We continue to study various methods of contraception. Hormonal contraceptives are the leaders among them.
In the first part of the article, I briefly talked about the mechanism of action of hormonal contraceptives.
If I were looking for an acceptable method of contraception for myself, then I would be interested in comparing the advantages and disadvantages of different types of contraception.
In the article “Contraception - find out what they don’t talk about,” I listed the different methods of contraception that exist in the world at the moment and talked a little about them.
Hormonal contraception is considered to be a breakthrough in science. But is it?
Contraceptive methods for breastfeeding: comparison of effectiveness
Birth control pills
There are two types of birth control pills:
- gestagenic, so-called. mini-pills (efficacy is 99% when taken correctly, otherwise – 92%) [2];
- combination drugs, or COCs.
Mini-pills are single-component products containing gestagen or progestogen. Efficacy is based on the ability of progestogens to act on the mucus that closes the entrance to the cervix. The mucus becomes thicker, creating a barrier for sperm. You can take it immediately after childbirth (in the absence of contraindications).
A small amount of hormones is transferred to the baby through breast milk, and this does not cause him harm. Such contraceptive pills are safe during breastfeeding because they do not affect the functioning of the mammary glands. Side effects are rare.
COCs contain two types of hormones: synthetic estrogen and progestogen. These drugs are one-, two- and three-phase, depending on the percentage of hormones in the composition.
Combined contraceptives are prohibited during lactation.
Other methods of contraception: list
At any time after childbirth, if a woman has no contraindications, she can use:
- contraceptive implant (more than 99% effective) [3];
- contraceptive injection (more than 99% effective) [4];
- male condoms (98% effective when used correctly) [5];
- female condoms (95% when used correctly) [6]: IUD (intrauterine device) (more than 99% effective) [7]; IUD (intrauterine system) (more than 99% effective) [8].
The IUD can be inserted within 48 hours after birth. If the device/IUD has not been inserted within 48 hours, it is recommended to wait until four weeks after birth to start using it. [10]
Are there any side effects?
Like any medications, contraceptives also have side effects, which include:
- frequent migraines;
- nausea and vomiting;
- absence of menstruation;
- modification of menstruation (discharge may be abundant or, conversely, discharge in very small quantities, smell and color may change);
- change in the duration of menstruation;
- increased breast sensitivity;
- the appearance of ovarian cysts (they disappear on their own within 60–90 days after stopping the medication);
- increased hair growth;
- the appearance of cosmetic problems (pimples may appear, the skin may become oily, etc.).
In case of diabetes mellitus, taking progestogen drugs must be done under special supervision, as a woman may experience frequent dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and even fainting.
If vision is impaired, taking birth control pills requires consultation with an ophthalmologist, as there is a risk of a sharp deterioration in the quality of vision.
Approved tablets
A breastfeeding mother thinks she won't get pregnant while breastfeeding, but that's only half true. Only in the first six months is the risk of pregnancy reduced to a minimum.
Lactation amenorrhea is a period of natural contraception. Breastfeeding your baby inhibits ovulation and is 98-99.5% effective in preventing pregnancy. [1]
However, even at this time, there is still a small risk of becoming pregnant. Each woman is individual; the menstrual cycle can begin in the second month of breastfeeding.
Oral medications are 99% effective. Previously, nursing mothers were not allowed to use this method of contraception, but with the development of medicine, medications appeared that were approved for use by women with breastfeeding. Birth control pills during lactation are prescribed by a specialist, taking into account the physiological characteristics of the body. After all, many women don’t even have an idea about what kind of birth control pills they can use while breastfeeding.
Mini-pill
Mini-pills are recommended for use during breastfeeding.
Mini-pills are suitable postpartum birth control pills while breastfeeding.
They are gestagen-containing contraceptives. They do not affect lactation activity or the duration of feeding. Side effects are absent or minimized. Their use reduces the risk of thrombosis. Libido does not decrease.
If you stop taking the pills, the ability to conceive returns as soon as possible. Side effects such as headaches and nausea may occur at the beginning of treatment. After some time they disappear.
Even taking into account the fact that such contraception is allowed for breastfeeding, it is recommended to consult a specialist before using it.
