Pelvic organs in women - list
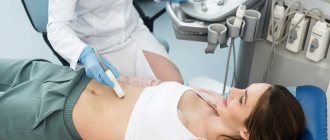
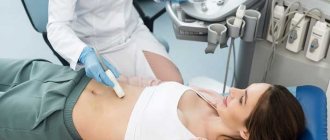
Women usually receive an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs from a gynecologist. Using an ultrasound machine, the doctor determines the condition of tissues in:
- Bladder;
- uterus;
- cervix;
- fallopian tubes;
- ovaries.
It is not only patients who receive ultrasound referrals. Women expecting babies are sent for ultrasound three times during pregnancy. Each trimester has its own control week, during which the doctor is obliged to assess the state of fetal development.
Advantages of the diagnostic method
The main advantage of ultrasound diagnostics of diseases of the pelvic organs is the high accuracy of the study, which allows you to determine the nature, size and location of tumors. Ultrasound also has a lower cost than computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
The method can be used when taking a biopsy or material for in vitro fertilization, as well as to examine the developing fetus during pregnancy. Ultrasound is absolutely safe and does not cause side effects.
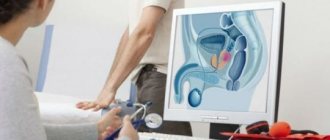
Diagnosis of pathologies of the pelvic organs can be supplemented by tomography (to determine the nature of tumors), as well as PSA analysis (PSA) and biopsy if prostate cancer is suspected in men.
Features of ultrasound examination
Using an ultrasound machine, a specialist can only assess the condition of non-hollow organs, that is, those that are not empty inside. In this connection, it is necessary to provide additional consultation to patients regarding the condition of the bladder. So, if you want to examine its walls for chronic cystitis or other pathology, you need to fulfill a mandatory condition - to carry out a full urinary diagnosis, which is not very convenient for those who suffer from incontinence. In this case, urine will act as a reflection of ultrasonic rays, and the bladder will be examined.
If other organs are to be examined, the bladder should be empty so as not to block the view.
Indications for ultrasound
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs of the female reproductive system is performed in a variety of cases, since it is currently one of the most convenient and accurate methods for studying the internal organs of a woman. Ultrasound is effective as a monitoring technique, as it allows to identify diseases in the preclinical stage. The optimal timing for routine ultrasound examinations for women of childbearing age is annually. In case of detection of various diseases, pathologies and anomalies of the uterus and uterine walls, ultrasound is performed more often.
You can find out the contact details of Moscow clinics and the cost of transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs on our resource.
What does a pelvic ultrasound show?
Using ultrasound you can determine:
- The position of the organ in the pelvic cavity: is it displaced?
- What are the dimensions of the organ?
- Is it properly developed? Are there any anomalies in shape or size?
- Myometrial structure.
- Endometrial thickness.
- Presence of scar tissue.
- Dinu and width of the cervix.
- Condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Presence of fertilized egg.
- The presence and absence of fetal development pathologies.
The simplicity and safety of this type of research has deservedly made this method one of the most popular.
Why should you do an ultrasound?
Ultrasound is an indispensable diagnostic method in obstetrics and gynecology. A healthy woman is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan at least once a year. During pregnancy, ultrasound is prescribed at least 3-4 times.
- Pelvic ultrasound helps identify various diseases in the field of gynecology;
- Ultrasound helps monitor women's health during puberty;
- Ultrasound allows us to identify the condition of the uterus, its location relative to other pelvic organs, the structure of the myometrium and endometrium, and identify vascular abnormalities;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed when selecting contraceptives;
- Ultrasound detects pregnancy in the early stages;
- Ultrasound makes it possible to monitor the condition and development of the fetus;
- Ultrasound allows you to find out the sex of the unborn baby in advance;
- Ultrasound helps to identify existing problems associated with pregnancy in a timely manner.
Are there any restrictions for ultrasound diagnostics?
When a woman suffers from pain during menstruation, or her cycle is unstable for a long time, the gynecologist gives a referral for an ultrasound. To obtain information about the condition of the fallopian tubes and follicles, it is important to conduct the examination on days 5-7 from the first day of the cycle, that is, from the day of menstrual bleeding.
