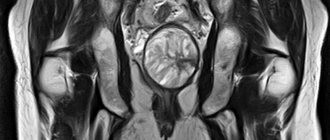
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an effective non-invasive (performed without surgery) diagnostic method that allows a detailed examination of the organs and tissues of the pelvis.
Based on MRI results, the doctor can determine the presence, cause, and extent of spread of diseases of the internal pelvic organs at different stages of development, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
For women, MRI is prescribed to examine the uterus, vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder and all tissues of the pelvis.
In men, the seminal vesicles, vas deferens, prostate gland, bladder, ureters and rectum are examined.
MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast is performed strictly according to indications, most often to detect oncology and various infectious diseases. It is in these pathologies that the “sick” areas of tissue are especially intensively nourished through an extensive network of small blood vessels, which is clearly visible in MRI images with contrast.
Indications
An MRI of the pelvic organs is prescribed by an oncologist, gynecologist, surgeon, urologist or proctologist. There are no age restrictions for this study.
Main general indications:
- diagnosis of cancer, detection of metastases;
- injuries and developmental abnormalities;
- pain for a long time in the sacrum and pelvis;
- cyst rupture or suspicion of this condition, other acute surgical pathologies;
- diseases of the urinary system (stones and sand in the ureters, etc.);
- infertility;
- pathological processes in the rectum.
- damage, defects and pain in the hip.
Indications for MRI in women:
- vaginal bleeding for no specific reason;
- endometriosis;
- inflammatory diseases (adnexitis, endometritis);
For men:
- inflammatory diseases (prostatitis, vesiculitis)
- neoplasms in the scrotum in men;
Also, MRI of the pelvic organs is prescribed to clarify the results of other diagnostic examinations, in the preoperative period and to monitor the patient’s condition after surgical treatment.
How to prepare for an MRI of the abdomen and retroperitoneum
Preparatory activities begin two days before the scan. You need to reconsider your diet and remove from it foods that lead to fermentation processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Eliminate gas-forming foods. This includes fresh bread and flour products, beans, peas, chickpeas, fresh vegetables, dairy products and soda. If you are prone to constipation, take a laxative the day before coming to the clinic. You can find out the required drug from your doctor or the operators of the medical center where you will come for the study. If it is scheduled for the morning, limit yourself to a light dinner; in the afternoon, you should eat 8 hours before the procedure. Avoid drinking 4 hours before your diagnostic visit.
Contraindications
As with any medical examination, there are a number of contraindications for MRI of the pelvic organs.
Absolute contraindications that make the procedure impossible include the following:
- implants and other foreign bodies containing metal (the only exception is implants in the oral cavity);
- implanted electronic devices (pacemakers, insulin pumps, etc.);
- installed Ilizarov apparatus (a system that fixes bone fragments in the correct position for complex bone fractures);
- allergy to contrast agent;
- chronic renal failure (with MRI with contrast, the substance is excreted from the body through the kidneys and can provoke an exacerbation of the disease);
- the patient is overweight (more than 130 kg) and waist circumference exceeds the diameter of the MR capsule.
A variety of implants and endoprostheses containing metal can affect the accuracy of the data obtained and distort the picture of the condition of the internal organs. And the magnetic field of the tomograph can disrupt the uninterrupted operation of life-supporting electronic devices (heart pacemaker, for example). Therefore, patients with such devices are prohibited from undergoing MRI.
There are contraindications for MRI, which do not prevent the procedure, but somewhat limit it. These include:
- Early pregnancy. MRI is not recommended for pregnant women under 20 weeks. However, in case of urgent vital need, the examination is considered acceptable.
- Lactation period (breastfeeding). The contrast agent passes into breast milk, so nursing mothers are advised to wean their baby off the breast for 2 days. Milk must be expressed and never given to the baby.
- Claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces) and hyperkinesis (a disease of the nervous system accompanied by increased motor tone). Patients with these diseases or a tendency to them will not be able to remain calm and completely still during the study. If an MRI is performed for emergency reasons, then the subject is put into medicated sleep for the duration of the procedure.
- Children's age up to 5 years. Although the procedure has no age restrictions, young patients are not always able to remain completely still for the required time. And if it is not possible to avoid the examination, it is recommended that the child be given a mild sedative before the procedure.
MRI OMT with contrast: indications and contraindications

There are many indications for MRI; this type of diagnosis has improved the detection of pathology of the pelvic organs at an early stage
Indications for pelvic MRI with contrast include the following:
- the need to clarify the diagnosis in case of ambiguous data from previous diagnostic methods;
- tracking changes in dynamics;
- preoperative planning;
- suspicion of a pathological process in the pelvic organs.
