Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - (Thyroid Ultraschall) is the simplest and most highly informative diagnostic method, which provides a detailed assessment of the condition of the gland itself, as well as the anatomical formations adjacent to it - blood vessels and muscles. This is possible using modern ultrasonic sensors with additional capabilities. In particular, Doppler ultrasound allows you to examine the blood supply to the thyroid gland and nearby lymph nodes.
Make an appointment, ultrasound or tests
PRICE OF THYROID ULTRASOUND 1000 rub.
Indications for thyroid ultrasound
The content of the article
Before scheduling a procedure, please read the important information regarding indications and contraindications. A classic ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is recommended to be done regularly as part of an annual medical examination, regardless of the patient’s age and the absence of characteristic symptoms. If the following symptoms appear, it is necessary to make an appointment with an endocrinologist as soon as possible and undergo an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland:
- visible increase in the volume of the neck, the appearance of a compacted formation;
- redness of the neck area near the location of the gland;
- hoarseness not associated with colds;
- difficulty breathing, discomfort during swallowing;
- increase in body temperature within 37-37.5 degrees;
- the appearance of swelling;
- weakness, apathy, drowsiness, severe irritability;
- sweating, feeling hot or, conversely, cold;
- trembling of limbs;
- sudden change in body weight;
- cardiopalmus;
- baldness.
These symptoms may be an indicator of a malfunction of the thyroid gland, and therefore require examination by ultrasound. An endocrinologist may refer you for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland if palpation reveals lumps or the patient complains of pain when palpating the gland. A direct indication for ultrasound diagnostics is unsatisfactory results of hormone tests.
In addition, the following groups of people should sign up for a thyroid ultrasound :
- Pregnant women or those who are planning to conceive a child in the near future.
- People living in iodine-deficient areas.
- Patients diagnosed with obesity.
- For those taking hormone-containing medications.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is also prescribed to patients to monitor the treatment. In some cases, the frequency of such a procedure reaches several times a week, which is necessary for dynamic monitoring of the gland’s reaction to drug correction.
Ultrasound examination is completely safe for humans, has no contraindications, and if a pregnant woman undergoes it, it does not have any effect on the fetus. Therefore, ultrasound can be done as many times as needed.
When should you get tested?
The frequency of ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland depends on individual characteristics such as age, medical indications, and the presence or absence of ailments. Individual parameters:
- Age up to 50 years: preventive examination every five years
- For older people over 50: prophylaxis every two to three years
- During pregnancy and its planning: to eliminate negative effects on the fetus
For some medical indications and ailments, you need to be examined as soon as possible:
- In the presence of already established endocrine problems
- To monitor treatment or its results
- If there is a risk of recurrence of endocrine gland dysfunction
- With a noticeable enlargement of the thyroid organ, palpable seals and nodes
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain
- In case of unstable emotional state – apathy, nervousness
How to prepare for a thyroid ultrasound
This gland is absolutely accessible for research due to its convenient location: ultrasonic waves easily reach the thyroid gland and are fully reflected from its tissues. Therefore, this procedure does not require special preparation. But there are a couple of recommendations that should be considered when planning an ultrasound of this gland:
- Patients who take medications that affect cardiac output and blood pressure should stop taking them the day before ultrasound diagnostics.
- Do not drink alcohol during the day.
- Elderly people are advised to come for the procedure on an empty stomach. This recommendation is associated with the appearance of a gag reflex at this age when pressing on the neck area.
When coming for an ultrasound, you can take a personal towel with you to wipe off any remaining gel from your neck after the procedure.
Cloth
Choosing clothing will help you prepare for the examination. It is better to come to the examination without wearing restricting clothing. It should be as free as possible. Particular attention should be paid to ensuring that clothing does not restrict the neck area. If a person has not paid due attention to this moment, the doctor may ask him to undress to the waist. The examination is carried out lying on your back. In addition, you need to remove all jewelry and chains at home.
Advice: to get the best research result, you need to take your previous results with you. Thus, the doctor will have the opportunity to compare the patient’s condition and draw an appropriate conclusion.