But if you want to find out the cause of problems with conception, research must be carried out at least three times:
- from the 8th to the 10th day from the beginning of menstruation;
- from the 14th to the 16th day from the first day of bleeding;
- from the 22nd to the 24th day of the cycle.
For pregnant women, there are also certain time frames for assessing the condition of the fetus. Conducting an ultrasound examination at other times is not considered informative. Each trimester of pregnancy has its own weeks for diagnosis:
- from 10th to 14th week;
- from the 20th to the 24th week;
- from the 30th to the 34th week.
If there are suspicions of pathologies, the number of studies can be increased to determine the condition of the fetus over time.
In what phase of the menstrual cycle should a pelvic ultrasound be performed?
On what day of the cycle an ultrasound should be done is indicated by the doctor. The exact date depends on the expected diagnosis and the woman’s general well-being. For example, an emergency examination is carried out in case of bleeding or pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, the day of the menstrual cycle does not matter.
Reference! Most often, doctors recommend performing an ultrasound examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle.
If there is a suspicion of uterine fibroids, then the manipulation is carried out immediately after the end of menstruation. To diagnose endometriosis, an ultrasound is performed before the onset of menstruation. When planning a pregnancy, the patient undergoes research in the first and second phases of the cycle.
During pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics are performed to confirm the fact of pregnancy and in each trimester. At 11-12 weeks, the doctor conducts the first fetal screening, and at 18-22 weeks - a second screening and 32-34 weeks - an ultrasound of the fetus. Every study is important because... allows you to identify a certain pathology of the fetus at each stage.
What does a pregnant ultrasound tell you?
Pregnant women can refuse a routine examination with an ultrasound machine, but this is not recommended, because this painless type of diagnosis allows you to find out about very important changes in the child’s body, in particular, whether he has Down syndrome. According to the regulations of conduct, a medical worker is obliged to notify future parents about a serious genetic disease that entails disability from birth. In this case, the woman is given a complete plan of action if she decides to terminate the pregnancy. The antenatal clinic is obliged to provide all necessary medical care, regardless of the long period of time.
If there is a risk of miscarriage, the gynecologist will monitor the condition of the cervical canal, the length of the cervix and the location of the placenta.
Additionally, ultrasound can easily detect oligohydramnios, as well as:
- quality of blood flow, its intensity;
- location of the umbilical cord for entanglement;
- fetal heart rate;
- fetal presentation.
With the help of a modern three-dimensional imaging system, the expectant mother can see the face of her unborn child, which always cheers up a pregnant woman.
Advantages of transabdominal ultrasound
Transabdominal ultrasound is often the primary diagnostic method along with laboratory tests. With its help, you can study the functions of the abdominal organs, pelvis, and retroperitoneal space. Its advantages include:
- non-invasiveness and minimal intervention - the diagnostic method does not require violating the integrity of tissues or introducing a sensor;
- no restrictions;
- safety for the fetus at any stage when studying pregnant patients;
- the ability to assess the work and condition of several organs at once;
- accuracy and information content - both large and small tumors will be noticeable as a result of the study;
- painless, can be used in children of any age;
- efficiency - the procedure takes no more than 15-20 minutes, the patient receives the results immediately;
- minimum list of contraindications.
The disadvantages of the procedure include a decrease in its information content in patients with a large layer of subcutaneous fat, as well as those who suffer from adhesive disease in the gastrointestinal tract or pelvic organs. A drawback is also the lower accuracy of the results if the doctor’s simple recommendations are not followed.
Ultrasound methods
There are two types of sensors that are used for research. One is called transabdominal. It is enough for a specialist to apply it tightly to the body so that the ultrasound waves begin to show the internal organs.
Another type of sensor is called transvaginal. Based on the name, it is easy to guess that it is inserted into the vagina to look at the organs from a different angle. To conduct such a study, the doctor places a condom on the sensor to ensure sterility. Budgetary institutions often ask patients to buy it for themselves if the deposited funds are not enough to provide the office with consumables.
In addition, there are stationary and mobile devices. Ultrasound diagnostic rooms are equipped with stationary ones. The doctor can take the mobile device with him to visit patients at home. Modern ambulances are also equipped with such equipment.
