Tumor markers are proteins, the amount of which in the blood increases slightly if a tumor develops in the body. These elements are either secreted by tissues or represent a reaction of the body.
Until recently, tumor markers were used exclusively to determine the effectiveness of surgical treatment, but today their significance is interpreted much more broadly. It is known that an increase in the level of tumor markers occurs earlier than the formation can be determined using known diagnostic methods.
The peculiarity of tumor markers is the lack of sufficient specificity: indicators can increase at different tumor locations with different values. Therefore, to improve the quality and reliability of diagnosis, several different tumor markers are used in combination.
What does a tumor marker show?
The results of the analysis will confirm the presence of a tumor process or refute this assumption along with other research methods, and will also make it possible to distinguish a cancerous tumor from a benign one.
Comparing the results before and after treatment will allow us to draw a conclusion about its effectiveness.
The obtained values make it possible to monitor the patient’s condition after treatment and identify relapse at an early stage.
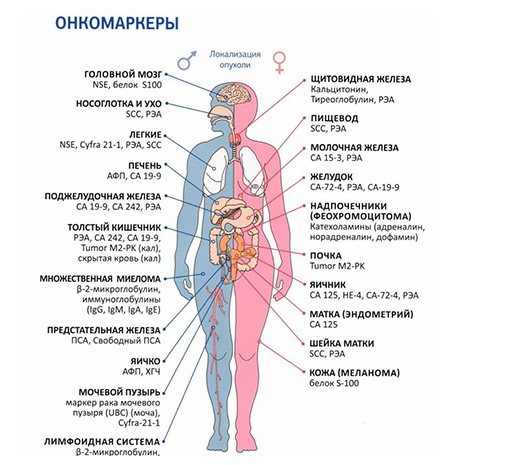
Common types of oncology and tumor markers
The table below will help you navigate the direction of analysis, characteristic features and classification of tests for a specific protein. You can move it to see all the data.
| Number | Oncology classification | Applicable Marker | Additional test | Screening, early diagnosis | Purpose of the survey | Additional Research |
| 1 | Bladder | NMP22, BTA | CA 125, CA 19-9, CEA | Impossible | Observation treatment, prevention of relapse. | Biopsy, general urinalysis, cystoscopic examination. |
| 2 | Breast | CEA, CA 15 -1, BRCA1 and BRCA2, | SA 27, SA 29, M20, M22 | Not carried out | Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy. | Tomography, examination by a mammologist, biopsy. |
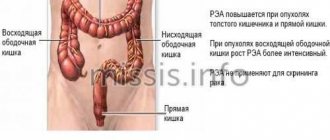
| 3 | Rectum | CA 19-9, CEA, b-hcg | Not used | Impossible | Prevention of relapse, monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, prognosis of the disease. | Stool analysis, sigmoidoscopy examination, colonoscopy, urine for general analysis. |
| 4 | Liver | AFP | Not carried out | Possible | Diagnosing oncology, prescribing therapy, monitoring the result. | Abdominal ultrasound, tomography. |
| 5 | Lungs | CEA, NCE | TRA | Not practiced | Prevention of relapses, monitoring the course of the disease. | X-ray, tomography. |
| 6 | Ovaries | CA 125 | LASA – P, AFP, ROMA index | Screening for high-risk cells | Monitoring the disease, excluding relapse, prescribing a course of therapeutic treatment. | Ultrasound, biopsy. |
| 7 | Melanoma | TA – 90, SU 100 | Not used | Impossible | Exclusion of the spread of metastases. | Biopsy. |
| 8 | Pancreas | SA 19-9 | PAP, PSMA | Not carried out | Monitoring the course of the disease, excluding relapse after therapy. | Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. |
For each individual type of oncology and pathology, a type of tumor marker has been developed. It allows you to identify the disease and prevent further spread of malignant tumors in the body using timely diagnosis.

How to feel about the results obtained?
These indicators are used to monitor the condition over time, so it is important to know their initial level. There are no universal tumor markers indicating a specific location, so they cannot be used as an independent diagnostic method.
Indicators may increase during pregnancy, acute and chronic diseases, so they cannot be interpreted unambiguously. Biochemical studies must be confirmed by clinical methods and consultation with specialists.
How much can you trust tests?
Tumor markers do not show 100% certainty of diagnosis or the presence of a malignant tumor. Fluctuations in indicators may be due to the development of pathologies, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and renal failure. Therefore, in addition to antigen tests, it is necessary to do an examination of the whole body, using complex procedures, this will increase the efficiency of the study.
