If you are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to do X-rays for children, then carrying out this diagnostic method will help prevent the development of many complications in various diseases. X-rays must be performed in case of skull injuries, the presence of a tumor, or various malignant formations in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
The permissible dose of radiation exposure per year is 1-5 mSv (microsievert). However, it is important to understand that this diagnostic option is prescribed only in the presence of serious illnesses that cause irreparable harm to the baby’s health, so the required number of x-ray studies will be determined by the attending physician.
The need for X-ray examination
X-rays of the lungs of a child are prescribed very rarely, since radiation has a negative effect on the body, especially children. X-ray radiation can lead to mutations and damage to the DNA chain, which can subsequently cause the development of various diseases. However, such consequences can only occur with a high dose of radiation; with a simple x-ray, the dosage is not exceeded.
Refusal to perform chest x-rays in children is extremely undesirable if there is a need for such a study. The reason is the different functioning of the immune system of babies. For them, a common cold often develops into pneumonia, which progresses very quickly. Therefore, you should not take a long time to decide whether a chest x-ray for a child is harmful, because the lack of diagnostic results can even lead to death.
Indications for chest X-ray in children
A child's lung x-ray is prescribed solely to identify the causes and complexity of the pathology, but not for preventive purposes. This is based on the possibility of negative consequences from exposure to rays. It is worth familiarizing yourself with the situations when a chest x-ray of a child
extremely necessary.
Confirmation or exclusion of pneumonia (pneumonia)
A chest x-ray can often save a child's health and life. Pneumonia in children can progress very quickly and requires immediate diagnosis. After receiving the results, the doctor can choose an effective treatment strategy.
Severe cough accompanied by a high temperature (above 38ºC) for more than three days
May indicate a cold, which should be treated with medication. Using an image, doctors determine why such symptoms arose and persist.
Leukocytosis and shift of the leukocyte formula to the left in a blood test
A shift of the formula to the left indicates an increase in the number of “new” neutrophils in the blood. This may indicate an inflammatory or necrotic process, various intoxications, infections, and may also appear when taking certain medications. In this case, the child is given a chest x-ray to determine the cause of this phenomenon. The shift is not necessarily a sign of illness; sometimes it occurs after significant physical exertion, and over time the situation improves.
Impossibility or lack of information content of other examination methods
You will have to think about how often you can do an X-ray of a small child’s lungs if other diagnostic methods do not provide the amount of information that is needed. In such a situation, you need to resort to x-ray examination.
Suspicion of pathology of the thymus gland
A chest X-ray, which shows a large number of pathological processes in children, is informative when examining the thymus gland. The main diseases are: aplasia, hypoplasia and dysplasia, accidental involution, thymomegaly, atrophy and hyperplasia. X-rays of the lungs in children can determine the cause of deterioration in health, based on the results of which the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis
In such a situation, you should not think about at what age a child can have an X-ray of the lungs - it is mandatory, since the disease is very serious. The doctor will examine all the shadows in the resulting image and draw up a conclusion that will allow you to understand whether the preliminary diagnosis has been confirmed.
Diagnosis of neoplasms
You also need to find out how often a child’s lungs can be x-rayed if there are suspicions of tumor processes of various types. Their manifestations can sometimes be subtle or completely unnoticeable, but a prompt reaction from parents will provide a more optimistic prognosis.
Examination of a child's chest using x-rays - MEDSI
Table of contents
- What is the harm of x-rays?
- When can the procedure be scheduled?
- Carrying out X-ray diagnostics
- Types of X-ray examinations
- How often can an x-ray be taken?
- Advantages of the procedure at MEDSI
Radiography is an informative and cheap method of radiation research.
Having passed ionizing rays through the area under study, the device produces a black and white image in which tissues of different densities receive different shades: the denser the tissue, the more rays it intercepts and reflects, the lighter the shadow in the image (example: the bone structures of the chest are visible on an x-ray like white, lung tissue is dark). In this way, compactions or gaps can be detected in uncharacteristic places, which allows one to suspect the presence of a neoplasm or a violation of the integrity of the organ. Advantages: non-invasiveness, accessibility (X-rays are available in all large clinics), speed, obtaining an image that can be presented to different doctors upon request.
What is the harm of x-rays?