Research methods
There are three types of ultrasound that are used to examine the pelvis: transabdominal, transrectal and transvaginal.
When using a transabdominal examination, the device's sensor comes into contact with the surface of the anterior abdominal wall. The method is used to diagnose large uterine fibroids and other problems of the genitourinary system.
When using transrectal ultrasound, a transducer with an elongated shape is inserted into the rectum. This type of ultrasound diagnostics is used when it is necessary to examine the male genital organs - the prostate and seminal vesicles.
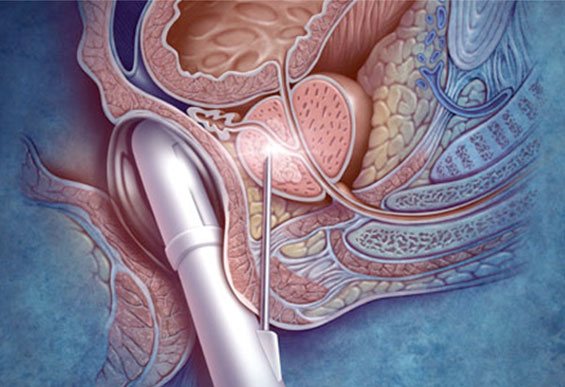
Transvaginal ultrasound uses an elongated probe (wider than transrectal ultrasound) that is inserted into the woman's vagina.
The method is used to:
- identify the problem of infertility;
- examine the uterine cavity and its contents;
- control of the position of the instruments during taking a biopsy from the uterus.
The method is used to examine women who have large fat deposits on the abdomen, as they make it difficult to obtain clear images of the pelvic organs.
With any type of pelvic ultrasound, the image is obtained thanks to sound waves reflected from tissues and structures and converted into a picture on a computer monitor. They can be saved in image or video format.
How the study is conducted and what you need to know
Carrying out diagnostics, as a rule, does not require special preparation, with the exception of the condition of the bladder, which the doctor will warn you about in advance. When a patient enters the office, she should remember that it is advisable to turn off her mobile phone during the examination.
After presenting her documents to the doctor, the woman can go to the couch. If the examination is carried out with a transabdominal sensor, it is not necessary to undress completely - you just need to lower your pants or lift your dress so that the lower abdomen is free from clothing.
When examined with a transvaginal probe, the patient must completely remove pants, tights and underwear. Her position on the couch is lying on her back with her knees bent.
It should be noted that neither one nor the other sensor causes any discomfort. The procedure is completely painless.
How to prepare
- Transabdominal.
The evening before the ultrasound, you need to do a cleansing enema. The examination is performed with a full bladder, so 3-4 hours before the procedure you should not urinate, 1 hour before the examination you need to drink 1 liter of still water. - Transvaginally.
Before the study, you must empty your bladder.
Preparation for different types of examination is fundamentally different, so you need to carefully listen to your doctor’s recommendations. You can call the contact number at any time and get additional information.
How is a transabdominal examination performed?
An ultrasound examination is carried out in an ultrasound room, which has all the necessary equipment for modern, high-precision diagnostics. First, the doctor will ask the patient to free the upper body from clothing, then ask him to lie down on the couch and relax.
The anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is lubricated with a special gel, which enhances the conductivity of ultrasonic waves. Next, using a sensor, the specialist slowly moves it along the surface of the abdomen, examining the pelvic organs. During diagnosis, the patient does not feel any pain or discomfort. The procedure is safe for children and the elderly because it does not cause complications and does not cause radiation exposure. The examination takes on average 15 – 25 minutes. After this, the patient can return home and do their usual activities.
Ultrasound of fetoplacental blood flow
In obstetrics, this type of ultrasound diagnostics is used, such as ultrasound of the fetoplacental blood flow, which allows timely detection of disturbances in the blood supply to the fetus in the prenatal period. The method is a triplex ultrasound scan, that is, when it is carried out, a specialist using Doppler ultrasound receives color images of the blood flow.
