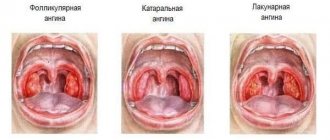
What is a cold
The concept of a cold includes a group of respiratory infections that occur against the background of hypothermia. Most of them are accompanied by inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, which manifests itself in unpleasant symptoms (runny nose, cough). At the same time, viral and bacterial diseases proceed almost identically. The exact cause of a cold can only be determined through laboratory tests.
Clinical signs
- The result of irritation of the mucous membranes is sneezing, runny nose, cough.
- 12 hours after infection, signs of intoxication appear - headache, weakness, drowsiness.
- An increase in body temperature to 38.5°C is the body’s immune response to the introduction of infectious agents.
- Aches in muscles and joints - harmful microorganisms, moving with the blood and lymph flow, irritate pain receptors.
A viral cold develops in 3-5 days. Symptoms are acute. In 80% of cases, the mucous membrane of the eye is irritated. The temperature rises to 37.0-37.8°C and subsides on the 3rd day after the start of therapy. If treatment is started on the 1st or 2nd day, the risk of complications of a viral cold is minimal. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets.
A bacterial infection is characterized by an asymptomatic incubation period of up to two weeks. The disease develops locally, affecting a specific area - ear, throat, bronchi, etc. It is severe, with a temperature of up to 39.5°C. In half of the cases it develops as a complication of a viral cold. More often diagnosed are otitis media, tonsillitis, meningitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Regardless of the nature of the pathogenic agent (bacteria or virus), the infection must be treated, since a cold in a nursing woman goes away on its own in only 12% of cases. The protective function of the body after childbirth is weakened; without therapy, the disease will drag on for 2-3 weeks, the inflammation will “descend” to the lower respiratory tract.
Drug treatment
Safe treatment of colds during lactation using medications
Colds during lactation should be treated with medications that do not contain any harmful components:
- To eliminate a severe cough, you should take expectorants. During lactation, a good choice would be to take Lazolvan or Ambroxol. To make breathing easier, products such as Chest Elixir or Doctor Mom are recommended, that is, those syrups that contain medicinal herbs.
- Severe congestion in the nasal sinuses is eliminated with the help of vasoconstrictor drops such as Tizin, Farmazolin or Nazivin. Abuse of such drugs can lead to complications in the form of atrophic rhinitis, so you should not get carried away with these drugs. They can be used for no more than seven days.
- During a sore throat, you should use products that have a local effect and are antimicrobial in nature. These include Hexoral, Iodinol and Strepsils. As for the mucous membrane, it can be smeared with Lugol.
- Herbal oil drops have an excellent anti-inflammatory effect on the sinus area.
- Acute respiratory infections caused by infections of viral origin can be eliminated with the help of Grippferon. This drug has no contraindications to treatment during lactation. In addition, the body tolerates it well.
- During a cold, the nasal mucosa must be additionally moisturized. This can be achieved using sea salt drops and sprays.
It should be remembered that during lactation it is strictly forbidden to use drugs containing bromhexine.
Traditional methods of treatment
The best folk recipes
Since ancient times, treatment of acute respiratory infections using traditional medicine recipes has been not only safe, but also had a fairly good effect:
- The use of inhalations is as safe as possible for the mother’s body. They can be made using herbs (for example, steaming eucalyptus leaves). Using steam from boiled potatoes gives excellent results. To facilitate the process, you can purchase a special drug - a nebulizer. It will also be useful to the mother when the child grows up to treat colds. Inhalations with its help are done using Borjomi, Ambrobene (solution) or saline. The doctor must decide which remedy will be most effective for acute respiratory infections. By doing inhalations three to four times a day, after just two days you can see how your health has improved.
- With the help of raspberry tea, you can easily soften the general condition during such a disease.
- To help a sore throat, use a gargling solution that contains water (1 glass) and apple cider vinegar (1 tablespoon). Procedures with its help should be carried out at least once every hour.
- To make breathing through the nose easier, use the following recipe: heat a quarter cup of sunflower oil in a water bath and mix with garlic and onion, previously crushed into fine crumbs. This mixture is infused for an hour to two, and the resulting composition is lubricated inside the nasal sinuses.
- Linden tea with the addition of honey has an excellent effect. The concentration of such a drink should not be too strong; it should be slightly darker than water. You should not be overzealous with the use of linden; its excessive use is fraught with the appearance of pain in the heart area.