The doctor will choose the appropriate contraceptive and the appropriate dose. It should be noted that there are drugs that are prohibited to be used after an artificial birth (caesarean section), when treated with antibiotics.
Lactinette ®
Dispensed by prescription. The active substance is Desogestrel.
These contraceptive pills are widely used during breastfeeding. Lactinet is effective and contains small doses of gestagen. Its effect is aimed at inhibiting ovulation. Studies have been conducted that show no difference between the mental and physical development of children whose mothers took Lactinet and the development of other children.
Charozette (Cerazette ®)
Dispensed by prescription. The active substance is Desogestrel.
Contraceptive pills Charozetta are similar in composition to Lactinet. Charozetta is contraindicated for liver problems, uterine bleeding, tumors, blood clots in the deep veins, kidney dysfunction, and individual intolerance. The effect of the drug is similar to most COCs.
If you choose: Lactinet or Charozetta, you should take into account that the composition and effect of the drugs are identical, but the price of Charozetta is twice as much.
Exluton
Dispensed by prescription. The active substance is Linestrenol.
Exluton suppresses ovulation. Synthetic gestagen increases the amount and viscosity of cervical mucus and reduces the penetrating ability of sperm. Reduces the transport capacity of the fallopian tubes.
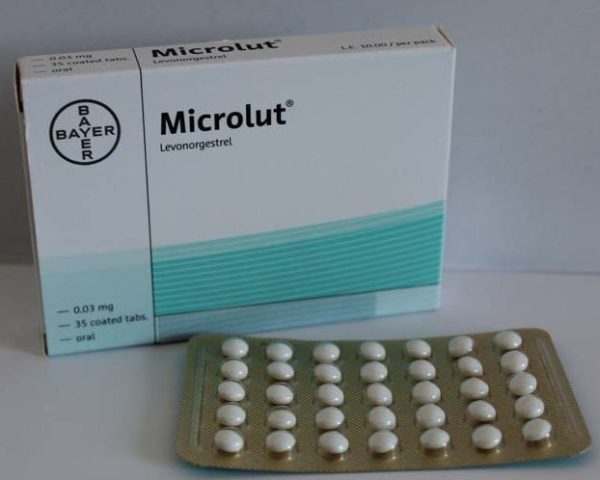
Microlut ®
The main component of the contraceptive is Levonorgestrel. The amount of active ingredient is minimal, so the tablets are well tolerated.
Suppresses ovulation. Reduces menstrual bleeding, eliminates menstrual pain. Microlut is not prescribed for liver diseases or bleeding from the uterus.
comparison table
Table 1 - Comparison of approved contraceptive pills for breastfeeding
| Name: | Active substance: | Mode of application: | Price: |
| Lactinet | Desogestrel | 1 tablet per day, 28 days | 650 rub. |
| Charosetta | Desogestrel | 1 tablet per day, 28 days | 1300 rub. |
| Exluton | Linestrenol | 1 tablet per day, 28 days | 2100 rub. |
| Microlute | Levonorgestrel | 1 tablet per day | Not for sale |
If side effects occur, stop taking the tablets. You need to consult a doctor who will select a different type of means or method of protection.
Subcutaneous implants for breastfeeding
As previously mentioned, subcutaneous implants are the most effective means of contraception for breastfeeding. An example of this is the Norplan, which is a small rod 4 cm long and 2 cm in diameter, which is inserted into the inside of the shoulder under local anesthesia.
The advantage of a subdermal implant is that you do not need to take pills every day. The drug independently releases progesterone hormones, which block ovulation. Norplan also has virtually no side effects.
The only drawback is the possible bleeding that may occur between periods. They usually last no more than 2 hours. You can use this drug 6 to 8 weeks after birth.
Subcutaneous implants, although they are the most reliable and safe means of contraception, cannot be used independently. A doctor's consultation is required, as well as close attention to your well-being, since 2% of women still experience side effects that require immediate cessation of the drug's effect on the body.
Prohibited pills
When breastfeeding, it is prohibited to take combination medications, no matter whether they are single-, two-, or three-phase. They significantly increase the amount of estrogen in a woman’s body. This negatively affects the physical development of the baby. COCs have many side effects.