One of the few disadvantages of the method is its radioactivity. Large doses of radiation can provoke changes in the structure of cells and serve as an impetus for the development of tumors and the malignancy of hyperplasias. Therefore, irradiation is strictly dosed - the study is rarely carried out more than 3 times a year.
This is why, unlike adults, children do not undergo fluorography: increased cell division in childhood increases the risk of developing cancer pathologies.
Only after carefully assessing the balance of harm and benefit can a doctor prescribe a chest x-ray for a child.
When can the procedure be scheduled?
- If serious diseases of the lungs and bronchi are suspected: pneumonia, obstructive bronchitis, asthma, tuberculosis, abscess, pleurisy, tumors
- To assess the condition of the thymus (thymus gland) if a tumor is suspected or there are problems with the immune system
- After injury with a high probability of dislocations, fractures, pneumothorax, hemothorax, the presence of traumatic foreign bodies
- For symptoms of asphyxia (suffocation) to detect the cause of obstruction (clogging) of the trachea, examining blood vessels for damage or the presence of blood clots
- When planning surgery for a child with cardiac pathologies
Carrying out X-ray diagnostics
X-rays of a child’s lungs should not be performed using adult equipment, as it requires a reduction in the radiation dose. Modern digital devices for pediatric use make it possible to minimize radiation exposure, and in addition, they are adjusted to children's dimensions and equipped with special non-traumatic clamps.
The procedure is quick:
Small children are restrained upright or examined lying down with soft straps on a couch. Parts of the body not involved in the study are covered with a lead apron of the appropriate size.
- The baby can be held by the mother, who is also given an apron for protection
- Adult children who are able to remain still for the required time are examined while standing.
The procedure takes no more than a few seconds. It is important to remain completely still in a given position during this time in order to obtain a clear image.
Types of X-ray examinations
In addition to static radiography, there are other methods of radiation examination.
- Fluorography is a photograph taken from a fluorescent screen, capturing the organ under study in a reduced form.
- X-ray (X-ray television) - demonstrates the organ on the screen in real time. Previously, fluorescent screens were used to display images of the organ. With the development of digital technologies, images began to be broadcast on a monitor and also saved on digital media. The radiation dose during fluoroscopy is higher than during radiography, but the method is indispensable for some manipulations, as it allows you to observe instant changes in the organ (during bronchoscopy, some operations)
- Computed tomography allows you to examine the structures of an organ in detail, section by section. Some operations are also performed under CT guidance. However, up to 7 years of age, the examination is carried out under anesthesia, since the patient is required to lie still for 15–20 minutes
These chest X-ray methods are performed strictly according to indications (for example, in cardiac surgery).
How often can an x-ray be taken?
Unlike radioactive substances, rays do not accumulate in the body; the effects of radiation stop along with the procedure. Therefore, when performing an X-ray of a child’s lungs, the single dose of radiation, duration and frequency of exposure will be important.
Radiation exposure during radiography is measured in Sieverts and averages from 0.1 to 0.42 millisieverts for one image (for a chest CT scan it is about 7 mSv). Digital devices allow you to further reduce the dose.
At the same time, according to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the maximum annual radiation dose should not exceed 1 mSv per year on average (over the next 5 years) and a maximum of 5 mSv per year.
Thus, radiological diagnostics of the chest can be carried out from 3 to 10 times a year without harm to health (depending on the settings of the device, the age and state of health of the child).
Advantages of the procedure at MEDSI
- Availability of the latest generation of children's digital devices with comfortable fixation devices - safe research in a relaxed environment
- Visit at a time convenient for you
- Image interpretation by experienced diagnosticians
- Possibility of carrying out the procedure and visiting a pulmonologist, phthisiatrician or pediatrician with examination results in the same place
To make an appointment, call 24/7 8 (495) 7-800-500.
How is the examination done in children?
First of all, you should know at what age children are given lung x-rays
. Ages over 14 years are considered safe. However, exceptions are possible.
Before undergoing the procedure, you need to find out how children get x-rays of their lungs. The examination of the chest organs of babies is somewhat different from that of adults. The fact is that in order to obtain clear images, it is necessary for the patient to remain absolutely still.
If you don’t know how a child’s chest X-ray is done, it’s worth knowing that a special device that looks like a stand is used for this. The child is placed on it and the legs, arms, head and torso are secured with belts. Organs that will not be examined are covered with a lead apron. At the time of the study, parents are with the child and are provided with radiation protection equipment. For 12-year-old and older children, a chest x-ray is performed without the presence of parents.