Complaints that are considered as indications for MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast in a woman, taking into account the general clinical situation:
- absence of a desired pregnancy within 12 months, subject to regular sexual contact without contraception;
- dyspareunia (pain during intimacy);
- repeated self-termination of pregnancy with normal tests;
- the appearance of bloody discharge in the interval between regular menstruation, a change in its character: more abundant, scanty, with large blood clots, the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- pain in the lower abdomen of unknown etiology;
- dysfunction of urination: the need to strain, a feeling of incomplete emptying, urine mixed with blood, frequent urges, etc.;
- irregular bowel movements: diarrhea, constipation, bloating, bloody stool.
Common symptoms that are suspicious of a neoplastic process in the pelvic organs: weakness, fatigue, unexplained fever, sweating, weight loss, anemia. MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast is performed as part of the general diagnosis if changes in the hormonal background are detected: increase/decrease in FSH, LH, prolactin. According to indications, the search can be expanded: the brain (pituitary gland), which is responsible for the production of biologically active substances that regulate the functioning of the female reproductive system, is additionally examined.
Contraindications for MRI

The risk of MRI in some cases outweighs the benefits; before going to the clinic, read the contraindications
There are a number of contraindications to MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast:
- Metal objects in the body. Any implants with electrical, magnetic or mechanical activation (cardiac and neurostimulators, insulin pumps), cochlear devices, ferromagnetic clamps, brackets, orthopedic structures will cause artifacts to appear on the images during the procedure. There is a risk of failure of equipment providing vital functions. Metal shrapnel, shavings or a bullet under the influence of a magnetic field can begin to move, as a result of which neighboring tissues are injured. The intrauterine device, as a means of contraception, can also lead to image defects.
- Inability to remain still during pelvic MRI with contrast. Some neurological pathology (Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, etc.), psychiatric illnesses in the acute stage, severe curvature of the spine, severe pain are an obstacle to magnetic scanning. For tremors and obsessive movements, the examination can be performed after the administration of sedatives, which is also important for patients suffering from claustrophobia. Immersion in medicinal sleep is one of the ways out in this situation, but the issue is always resolved on an individual basis.
- Obesity. If you have a high body mass index, it will not be possible to do an MRI of the pelvic organs for technical reasons: too much weight (120 kg or more) will not allow the patient to move inside the device. For this category of people, scanning is performed on open-type tomographs, which significantly reduces the quality of diagnosis due to low power, or they resort to other testing methods. Sometimes it is recommended to follow a diet for 1.5-2 months in order to lose weight and undergo a full examination.
An MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast in a woman has an additional obstacle to performing: pregnancy in the first trimester. In world practice, there is no data on the teratogenic effect of a magnetic field on a developing embryo, but it is more rational to conduct research after the 12th week of gestation, when the main formation of organs and systems of the fetus is completed. According to vital indications, magnetic resonance scanning can be performed at any time. MRI of the pelvic organs helps in diagnosing intrauterine malformations of the fetus, but there must be compelling reasons for carrying out the procedure, for example, if ultrasound detects abnormalities that are suspicious of a serious pathology in both the mother and the unborn child. Compared to other research methods - cordocentesis, amniocentesis - magnetic resonance scanning has no side effects.
Preparing for an MRI of the pelvis
The specifics of preparatory measures for MRI of the pelvic organs depend on the purpose of the study.
- For 2 days before the procedure, you must adhere to a diet that excludes foods that can cause increased gas formation in the intestines (vegetables, fruits, legumes, carbonated drinks).
- On the day of the study, 1 hour before the MRI, it is recommended to take any antispasmodic (no-spa, drotaverine, papaverine).
Important! MRI with contrast is performed strictly on an empty stomach. For a procedure without contrast, a light breakfast is allowed.
- With MRI of the bladder, it is important not to urinate before the examination, as the bladder must be full (for better visualization);
- When examining other organs, on the contrary, it is advisable to empty the bladder in order to obtain the highest quality images;
- Before MRI of the rectum, it is necessary to empty the intestines (if the patient suffers from constipation, then a cleansing enema must be done);
- For women with gynecological diseases, MRI of the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes is performed in the 2nd week of the menstrual cycle (from 6 to 9 days).
MRI of the pelvis with contrast: how is it done?
