Ultrasound of the vessels of the penis, Doppler ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound is a diagnostic study of the vascular system using ultrasound, based on the Doppler effect. The procedure is based on the ability of ultrasound to be reflected from moving blood cells, which makes it possible to assess the speed and quality of blood flow, vascular patency, and the condition of the vascular walls.
Where to do an ultrasound of the vessels of the penis
You can undergo an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the penis in the MedCentreService network of clinics. Patients of a medical institution receive many benefits:
- Accurate results. Medical centers are equipped according to modern medical standards.
- Competent approach, individual relationships. All medical personnel are highly qualified and have extensive experience.
- Convenient location and comfortable environment. The clinics are equipped taking into account the wishes of patients of different ages.
- Loyal pricing policy.
Another advantage is the quick result, which will be ready immediately after diagnosis. If desired, the patient can immediately contact a urologist-andrologist for deciphering and prescribing treatment measures.
Who needs an ultrasound of the penis?
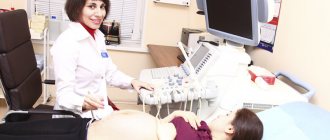
A man enters the office and the doctor invites him to lie down on the couch. Examination of the genital organs in men requires their exposure. The specialist will apply a hypoallergenic gel to it and begin an ultrasound of the genital organs. The gel helps the device come into tight contact with the skin so that no air gets in. An ultrasound of the female genital organs is done in the same way.
The sensor is moved over a man's skin to:
- Completely visualize the structure of the genital organs. Doppler spectra of deep arteries are recorded. If necessary, doctors make an erection using pharmacological agents and analyze how the blood flow moves in the cavernous bodies and its inflow in the arteries;
- A tourniquet will be placed on the penis;
- They will introduce Vazoprostan with Caverject;
- It will enter another corpus cavernosum and an erection will occur. An ultrasound of the penis will be performed again, supplemented with Doppler mapping. Thanks to self-stimulation, the pharmacological effect is removed.
In order for the patient to perform the last manipulation independently, the doctor will tactfully leave the office. A man may subjectively feel some discomfort due to an injection into the penis. It also happens that the erection is partial. Then the patient independently makes it complete and is ready for examination.
After all procedures, urologists tell men that an erection should not be allowed to last more than 4 hours. Erectile functions may be lost.
What does an ultrasound scan of the penis show?
During the examination of the penis, the doctor examines the cavernous bodies and the blood vessels communicating with them. The speed of blood flow in the vessels is assessed during rest and during erection, and the doctor also measures the diameter of the arteries, their patency, and the elasticity of the vascular walls.
Using ultrasound of the vessels of the penis, the following abnormalities can be detected:
- Causes of erectile dysfunction.
- Consequences of mechanical injury.
- Impaired urethral patency.
- Pathology of the vascular system.
- Inflammatory process in the urethra.
Ultrasound is a highly informative diagnostic method, while being safe and painless. The patient can undergo testing as often as necessary. Therefore, the procedure is often prescribed during treatment to monitor effectiveness.
Ultrasound of the penis in Lyubertsy
Ultrasound of the penis is a diagnostic procedure, which is classified as a urological ultrasound, which allows you to obtain information about the condition of the male genitals and the presence of pathologies or diseases.
The study is publicly available and absolutely safe, often has no alternative, and can be administered many times without harm to health.
Such ultrasound diagnostics is almost never prescribed as an independent procedure; in most cases, ultrasound is complemented by Doppler ultrasound.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the penis if the following pathologies are suspected:
- Erectile disfunction.
- Peyronie's disease. A fibrous change that causes curvature of the penis.
- Penile fracture.
- Urethral rupture. Trauma to the urethra.
- Priapism. Pathological erection not associated with sexual arousal.
- Urethral stricture. Narrowing of the urethra due to injury or inflammation.
- Chronic urethritis. Sluggish inflammation of the urethra.
It is recommended to undergo diagnostics if the following symptoms appear:
- Lack of erection, or weak erection, during which sexual intercourse is impossible.
- Pain in the penile area, both at rest and during arousal.
- Burning and pain during ejaculation and urination, in the absence of obvious signs of the inflammatory process.
- Difficulty urinating and split urine stream.
- Infertility due to the health of the testes and prostate gland.