How to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
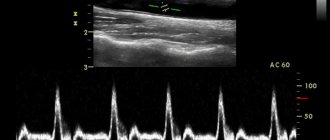
The procedure uses a linear sensor with a high scanning frequency. With its help, you can obtain a high-quality image that shows the structure of the organ and focal changes. During the procedure, the size of the gland, its structure, configuration, and blood flow condition are determined. In parallel, the parathyroid glands and regional lymph nodes are examined.
No preparation is required for diagnosis, since nothing interferes with the examination of the organ. Ultrasound diagnosis of thyroid pathologies is an accessible, non-traumatic and painless diagnostic method. Complications after ultrasound are not observed. During the study, the patient is not administered drugs, and the organs are not irradiated, but the diagnostic efficiency is high. There are no contraindications to the ultrasound procedure. It can be done many times even during pregnancy.
The examination is carried out in a lying position. A special gel is applied to the patient’s neck to increase the conductivity of ultrasound. The results are displayed on the screen. Modern ultrasound machines determine not only the presence, but also the size of thyroid nodules, which is important for choosing treatment tactics.
The patient is given an image and a description, based on which the endocrinologist will prescribe treatment for the identified pathologies. To make a final diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo blood and urine tests and consult with a therapist and oncologist.
Why get your thyroid examined?
All glands in our body secrete hormones that regulate the functioning of internal organs and systems. Glands and hormones make up the human endocrine system. These include the thyroid gland.
Doctors recommend regular preventive thyroid examinations for all people over 35 years of age. By this age, problems with this organ are quite common. Diseases of the endocrine system also occur in children, pregnant women, and young men. Timely diagnosis can prevent the development of pathologies in this area and avoid complications in the future.
Content:
- Why get your thyroid examined?
- When to get tested
- Preparation and conduct of the survey
- Decoding the results
- Where to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
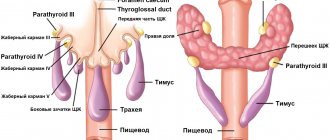
Iron gets its name from its shape. Located in the neck area under the thyroid cartilage, it connects to the larynx and trachea. It is formed from the right and left lobes, which are connected by an isthmus. It performs two important functions: it preserves iodine and produces hormones. These hormones, in turn, perform a number of other important health tasks. Triiodothyronine and thyroxine ensure the growth and physical development of the body; the lack of these components affects the appearance and functionality of internal organs. They also affect mental activity, blood pressure, and vital activity.
Another important thyroid hormone is thyrocalcitonin. With its help, normal calcium levels are maintained in bone tissue. If the body lacks this mineral, then bone fragility occurs, teeth deteriorate, and the spine weakens. In some cases, the absence of thyrocalcitonin leads to too high calcium levels, which leads to equally serious consequences.
Taken together, malfunctioning of the thyroid gland threatens weight gain or critical loss, hair loss, tumor formation, depression, and lethargy. This picture is especially dangerous for pregnant women and children; a lack of hormones in this case leads to fetal pathologies, developmental delays, mental disorders and mental activity.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the thyroid gland
To obtain comprehensive information that reflects the condition of the thyroid gland, the diagnostician during the ultrasound procedure evaluates and enters into the protocol the following parameters:
- Location . The typical location of the gland is considered standard when it is within the anatomical norm. If there is a pathology, a record of its aberrant location is entered into the protocol, when the thyroid gland may be located behind the sternum, in the area of the root of the tongue, etc.
- Size . Determining this parameter allows one to judge the presence or absence of hypo- or hyperplasia of the thyroid gland.
- Structure . Normally, the thyroid gland consists of two symmetrical lobes, which are connected by a small isthmus. In the case of abnormal intrauterine development of the gland or its pathological acquired modification, tissue outgrowths, an additional lobe, and bifurcation may be absent.
- Form . Normally, the thyroid gland is flat, but may be slightly elongated. If it is greatly increased in volume, swollen, with thyroid tissue, diffuse goiter, viral or bacterial pathology is suspected.
- Outlines . The clear contours of the thyroid gland are taken as normal. Otherwise, if its contours are not clearly visualized, one can judge the presence of a tumor or inflammatory focus in the gland.
- Structure . If there is no pathological process in the gland, its structure is homogeneous and has a specific granularity.
- Echogenicity . Visually, this parameter can be defined as a gradation of gray shades over the entire area of the study area. Normally, the echogenicity of thyroid tissue should be visible in light gray shades.
