What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia, popularly called “pneumonia,” is damage to the lung tissue. Depending on the stage of the disease, it can affect the lining of the lung and various parts, including the diaphragmatic pleura. Pneumonia is a very dangerous disease, often leading to death, so if there are signs of the disease, doctors prescribe an x-ray.
Causes of the disease
In most cases, pneumonia occurs due to harmful microorganisms entering the organ: viruses, bacteria, fungi. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Another type, eosinophilic pneumonia, is allergic in nature and requires urgent X-ray examination. Much less often, pneumonia is congestive, for example, when it occurs as a result of prolonged bed rest. It can also be a complication of other diseases. What pneumonia looks like on an X-ray largely depends on the nature and stage of the disease.
Signs of illness
Symptoms of pneumonia do not take long to appear, manifested by a dry or wet cough, with a temperature of up to 40 degrees. With a wet cough, the doctor pays attention to the nature of the sputum: “rusty”, bloody with pus, the presence or absence of odor. Other signs of pneumonia include pain in the chest, side, and even stomach—in this case, an x-ray is needed to confirm the location of the lesions in the lung.
Fluorography as a diagnostic method
Many diagnostic procedures are based on the ability of an x-ray beam to pass through opaque objects and remain active. It is on this principle that fluorography of the chest organs, x-rays, fluoroscopy and other examinations of the lungs are based.
All these methods of examining patients differ only in the way they obtain images. This means that, depending on the chosen method, a person will receive a different dose of radiation. The harm caused to the body will vary. There are different types of tissues in the human body. This means that they all absorb X-rays differently. It is this difference that can be seen upon careful examination of the image:
- the densest parts appear white (including bones);
- empty parts - black;
- organs are gray of varying intensity.
Below we will look at the most common fluorography methods and find out what lung pathologies can be detected after such a procedure.
Film and digital fluorography
Film fluorography
Film fluorography of human lungs is a cheap diagnostic method, but in 15% of cases the study does not give an accurate result. This examination method was invented back in the 19th century, then replaced by an innovative one, although film fluorography is still actively used in many small settlements.
Due to the high percentage of defects received, many patients have to undergo repeated lung examinations. This entails receiving a second dose of radiation, which is harmful to their health.
Unlike film, digital fluorographic examination of the lungs is free of all these disadvantages. There is no need to repeat the image, since the doctor, using special software, is able to work with the resulting image after the examination is completed. If necessary, the specialist can return to the saved data.
Digital fluorography
Digital images of the lungs, in contrast to film versions, have other advantages. Even a single procedure carries a lower dose of radiation for a person. This means that this technique is much safer for the patient. When you consider how many patients avoid repeated examinations, the advantages of the method become more obvious.
If necessary, after undergoing digital fluorography of the lungs, the patient can ask the attending physician to print out the required number of images. With a film examination, this can be done in only one copy. Multiple copies may be required in complex cases of illness when the patient wishes to see several doctors in order to receive qualified advice.
The digital method of fluorographic examination makes it possible to examine the condition of the lungs, but radiography still remains the leading method of examination after a preliminary diagnosis has been made.
Features of radiography
X-rays in modern conditions can also be performed both film and digital. The sensitivity of the X-ray screen is higher than that of fluorography. But when performing an X-ray, the amount of radiation is greater, since all internal organs are exposed to the process, and not just the chest.

What to choose: X-ray or fluorography
X-ray allows the doctor to carefully examine the condition of the lungs and make a diagnosis
Fluorography of the chest organs gives a less clear picture, and x-rays allow the doctor to carefully examine the condition of the lungs. Why is fluorography used more often?
The purpose of lung fluorography is to detect pathologies such as cancer, tuberculosis or pneumonia at an early stage. X-rays are more expensive, and the doctor may refer you for this procedure if the fluorography image does not provide complete information or the doctor doubts its reliability. Additional research is also required when the picture turns out to be blurry, with an unclear image.
We can conclude: fluorography is a preventive examination method, and radiography is a diagnostic method. Therefore, both methods are important for a reliable diagnosis and prevention of severe respiratory diseases.
How is an x-ray taken for pneumonia?