The components of these drugs are excreted in breast milk, and the amount may decrease.
List of prohibited contraceptive pills: Jess, Logest, Lindinet, Silest, Zoeli, Qlaira, Dimia, Miniziston, Novinet, Mercilon, Janine, Femoden, Demoulen, Chloe, Tri-Mercy, Microgynon, Silhouette, Marvelon, Miniziston, Rigevidon, Belara, Lindinet , Regulon, Triquilar, Non-Ovlon, Tri-Regol, Ovidon, Trizeston.
Contraindications for use
Although tablets have many advantages over other methods of protection, they still have their disadvantages. For example, a significant disadvantage is the fact that the product does not in any way protect against diseases that are transmitted through intimate relations. It is worth telling in more detail about what contraindications to taking birth control pills may be:
- malignant tumors;
- epilepsy attacks;
- various heart pathologies;
- hepatitis of any form in the acute stage;
- pathology of the liver or kidneys.

If side effects occur in the first month, the oral contraceptive (OC) should be discontinued. You can start using tablets only after consulting a doctor, otherwise hormonal imbalance may occur. In addition, there are a number of side effects:
- formation of cysts in the ovaries;
- general malaise and feeling of nausea;
- attacks of headaches;
- the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases;
- thrush worsens more often;
- menstruation fails;
- skin oiliness increases;
- possible uterine bleeding;
- swelling of the extremities may occur;
- hair grows faster on legs;
- the mood changes often.
Some OCs have individual side effects, for example, acne or abdominal pain. Any side effects should decrease in intensity after three months of taking the pills. If this does not happen, you should change your contraceptive method.
We recommend reading: Diarrhea during breastfeeding in a mother
Rules for taking birth control pills during lactation
When taking birth control pills, a nursing woman must strictly follow the instructions and recommendations of the doctor.
- Preparations containing progestogen are started on the 21st day after birth.
- Do not increase or decrease the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Excessiveness will lead to unwanted side effects, and a small dose will not give results.
- Observe the timing of taking the drug: the 3-hour tablet (a traditional progestogen-only tablet) should be taken no later than 3 hours (after sexual intercourse) at the same time every day; The 12-hour tablet (progestogen-only desogestrel) should be taken no later than 12 hours at the same time every day [2].
- When conception is diagnosed, use is stopped (since the drugs have an abortifacient effect).
- Do not use during antibiotic treatment.
The effect of contraceptives on infants
Birth control pills that can be taken during breastfeeding should not contain estrogen. These hormones have a negative effect not only on the lactation process, but also on the baby, inhibiting its development.
A small amount of synthetic gestagen from contraceptives passes into breast milk. However, there is no evidence that it is dangerous for the child. Some babies under six weeks of age may have problems metabolizing hormones. For this reason, it is not recommended to start using hormonal contraceptives until your child is older. [9]
Oral contraceptives for breastfeeding
After the birth of a child, the life of a young mother changes completely - diapers, baby vests, feeding, bathing, etc. It would seem that there is not a single free minute. However, time passes, the baby grows up, life gradually returns to normal and it’s time to establish intimate relationships with your soulmate.
However, this can lead to a repeat pregnancy, which is undesirable for the first 6 to 12 months after the birth of the first child. Accordingly, a nursing woman faces the question: “What contraceptives can be used during lactation?”
Alternative methods of contraception
There are individual reasons when a woman breastfeeding a child should not take birth control pills. In this case, you need to choose alternative contraceptives when breastfeeding.
Barrier methods
Barrier methods - the use of condoms, diaphragms and caps. This contraception does not affect the functioning of the mammary glands, which is very important for nursing mothers. There is no effect on the baby. Before use, it is necessary to determine the size of barrier feminine products, since after the birth of the baby the size of the vagina has changed. To improve the effect, the use of spermicides is allowed.
Expert opinion
Sokolova L. S.
Pediatrician of the highest category
Contraceptive pills for breastfeeding may be inferior in effectiveness to barrier methods of contraception.