- Focal formations . During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor must examine the gland for the presence of pathological formations - nodes, calcifications, cysts or tumors.
- Blood supply to tissues . Impaired blood supply to the thyroid gland can lead to the death of its tissue. Normally, the multi-colored signals visualized on the ultrasound monitor screen should be uniform over the entire area of the thyroid gland. An increase in color and “pulsation” of shades indicates an increase in blood flow, which may be associated with an inflammatory process inside the gland.
- The structure of the cervical lymph nodes . To determine their condition, the following indicators are determined: structure, size, presence of pathological inclusions, cystic transformation, presence of the “gate” of the lymph node, assessment of blood flow.
Diagnosis of women
Women need more preparation than men. The latter will only need to not be late for the procedure. In women, the effectiveness of the procedure depends on the menstrual cycle. The most optimal time would be between 7-9 days after the discharge ends.
Testing should not be done during menstruation
During pregnancy
In pregnant women, impaired thyroid function is most common. Because her body is being rebuilt to meet the needs of the baby. The hormones produced by this organ not only affect the development and growth of the fetus, but also the course of pregnancy. Impaired activity of the thyroid gland can lead to miscarriage.
If the doctor suspects organ dysfunction, the woman is prescribed an ultrasound. This diagnosis is completely safe for the unborn baby. It can be carried out without any fear for the baby’s health. Any violation of an organ negatively affects its health, causing deviations in growth, development, and decreased intelligence.
How much does a thyroid ultrasound cost?
The cost of the procedure depends on the medical center where the study is carried out and on the quality of the device used to perform the procedure. In St. Petersburg, the price of an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland varies from 1000 rubles to 2000 rubles. At the Diana Clinic, you can undergo a study on a new device for 1 thousand rubles.
ADDITIONAL RESEARCH
How to carry out the procedure
Carrying out an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is a simple, painless procedure, its rules are simple:
- The patient lies down on the medical couch face up, throwing his head back and opening his neck as much as possible. A cushion or pillow is placed at the level of the shoulder girdle.
- A gel with good ultrasound conductivity is applied to the skin in the area of the gland.
- The sensor is applied to the neck. It emits ultrasound and then receives the reflected signal.
- The signal is processed by the program, the image is displayed on the screen.
- The study takes place within 10–20 minutes. Discomfort can only be caused by an awkward neck position.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the thyroid gland: norm and deviations
To understand whether a pathological process is present in the thyroid gland, the following points must be carefully assessed:
Structure, contours
The homogeneous structure of the gland is considered standard; its granularity is clearly visible. Normal variants include a moderately heterogeneous structure in patients in whom laboratory tests have revealed an increase in the titer of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin. If the gland is visualized as a “honeycomb,” it means that there is an abnormal degeneration of its tissues. The contours of the gland should be clear. If they are blurred and difficult to read, it means that an inflammatory process or tumor is developing in the gland. If the structural outlines of the thyroid gland are poorly visualized, there is reason to believe that malignant tumors have grown into nearby organs.
Main settings
To determine the presence of edema, tumor or thyroid tissue, the sizes of the lobes must be assessed: the length should not go beyond the range of 2.5-4 cm, width - 1.5-2 cm, and the range of 1-1.5 cm is taken as the norm for the thickness of the gland During the study, the volume of the thyroid gland is determined. Its norms may vary based on the patient’s weight:
| Patient weight (kg) | Maximum gland volume (cm cube) |
| Up to 55 | 15,5 |
| 56-65 | 18,5 |
| 66-75 | 22 |
| 76-85 | 25 |
| 86-95 | 28,5 |
| More than 96 | 32 |
In case of non-compliance with the standards, a record is made in the study protocol - a diffuse increase, which may indicate the presence of bacterial or viral damage to the gland, diffuse goiter, an oncological process, etc.
Echogenicity
The density of the echostructure may vary depending on the age and gender of the patient, but should be visualized in light gray tones. Inflammatory foci are visualized in a dark gray color, closer to black. Black echogenicity is a sign of a malignant process in the thyroid tissue. The following echogenicity characteristics may be included in the study protocol:
- isoechoic area – a sign of the absence of pathological processes in the tissues of the gland;
- hyperechogenicity - light areas that indicate the absence of diffuse changes in the area under study;
- hypoechogenicity - the presence of dark areas in the examined area, which indicate the presence of inflammation;
- anechogenic zone - black areas indicating the presence of cysts or tumors in the thyroid gland.
