Female reproductive system: a little physiology
Ovaries (lat. ovarium) are paired female genital organs in which the development and maturation of the egg occurs.
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, follicle-stimulating hormone is produced. This hormone stimulates the ovaries to synthesize follicles that contain immature eggs, and also promotes the production of estrogen. The follicular apparatus is formed during the intrauterine development of the fetus.
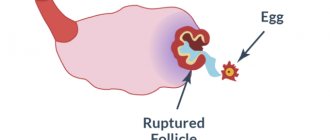
As a rule, one of these follicles becomes “dominant” and when the required size (15-18 mm) is reached, the development of the remaining follicles stops and their atresia (reverse development) begins. Soon the “dominant” follicle bursts, releasing a mature egg, which leaves the ovary. This is ovulation.
On the day of ovulation, there is a decrease in basal temperature, an increase in progesterone levels, and an abundance of vaginal discharge. In rare cases, a woman may feel a short-term nagging pain in the lower abdomen. When there are hormonal imbalances in the body, the follicle does not rupture, or follicles are not synthesized at all. Ultrasound folliculometry is an informative diagnostic that helps monitor egg maturation.
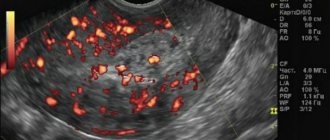
Dominant follicle in the ovary
Cyclic changes in a woman’s reproductive system that ensure the development of pregnancy also include the phases of maturation of follicles in the ovaries. In the early stages of the cycle, several follicles begin to mature at once, and only one of them (rarely more) overtakes the rest and subsequently reaches the stage of ovulation. This is the dominant follicle. How is a dominant follicle formed in the ovary? Can there be two dominant follicles at once?
Follicles before and during puberty
Even in the embryonic period, follicles are formed in the female body. Of the approximately two million follicles that are present in a girl’s body immediately after birth, only 200-300 thousand remain until puberty, the rest are absorbed. The role of follicles is that the egg matures in them. In addition, follicle cells produce hormones - estrogens, which are directly involved in the processes of reproduction.
Dominant follicle in the ovary
The dominant follicle is the most developed follicle preparing for ovulation. Usually only one dominant follicle is determined in the left or right ovary. However, there are situations when the dominant follicle of the right ovary and the dominant follicle of the left ovary develop simultaneously.
By the time of ovulation, the dominant follicle has a diameter of 18-22 mm. When, under the influence of estrogen, luteinizing hormone is released and the follicle ruptures, ovulation occurs. If the dominant follicle in the right ovary and the left develop simultaneously, after ovulation two eggs are released at once, and a multiple pregnancy may occur. 2 dominant follicles are the cause of twin pregnancy.
The dominant follicle can further develop in two ways:
| increase in size of the follicle, its rupture (ovulation). Normally, the process occurs in exactly this way, and on days 12-18 of the cycle, ovulation occurs, and a corpus luteum is formed in place of the follicle, which plays a hormone-producing role; |
| if the follicle does not rupture, it further increases in size, transforming into a cyst. In this case, the egg is not released. A menstrual cycle without ovulation is called anovulatory. |
In a woman, ovulation can occur in both ovaries, and normally this process develops alternately. However, it has been proven that the dominant follicle in the right ovary develops more often. This explains the fact that ectopic pregnancy most often develops in the right fallopian tube. Moreover, it is the right ovary that is more prone to the development of follicular cysts.
Violation of the development of the dominant follicle
A common cause of infertility is the ovarian factor, which is a disruption of the ovulation process. Often, due to certain changes (usually hormonal) in the body, the development of the dominant follicle is disrupted. To diagnose such disorders, an ultrasound examination is performed.
The follicles are very clearly visualized, and the specialist can give the following conclusion:
| normal ovulation; |
| follicle persistence; |
| follicle regression; |
| follicular cyst. |
The dominant follicle in the ovary immediately precedes the development of pregnancy. It is from them that the egg is released, ready for fertilization. When the follicular wall ruptures, the egg enters the abdominal cavity. When exposed to pressure differences and characteristic movements of the villi of the fallopian tubes, the egg moves into the fallopian tube. It is in the tube that fertilization of the egg normally occurs. When moving into the uterine cavity, the embryo goes through the initial stages of development; during this period, under the influence of hormones, the structure of the endometrium changes: it becomes loose, ideal for implantation of the embryo and its trophism. With the normal development of all these complex processes, pregnancy occurs.