When carrying out such diagnostics, special attention is paid to assessing the blood flow in the umbilical cord, the middle cerebral artery of the fetus and the arteries of the uterus of the expectant mother. It is worth noting that one of the most common causes of the pathological course of pregnancy is precisely the disruption of the blood supply to the fetus, and the diagnostic method under consideration makes it possible to detect it in a timely manner and take appropriate measures.
A planned ultrasound of the fetoplacental blood flow is prescribed starting from the twenty-fourth week. At any stage, the study can be carried out in the presence of such indications as severe gestosis, premature maturation of the placenta, the presence of general somatic pathologies in the expectant mother, Rh-conflict pregnancy, the presence of congenital defects in the fetus and other features of the course of pregnancy.
Types of ultrasound in gynecology
Ultrasound examination is of utmost importance for women's health. With its help in gynecology, the anatomical structure of the female genital organs, pathological changes in them, and functional characteristics are determined.
What types of ultrasound are there for women’s diseases? In gynecology, ultrasound with different sensors is used. Depending on this, the following types of gynecological ultrasound are distinguished:
- Transabdominal (percutaneous) examination. This is a popular type of examination that can be performed on women at any stage of the menstrual cycle. With its help, you can determine the position, size, structure of the uterus, cervix, tubes, ovaries, appendages, the size of the follicles in the ovaries, and the presence of formations in them. Before this type of ultrasound, a non-pregnant woman needs to drink 0.5-1 liters of water so that the bladder is full before the examination.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. It is carried out using a vaginal sensor. This type of diagnosis provides clearer characteristics of the female reproductive organs. There is no need to wait for the bladder to fill for the test, so it can be performed even in emergency cases. Currently, transvaginal ultrasound is the most popular method for diagnosing pathologies of the female reproductive system.
- Transrectal (rectal) examination. This type of ultrasound provides the same clear information as an ultrasound with a vaginal probe. It is carried out only in cases where it is not possible to conduct a vaginal ultrasound examination, and for virgins.
Which of these types of ultrasound should be performed in a particular case is decided by the obstetrician-gynecologist who prescribes it. An ultrasound examination for suspected pathological processes in the genital organs in non-pregnant women provides preliminary information that allows the doctor to make a decision about prescribing more informative types of diagnostics. For non-pregnant women, additional information can be provided by MRI, biopsy, and endoscopy.
Ultrasound of the pelvis Ultrasound of the prostate Ultrasound of the kidneys Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta Ultrasound of the vessels of the upper extremities Ultrasound of the vessels of the heart Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck Ultrasound of the hip joint Ultrasound of the knee joint Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity Ultrasound of the gallbladder Ultrasound of the thyroid gland Ultrasound of the bladder Ultrasound of the spleen Ultrasound of the pancreas Ultrasound of the liver Ultrasound of the mammary glands Ultrasound of the lumbosacral spine Ultrasound of the cervical spine Ultrasound of the salivary gland Ultrasound of the brain Ultrasound of the ankle joint Ultrasound of the shoulder joint Ultrasound of the soft tissues of the neck Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages Ultrasound of the eyes Ultrasound of the wrist joint Ultrasound of the elbow joint Ultrasound of the stomach Ultrasound of the soft tissues facial tissues Ultrasound of the maxillary sinuses Ultrasound of the large intestine Ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses Ultrasound of the urinary tract Ultrasound of the vessels of the spermatic cord Ultrasound of the parotid glands Ultrasound of the vessels of the penis Ultrasound in the third trimester Ultrasound of the renal arteries Ultrasound of the scrotal organs Ultrasound of the ovaries Ultrasound of the adrenal glands Ultrasound in the second trimester Ultrasound in the first trimester Ultrasound bladder with residual urine Ultrasound of the lymph nodes Folliculometry Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space Doppler ultrasound of the uteroplacental blood flow Ultrasound of the cervix Ultrasound of the fallopian tubes Ultrasound of the vessels of the eyeball Ultrasound of the abdominal portion of the inferior vena cava 3D ultrasound during pregnancy 4D ultrasound during pregnancy Ultrasound of the pleural cavity Ultrasound of the thymus Ultrasound of the genital member Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function Ultrasound of the hand Ultrasound of the temporomandibular joints Ultrasound of peripheral nerves Ultrasound of the lumbar spine Ultrasound of the pericardium Ultrasound of the foot