Focal changes
The study protocol must indicate the absence or presence of focal formations - neoplasms of a benign or oncological nature. If cysts or nodes are identified, the protocol indicates a focal lesion with a description of their location and nature.
Small cyst-shaped inclusions up to 4 mm are considered an acceptable variant of the norm.
Benign neoplasms are visible on ultrasound as clearly isolated objects, while a cancerous tumor has blurred boundaries and is black in color.
Cysts are fluid-filled blisters and can be congenital or acquired. If the doctor diagnoses the presence of nodes, then they were formed from the growing tissue of the gland itself. The presence of calcifications in the thyroid gland suggests that these formations consist of potassium salts, and therefore can contribute to the death of thyroid cells and their further degeneration into a tumor.
Blood supply to tissues
The intensity of this parameter is determined using Doppler ultrasound. Normally, single signals of pulsating blood flow can be seen on the surface of the thyroid gland. When its speed increases, one can judge the inflammatory process or tumor inside the gland.
Regional lymph nodes
The norm is smooth, clearly visualized contours, the absence of any neoplasms, cysts, the presence of a “gate” of the lymph node, moderate blood flow, length greater than width. Any deviation from the norm indicates a developing pathology.
The protocol has a conclusion, which indicates all the information about the study performed and the presence or absence of identified pathologies. Based on the ultrasound examination, the endocrinologist can clarify the diagnosis and select the appropriate treatment.
What does an ultrasound show?
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland provides the endocrinologist with a large amount of important information about the condition of the thyroid gland. Based on its results, it is possible to clarify, for example, whether the detected enlargement of the gland is a diffuse goiter.
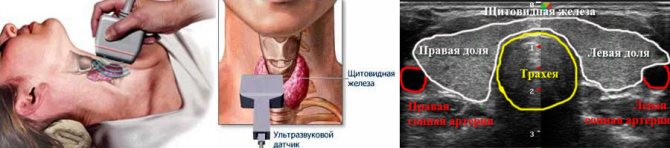
Ultrasound picture of the thyroid gland
If there are nodules in the thyroid gland, examination can reveal:
- whether the tumors are filled with liquid or are they solid;
- number of nodules, their location;
- echogenicity of nodular formations;
- structure of nodes (homogeneous, heterogeneous)
- whether the neoplasms have clear boundaries;
- is there blood flow to the tumors;
- presence of microcalcifications;
- condition of the lymph nodes.
If the doctor suspects that the existing formation in the thyroid gland is of poor quality, he will prescribe further procedures to clarify the diagnosis.
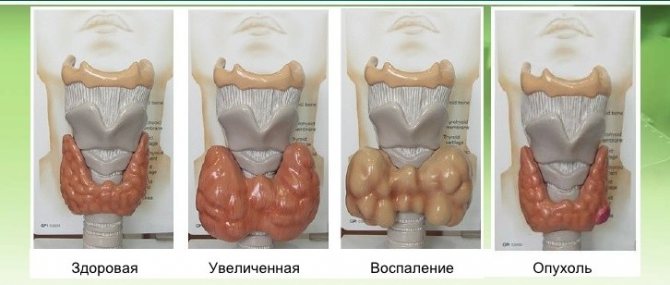
Thyroid diseases
Ultrasound scanning of the lymph nodes is of great importance in a comprehensive examination of patients with thyroid pathology. The risk of lymphatic metastasis of thyroid cancer is very high. Often the detection of hypoechoic and (or) enlarged lymph nodes in the neck is the first sign of the development of malignant tumors. Based on the results of screening studies and refined diagnosis of thyroid diseases, echo scanning of possible lymphogenous metastases of cancer in the thyroid gland is performed. In this case, specialists are guided by known anatomical information about the outflow of lymph from the thyroid gland, and on data on the topography of the superficial and deep lymph nodes of the neck.