Temporary contraindications to the procedure:
- blockage of blood vessels in the penis;
- acute inflammatory process;
- damage to the skin of the penis with ulcers, open wounds;
- low blood clotting.
In such cases, it is impossible to conduct a study, or the scan will simply be uninformative. It is recommended to correct these conditions and then go for an ultrasound.
Ultrasound monitoring of the penis
Vilner E.L., Andreychikov A.V., Zhestovskaya S.I.
Krasnoyarsk State Medical University named after. prof. V.F. Voino-Yasenetsky,
rector - doctor of medical sciences, prof. I.P. Artyukhov;
Regional Clinical Hospital, chief physician -
B.P. Mashtakov
Relevance.
Ultrasound examination of the penis, of course, is of leading importance in the diagnosis of diseases of the penis, identifying the degree of their activity and differential diagnosis of the etiology of erectile dysfunction.
Material and methods.
The studies were carried out on an ultrasound scanner “LOGIQ-3”, with a linear multi-frequency sensor 7.5-12 MHz. From 2006 to 2008 examined 289 patients (379 studies) who applied to the clinic of the Krasnoyarsk regional hospital mainly with complaints of erectile dysfunction of varying severity (ED; 236 people; 81.7%), of which 54 patients also noted deformities of the penis (penile deformities without ED - 2). Pathology of the foreskin, urethra, and focal formations of the corpora cavernosa were detected extremely rarely.
results
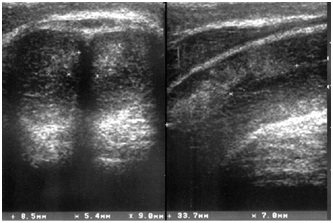
. In patients with complaints of ED, in 144 cases (49.9% of all patients; 61% of those complaining of ED), diffuse fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa was detected, visualized as multilocular hyperechoic inclusions in the tissue of the cavernous bodies with a diameter of up to 0.15 cm (Fig. . 1). The overwhelming number of patients complained of a sluggish, quickly stopping erection. 78 of them (54.2%) suffered from type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figure 1. Diffuse fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa
In 4 (1.38%) patients who suffered priapism, massive local fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa was detected in the form of extended areas of medium echogenicity without clear contours from 0.5 to 4 cm. A similar ultrasound picture occurred in 10 (3.5%) patients after injuries (bruises, “fractures”) of the penis in the stage of organizing hematomas (injury more than 30 days ago). It was noted that the greatest echographic changes in the structure of the cavernous bodies are observed after the use of intracavernous injections of erectogens for 6 months. and more (Fig. 2,3).
Of the 80 patients examined using vasoactive drugs, 35 were diagnosed with arteriogenic erectile dysfunction, 5 with venous and 5 with a mixed form of erectile dysfunction.
Post-traumatic hematoma (less than 7 days after injury; 10 patients – 3.5%;) was visualized as irregularly shaped foci of reduced echogenicity with clear contours, measuring 2-4.5 cm (Fig. 4, 5)
Figure 2. Local fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa after priapism | Figure 3. Massive fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa (middle third) after priapism |
Figure 4. Penile hematoma | Figure 5. Organized hematoma of the penis. Longitudinal (right) and transverse (left) scanning |
Peyronie's disease
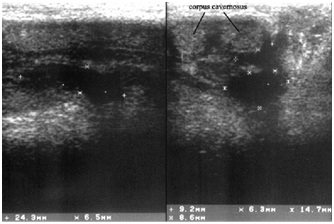
(fibroplastic induration of the penis) was diagnosed in 56 patients (19.4%). Of these, in the majority (41.1% - 23 people) the plaque was localized proximally, in 35.7% (20 patients) distally, in the rest - in the middle sections of the penis (Fig. 5). Fibrous plaques were located with equal frequency along the dorsal surface and on the lateral surfaces of the corpora cavernosa. In 6 cases (10.7%) signs of activity were detected in the form of an anechoic rim and perinodular vascularization in CDK and ED. During dynamic observation of the majority of patients in this group, in half of the cases negative dynamics were revealed in the form of an increase in size and the appearance of new plaques (Fig. 6). Only two patients with Peyronie's disease did not complain of ED.
Focal formations of cavernous bodies of unknown origin were found in 3 people (1.2%). Lipomas of the foreskin were diagnosed in 2 patients, oleogranulomas - in 4 patients.
