Home / Gynecologist / Cervical biopsy
The cervix is the narrowest part of the organ, located at the bottom and connecting it to the vagina. The cervical canal is located deep in the cervix. One of the common diagnostic procedures for cervical diseases is a biopsy.
Cervical biopsy
is a gynecological procedure in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the cervix. This tissue sample is sent to the laboratory for histological examination, which provides the necessary answers to the doctor’s suspicions and establishes the final and most accurate diagnosis: it will identify pathologies and tissue abnormalities - inflammation, erosion, confirm or deny the likelihood of a precancerous condition or cancer.
The result of the study is one of the most reliable; on its basis, a further treatment plan is drawn up.
Indications for cervical biopsy
Taking cellular material from the cervix is prescribed by doctors when they identify changes and abnormalities in the tissue structure. It is usually done when the following abnormal signs are detected:
- areas of white epithelium that appear after treatment with acetic acid (solution) and are an accurate sign of dysplasia;
- areas that do not stain after treatment with iodine solution during the Schiller test; usually they are represented by keratinizing cells, under which altered tissues may be hidden; this picture is observed, in particular, with cervical leukoplakia;
- punctuation, or red dots on the surface of the mucosa, caused by the proliferation of blood vessels;
- mosaic, which is areas of branched stromal (submucosal) papillae, separated by small vessels;
- atypical transformation zone, combining several of the above symptoms;
- an uneven or bumpy surface, which may be a sign of cancer;
- condylomas;
- inflammation;
- atrophy;
- true erosion;
- polyp;
- endometriosis.
For all of the listed conditions and diseases, histological examination of the altered tissues is necessary.
In addition, a biopsy is performed when there is a combination of colposcopic signs of papillomavirus infection in combination with the detection of this highly oncogenic virus:
- leukoplakia;
- mosaic and punctuation.
Such changes may be an early sign of cervical cancer.
The study is also indicated if the patient has Pap smears of grade 3-5:
- single cells with a disturbed structure of the nucleus or cytoplasm (koilocytes);
- single cells with obvious signs of malignancy;
- cancer cells in large numbers.
In deciphering the Pap smear, which requires a biopsy, the following designations may appear:
- ASC-US – altered epithelial cells that appear for an unknown reason;
- ASC-H – altered cells indicating precancer or tumor;
- AGC – altered columnar epithelial cells characteristic of the cervical canal;
- HSIL – epithelial precancer;
- AIS is a precancer of the cervical canal.
The examination is recommended to be carried out immediately after the end of menstruation or 7-13 days from its beginning.
Cost of the procedure
Currently, cervical biopsies are performed in public health institutions.
And therefore, the cervical biopsy procedure becomes free for women.
The procedure is also free at the oncology clinic.
If a woman plans to perform a cervical biopsy in commercial institutions, then the cost may vary and depends on the technique used, as well as on the use of anesthesia.
On average, the price is about 1000-2000 rubles . It can also vary depending on the level of the commercial organization.
Based on all of the above, it should be concluded that although this procedure is traumatic, it is currently recognized as the most informative.
Contraindications to performing a cervical biopsy
Taking tissue for research is contraindicated:
- with inflammatory processes developing in the cervix and vagina;
- during menstruation;
- for diseases associated with blood clotting problems.
A cervical biopsy during pregnancy is prescribed only in exceptional cases, for example, to diagnose cancer in which it is impossible to bear a child. It is usually not performed in the first trimester, as it increases the risk of miscarriage. In the second trimester, this procedure is safer. In the third trimester, a biopsy is also usually not used so as not to provoke premature labor.

Care after biopsy.
In order to prevent the development of negative symptoms and a speedy recovery after the diagnostic procedure, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and advice. In this case, after the procedure, it is worth minimizing or eliminating physical activity and taking analgesics to relieve pain.
It is also worth taking care of the injection site or the suture at the site where the biopath is taken - the procedures themselves may vary somewhat, but in general they are reduced to treating the wound and changing the bandage. You can take a shower or bath 1-3 days after the biopsy, or you can limit the place where the biopath was taken from contact with water.
02.04.2018
Preparation and performance of cervical biopsy in the medical city of Aleksandrov
The patient must first undergo a general clinical and laboratory examination . The service is performed only if there is a preliminary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, colposcopy, and the results of a minimum laboratory examination:
- clinical blood test;
- cytological examination of a smear from the cervix;
- examinations for HIV, Syphilis, Hepatitis B, C;
- smear on flora.
The patient also gives written consent to the biopsy. If intravenous anesthesia is planned, the procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach - the woman should not take liquid or food for twelve hours before the procedure.
At least one day before the procedure, you must stop vaginal douching, do not use tampons, and do not use medicated vaginal creams or suppositories.
If anesthesia is planned, preparation for a cervical biopsy is accompanied by refusal to eat, drink, or take medications for 12 hours before the procedure.
It is possible that a woman will have some bleeding after the biopsy. Therefore, you should take a pack of pads with you. After anesthesia, the patient will experience some drowsiness, so she will need to be taken home by relatives. It is extremely undesirable for her to get behind the wheel herself.
After the procedure has been completed, you should refrain from the following actions:
- heavy physical activity for two weeks;
- sexual activity for 10-14 days;
- going to the sauna, bathhouse, and also for the next two weeks you should not take a bath, you can only wash in the shower;
- taking aspirin, since this drug thins the blood, which can lead to more heavy and prolonged bleeding.