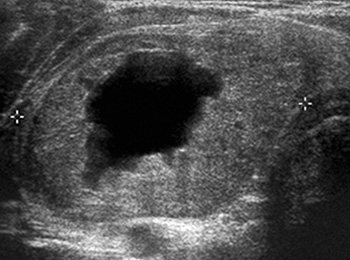
Ultrasound picture of thyroid cancer
What diseases can be detected by ultrasound of the thyroid gland?
Based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics, an endocrinologist can diagnose the following diseases:
- Nodular goiter : a disease in which compactions are clearly palpable in the area of the gland. Ultrasound reveals an increased density of formations bordering unchanged tissues.
- Diffuse toxic goiter : a pathology in which the diffuse toxic state of the thyroid gland is within normal limits, but the volume of the gland is increased, and laboratory diagnostics show increased synthesis of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T3.
- Hashimogo's thyroiditis : an inflammatory disease of an autoimmune nature, in which part of the thyroid tissue dies, therefore the function of the gland is impaired.
- Hypothyroidism : an endocrine disease characterized by the presence of diffuse degenerative changes in the thyroid tissues. In this case, the gland is small in size compared to the norm; thyroid hormones are produced in insufficient quantities.
- Thyroiditis : a disease in which inflammation develops in the gland. The main symptoms of this condition are an increase in the volume of the neck, pain in the thyroid gland, swelling of adjacent tissues.
- Cyst : a formation that resembles a bubble with fluid inside. On ultrasound it is visible in the form of formations with clear contours.
- Follicular adenoma : a nodular formation of a benign nature that may contain colloid.
- Papillary adenoma : a benign formation with a cystic structure and papillary growths inside.
- Cancerous tumor : a malignant neoplasm that is a mass accumulation of cancer cells.
In some cases, to clarify the diagnosis, additional tests for thyroid hormones are required, which reflect the balance of the production of T3 and TSH hormones.
Thyroid gland and cycle
The menstrual cycle and the functions of the endocrine system have a direct relationship, since the body’s hormonal levels directly affect a woman’s reproductive ability. One of the signs of many thyroid diseases is a disruption of the menstrual cycle.
If we consider the relationship between the female reproductive system and the functioning of the gland, the hormones synthesized by this organ (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) contribute to:
- Stimulating the functions of the ovaries, as well as other systems, in particular the pituitary gland, for the production of other hormonal compounds that affect the likelihood of conception and the success of pregnancy.
- Ensuring the cyclicality of the ovulation process and the frequency of the menstrual cycle.
- The normal course of metabolic processes occurring at various levels.
- Normalizing the volume of discharge, regulating the duration of the cycle.
In addition to its impact on women’s health, the thyroid gland has a significant impact on many other processes, so it is very important to promptly identify developing pathology of the organ.
Advantages of the method - ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland
If there is a suspicion of a malfunction in the endocrine system, the doctor will refer the patient for an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland. This study is informative enough to determine the presence of pathologies in the area under study, while being absolutely safe for humans. MRI and CT are indicated only in cases where it is necessary to detail the structure of the pathological formation inside the gland.
The main advantages of ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland include:
- lack of special training;
- simplicity and speed of the procedure;
- absence of ionizing radiation;
- harmlessness, including for pregnant women and the fetus;
- no risk of infection.
Such diagnostics have no contraindications, so they can be performed on children of any age, pregnant and lactating women and the elderly.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Ultrasound – what is it and why is it needed?
Ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland is a simple and safe procedure for the patient
. It is necessary to determine the presence (or absence) of pathologies, inflammation, neoplasms or other problems in this organ.
The study helps to identify:
- Enlargement or reduction of an organ
- Presence of nodes, cysts and tumors
- General inflammation or tissue damage
- Obstruction of blood flow
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Impossibility of pregnancy
The examination mechanism is quite simple and painless:
- The patient is placed on a chair or couch in such a way as to provide access to the neck
- The doctor applies a special composition to the patient's throat
- Then the doctor picks up the sensor and moves it from different sides over the part of the body being examined.
- During the process, signals about the state of this endocrine organ are transmitted to the monitor and are also recorded on magnetic media
- The result is an image and data on the condition of the organ, which the doctor compares with normal
If any signs of abnormalities are found in the tissues or structure of the thyroid gland, the doctor prescribes other tests to clarify, confirm or refute the diagnosis.