To decipher the results obtained, qualifications and information content in the field of medicine are required. By independently making a diagnosis, studying codes, standards and indicators of the examination, you can come to false conclusions. You can trust the diagnosis made by the attending physician after a complex of procedures and examinations.
Explanation of meanings
Each cancer produces a specific antigen. The following tumor markers are most often diagnosed.
- Tumor markers of the gastrointestinal tract are CA 19-9 and CA 242. They are produced only in the intestines and stomach, but the level may also increase if the pancreas is damaged. The first indicator responds in 80% of patients. Its norm is 35 IU/ml. If the value increases by 5 units, the patient is highly likely to develop a malignant tumor.
- Thyroid cancer can be suspected by determining the level of the tumor marker CEA. It cannot be detected in healthy adults. A high rate indicates a malignant process. In small quantities it manifests itself in pneumonia, tuberculosis, and inflammatory diseases.
- Another marker for the thyroid gland is thyroglobulin. Its level when the thyroid gland is removed should be zero. If the value is determined, it means that the gland is not completely removed or metastases are developing.
- Liver cancer often manifests itself in later stages, but oncarmers allow early diagnosis. A comprehensive study includes determining the concentration of AFP, CEA (CEA) and ferritin. Using these values, primary liver cancer and the presence of metastases from other organs are diagnosed. After chemotherapy, due to tumor disintegration, the concentration of tumor markers may increase. A follow-up study should be done after 2 or 3 months.
Analysis of tumor markers for lung gives the most accurate result. The technique is considered basic.
- In squamous cell carcinoma, a fragment of cytokeratin 19, Cyfra-21-1, is determined.
- CEA and CEA - if adenocarcinoma is suspected;
- NSE – for small cell carcinoma.
Indicators of malignant processes in female diseases are the following:
- CA-125 – ovarian cancer marketer;
- SAV-15-30 – mammary gland;
- CEA, CEA – embryonic antigen;
- HE4 is an epidermal protein.
List of tumor markers for men:
- CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) - values increase with prostate cancer;
- CA 19-9 (carbohydrate antigen 19-9, cancer antigen 19-9);
- CA 72-4 (carbohydrate antigen 72-4, cancer antigen 72-4);
- CYFRA 21-1 (cytokeratin 19 fragment);
- Thyroglobulin;
- PSA – indicates prostate cancer.
Blood test for tumor markers at Family Doctor
When carrying out the analysis, the following indicators (tumor markers) are assessed first of all:
- AFP (alpha fetoprotein) is normally produced by the fetal membrane and is registered during pregnancy. In the absence of pregnancy, it indicates an oncological disease, primarily liver cancer;
- CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) - indicates, first of all, rectal cancer; however, it can be detected in cancer of the lungs, mammary glands, and in some cases - in cancer of the thyroid gland, liver, bladder, cervix, and pancreas. Therefore, this tumor marker is considered nonspecific (i.e., indicating the presence of a malignant tumor in the body without being tied to any specific organ);
- PSA (prostate-specific antigen) is a marker of prostate cancer. Men over the age of 35 are recommended to undergo a PSA test annually to detect the disease at an early stage;
- CA 19-9 – pancreatic cancer marker;
- CA 15-3 – breast cancer marker;
- CA 125 is a marker for ovarian cancer.
- SCC – squamous cell carcinoma marker;
- Pro-GRP is a marker for small cell lung cancer.
At Family Doctor you can take a blood test for tumor markers at any of the clinics, choosing the one that is located in the area of Moscow you need. You can take a blood test for tumor markers on any day (including on weekends).
How much does the analysis cost?
The price of research in many cases is human life. Often these tests are indispensable, since other types of diagnostics are difficult. The cost of the analysis will be determined:
- Research methodology;
- Costs of reagents;
- Availability of modern equipment;
- Peculiarities of pricing of a particular establishment.
You can undergo diagnostics, take tests for tumor markers and get advice from a specialist in Moscow, at the RAS clinic. Appointments can be made on the website or by calling the numbers provided.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing values
An increase in values can be caused not only by the development of a cancerous tumor, but also by many other reasons. A slight increase in the content of antigens in the blood leads to:
- inflammatory diseases of internal organs and autoimmune pathologies;
- poor nutrition;
- alcoholism;
- severe stress;
- heavy sports;
- surgical intervention;
- some medical and physiotherapeutic procedures;
- taking medications;
- hormonal imbalance.
Also, the results of the study can be affected by improper preparation of the patient for blood donation: smoking, drinking alcohol, failure to comply with the period of abstinence from food, taking medications overestimate the results of the analysis for tumor markers.
