What will a CT scan of the temporal bones show?
During a CT scan, layer-by-layer images of the temporal bone and surrounding tissues are obtained in three planes. The slice thickness is only a few millimeters, which allows the radiologist to examine not only all anatomical formations, but also minimal pathological changes.
The following structures are clearly visible in the resulting images:
- pyramid of the temporal bone;
- cells and antrum of the mastoid process;
- cochlea, vestibule, anterior and posterior semicircular canals;
- auditory ossicles of the middle ear;
- walls of the external auditory canal;
- jugular fossa.
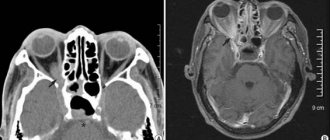
Image (tomogram) of the temporal bones in axial projection
Using a CT scan of the temporal bones, you can identify any diseases of an inflammatory, traumatic, or tumor nature. The method is used to diagnose the following pathologies:
- space-occupying formations, bone tissue and hearing aid cysts;
- inflammatory processes (mastoiditis, otitis, osteomyelitis);
- traumatic injuries (cracks, fractures);
- degenerative changes (otosclerosis, dysplasia);
- developmental anomalies.
The great advantage of CT over other diagnostic methods is the ability to obtain a three-dimensional model of the temporal bone. 3D imaging is essential before surgery, often for an inner ear implant, as it provides the clearest possible picture of an individual patient's anatomy.
Sometimes, during a CT scan of the temporal bone, an iodine-based contrast agent is additionally injected. The injected pharmaceutical absorbs X-rays well and makes the images clearer. Contrast is necessary to clarify the nature of changes in the soft tissue formations adjacent to the temporal bone. The technique also allows one to clearly visualize cerebral arteries and veins. However, this procedure is slightly more expensive than a standard study: the patient will need to pay extra for the amount of contrast used.
Preparation for the procedure
For tomography without contrast, no preparatory measures are required. The iodine-containing drug is administered on an empty stomach, with the last meal no later than 6 hours before the examination.
CT with contrast requires a fresh blood test for creatine and urea, reflecting the state of renal filtration. In case of functional disorders, the method is contraindicated.
Two days before the examination, stop taking the diabetes medication - metformin. Using the drug together with the administration of a contrast agent can cause biochemical blood disorders.
Applying Contrast
Sometimes, during a CT scan, an iodinated contrast agent is injected into the patient's cubital vein. The substance makes images clearer and improves visualization of cerebral arteries and veins. It is used in the study of soft tissues, to detect tumors, assess their size and configuration.
Indications for CT of the temporal bones
In most cases, CT scans of the temporal bones are prescribed by ENT doctors, neurologists, neurosurgeons, and less often by specialists in other fields. Typically, the basis for tomography is pathological changes identified on an x-ray or during an ultrasound. It is CT of the temporal bones that allows you to resolve all doubts and make an accurate diagnosis.
Indications for computed tomography of the temporal bone are:
- disruption of the hearing aid (progressive hearing loss, ringing or noise in the ear, etc.);
- vestibular disorders (dizziness, unsteadiness when walking);
- prolonged pain in the ear area, in half of the head, especially accompanied by neurological symptoms;
- discharge from the ear canal of various types (pus, blood, cerebrospinal fluid);
- clinical data indicating a tumor process;
- disruption of the facial nerve with the development of weakness of facial muscles;
- head injuries with suspected fracture of the base of the skull and temporal bone.
A CT scan of the temporal bones is also recommended before planned surgery to monitor the therapy.
How to diagnose
During the CT scan, all metal jewelry, removable dentures, and hearing aids are removed. The patient lies on his back on the tomograph table, his head is fixed with a pillow or straps. The surface moves smoothly inside the device.
Medical staff watch from an adjacent room, interacting using a built-in audio communication system. The patient may be required to hold their breath for a short time.
Contrast-enhanced tomography uses an iodinated substance. There are two types of its use: orally, intravenously through a catheter. First, a study without contrast is performed. Then, after the dose of the substance is administered, a second scan is performed.
After obtaining images of the area being examined, the doctor checks the quality of the images. When clear results are obtained, the diagnosis is completed and the patient is allowed to stand up.