The examination will last a couple of seconds, the patient will not experience discomfort, except for possible inconvenience from fixation.
How is the load reduced during x-rays?

All information about the radiation examinations performed, their number and radiation dose is entered into the medical record. If a critical dose accumulates over the course of a year, then prescribing another x-ray is highly undesirable.
To control the workload, the radiographer must have maximum information, so it is important to report all previous examinations and possible contraindications.
To protect the body, three main methods of protection are used:
- Protection by distance. The X-ray tube is placed in a special protective casing. It does not allow X-rays to pass through, which are directed at the patient through a special “window”. In addition, at the exit of the rays from the tube, an X-ray machine diaphragm is installed, with the help of which the irradiation field is increased or decreased.
- Time protection. The patient should be irradiated for as little time as possible (short shutter speeds when taking pictures), but not to the detriment of diagnostics. In this sense, images provide less radiation exposure than transillumination.
- Shielding protection. Parts of the body that are not to be photographed are covered with sheets and aprons-skirts made of leaded rubber. Particular attention is paid to the protection of the genital organs and thyroid gland, as they are the most sensitive to x-ray radiation.
How often can children have a chest x-ray?
It is important to find out not only whether it is harmful for a child to have a chest x-ray, but also how often the procedure can be performed. The frequency will depend on what disease is suspected or what diagnosed disease is being treated. For example, if there is a suspicion of tuberculosis, you need to be examined every three months to assess the condition and effectiveness of treatment.
In the case of pneumonia, after it is diagnosed, it is necessary to undergo the procedure 3-5 days after finishing the course of antibiotics. There is no need to worry about the negative impact on the child’s body. If you need to find out what a chest x-ray shows in children, it is best to carry out the study and not refuse it, since the benefits are much higher than the likely risks.
Older children
A pediatric chest x-ray is performed if the following indications exist:
- confirmation or refutation of the preliminary diagnosis - pneumonia (pneumonia);
- fever associated with severe cough for 72 hours;
- in the blood test there is an increase in the total number of leukocytes, in particular, stab cells;
- other examination methods turned out to be uninformative;
- examination of possible pathologies of the thymus gland;
- suspected pulmonary tuberculosis;
- identifying the nature of neoplasms.
X-rays for preventive purposes (fluorography) are not recommended until the age of 15. In any case, it is better for children to have x-rays done using digital equipment, which will significantly reduce the dose of radioactive exposure on the young body. Fluoroscopy is a separate type of x-ray examination. It allows you to visualize the examined organs on a fluorescent screen.
This method allows you to study organs in the process of their natural movements (lungs, heart). However, the obvious disadvantage of this version of x-ray examination is that the body is in contact with x-ray radiation for much longer, and therefore receives a higher dose of radiation than with conventional x-rays. In this regard, it is rarely done for children.
Radiation exposure
Parents need answers not only to questions about how an X-ray of a child’s lungs is done, at what age it is prescribed and what are the features, but also what the radiation dose will be. An image in a frontal projection assumes a load of 0.18 mSv, and in an additional side projection - 0.42 mSv. The annual norm, which should not be exceeded, is 1 mSv. After the first procedure, a passport is created for the patient, in which data on all scans is entered. There are few analogues of X-ray, except for computed tomography, but it is prescribed very rarely, because the radiation dose with it is several times higher.
Decoding the results
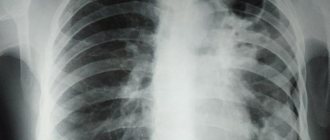
An X-ray of a child’s lungs is interpreted by a radiologist. Each pathology has its own characteristics and is displayed differently on images. For example, pneumonia looks like darkening of areas of the lungs. The type of inflammation is determined by the location of the darkening. It can be total, segmental, lobar or focal. The intensity of the darkening demonstrates the degree of inflammation.
It is not possible to decipher a child’s lung x-ray on your own; this must be done by a doctor. Detection of tuberculosis will also have features; it looks different in the picture. The disseminated type of the disease looks like small focal darkening with clearly defined edges. Focal looks like darkening in one or a couple of places, the size can be up to 2 cm.
Thinking about the age at which children get x-rays of their lungs
, it is worth understanding that even adults cannot resort to it without clear indications.