At initially high values, a decrease in the level of tumor markers indicates the effectiveness of the chosen treatment tactics and the positive dynamics of the disease.
In medicine there is no concept of “reduced level of tumor markers”: the closer to zero the value of a particular antigen, the stronger the man’s health and the lower the likelihood of oncological and inflammatory diseases.
Modern medicine has not yet developed a 100% correct method for diagnosing cancer. Oncological markers in men are 70-90% sensitive and can only be used in combination with other diagnostic measures. However, regular blood tests for antigens to cancer tumors increase the patient's chances of successful cancer treatment.
History of appearance
Cancer waste products and the first signs of a malignant breast tumor were discovered in 1600. They were first discovered during the study of liver tumors. The authors of the discovery G.I. Abelev and L.A. Zilber.
A marker of liver cancer is alpha-fetoprotein. The protein is also increased in patients suffering from ovarian cancer.
AFP is the first cancer marker used in clinical practice. Associated antigens allow the doctor to diagnose a tumor at an early stage of its development.
Markers of a malignant process are:
- hormones;
- metabolic products;
- enzymes;
- protein substances formed during the breakdown of a cancerous tumor.
Bladder tumor marker
To diagnose bladder cancer, several tumor markers are tested.
The most specific tumor marker is UBC.
Also being researched
- NMP22 (nuclear matrix protein) levels,
- fibrinogen degradation products, VTA (bladder cancer marker),
- TRAP,
- soluble fragments of cytokeratins (TPA, TPS) and calreticulin.
Tumor marker for bladder cancer UBC
A promising tumor marker for bladder cancer is UBC (soluble regions of cytokeratins 8 and 18).
The UBC tumor marker is a fragment of a protein that enters the bloodstream as a result of proliferation (growth) of cancer cells.
The UBC tumor marker is sensitive in 70 percent of cancers in the early stages.
This tumor marker can reliably diagnose cancer - it is specific in ninety percent of cases.
Determination of the UBC tumor marker is also indicated for identifying recurrent bladder cancer.
According to statistics, in 41% of cases, determining the UBC marker helped confirm the diagnosis in the presence of atypical cells in the urine sediment. In thirty-nine percent of cases, tumor markers detected bladder cancer even when microscopy of urine sediment revealed no cancer cells.
Where to get tested. results
Tumor markers for bladder cancer can be determined at the Innovative Technologies LLC Polyclinic. The study is carried out using the enzyme immunoassay method - ELISA. UBC tumor marker reference values may vary between laboratories, so test results should be interpreted in the laboratory where the study was performed. The normal content of tumor markers in urine is from 0 to 12 micrograms per liter.
What does the increase in UBC level indicate?
The UBC tumor marker is determined to
- diagnosis of bladder cancer,
- control over the course of the disease,
- monitoring the effectiveness of bladder cancer treatment and
- for diagnosing tumor recurrences.
Tumor marker levels exceed the norm in the following cases:
- bladder cancer;
- breast cancer;
- colorectal cancer;
- bronchial cancer;
- bowel cancer;
- liver cancer;
- liver cirrhosis;
- diabetes mellitus
A decrease in UBC tumor marker values to zero is considered normal.
Other bladder tumor markers
NMP22
NMP22 is a specific protein that can be found in bladder cancer. It is advisable to determine this tumor marker in order to monitor the effectiveness of antitumor treatment. The bladder tumor marker VTA is less valuable in diagnostic terms, so at present they try not to resort to its study.
TPS
The tumor marker TPS is a tissue polypeptide, or cytokeratin 18.
TPS levels are determined in patients suffering from epithelial cell carcinomas, such as breast, prostate, bladder, ovarian and gastrointestinal carcinoma. Particularly high concentrations in the blood are observed in patients with metastases. It is important to know the indicators of this tumor marker both before and after surgery. If, after chemotherapy treatment, its level remains at high levels, this indicates an unfavorable prognosis for the patient’s survival for one year.
How to prepare for a bladder tumor marker test
In order for the indicators of bladder tumor markers to correspond to reality and to help in making the correct diagnosis, the patient should adhere to certain rules on the eve of urine collection.
- First of all, he needs to give up smoking for several days.
- Contact with aniline dyes should also be avoided.
- The patient should not eat spicy or spiced foods.
- On the eve of the test, you must refrain from urinating for three hours.
For the study, you need an average portion of urine, collected in the morning in a special container.
When is a tumor marker study prescribed for bladder cancer?