Examination time
CT scan lasts no more than 5-10 minutes. With contrast enhancement, the diagnostic time increases to 30 minutes. Formulation of the conclusion takes 30-60 minutes; in complex cases, the period may be extended to 2 days.
For whom is CT of the temporal bone contraindicated?
Computed tomography of the temporal bones is not performed on women during pregnancy, since X-rays negatively affect the development of the fetus. In the case of tomography with contrast, the contraindications are:
- violation of the filtration characteristics of the kidneys;
- intolerance to iodine-based drugs;
- increased thyroid function.
How is a computed tomography scan of the temporal bones performed?
You can sign up for a diagnostic appointment by calling the phone number listed on the website. The employee will select the most convenient time for you, explain the features of the procedure, and at the same time you will be able to clarify the exact cost of the examination.
When going for a tomography, you will need to take with you a referral and any medical documents you have on hand. In the case of a planned CT scan of the temporal bones with contrast, you must take a creatinine test in advance. It is necessary to assess the functional state of the kidneys.
The examination is carried out using a modern Siemens multislice tomograph. The device is installed in a separate room where the scanning will take place.
Appearance of the computed tomograph and the position of the patient on the machine table before the start of the study
Immediately before the study, the center specialist will instruct the patient and ask him to take a supine position on the tomograph table.
During scanning, the table with the patient will move smoothly towards the apparatus tunnel. Thus, the head will be at the level of the radiation source and sensors. There are no unpleasant sensations during the examination, especially since the procedure itself lasts only 1-2 minutes.
During this time, staff will remain in the next room and monitor the progress of the study. There is an intercom in the tomograph tunnel through which the patient can always contact the medical staff.
A CT scan of the temporal bone with contrast injection lasts a little longer: from 15 to 25 minutes, since the study includes several stages. Initially, a native scan is performed, after which an iodine-containing drug (Ultravist) is administered intravenously. Contrast relatively rarely causes adverse reactions; sometimes slight dizziness or nausea is observed. These unpleasant phenomena go away on their own within a few minutes. The final stage is repeated scanning to obtain the highest contrast images.
After receiving the images and processing them with a computer program, the doctor will need some time to analyze the data. Usually this takes no more than 1.5-2 hours.
The patient can wait for the result directly or go home. In the latter case, the conclusion will be sent by email. If a patient has questions about the results of a CT scan, he can always get a free consultation with the doctor who compiled the report.
Contraindications
CT scanning is not performed if the patient’s body weight is more than 120-150 kg (depending on the capabilities of the device).
The use of the method for children under 5 years of age is limited due to the child’s inability to remain still during the procedure and greater sensitivity to radiation. However, it is permissible if there are compelling reasons, there is a risk to life, or it is impossible to make a diagnosis using other methods (ultrasound, MRI).
Computed tomography is contraindicated in pregnant women, as X-rays have a negative effect on the fetus.
Tomography with contrast is contraindicated for:
- intolerance to iodine-containing drugs;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- renal failure;
- multiple myeloma;
- severe diabetes mellitus.
During lactation, a woman should not breastfeed for 3 days after a CT scan.
When is a CT scan of the temporal bones prescribed for children?
This type of study is recommended for children only if there are compelling reasons. This is due to the fact that a child’s body is more sensitive to x-rays than an adult patient. CT scan of the temporal bones is prescribed when other research methods (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI) do not provide enough information to make a diagnosis. For children, computed tomography of the temporal bones is most often performed in cases of traumatic brain injury with skull fractures, unilateral hearing loss, or if a neoplasm is suspected.
Multislice CT scans are performed on children starting from the age of five. Modern equipment and software make it possible to select the optimal scanning mode and, thus, significantly reduce the radiation dose to the body. The procedure with contrast in our center is performed on children over the age of twelve.
Position of the child on the CT scanner table before the examination
Computed tomography of the temporal bone does not cause discomfort or pain to the little patient. Because the scan takes only a few minutes, children tolerate the diagnosis well. However, with a planned tomography, parents should still psychologically prepare the child: talk about the procedure and why it is so important to undergo it.
CT diagnostics in Moscow. Why do patients choose the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences?
At the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, you can undergo a CT scan of the temporal bones of the skull using high-quality equipment, and we have some of the most affordable prices in Moscow.