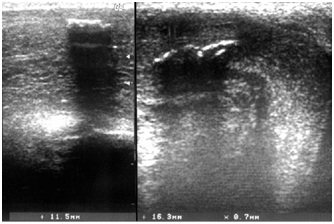
Thrombosis of the superficial dorsal vein was detected in 3 patients (in 2 of them in combination with phleboliths; Fig. 7). Dynamic observation showed lysis of the thrombus and restoration of blood flow through the vessel after 14-24 days.
20 patients with ED had previously undergone penile endothesis with a rigid prosthesis. In 7 of them, prolapse of one or both penile prostheses into the head of the infarct was detected (Fig. 8, 9).
Papillomas were detected in 2 patients, strictures in 2 and calcifications of the corpus spongiosum of the pendulous urethra in 1.
Figure 6. Localization of plaques in Peyronie’s disease in the middle third (left) and proximal parts (right) of the corpora cavernosa | Figure 7. Thrombosis v. dorsalis penis |
| Figure 8. Falloendoprosthesis (longitudinal scan) | Figure 9. Prolapse of the right phalloidal endoprosthesis into the head (the arrow marks the phallic endoprosthesis of the right cavernous body |
Conclusion
The absence of changes in the ultrasonic structure of penile tissue was recorded only in 28 examined patients (9.7% of all examined; 11.9% of all examined with ED), mainly in patients under 25 years of age. Echostructural changes in the form of fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa of a diffuse nature were noted in the vast majority of cases.
Most pathological processes, such as Peyronie's disease, cavernous fibrosis, priapism, tumors, and traumatic lesions have a characteristic ultrasound pattern, which is very important for their differential diagnosis.
The use of color Doppler mapping and power Doppler studies allows us to identify microvascularization around plaques in Peyronie's disease and thus makes it possible to determine the activity of the process, which in turn makes it possible to predict the course of the disease.
Erectile dysfunction in various diseases has a combined etiology. For example, in diabetes mellitus there is a combination of factors detected by ultrasound (vascular disorder and loss of sinusoidal elasticity). Our data generally confirm the maxim known from the literature that the severity of ultrasound changes in penile tissue largely reflects the prognosis of the course of the underlying disease - diabetes mellitus. Considering the corpora cavernosa of the penis as a “mirror” of the state of the vascular bed of the body as a whole, we can say this with confidence.
Bibliography
- Prives M.G., Lysenkov N.K., Bushkovich V.I. Human anatomy. 11th ed., revised. And additional St. Petersburg: Hippocrates, 1998. pp. 335-337.
- Guide to Andrology / Ed. Tiktinsky O.L. L.: Medicine, 1990. P. 185-205.
- Mazo E.B., Zubarev A.R., Zhukov O.B. Ultrasound diagnosis of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. – M.: Medicine, 2003.
- Zubarev A.R., Koryakin M.V. Ultrasound diagnosis of venous and corpovenous insufficiency of the penis // Ultrasound diagnostics. – 2000. – No. 2. – P. 56-61.
Preparation and performance of ultrasound of the vessels of the penis
The procedure does not require special preparation; it is enough to wash the genitals before the examination. To get the most accurate result, you should not take medications that affect the functioning of blood vessels on the day of diagnosis, as well as smoke, drink alcohol, coffee, tea and energy drinks.
The research is carried out in the following order:
- The patient undresses from the waist down and sits on the couch.
- The penis is lubricated with a water-based gel for better conductivity.
- An ultrasound sensor is applied to the penis and moved around the entire perimeter to study the state of the vessels at rest.
- Using the drug Caverject, a rush of blood and an erection are provoked, then the condition of the blood vessels is examined again. The drug is injected into the penis.
After the procedure, an erection may persist for some time, this is due to the effect of the drug. The patient can relieve tension through masturbation.
The ultrasound procedure takes 30-40 minutes. The results are given to the patient immediately.
What do they look for on an ultrasound of the penis?
Ultrasound provides a valuable opportunity to assess the underlying changes occurring in the structure of the penis, as well as to see the condition of all parts of the penis (spongy and cavernous bodies, tunica albuginea, arteries and veins).
If you examine the male genital organ using ultrasound, you can:
- identify neoplasms of the urethra and penis or ensure their absence;
- identify vascular thrombi;
- not only assess the condition of the organ, but also see the beginning changes in it;
- if formations are present, examine their structure and determine the quality of the process.
Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels is a diagnostic method that is highly informative. It is a combination of ultrasound diagnostics and the Doppler method. It is he who allows the urologist to find out:
- about the level of vascular tone;
- about the condition of the vascular walls, their elasticity or structural changes;
- about the characteristics of arterial inflow and venous outflow of blood from the organ;
- about the speed of blood flow.
Thus, Doppler ultrasound plays an important role in determining disruptions in blood flow. And if the blood flow through the vessels supplying blood to the penis is reduced, or the outflow of blood is impaired, then problems with the functions of the organ cannot be avoided.
Where can I get an ultrasound examination of the genital organs?
Male genital disease is a serious problem that needs to be solved quickly and effectively. Without an ultrasound of the scrotal organs, this issue cannot be resolved. You can, of course, seek help at a local hospital, but everyone knows what equipment and attitude they have towards people, so today more and more people prefer to turn to the services of private specialists.
An ultrasound of the penis can be done immediately upon arrival at the clinic. Thanks to the use of the latest equipment, doctors quickly obtain highly accurate research results and make the most accurate diagnoses.
Ultrasound ultrasound standards
The highest speed of blood flow during contraction, at rest, in the arteries of each of the structural parts of the penis is 15-25 cm/s. At the beginning of the process of blood filling the cavities, the speed is more than 35 cm/s, but with a full erection it drops slightly. If the values are less than normal, we are talking about arterial dysfunction. During systole, significant arterial resistance should be observed.
- The final speed of blood flow through the arteries in diastole is approximately equal to 0, but during an erection it will be 10 cm/s or more.
- Pulsatility index is normally more than 4.
- Resistance index - at rest should be more than 0.8, at the beginning of an erection it decreases by 0.1 or more, but then reaches 1.0.
The blood flow in the deep dorsal vein is determined - when the drug is administered in a state of full erection, the outflow of blood should completely stop. If it persists even to a small extent, this is a sign of erectile dysfunction.
Indications for the study
Erectile dysfunction is one of the indications for Dopplerography of the vessels of the penis
Erectile dysfunction of any origin.
- Congenital and acquired injuries and deformations of the penis. Curvature and the like.
- Volumetric neoplasms of the penis. Tumors can directly affect the nature of vascularization of the “genital organ.” In addition, the degree of blood supply to the neoplastic structure itself is determined. This is important for identifying the type of tumor process.
During the study, the following changes can be detected in the penis and its structures:
- disturbances in the blood supply to the cavernous bodies with arterial blood;
- change in the speed of venous outflow;
- compression of the vascular structures of the penis;
- narrowing of the veins and arteries of the penis;
- decreased elasticity of veins and arteries;
- the presence of foreign bodies and cicatricial changes in the structure of the urethral canal;
- atherosclerosis of the penis, fibrosis of anatomical structures.
Description of the study
The patient undresses, takes off his underwear and lies down on the couch. The doctor lubricates the penis area with a special gel and applies an ultrasound sensor. By its nature, Doppler ultrasound is a variation of vascular ultrasound. After a thorough examination of the non-erect penis, a special drug is injected into the corpora cavernosa to cause a spontaneous erection.
Unlike a normal erection, an induced erection does not begin as quickly and develops over a longer period of time, thanks to which a diagnostic specialist can track the nature and intensity of blood flow in each phase. The duration of the study is 30-40 minutes. Measurements are taken every 3-5 minutes, after which the doctor records the results in a protocol.
Instead of injecting the drug into the organ area, it is possible to take Viagra and its analogues. The use of sedative pharmaceuticals is not recommended, since there is a high risk of stopping potency. Depending on the clinic, other methods of stimulation are also possible, for example manual stimulation, viewing pornographic materials. However, these methods do not give a reliable result: natural erection is unstable and develops rapidly, so there is no way to study each of its phases. In addition, the procedure lasts 30-60 minutes; it is impossible to maintain potency for such a long time naturally.
The results are given to the patient 20-30 minutes after the examination is completed. As a result of the manipulation, the following diseases and pathological conditions can be identified:
- injuries of vascular structures (venous and arterial);
- thrombosis of the great vessels of the penis;
- cavernous fibrosis;
- neoplastic processes in the penis;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the penis (as a result of occlusion or stenosis);
- Peyronie's disease (curvature of the penis).