A urine test to determine the tumor marker for bladder cancer UBC is prescribed
- if a malignant neoplasm is suspected,
- to control the radicality of tumor removal during surgery,
- in order to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment,
- to predict tumor metastasis.
An increase in the level of the UBC tumor marker after radical tumor removal may indicate tumor recurrence or the presence of distant metastases.
Bladder cancer: characteristics of pathology
Bladder cancer develops from cells in the lining of the bladder. Based on their histological structure, the following types of bladder cancer are distinguished:
- urothelial carcinoma (transitional cell carcinoma);
- adenocarcinoma;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
Causes of bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is thought to be caused by a disorder of the gene structure. Bladder cancer also develops under the influence of various chemicals, especially aniline dyes. Tobacco smoking is one of the main risk factors for bladder cancer.
A malignant tumor in the bladder can be caused by ionizing radiation, parasites and catheters that remain in the urinary ducts for a long time.
Signs of Bladder Cancer
The most typical symptoms of bladder cancer are:
- Hematuria (blood in the urine). It occurs in nine out of ten patients with bladder cancer. Hematuria is not accompanied by pain.
- Dysuric disorders (pain during urination, frequent urge to urinate). Typically, a small amount of urine is released during one act of urination.
- Frequent urinary tract infections.
In the later stages of the disease the following signs appear:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- swelling of the legs;
- tumor formation in the pelvis.
Bladder cancer treatment
Both local and systemic therapies are used to treat bladder cancer. Local treatment methods affect malignant cells directly in the pathological focus and include surgery and radiotherapy. Systemic therapy involves the fight against malignant cells throughout the body, in all places where they are distributed. Chemotherapy is used for this purpose.
If you suspect bladder cancer, contact your doctor immediately. Such localization of cancer should be detected in the early stages of the development of the tumor process.
This is facilitated by the fact that bladder cancer can be seen visually during cystoscopy.
The UBC tumor marker, which is determined when a malignant neoplasm is suspected, is a specific marker.
This article is for informational purposes only. A urologist at our Clinic can tell you in more detail about the prevention of diabetes.
The Polyclinic of Innovative Technologies LLC has developed a special program for the early detection of diseases, including cancer in men
, diagnostics are available to the population of all ages, you MUST undergo it and you will get rid of the “mass” of problems in your body.
In your free time, call him by phone: call center 8 (495) 356 3003.
LLC "Innovative Technologies" thanks you for
that you took the time to read this information.
Most frequently identified tumor markers
75% of cancer patients have elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels. Most often it is elevated in liver cancer; also, its high level can indicate testicular and ovarian cancer (in 5% of cases).
The tumor marker beta-2-microglobulin indicates the development of lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Markers CA 27-29, CA 15-3 indicate possible breast cancer, CA 125 - ovarian cancer. Biomarkers LASA-P, CA 72-4 make one suspect the presence of ovarian cancer and gastrointestinal tumors. The CA 19-9 marker is detected in cancer of the pancreas.
Indications for cancer screening
It is advisable to carry out cancer screening for men over 50 years of age every 2 years. Younger people can be examined at their own request or according to indications.
- Belonging to risk groups for oncology: genetic predisposition (recorded cases of cancer in close relatives);
- previously diagnosed cancer, regardless of form and location;
- identified and persistent excess of permissible testosterone levels;
- harmful working conditions;
- environmentally unfavorable conditions in the place of residence;
- nicotine and/or alcohol addiction;
- chronic stress and overexertion;
- benign prostatic hyperplasia;
- sexual dysfunction (decreased erection, impotence, decreased ejaculate volume);
Who needs to be tested for tumor markers?
People whose relatives have been diagnosed with tumors of various locations should take tests for tumor biomarkers as screening tests 1–2 times a year.
People who have benign tumors (adenoma, myoma, fibroma) or tumor-like formations (kidney cysts, ovarian cysts) need to be examined with the same frequency. The rest can be tested for tumor markers once every 2-3 years.
People who have undergone cancer therapy should be tested for tumor biomarkers: every month during the first year, once every 2 months during the second year, once every 3 months during the third to fifth year. Five years after cancer treatment, it is sufficient to undergo tumor marker testing once every 6–12 months.
Tumor biomarkers can be detected in urine, blood, prostatic juice, fluid taken from the pleura or abdominal cavity. Specific antibodies are added to a sample of biological fluid taken from the patient. They form specific complexes with the protein structure of the tumor marker, which are identified by laboratory methods. Non-protein tumor biomarkers are determined by other methods.