We guarantee:
- examination on a modern tomograph, which provides high information content and safety;
- reliability of diagnostic results;
- the ability to visit the clinic at a time convenient for you;
- comfortable conditions and psychological support for patients;
- possibility of inpatient treatment of identified diseases.
To register for an examination at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences and clarify the cost of services, you can call or use the online form on the website.
Benefits and Risks
- Computed tomography (MSCT) of the temporal bones allows high-quality visualization of not only bone tissue, but also soft tissue, and the quality of the image of bone tissue is better than on MRI.
- The procedure is absolutely painless and takes on average 10 minutes.
- The procedure does not require special preparation and only when conducting a study with contrast, it is recommended to conduct the study on an empty stomach.
- The dose of ionizing radiation during the study is quite low, but, nevertheless, it is not recommended to conduct multiple studies, since a certain risk of harmful effects on humans in such cases is much higher. However, the diagnostic value of this method of studying the temporal bones is much higher than the risks. The image quality of soft tissues on MRI is higher and, therefore, if more detailed visualization of the soft tissue structures of this area is necessary, an MRI study is recommended.
CT scan of facial bones: what does it show?
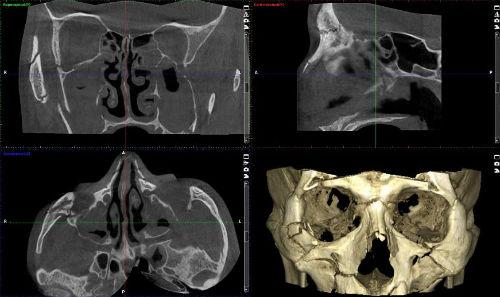
The most common injuries to the skull occur on the facial part. They are accompanied by fractures and displacements of the facial bones. The structure of the front part is quite complex. It is represented by the frontal, jaw and many smaller bones. Standard radiography does not give a complete picture of injuries and fractures of small bone parts of the face. The CT model visualizes tumor formations of benign or malignant origin. The examination is often performed using contrast.
Indications for scanning the facial part of the skull are:
- facial injuries with visual determination of displacement of fragments, swelling of soft tissues, hematomas, internal hemorrhages;
- signs of inflammation on the skin surface of the face;
- changes in the tone of facial muscles;
- assumption of the presence of a tumor;
- with certain contraindications to MRI.
In certain circumstances, the information content of the study is necessary for the surgeon, ENT doctor, CT scan of the facial bones, which shows the condition of the air sinuses of the nose, orbits, the position of an unerupted tooth, adjacent soft tissue structures, the presence of original or metastatic tumors, and also before surgery.
Decoding the results
The interpretation includes a description of the images obtained during diagnosis and a conclusion regarding the identified pathology.
A CT scan of the temporal bone shows in detail the anatomy of the pyramid, mastoid process, middle and inner ear, and jugular cavity. The data is deciphered by a radiology doctor.
Based on the images obtained, the following is revealed:
- chronic, acute otitis;
- hemorrhages;
- purulent accumulations;
- hidden fractures and cracks;
- mastoiditis, otosclerosis;
- soft tissue injuries;
- development of tumors and infections.
The diagnostic results are given to the patient in the form of a sheet with images and a conclusion. Data can be recorded on external electronic media (disk or flash drive).
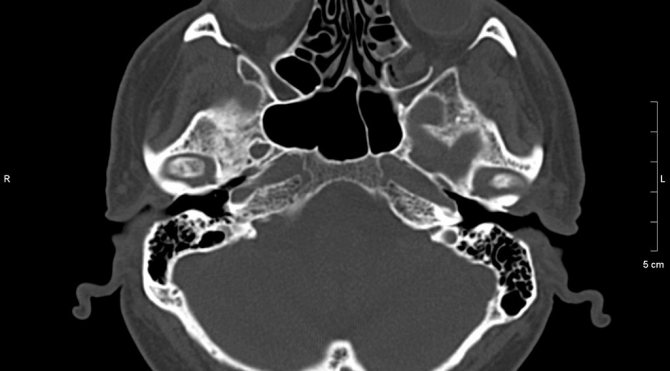
Norm
It is important to remember that a CT scan is not a definitive diagnosis. Only a comprehensive examination using instrumental and laboratory methods, taking into account the clinical picture, will allow the attending physician to establish the disease and choose the tactics for managing the patient.