Consequences.
Doctors say that one of the most common negative consequences when performing a biopsy is heavy bleeding, pain, and swelling at the site where the biomaterial is directly taken using a biopsy. In particular, doctors diagnose such negative consequences in 3% of patients. In terms of deaths, these happen very rarely and, according to statistics, account for 1 case out of 10,000, which develops when vital structural organs are damaged, as well as when pathogenic microorganisms are introduced into the body.
Interpretation of cervical biopsy results
Cervical biopsy results contain information about:
- The presence or absence of koilocytes (appears during HPV infection).
- The presence of processes of keratinization of the epithelium (acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, leukoplakia).
- Detection of cervical dysplasia - its precancerous condition.
However, deciphering the results of a cervical biopsy should be entrusted to the attending physician in the medical city of Aleksandrov , since unprofessional attempts to make a diagnosis will lead to erroneous conclusions and unwanted worries.
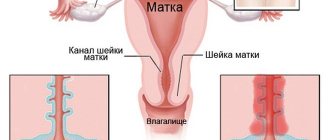
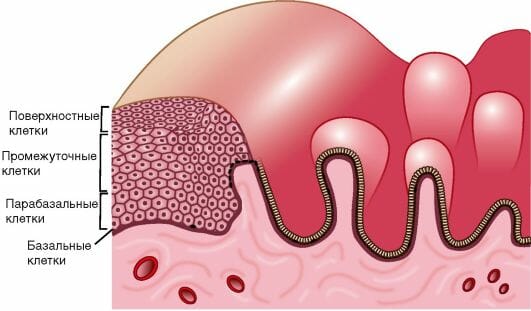
Structure of the cervix
The structure of the cervix is quite simple. It has a vaginal part or exocervix and endocervix, the section that faces the uterine cavity.
In its middle section along its entire length it has a cylindrical or oblong-shaped formation representing a cavity. It is this area that is the element of communication between the areas of the internal and external genital organs. The cervix is surrounded by a mucous membrane, and there is a muscular layer inside.
Cellular composition
The cervix, in its cellular composition, is a rather complex organ, since it is where two different tissues, not only in structure but also in origin, meet. This is a connection between stratified squamous epithelium and columnar epithelium.
Where to do a cervical biopsy in Aleksandrov?
Sever Clinic in a cervical biopsy is performed using modern equipment and high-quality medical instruments. Our doctors have extensive experience in such studies, so they prescribe only the most optimal type of procedure for each patient. In case of a bad cervical biopsy, the woman is prescribed timely treatment, accompanied by constant monitoring by the leading gynecologists of the medical center.
To conduct a study, call the Alexandrov medical and sign up for a consultation by phone: 8 (49244) 9-32-49, 8 (910) 174-77-72 .
What to expect during the procedure
A cervical biopsy may be performed in a doctor's office at a health care facility, as an outpatient setting, or during a hospital stay. Some biopsy procedures require only local anesthesia. Others require regional or general anesthesia. How the test is performed may vary depending on the condition and the physician's practice.
Typically, a cervical biopsy follows this process:
- The patient needs to undress completely and put on a hospital gown.
- Before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder.
- A woman lies on a chair, supporting her legs, as during a gynecological examination.
- The doctor will place an instrument called a speculum into your vagina. This will expand the vaginal walls to reach the cervix.
- Often a healthcare professional will use a colposcope. This is an instrument with a special lens, like a microscope, to help see cervical tissue. The doctor will use a colposcope to open the vagina. It will not enter the vagina.
- The doctor will use a colposcope to look at your cervix to look for any problem areas on the cervix or vagina.
- The doctor may clean and soak the cervix with a vinegar solution (acetic acid solution). This solution helps make abnormal tissue appear white so it is easier to see. At this time, the woman may feel a slight burning sensation. An iodine solution can be used to cover the cervix. This is called the Schiller test.
- The type of biopsy will depend on the size and shape of the abnormal cells and where they are located. The doctor may numb the area using a small injection needle. The doctor may use forceps to hold the cervix for the biopsy.
- The amount of tissue removed and its removal depend on the type of biopsy. For a simple cervical biopsy, one or more small tissue samples will be removed using a special type of forceps. When this is done, the patient may feel a slight pressure or cramp. Cells from inside the cervical canal can be removed with a special instrument called an endocervical curette or endocervical brush. It may also cause some cramping. The doctor may also use a probe (electrocautery) or stitches to stop the bleeding.
- After all this, the doctor will send the tissue to the laboratory for testing.

Most women experience little or no discomfort during a cervical biopsy. However, the woman may experience some mild discomfort in the following days.