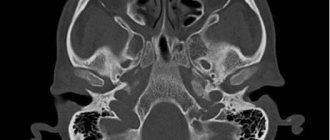
A contrast-enhanced CT scan involves examining the patient’s body using a minimal dose of X-ray radiation. Before such a diagnostic examination, it is necessary to inject a contrast agent into the human body. This is necessary in order to make tomography very accurate; contrast allows you to examine even the smallest tumors, metastases, blood clots and hematomas; this method is used when it is necessary to detail the pathology picture. CT with contrast significantly increases the contrast between normal and pathological tissues, which helps make a diagnosis at the earliest stages of the disease.
A contrast agent with CT allows one to identify the size and location of a particular pathology, as it accumulates in diseased tissues that are better supplied with blood.
Computed tomography with a contrast agent is also performed to examine the lymph nodes, blood vessels through which the iodine-containing drug moves. All areas that accumulate contrast agent are highlighted in white on computer images, which allows even small pathological changes to be immediately identified.
At the Yusupov Hospital, computed tomography is performed both with and without contrast, depending on the indications. Highly qualified doctors are able to decipher images very competently and quickly, as they have extensive experience in this field of activity. At the Yusupov Hospital, emergency CT scans are performed at any time of the day or night, including weekends.
What substances are used in contrast?
As a rule, various iodine-containing preparations are used for contrast CT to increase the contrast of the resulting images. Such substances are divided into two groups:
- Fat soluble;
- Water soluble.
Drugs of the first group are quite viscous, so their use is limited. Such substances are administered only locally, for example, into the abdominal cavity to identify fistulas, etc. If the patient needs a computed tomography scan with bolus contrast (intravenous administration of a substance using a special injector) or oral administration of a contrast agent, a water-soluble drug is used. The toxicity of such substances is very low, and these drugs penetrate the blood vessels very quickly.
In what situations is it prohibited to do a CT scan of the brain with contrast?
Despite the numerous privileges of the described examination, there are special restrictions for carrying out diagnostics with the introduction of an additional amplifier for a certain category of people:
- The presence of individual intolerance to the components of the contrast drug.
- The presence of chronic renal failure and myeloma.
- Problems with the thyroid gland.
- Severe stage of diabetes mellitus.
- The patient's condition is described in a clinical sense as severe (coma, connection to a ventilator, etc.).
How research is done
Computed tomography with contrast involves several ways of administering a drug. The choice of method depends on what exactly needs to be visualized. The contrast agent can be administered orally, intravenously, rectally, directly into an organ, or even into the pathological formation itself. And now in more detail about each individual method:
- Oral method. This method is most often used when examining the gastrointestinal tract; in such a situation, the patient drinks a contrast agent according to the recommendations specified in the instructions. The drug is quickly absorbed, and the resolution of computer images of the gastric mucosa is significantly increased, which allows the visualization of polyps or narrowings. A combination with intravenous contrast is often used;
- Intravenous administration. Computed tomography with intravenous contrast involves several types of injection of a substance into the patient’s body:
- The patient is injected into a vein immediately before the tomography;
- A computed tomography scan is performed without contrast, then the tomograph is stopped, the patient is given the drug intravenously, and the examination continues with a contrast agent;
- The contrast agent is administered as a bolus using a special syringe, or a drip is inserted, and the drug is injected slowly.
It is this technique that is most often used in leading clinics in Russia.
- Introduction of contrast into the lumen of the cavity. This method uses fat-soluble substances that allow visualization of the presence of fistulas, diverticula and other abnormal formations. In some cases, during diagnostic examination of hollow organs (for example, bladder, large intestine), a contrast agent is injected into them before performing the procedure. The harm of such contrasting will be much higher, since fat-soluble compounds have greater toxicity compared to water-soluble ones. But, despite this fact, problems with removing the drug from the patient’s body do not arise if all the recommendations of the radiologist are followed;
- Rectal. It is used for intestinal scanning, in which a contrast agent is injected once through the patient's rectum.
MRI and CT with and without contrast - what is the difference?
