. Also, infection with this infection leads to the appearance of growths on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Such growths are called condylomas. Although the formations are benign, they must be removed in time to avoid injury, infection and malignant tissue degeneration. The incubation period of this latent infection in women reaches 1 year. During this period, the patient does not know that she is infected. - Cytomegalovirus.
This is a very dangerous disease, the asymptomatic course of which can lead to severe damage to internal organs and tissues of the central nervous system. The danger of cytomegalovirus is that it can be infected not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact and airborne droplets. The symptoms of the disease are very difficult to recognize. The patient notes general weakness, severe headaches, and frequent colds. In severe forms, the virus affects the uterus and cervix. - Herpes virus.
The small size of the virus allows it to integrate directly into the cells of the body. Thanks to this, herpes viruses can exist for a long time without symptoms. When herpes worsens, the patient develops small blistering rashes filled with clear liquid. The rash appears on the mucous membranes of the lips, eyes, nose, and genitals. Herpes is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since the virus can cause severe intrauterine pathologies of the fetus.
When answering the question of what hidden infections women have, doctors also name the following diseases:
- trichomoniasis;
- HIV;
- candidiasis (thrush);
- scabies;
- flat spots (pediculosis pubis);
- molluscum contagiosum.
Screening for hidden infections for women
A gynecologist prescribes a test for hidden infections in a woman. Blood and urine can be used as biological material, but most often a smear is taken from the genital tract. It is important to take a smear test for hidden infections in women at every visit to the gynecologist, even in the absence of complaints. A smear is taken from the genital tract and urethra.
Biological material is delivered to the laboratory, where it is examined using the following methods:
- Microscopy.
The sample is placed on a glass slide, dried and examined under a microscope. Already at this stage, the laboratory technician can detect a number of pathogens of infectious diseases. However, this method is not informative for many types of STIs. - Cultural research.
This test for hidden infections in women involves plating a sample on a nutrient medium. After 1-2 weeks of infection, colonies of pathogens grow on the nutrient medium. They can be identified and examined. Bacterial culture also allows you to test the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics. - ELISA method.
Enzyme immunoassay is carried out using an antigen-antibody reaction. They try to detect specific antibodies to various STD pathogens in the patient’s blood. They are released in the body in response to infection. The technique is relatively sensitive, but can sometimes give false results. For example, if the patient has recently been infected, the immune system may not yet produce antibodies. Conversely, after the death of bacteria and viruses, antibodies to them can remain in the blood for some time. - PCR diagnostics.
The polymerase chain reaction method is considered the most accurate blood test for hidden infections in women. After the DNA of the pathogen is detected, the genetic material is subjected to repeated replication. The result is an extended DNA chain that is easy to identify. The accuracy of this study reaches 100%. However, such an analysis requires special diagnostic equipment and highly qualified doctors.
It is mandatory for women to undergo a comprehensive examination for hidden infections when planning a pregnancy and when registering with an antenatal clinic.
STI test
Testing for sexually transmitted infections is the main diagnostic method in gynecology. These studies are completely safe and painless for a woman and very informative for a doctor.
What tests should be taken for sexually transmitted infections:
- Microflora smear
- Bacterial culture with selection of antibiotics
- Florocenosis
- PCR analysis 12-18
- NASBA RNA Assays
- Blood test ELISA and PCR.
How to prepare properly
- 1-2 days before visiting the doctor, refrain from intimacy;
- Before taking an STI test from the urethra, it is recommended not to urinate for 2 hours.
- On the eve of going to the clinic, it is recommended to carry out a provocation. The simplest and most reliable method is considered to be food (alcohol, salty, spicy).
- If possible, it is best for girls to get tested for STDs and any sexually transmitted infections before or immediately after their period.
Places (points) of capture. Women (F), virgin girls (D) and men (M) can get tested for sexually transmitted infections from the following places:
| Take points | M | AND | D |
| "C" - cervix | — | + | — |
| "V" - vagina | — | + | + |
| "U" - urethra | + | + | + |
| "R" - rectum | + | + | + |
| "O" - oropharynx | — | + | + |
Diagnostics
How much does it cost to get tested for sexually transmitted infections, ₽
| List of studies | Price |
| STI smear | 550 |
| Gram microscopy | 750 |
| Sowing on flora and a/h | 1 750 |
| PCR tests | 450 |
| Florocenosis, from | 3 000 |
| NASBA | 1 300 |
| Blood test for syphilis | 750 |
| Test for HIV (AIDS) | 750 |
| Blood test hepatitis B, C | 750 |
| Rapid blood tests | 750 |
| Taking blood from a vein | 450 |
| Taking material | 450 |
home
Where to get tested for STIs
We invite women and men to get tested for STIs in our paid clinic in Moscow. During the consultation, the doctor will listen to your complaints and, based on them, recommend the optimal list of studies. Once the analysis result is ready, we can offer to draw up an individual treatment regimen for sexually transmitted infections. Remember that timely contacting a doctor when symptoms of ill health appear will allow you to solve the problem faster and with less loss of time and effort!
Treatment of hidden infections in women
Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor, based on the results of the therapy. Each type of pathogen is sensitive to certain drugs. The treatment regimen for most patients includes the following medications:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral agents;
- antifungal drugs;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- restoratives.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the patient must adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and be careful about genital hygiene. Pregnancy should be postponed until complete recovery. The optimal method of contraception at this time is condoms. Modern medical capabilities make it possible to get rid of most pathogens and return to a full life.
To get tested for hidden infections in St. Petersburg, a woman needs to make an appointment with a medical gynecologist. During the appointment, the doctor will collect biological material for analysis in a comfortable environment for the patient. Laboratory diagnostic results will be ready within a few days, and they will be interpreted by an STI specialist.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What infections can be detected using PCR diagnostics?
Taking into account the entire spectrum of pathogens, PCR diagnostics in modern medicine is used in urology, gynecology, dermatovenereology, gastroenterology and many other branches of medicine.
Currently, PCR diagnostics of latent infections allows us to identify the following diseases:
1) HIV infection
2) Viral hepatitis A, B, C, G, E
3) Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus DNA - EBV)
4) Cytomegalovirus infection
5) Herpetic infection
6) STIs (sexually transmitted infections) – ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, candidiasis (Thrush)
7) Tuberculosis


9) Borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis
10) Listeriosis
11) Candidiasis
12) Helicobacter pylori infection
and many others