The Russian Oocyte Donor Center offers a wide selection of donors to women in need of infertility treatment using donor eggs. Contact you - and we will definitely help you!
Folliculometry: what is it?
This is monitoring using sonography (ultrasound). It monitors not only the state of the follicles located in the ovaries and their further transformation into the corpus luteum, but also changes in the uterus. Folliculometry is prescribed at the slightest suspicion of ovulation disorders and is an alternative to the introduction of basal temperature charts. The procedure uses a sensor and an ultrasound scanner. Ultrasound folliculometry is usually necessary for women with various menstrual irregularities, as well as the inability to conceive for more than six months of active intimate life.
Medical prescriptions after ultrasound diagnostics
Usually, if the ovaries do not function normally, this is an indicator of the presence of a hormonal imbalance in the female body. In this case, the doctor prescribes additional blood tests to confirm the state of hormonal levels. Based on the results of the tests, drug therapy is prescribed, which after a certain period of time will help the woman become pregnant, carry and give birth to a baby.
In cases where there is a disturbance in the corpus luteum, the gynecologist may prescribe the use of progesterone-based medications. During anovulatory periods, medications are prescribed to stimulate ovulation. When determining endocrine infertility, when drug stimulation has not shown positive dynamics, the patient is offered IVF (in vitro fertilization).
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Folliculometry: indications for use
- Confirmation of the normal course of ovulation, or its absence.
- Finding out the day of ovulation, as well as the so-called fertile days.
- Control of the structure and function of the ovaries.
- Diagnosis of infertility.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Determination of the effect of hormonal drugs on the ovaries.
- Assessment of the menstrual cycle.
- Diagnosis of certain diseases of the reproductive organs (PCOS, cysts, fibroids). Determination of types of cysts.
Why is folliculometry needed?
- determines the absence or presence of ovulation;
- allows you to set ovulatory days;
- helps determine the most favorable day for conception;
- identifies the need to stimulate ovulation;
- assesses the level of ovarian functionality;
- helps determine the best days to conceive a boy, since it has been established that the likelihood of having a male baby increases several times if he was conceived a few days before or after ovulation;
- increases or decreases the possibility of multiple pregnancy;
- determines the degree of completeness of the menstrual cycle or the reasons for its failure;
- as a means of monitoring the condition of the reproductive organs during treatment, including homeopathy;
- allows you to identify some diseases of the female organs.
Folliculometry: on what day of the menstrual cycle?
The attending physician decides on what day folliculometry is performed. As a rule, the study is scheduled on days 8-10 of the menstrual cycle (with an ideal 28-day menstrual cycle).
In the first days of the cycle, it is impossible to predict whether ovulation will occur or not, since the follicles are just beginning to develop and their size does not exceed 2 mm. However, at this stage it is possible to find the remaining follicle from the last menstrual cycle that has developed into a follicular cyst. During initial ultrasound folliculometry, a newly formed cyst can be confused with a “dominant” follicle. Thus, ultrasound monitors the number of follicles, as well as the condition of the endometrium of the uterus.
Subsequent ultrasounds occur at intervals of 3 days until the fact of ovulation is established. With a 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs, on average, on the 14th day. In this case, the size of the dominant follicle is up to 25 mm, and the endometrium of the uterus is up to 12 mm.
If a woman’s menstrual cycle is shorter than 28 days, then an ultrasound is prescribed earlier than the 8th day of the cycle. If longer than 28 days, then later.
Please note: the above schedule is approximate. On what day to do folliculometry, the attending physician can tell you with certainty.
Control ultrasound
In order to know as accurately as possible whether ovulation has occurred or not, it is necessary to perform a control ultrasound examination, because the presence of an already mature large follicle does not guarantee the breakthrough of its capsule and the release of the egg. Control diagnosis is carried out on the third day after the planned ovulation. The specialist examines the condition of the ovaries as carefully as possible and determines whether ovulation has taken place or not based on the following signs: the absence of a mature follicle, the presence of a corpus luteum, and a small amount of fluid forms in the retrouterine space.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
It is important to understand that a control ultrasound must be done strictly after 3 days, otherwise it will no longer be possible to visualize the fluid and the corpus luteum.