- For acute respiratory infections, the use of onions and garlic is very useful. They can be pre-chopped and mixed with honey. To get rid of colds, one or two teaspoons of this composition are eaten after each meal. However, we should not forget that these odorous products can provoke allergies in an infant. Therefore, before using such a drug, you should consult your doctor.
Useful video - Colds during lactation.
Vodka with pepper for colds, what effect it gives, can the flu be treated with it?
Many nursing mothers are concerned about the question: is it possible to steam their feet if they have a cold during lactation? Yes, such procedures are indicated during acute respiratory infections. It is very important to follow one rule: the water temperature should not be more than 40 degrees, and the process itself should last approximately 8-12 minutes. This method is quite effective. And to make its effect even better, you can add a small amount of mustard to the water. Immediately after the procedure, you must put on cotton socks.
Actions at temperature
Effective and safe methods for normalizing body temperature during lactation
If the temperature during lactation rises to 38.5 degrees, the nursing mother can take paracetamol (one tablet) or drugs based on it. This medicine is the safest for reducing high fever. This drug perfectly eliminates pain in the head and muscles that accompany acute respiratory infections.
But before doing this, you should consult your doctor to avoid unwanted effects. As for drugs like Theraflu, Fervex or Coldrex, it is better not to take them on your own, since it has not yet been established how they can affect the baby’s body.
At temperatures below 38 degrees, you can use a wipe based on a weak vinegar solution. Vodka in equal proportions with water is also suitable for this purpose. After the whole body has been rubbed, you need to cover yourself with a light sheet. These steps should be repeated every 15-25 minutes. If the thermometer shows a temperature of 37.5, then there is no need to bring it down.
But when the temperature is very high (more than 38 - 38.5 degrees), the milk may well “burn out” and lactation will stop.
One important rule during acute respiratory infections is that if a prolonged increase in body temperature occurs, you should never self-medicate. You should immediately seek the help of a general practitioner, and do not forget to mention breastfeeding at your appointment. A specialist can prescribe antibiotics and other drugs against this viral infection that will not harm the baby’s health.
Can I breastfeed if I have a cold?
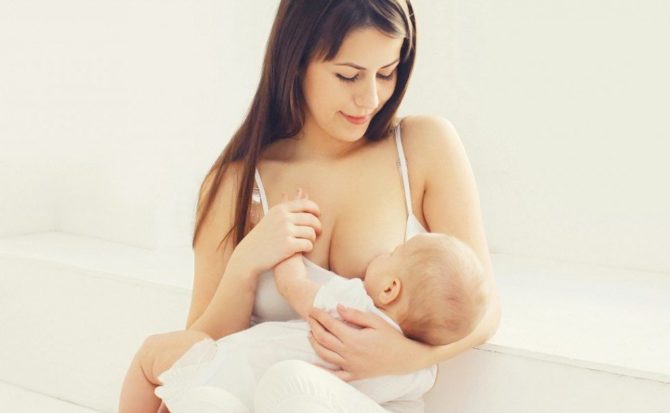

A cold is not a contraindication for breastfeeding. Even before the first symptoms of the disease appear, the mother’s body produces protective antibodies aimed at fighting the infection. These immunoglobulins pass into breast milk and are passed on to the baby, forming passive immunity.
Breast milk does not lose its quality even when the temperature of a nursing mother rises. Boiling expressed milk does not make sense, since when heated it loses its beneficial properties.
The protective effect of milk is the main argument in favor of continuing breastfeeding during colds. According to Rospotrebnadzor [1] and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention [2], influenza-like viruses do not penetrate milk, so the mother is only advised to increase the frequency of breastfeeding to immunize her body.
Temporary suspension of breastfeeding is recommended only when taking antibiotics (tetracyclines, aminoglycosides) and sulfonamides. These drugs are toxic and harmful to the child.
What are the dangers of a cold for a nursing mother?

A woman can become ill with acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory infections at the slightest hypothermia or the slightest contact with a carrier of the virus. When the mother feels the first symptoms of the disease (fever, lethargy, cough, sore throat), the child has already become infected. Within 1-3 days of the incubation period, the baby has already become acquainted with foreign bacteria and his body is fighting them. With viruses, he also receives antibodies to fight them. If the protective function of the baby’s body works well, then he will not feel the same symptoms as his mother. In addition, the developed immunity after suffering from the disease will allow you to protect yourself from infection in subsequent times or reduce the risk of complications. A cold that a mother develops while breastfeeding, if treated incompletely or untimely, can lead to complications in the form of bronchitis, pneumonia, and other ENT infections.
Can a baby catch a cold from its mother?