Check the possibility of treatment in this area at the moment
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are considered the most informative, safe and fast diagnostic methods in modern medicine. With their help, pathologies of various organs and systems are identified, the condition of the body is monitored during the rehabilitation period, and congenital anomalies are found. At CDC-24 you can undergo examinations using new generation tomographs, including MRI and CT with and without contrast
. The difference lies in the need to use medications that are administered intravenously or orally. Enhanced examinations are safe, but require certain preparation and are done exclusively as prescribed by a specialist: cardiologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, traumatologist, etc.
Why is contrast used in MRI?
In most cases, diagnostics using radio waves and magnetic fields is sufficient to detect abnormalities in internal organs, joints, brain structures and the spine. But sometimes there is a need to obtain the most accurate and detailed image, and then the doctor recommends a contrast method. The injected substance influences the properties of water molecules in the area under study, thereby improving visualization and making it possible to find the smallest anomalies due to the amplified signal.
Some people think that the main difference between an MRI with and without contrast is
is that enhanced diagnostics are harmful, but conventional magnetic resonance imaging is not. In fact, both procedures are safe, and the substances used do not affect the body in any way; their purpose is to “illuminate” the picture. They are quickly eliminated from the body and do not cause a hypersensitivity reaction (with rare exceptions). As for adverse reactions, they occur infrequently and disappear within 1-2 hours - as a rule, they are a slight headache, rashes and dizziness.
Depending on the area under study, enhancer substances may differ in composition (with iron oxide, manganese compounds, gadolinium, etc.) and method of use. Most drugs are administered by intravenous injection, but when studying the state of the gastrointestinal tract, oral varieties are used.
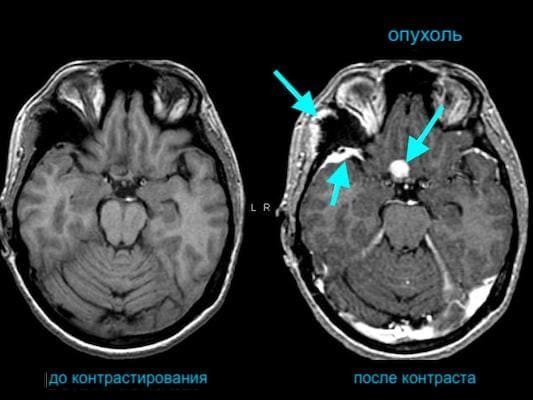
Does MRI without contrast show tumors?
It is possible to detect neoplasms without introducing special drugs into the patient’s body. However, in some cases, for example, with a small tumor or its complex location, amplification is required in order to most accurately determine the type and stage of the pathology. The study is also prescribed to determine malignancy and when deciding on surgical intervention.
Indications and contraindications
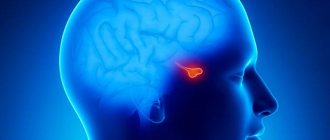
Enhanced MRI is performed on patients with suspected cancer, aneurysms, pituitary gland pathologies, as well as nerve damage and disorders of the cardiovascular system. Diagnostics allows us to identify necrotic lesions of soft tissues of any location, injuries of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus, diseases of the reproductive organs, lungs, liver, gallbladder and spleen, as well as degenerative changes in the central nervous system.
Indications for the examination include:
- convulsions, migraines, frequent fainting;
- decrease or loss of hearing, vision;
- palpable neoplasms in the neck area;
- arthrosis of joints, hernias, protrusions;
- multiple sclerosis;
- joint pain;
- muscle atrophy, paralysis, paresis of the lower and upper extremities;
- infectious lesions of the brain or spinal cord;
- neoplasms in the chest, pelvic organs and gastrointestinal tract;
- infertility in men and women.
There are no restrictions on the frequency of the procedure - it is prescribed as many times as required for effective treatment of the patient. Before conducting diagnostics at CDC-24, it is mandatory to check for contraindications, which include:
- pregnancy, regardless of trimester;
- individual intolerance to contrast agent;
- chronic heart failure;
- serious diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system;
- the presence of metal objects and devices in the body;
- fear of closed spaces.
MRI with and without contrast: which is better?
Both methods are effective and safe, and their differences are due to the use of drugs that enhance the signal. Compared to conventional magnetic resonance imaging, enhanced MRI:
- Lasts longer - the patient will have to stay 30-40 minutes longer inside the tomograph.
- Allows you to get more detailed pictures.
- May cause minor allergic reactions.
- Provides additional information about the state of the structures under study.
- Requires large financial costs.