When is an ultrasound of the penile veins prescribed?
- curvature or shortening of the penis;
- pain during urination or sexual intercourse;
- erectile disfunction;
- swelling of the penis;
- suspicion of a foreign body in the urethra;
- the presence of tumors and formations of unknown origin;
- penis fracture;
- preparing the patient for surgery;
- assessment of the patient's condition after the operation;
- for monitoring and assessing the condition of the penis during therapy.
What will a testicular ultrasound show?
During the procedure, the doctor evaluates:
- organ structure, shape, size of the testicles, clarity of contours;
- echogenicity;
- amount of free liquid;
- whether there are new formations in the area of study, and if so, then their number, density and structure;
- The vascular network and its symmetry are assessed.
If a detailed analysis of blood vessels is necessary, Doppler is used. Using an ultrasound scan of the scrotum and testicles, the following pathologies can be diagnosed: Cryptorchidism - absence of a testicle. During an ultrasound in such a situation, the doctor clarifies the location of the disappeared testicle. With such problems in the male body, the testicle is most often retained in the abdominal cavity. It is usually found in the inguinal canal. As a rule, it is reduced and does not have a clear contour, the structure is heterogeneous. Varicocele is another pathology that can be detected using ultrasound. This problem is associated with varicose veins of the seminal canal and requires immediate treatment as it can lead to infertility in men. An ultrasound of the testicles with this disease clearly shows veins, the thickness of which exceeds 3 mm. Hydrocele or dropsy . With this pathology, fluid accumulates between the two layers of the testicular membranes. The disease can be acquired and manifest after injuries, inflammatory processes and surgical interventions, as well as congenital. Hydrocele is diagnosed by ultrasound without much difficulty. Sometimes this anomaly occurs in the form of a figure eight and is multi-chambered. Cystic neoplasms of the testicle and its epididymis can be congenital, then on ultrasound they usually appear as small formations, and the fluid contained in them is transparent. Acquired testicular cysts usually occur when a duct is blocked due to injury or inflammation. An ultrasound with this disease shows a formation that has clear, rounded shapes. Orchitis and orchiepididymitis - inflammation of the epididymis. Acute inflammation of testicular tissue (orchitis) - a sharply increased volume of gland, often accompanied by dropsy. Chronic orchiepididymitis - the size of the testicle is changed in one direction or another. Enlargement of the appendage is visible. This disease is provoked by microbial flora, which affects tissues with reduced immunity. Ultrasound of the testicle with orchitis clearly shows an enlargement of the epididymis, the structure of which is heterogeneous. Oncological processes in the testicle cannot be diagnosed with high accuracy using ultrasound. With this disease, it is necessary to perform an MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast or do a biopsy to identify the malignant nature of the disease. Most often, cancerous tumors are found in the right testicle. On ultrasound, the tumor will appear as a formation or several formations of an uneven shape, and the organ will be enlarged in size. An abscess is a formation that requires urgent treatment, sometimes even surgery. On an ultrasound scan of the scrotum and testicles, it is easy to distinguish it from a cyst and tumor, since this formation has an even contour. Tuberculosis of the testicle and appendages is, as a rule, a bilateral process and is manifested on ultrasound by multiple calcifications.
| Ultrasound service of pelvic organs | Price, rub | Promotion Price |
| Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women and men with an abdominal sensor | 1200 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women with a vaginal probe | 1300 rub. | |
| Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound with abdominal and vaginal probe | 1400 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of folliculogenesis | 750 rub. | |
| Ultrasound cervicometry | 1100 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland with a rectal probe | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (testicles, appendages) | 1000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder with an abdominal probe | 1900 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
Preparation for ultrasound of the scrotum and testicles
The procedure is performed painlessly and without prior preparation. If an additional ultrasound examination of the prostate gland through the rectum is planned, preparation is necessary. It will consist of clearing the intestines of toxins using an enema and a preliminary diet to protect against flatulence. Sometimes patients have a question: do they need to take anything with them to the study? Modern private clinics in St. Petersburg are equipped with all the necessary materials: shoe covers, disposable towels, napkins and other necessary supplies. However, if you plan to go to a city or regional clinic, then it is better to take care of what you may need, namely: shoe covers or replacement shoes, a sheet and a towel or napkin in order to remove any remaining gel from the screening area after the procedure.