In 90% of cases, the cause of a cold in a nursing mother is a virus that is transmitted by airborne droplets. Therefore, preventing a baby from becoming infected is necessary and includes a standard algorithm of actions.
Preventive measures
To avoid infecting the child, a sick mother should take precautions:
- in the room where the baby is located, wear a three-layer gauze bandage;
- exclude physical contact with the baby - kissing, hugging, sleeping together. Move the crib 2-3 meters away from the mother’s sleeping place. It is better to sleep in the next room, and leave the child with a healthy family member who will call the mother at night for feeding;
- Before feeding, apply oxolinic ointment under the baby’s nose (rub with your fingertip);
- ventilate the room every hour (take the baby out);
- Carry out wet cleaning with disinfectant 3 times a day;
- maintain the room temperature within 18-23°C;
- if possible, quartz the room in the morning and evening for 20 minutes;
- light an aroma lamp with essential oils in the room (you can do it once a day, before going to bed);
- sterilize bottles and hygiene items, as well as toys and pacifiers daily;
- Maintain personal hygiene - wash your hands every hour;
- increase the frequency of your baby's breastfeeding.
Medications are not used for prophylactic purposes in infancy. The doctor prescribes them only when signs of acute respiratory infections appear in the baby.
When a nursing mother has a cold, her breast milk is an immunomodulatory agent for the baby.
Cold medications for babies
- Nasal drops – Derinat (immunomodulatory effect).
- Grippferon, Viferon (based on interferon - an antiviral protein).
- Sea water in drops - for rinsing the nose with a runny nose.
- Paracetamol in suppositories or suspension is an antipyretic, at a temperature of 38°C.
Medicines are prescribed by a doctor after diagnosing the symptoms. Drug treatment of an infant under one year of age is justified only if there are clear signs of intoxication and a temperature of 38°C or more. In other cases, it is better to give the child the opportunity to cope with the infection on his own. Breastfeeding is the main assistant in this matter.
What is the risk for the baby?
It is impossible to provide one hundred percent protection for a child from colds. But you can reduce the risks if you follow simple recommendations:
- Don't give up breastfeeding. With milk, the baby gains immunity, which will help him fight viral infections.
- You should wear a protective mask that will prevent viruses from spreading through the air. It needs to be changed after two hours.
- You should wash your hands regularly. Many viruses accumulate on your hands, so before touching your child, you need to wash them with soap.
If you isolate your baby from the breast if you have a cold during breastfeeding, your baby will get sick much longer. It is very dangerous to deprive premature babies of mother's milk, since their immunity is poorly developed and serious complications can develop.
Some drugs are very dangerous for young children:
- Analgin can cause anaphylactic shock.
- Phenobarbital disrupts the functioning of the kidneys, liver, and nervous system.
- Codeine causes constipation.
- Tetracycline and sulfonamide cause bleeding.
- Macrolides are dangerous due to dysbacteriosis.
Treatment of colds during breastfeeding
For a nursing mother, the choice of medications is limited. Medicines based on aspirin and analgin are excluded, as well as complex symptomatic powders - Fervex, Theraflu, Coldrex, etc. It is better to prefer treatment with traditional methods and maintain immunity. A temperature of up to 38°C indicates that the body is producing antibodies against infection, so it is not recommended to fight hyperthermia.
If the thermometer rises above 38°, it means that the body cannot cope with intoxication. It is necessary to call a doctor to prescribe therapy.
Medications
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- antiviral - Tamiflu (with caution);
- nasal rinsing - Aqua Maris, Dolphin, saline solution;
- for a runny nose - Nazivin; Oxymetazoline (no more than 3-5 days);
- antihistamines, to relieve edema - Semprex, Fexofenadine;
- for cough – Ambroxol, ACC, Mucaltin;
- gargling - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, chamomile decoction.
Expert opinion
Sokolova L. S.
Pediatrician of the highest category
Antibiotics in the treatment of a mother with a cold are used only when a bacterial infection is diagnosed, strictly as prescribed by a doctor. If the need for antibacterial therapy is established, in 70% of cases it is recommended to suspend breastfeeding. If the disease is viral, antibiotics are useless for the mother and toxic for the baby.
To be treated or not to be treated?
Many mothers are not prepared for the appearance of a cold, so they find themselves in a difficult situation when the virus enters the body and begins to multiply. Therapy in the event of a disease occurring during breastfeeding requires the use of safe, fast-acting and effective medications. When breastfeeding, many drugs traditionally used for most acute respiratory viral infections are not used due to the possibility of drugs entering the child’s body through breast milk with the development of various side effects. However, there is also a fairly large group of drugs approved for use both during pregnancy and lactation. They are selected by a general practitioner during a face-to-face appointment after the necessary examination and examination.