Maximum immobility during the procedure is a prerequisite for obtaining high-quality images
MRI OMT with contrast is done by appointment; an unscheduled study on the day of treatment may cost more; the prospects for its implementation must be checked with the operators. Before the procedure, the doctor talks with the patient to identify contraindications. Medical documentation is filled out; without signing voluntary informed consent for an MRI, the procedure cannot be performed. At the appointed hour, the subject is placed on the tomograph table, lying on his back. The patient is automatically transported deep into the drum ring; sensors rotate in the body of the device around the area under study, capturing the response of organs and tissues to the influence of the magnetic field. There are no unpleasant sensations; to reduce mechanical noise from operating equipment, you can use headphones or earplugs.
Duration of MRI OMT with contrast is 45-60 minutes. During certain phases of the examination, you need to hold your breath for a few seconds; the technician will tell you this over the speakerphone.
The resulting tomograms are interpreted by a radiologist, the conclusion will be ready in an hour, unless otherwise agreed. The results can be printed on film, copied to electronic media, or sent by e-mail. There are no contraindications to normal activities after MRI with contrast.
What does an MRI of the pelvic organs show?
The test result is usually prepared within 1-2 hours after the procedure and given to the patient.
In women, examination may reveal:
- cancer (ovarian, cervical and others);
- endometriosis and uterine fibroids;
- neoplasms and various pathologies in the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
In men, diagnostics can detect cancer of the testicles, bladder and prostate gland.
In addition, pelvic MRI can detect birth defects, bone tumors, arthrosis, and hip fractures.
How does the procedure work?
An abdominal scan requires preparation: the day before, the patient must avoid foods that cause gas formation. Before an MRI of the abdominal cavity, you should refrain from alcohol, mineral water and other carbonated drinks, kefir, legumes, black bread, fruit, as well as tea and coffee.
The patient should not eat anything for 6-8 hours or drink anything for 4-6 hours before having an MRI. If severe pain occurs, then half an hour before the examination you need to take a painkiller.
Jewelry and clothing should be removed in the doctor's office. Then you will find yourself on a movable table inside the tube, in which the scanning will be carried out. During the examination, you must strictly follow all the instructions of the diagnostician.
The examination is painless. The only drawback is that you have to be in a small enclosed space, which can cause some discomfort.
An MRI lasts about 40 minutes, and our patients receive a transcript within 1.5 hours.
Technique
Before starting the diagnosis, the radiologist conducts a survey of the patient to identify allergic reactions, the presence of metal implants in the body or tattoos with metal-containing inks.
For women, it is determined whether they are pregnant or whether she is a nursing mother. All this is necessary to once again make sure that the patient has no contraindications to the examination. During the conversation, the patient is explained the tactics of his behavior in case of unforeseen situations (panic, fear) and/or if his health worsens.
The subject changes into cotton clothes, removes all jewelry, wristwatches, hairpins and other metal objects. Then it is positioned horizontally on the scanner table, its limbs are secured with special clamps (to avoid involuntary movements during the procedure). The table, together with the patient, slides into the tunnel of the tomograph (a large round magnet).
In the shooting mode, the tomograph produces characteristic sounds (clicks, hums), which the patient may not hear if he used the headphones suggested by the nurse. But the patient can judge that the device is working by a feeling of burning in the pelvic area and an increase in local temperature. There is no need to be afraid, this is how the magnetic field and high-frequency impulses affect the body.
If it is necessary to administer a contrast agent before the procedure, the nurse will place an intravenous catheter. During the procedure, the product is injected automatically. Its entry into the vein is accompanied by a feeling of heat or cold spreading through the bloodstream.
An MRI of the pelvic organs takes 30-45 minutes. An MRI scan with contrast may take a little longer.
Side effects
MRI does not harm human health. However, in some cases (about 1-2%), manifestations of increased sensitivity to the contrast agent may be observed: symptoms of urticaria, itching and burning in the area where the catheter is installed, bronchopulmonary symptoms (heaviness in the chest, difficulty breathing, sometimes suffocation, cough) and other reactions.
More often, this reaction occurs in people who hid from the doctor or did not warn him due to their ignorance about their tendency to allergies.
Alternative diagnostic methods
Compared with ultrasound (US), radiography and computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging has undeniable advantages. This
- “full immersion” in the area under study;
- the ability to examine organs and tissues in all planes;
- high contrast and better resolution;
- the ability to detect even minor changes in organs and tissues;
- higher information content in terms of diagnosing benign tumors, cancer and infections.
Such a volume of information as an MRI can only be provided by hysteroscopy - an endoscopic examination of the internal organs and tissues of the pelvis using special surgical equipment. MRI is a non-invasive (non-traumatic) procedure, making it the most popular diagnostic method. In addition, the safety of the procedure makes it possible to repeatedly examine one patient at relatively short intervals.