Birth control suppositories
The active substances of the suppositories are not absorbed into the blood, do not penetrate into the milk and do not affect the child. Some disadvantages lie in the chemical composition of the contraceptive: contraceptive suppositories for breastfeeding, when used for a long time, disrupt the vaginal microflora. Also, sexual intercourse itself depends on the duration of action of the drug - you have to wait until it takes effect. And after intimacy, you need to wait a certain period for hygiene.
Despite the inconvenience, contraceptive suppositories during breastfeeding have an advantage over oral contraceptives: they are not used regularly, but only when needed.
Intrauterine device
Experts are inclined to use the IUD because it has a high degree of effectiveness. What is better to use when breastfeeding - contraceptives or an IUD - is up to the mother to decide after consultation with a gynecologist. There are hormonal IUDs, they are also used to treat endometriosis. The spiral is installed for several years. It does not have any effect on the baby or lactation.
In the absence of contraindications, if the birth proceeded normally, this method may be used in the postpartum period. The spiral can be installed within 48 hours after birth, or after 4 weeks [10]. This method is not used after artificial birth (caesarean section).
Intrauterine devices do not protect against infections.
Calendar method
When using the calendar method, the estimated date of ovulation is calculated and abstaining from sexual intercourse on “dangerous” days. This method is ineffective. Out of 100 women, 9-40 will become pregnant.
Birth control pills are more effective during breastfeeding.
Contraceptives for nursing mothers
A few weeks after giving birth, the question arises of how to protect against unwanted pregnancy without harming the baby. There are some oral contraceptives that are allowed for breastfeeding. Let's review the drugs that a woman can use:
- Lactinet. The drug contains only synthetic progesterone, the main active ingredient here is desogestrel. The product increases the viscosity of cervical mucus and also inhibits the ovulation process. Although the main component penetrates into the milk, it does not cause any harm to the child, and in addition does not change the taste or smell of the milk. When using Lactinet, women did not notice a decrease in lactation.
- Charosetta. If a mother is looking for which birth control pills she can take while breastfeeding, this drug should be noted. When taking the tablet, the protective effect will be very high, while the drug does not in any way affect the amount of milk produced. The main active ingredient is also desogestrel. The dose is designed for 28 days, and the medication does not require a break in use.
- Exluton. Birth control pills with this name are not contraindicated during breastfeeding, and they provide a high guarantee of protection. This type of medication should only be used if you have a regular sexual partner. The drug has an effect on the endometrium, which prevents the egg from implanting in the uterine cavity; the main substance is called linestrenol. Application should begin on the first day of the cycle; subsequent doses are recommended to be taken at the same time. There is no need to take a break between packs.
- Femulen. The medicine contains progesterone of synthetic origin, its name is ethynodiol. The drug affects ovulation, thereby inhibiting this process in the body. The peristalsis of the fallopian tubes is significantly reduced, and the walls of the uterus become smooth, preventing the egg from implanting. Reception is started according to the instructions, and no break is required.
- Microlute. The main component of the tablets is levonorgestrel. The product has an effect on the cervical mucus, making it more viscous; it also inhibits the ovulation process and makes the endometrium of the uterus thicker.
We recommend reading: Monural during breastfeeding: is it possible for a nursing mother, instructions for use, reviews
Such contraceptives have a significant drawback: if you miss one pill, you will have to use additional methods of protection for a week. Instead of condoms, a mother can use birth control suppositories when breastfeeding, but she will have to choose a safe drug. When used correctly, hormonal drugs will not have a negative effect on the child, and can also improve problems with breastfeeding in a nursing mother.
But the patient must remember that any drug, especially hormonal, has a lot of contraindications for use, as well as a list of side effects. You should not prescribe medication yourself to avoid health problems.
What contraceptive drugs are allowed while breastfeeding?
Birth control medications that can be used while breastfeeding should not contain estrogen. This hormone disrupts lactation and slows down the development of the child.

Approved medications include one-component tablets with progestin (an analogue of the hormone progesterone). It is contained in tablets in a microdose - 300-500 mcg, which is why such preparations are called mini-pills.
Hormonal tablets with estrogen are approved for use when the child reaches six months.