- Assumes compliance with additional training recommendations.
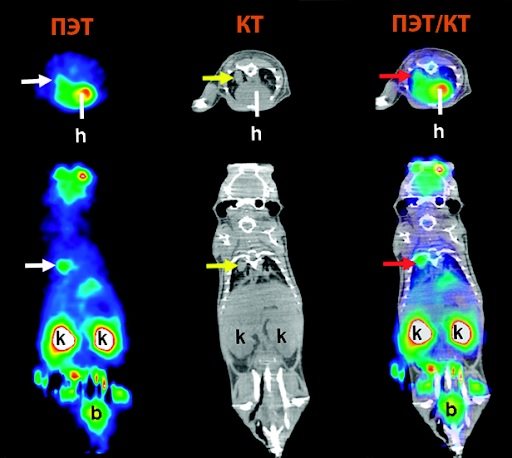
PET CT, CT with and without contrast: what studies show, what are their differences
If we are talking about injuries and diseases of dense structures, then patients are prescribed computed tomography and PET CT, and CT can also be performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. In the first case, the radiologist studies the anatomical features of organs and tissues, using signal-enhancing drugs if necessary, and in the second, he determines deviations in dynamics by examining functional activity. Positron emission tomography is considered the most advanced method and provides more information than CT with contrast. The disadvantages of the examination include its duration (and the patient must remain motionless during the entire diagnosis) and high cost.
Conclusion
To summarize, we can say that the difference between MRI, CT with and without contrast
lies in the quality of visualization. Enhanced examination makes it possible to detect pathologies at the initial stage and is indispensable in differential diagnosis. Most often, the procedure is performed on patients with cardiac, neurological symptoms, as well as malignant and benign neoplasms. When contrast is administered, the examination takes longer and in some cases may be accompanied by side effects.
Patient preparation
Preparation for a computed tomography scan with a contrast agent is almost the same as without it. It does not require much effort and consists of the following measures:
- It is forbidden to eat food 4-8 hours before the procedure, it all depends on the area being examined;
- When examining the gastrointestinal tract, you should stop taking medications that reduce gas formation;
- You should come to the examination in loose clothing;
- Before tomography, all metal products, as well as removable medical devices, must be removed;
- It is also necessary to warn the doctor about the medications the patient is taking.
When is a brain MRI prescribed?
The presented examination method, which allows you to obtain maximum information, is prescribed by doctors in the following situations:
- Probability of oncology formation.
- Constant pain in the head area.
- The presence of dizziness and fainting.
- Previously suffered a stroke.
- An MRI of the brain with contrast will help understand the cause of the loss of hearing and visual ability.
- Damage and swelling.
- Reduced degree of memorization of various events.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Inability to perform a computed tomography scan with contrast.

Who is the study contraindicated for?
There are significantly more contraindications to contrast-enhanced computed tomography than to conventional tomography. It is not recommended to use this method in the following cases:
- Allergy to contrast agent;
- Pregnancy even in very early stages;
- A history of diabetes mellitus;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Diseases of the reproductive system;
- Large body weight (more than 150 kg), since the device is not designed for such weight;
- Minors;
- Patients with mental disorders;
- People suffering from claustrophobia.
If the procedure was performed on a nursing mother, she should stop breastfeeding for two days, as a small amount of the contrast agent may pass into the woman’s milk. In some cases, children and violent patients are prescribed light medicated sleep.

Is CT scanning with contrast dangerous?
In the absence of contraindications to CT and contrast, the examination is not dangerous for humans. In rare cases, patients experience allergic reactions. Which are easily removed with antihistamines or go away on their own after the contrast is removed. As for radiation exposure, modern drugs have a slightly greater effect on the human body than conventional household appliances. However, it should be remembered that it is not recommended to undergo examination more than twice a year. Only the attending physician can decide how often a CT scan can be done.
Where to do in Moscow
The Yusupov Hospital provides its clients with the opportunity to perform the highest quality research using innovative equipment.
Multislice computed tomography allows you to safely scan any part of the patient’s body. Such a device minimizes X-ray radiation for humans.
The Yusupov Hospital employs true professionals in their field who collaborate with the best European colleagues.
The hospital has polite medical staff who will be happy to answer your questions and also provide a comfortable atmosphere in the institution.