Traditional methods of treatment

A nursing mother is recommended to rest in bed and drink plenty of fluids, at least 1.5 liters per day (water, warm tea, compote).
It is better to invite an assistant to care for the baby (grandmother, sister) to avoid overwork and prevent infection of the baby. Overwork and lack of sleep waste the mother's body's defenses, creating a deficiency of immunity in the fight against colds. Free time from feeding should be devoted to treatment using traditional medicine recipes.
Recommended folk remedies
- For high fever and headache - a cold compress on the forehead, wiping with a weak solution of vinegar.
- Warming foot baths if the temperature is normal. Add a teaspoon of mustard powder to water (5 liters). After the procedure, dry your feet with a terry towel and put on warm socks.
- Linden decoction (pour boiling water over linden flowers, leave for 20 minutes) take 200 ml in the morning and evening.
- Warm tea with raspberries - every 4 hours.
- Viburnum compote (a glass 2 times a day) or viburnum jam.
- Freshly squeezed carrot juice (if the baby is not allergic) – a glass in the morning.
- Dandelion infusion – brew 2 tablespoons of roots with 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes. Take a glass in the morning and at lunch.
- For cough - warm milk with honey and butter.
- For a runny nose - moisten a cotton ball with propolis or aloe tincture and insert it into the nose for 15 minutes. Repeat every 3 hours. You can instill aloe juice 2 drops into each nostril 3 times a day.
The famous pediatrician E. O. Komarovsky claims that folk recipes do not act on the causative virus. But they are recommended to support the immune system and eliminate local symptoms of inflammation of the mucous membranes.
General recommendations for treating colds in a nursing mother

If it happens that a nursing woman feels the symptoms of a cold (cough, runny nose, sore throat, fever, weakness, dizziness), the first thing to do is consult a pediatrician. The main thing that treatment should be aimed at is the safety of the baby. All medications, their dosage, and duration of administration must be chosen by the doctor based on the degree of development of the disease in the mother and the possible negative impact on the baby. To prevent a cold during lactation from causing complications for the mother and child, every effort must be made to combat the disease.
General recommendations for the treatment of colds during lactation:
- Mandatory consultation with a pediatrician;
- Continue breastfeeding your baby until you take strong medications.
- Do not treat the baby. He will receive all acceptable medications from his mother along with breast milk.
- You should not self-medicate, especially at temperatures above 38.5. The type of medicine and dosage must be prescribed by a doctor. Exceeding the established norm or non-compliance with the rules for taking the drug can negatively affect the condition of the mother and child.
- Do not use medications to lower the temperature below 38 degrees.
- If the newborn is prone to drug allergies, the woman should also learn about the need to take antihistamines.
- To reduce the concentration of viruses in the air, a sick mother needs to wear a gauze bandage, changing it every 2-3 hours. It is also important to ventilate the room and wash your hands before contact with the child.
- Avoid dry airways. You need to often be in the fresh air, ventilate the room and put special drops into your nose that moisturize the mucous membrane.
Drinking for a cold
Drinking plenty of warm fluids is the simplest, cheapest and safest way to combat fever, as well as other symptoms of a cold. The fact is that those toxins that settle in the body during illness negatively affect overall well-being. Drinking fluids helps you get rid of harmful substances faster, reduce your temperature and improve your general condition. Therefore, during lactation, warm water, tea, compote, and fruit juice are good for colds. If the child does not have allergies, then you can add honey, ginger, and lemon slices.
Cold therapy
Colds during breastfeeding require adequate treatment, including the safest and most effective medications.
– Typically, the treatment regimen for colds during breastfeeding includes washing the nasal mucosa with solutions of sea salt or regular saline, which have a disinfecting and drying effect, as well as physically “washing out” viruses from the nasal passages.
– In addition, if there is severe swelling of the nasal mucosa, it is possible to prescribe vasoconstrictors and antiallergic drugs, but their frequent use is not recommended during lactation. This can lead to negative effects on the baby's body through breast milk. For coughs, expectorants and mucolytic herbal preparations or preparations that do not contain potent and active drugs (codeine, bromhexine, etc.) and help to liquefy and remove mucus from the respiratory tract are often prescribed.
– Increased body temperature (over 38.3-38.5°C) is reduced by antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen.
– In addition, a cold during breastfeeding requires the use of a wide group of auxiliary methods, including frequent ventilation in the room where the sick woman is, humidifying the air and drinking warm drinks.