Folliculometry: preparation for the procedure
When preparing for ultrasound folliculometry, the following rules are observed.
- The day before the examination, it is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods that cause increased gas formation in the intestines (alcohol, cabbage, legumes).
- For transabdominal ultrasound, you need to drink 0.7 liters of water an hour before the procedure. When the bladder fills, the pelvic organs are visualized.
- With the transvaginal form of ultrasound (using a vaginal sensor), the bladder, on the contrary, must be emptied.
Folliculometry - cost of the procedure
Many clinics in the country have added folliculometry to the list of services offered. One of the popular ultrasound procedures in the capital and other cities is folliculometry, the cost of which varies depending on the selected medical center and the location of the clinic where folliculometry is performed. The cost is indicated in the clinic’s price lists, indicating the number of procedures for this price. You can also find out about the folliculometry service and the cost of the procedure by calling the clinic.
Folliculometry: how it is done
Ultrasound is performed in two ways:
- The transabdominal method is used for girls who have not had sexual intercourse. The woman lies on her stomach, opens her stomach and lower pubic area. A special gel is applied to the sensor, after which ultrasound folliculometry is performed. /li>
- The transvaginal method is used for women who are sexually active. A woman needs to take off her underwear, lie on her back, and then bend her knees. The sonologist places a condom on the vaginal probe and inserts it into the vagina.
Diagnostic results
The key “points” listed above allow us not only to draw conclusions about the functioning of the reproductive system, but also to prescribe the correct treatment.
The results of folliculometry, carried out to determine the presence of ovulation, are interpreted immediately: the size of the follicle and the synchronism of its growth in comparison with the endometrium are assessed. And during the ovulation phase, the latter can be recorded by immediately drawing conclusions about whether the size (thickness) of the endometrium corresponds to the norm at the time of ovulation. It is believed that, with the “correct” structure, the thickness of the endometrium at the time of ovulation should not be less than 7.5 mm. With less thickness, the likelihood of implantation of the fertilized egg is sharply reduced, although it is possible. Typically, ovulation is recorded when the follicle reaches a size of 22-24mm. If there are no signs of ovulation at a larger size, during the observation process a conclusion is made about anovulation, which naturally affects treatment tactics.
Folliculometry in the IVF protocol is carried out to monitor the growth in the size of the follicles and endometrium, dose adjustment of gonadotropins (“stimulants”) and the timely administration of additional drugs (GnRH antagonists to prevent premature ovulation or trigger final follicular maturation). Failure to prescribe this or that drug in a timely manner may result in failure of the protocol and lack of results. It is customary to prescribe antagonists when follicles reach a size of 14 mm, and a trigger - when the diameter of most follicles is 18 mm.
Don't waste time! Make an appointment now!
By clicking the “Submit Application” button, you consent to the processing of your personal data in accordance with the terms
Privacy Policy and User Agreement
* - required fields
Signs of ovulation
- Registration of a “dominant” mature follicle immediately before ovulation.
- Reduction of the follicle in size, deformation of its walls, complete disappearance.
- After a few days, a corpus luteum, the size of which does not exceed 20 mm, forms in the ovary from which the egg was released.
- The presence of free (follicular) fluid in the posterior uterine space.
To confirm pregnancy, a week after ovulation, a woman’s blood is taken for progesterone. If progesterone is higher than normal, it means ovulation has occurred.
Physiology of folliculogenesis
The first day of the menstrual cycle is considered to be the first day of the onset of menstruation. After this, under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), several follicles begin to develop simultaneously in the ovaries. However, very soon one of them (much less often two or more) begins to outstrip the others in development - this is the dominant follicle. At this stage, its size exceeds 1.5 centimeters, and other follicles undergo reverse development (atresia). Changes in the size of the dominant follicle daily are approximately 2-3 millimeters and by the time of ovulation, which occurs under the influence of the peak release of luteinizing hormone, it has an average diameter of 1.75 to 2.4 centimeters. After ovulation, the process of formation of the corpus luteum begins - a temporary endocrine gland that produces progesterone, which, in the case of fertilization of the egg and successful implantation of the embryo, supports pregnancy until the formation of placental tissue.