For pneumonia, an X-ray of the lungs is usually taken, regardless of the cause of the disease. Before the study, it is necessary to remove everything that could distort the results: metal objects, jewelry, long hair, etc. X-ray of the lungs
done in a vertical position, having first undressed to the waist and stood in front of the machine as the radiologist says. At the doctor’s command, the patient draws air into his lungs and holds his breath, while the device takes a picture.
Features of the treatment of pneumonia in children
The child additionally needs to take mucolytics to thin the sputum.
Diagnosis and treatment of hilar pneumonia in children is not much different from the treatment features of adults. If characteristic symptoms are identified, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with lung cancer and tuberculosis.
To eliminate the inflammatory process in the lungs, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. A sick child additionally needs to take mucolytics to thin the sputum. For bronchial obstruction and severe shortness of breath, bronchodilators are prescribed.
If treatment is started in a timely manner and all doctor’s recommendations are followed, the course of hilar pneumonia in children is favorable. The development of complications is extremely rare.
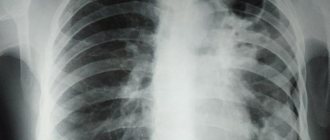
What does pneumonia look like on an x-ray?
What pneumonia looks like on an X-ray depends on the stage of the disease and its nature. However, in any case, signs of pneumonia on x-ray are visible as disturbances in the structure of the lung. Doctors pay attention to the features of the pulmonary pattern, the roots of the lung, the pleura and the location of infiltrative foci. Light areas in the image are interpreted as airless.
Krupoznaya
Croupous pneumonia on X-ray is characterized by increased pulmonary pattern and thickening of the root, slight compaction of the pleura, as well as reduced airiness of the lung. The reduction in airiness directly depends on the stage of the disease. This disease looks like medium-intensity shading. Lobar pneumonia is one of the most dangerous.
Focal
As with lobar pneumonia, with focal pneumonia, X-rays show an increase in the pulmonary pattern and thickening of the root, as well as thickening of the pleura. Such pneumonia is characterized by focal shadows of different sizes with unclear contours. There is also a deformation of the pulmonary pattern, which is very clearly visible on x-ray. It is difficult to identify symptoms of focal pneumonia on X-rays, so only an experienced doctor can diagnose this disease.
Viral
Viral pneumonia is classified as atypical. With the strengthening of the pulmonary pattern and compaction of the pleura in this case, the roots of the lungs do not change. The appearance on x-ray of focal shadows in the lower and middle parts of the lungs with bilateral viral pneumonia confirms the diagnosis. The whole world is aware of the rapid development and danger of this form of the disease, and this is another argument in favor of examining the signs of pneumonia on an X-ray.
Symptomatic manifestations of destructive pneumonia
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of pneumonia and the form of lung disease. At the early stage of acute pneumonia, an increase in temperature to critical levels, excessive sweating, headache, changes in pulse, and pale skin are detected. Severe respiratory failure manifests itself in the form of signs:
- dyspnea;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial area;
- change in respiratory rhythm;
- swelling of the wings of the nose;
- protrusion of the intercostal region at the moment of exhalation.
Severe pain in the chest area is explained by the action of the cough reflex. A dry cough gives way to a wet cough with the release of purulent mucus. Symptomatic manifestations of the destructive form of pneumonia are detected within two days from the onset of pneumonia.
When lung pathology passes into the second stage, patients experience cardiac and respiratory failure, weakness, and severe dizziness. The clinical picture of contact phase purulent pneumonia includes nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness, high body temperature, muscle pain, and bluish discoloration of the skin.
The third stage of lung damage, accompanied by the formation of metastases, is characterized by frequent cases of loss of consciousness, a sharp decrease in body weight, and impaired metabolic processes and digestive function.
Contraindications to X-rays
X-rays should not be taken for pregnant women at any stage, as well as for children under 15 years of age. In some cases, the patient's condition may be an obstacle to conducting the study. A patient in a supine position cannot undergo the study due to the inability to assume an upright position. In an inadequate condition, when the patient cannot stand still, signs of pneumonia on an x-ray cannot be recorded properly.
How often can an x-ray be taken for pneumonia?
A confirmed diagnosis is an indication for regular x-ray examinations to monitor the course of the disease. Whether the treatment prescribed by the doctor helps will show what pneumonia looks like on an x-ray. In this regard, many patients are concerned about how often this procedure can be performed without harm to health. After the start of treatment, depending on the type of disease, an x-ray for pneumonia must be done after 6-10 days. If positive dynamics are noticed, treatment continues as it was started. The patient, who is considered to be cured, is subsequently re-examined after 1, 3 and 6 months. With favorable treatment, the patient receives a small dose of radiation, far from acceptable levels. This is possible thanks to the development of medical technologies and protective measures during the procedure.
Ground glass sign in the lungs
The “frosted glass” symptom manifests itself in patients against the background of lung damage by the virus. Since the respiratory organ undergoes serious changes, areas of damage appear in it.
The density of lung tissue decreases. Moderately reduced airiness appears in the affected area, the main sign being the visibility of the lung vessels and bronchial walls.
It is difficult to notice this symptom on an x-ray, so an additional computed tomography is required.
Typical signs of frosted glass symptoms:
- the walls and structure of the bronchi are clearly visible;
- darkening is visible;
- the vascular pattern is preserved;
- The transparency of the lung tissue increases.
Reasons for which this symptom occurs:
- pulmonary edema;
- pneumonia caused by viral particles;
- chronic diseases of the lung tissue;
- respiratory distress syndrome;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- heart failure in the stage of alveolar pulmonary edema;
- bleeding from the pulmonary vessels.
The effectiveness of lung x-rays for coronavirus
Experts inform people who are faced with such a serious disease as COVID-19 what X-rays of the lungs show during coronavirus, its effectiveness, whether it is informative or not - even with moderate damage to the lungs, X-rays show changes. When there are few foci of inflammation, the result may be false negative. On average, the effectiveness of radiography is 70%.
Recently it has become possible to process images using artificial intelligence. This has made it possible to increase the efficiency of diagnosing pneumonia using radiography. The new method is especially relevant for medical institutions where there are no specialized specialists.
Does an X-ray of the lungs show pneumonia during coronavirus or not?
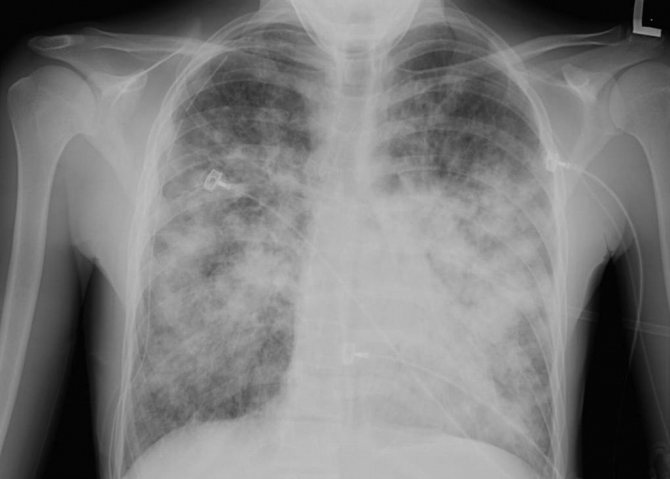
Radiography is one of the most inexpensive research methods. But for many, the question remains open whether X-rays always show pneumonia during a coronavirus infection. To begin with, it is worth clarifying that not in all cases, infection with coronavirus leads to lung damage. Pneumonia develops only with a complicated form of the disease and not immediately. The infection descends into the lower respiratory tract gradually.
X-rays are not given to all people who suspect they are infected with coronavirus. As a rule, it is prescribed some time after the first symptoms appear and only if the condition worsens and signs such as shortness of breath and weakness appear. It is impossible to make a diagnosis using radiography. Changes in the lungs can occur for other reasons. But in combination with taking a test for COVID-19, this research method is informative.
X-rays for coronavirus show pneumonia, but not in all cases. If the lesion is small, areas with changes may not be visible on the image. A computed tomography scan is more informative. This research method also uses X-rays, but the image is three-dimensional, since the rays pass even through the deep layers of tissue of the organ being examined. But CT is a more expensive type of examination.