Mastopathy - symptoms and treatment
A mammologist treats mastopathy. First of all, it consists in finding and eliminating the causes of mastopathy: nervous disorders, ovarian dysfunction, gynecological diseases, liver diseases, etc.
The main objectives of mastopathy treatment are: to reduce pain, reduce cysts and fibrous tissue in the mammary gland, prevent relapses of tumors and oncopathology, and also correct hormonal status (after detecting hormonal disorders and consulting a gynecologist-endocrinologist).
If the patient’s body has concomitant inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, nodular goiter, diabetes mellitus, etc.), then treatment must be carried out together with a gynecologist, endocrinologist and therapist.
Treatment of mastopathy can be divided into two main types - conservative (drug) and operative (surgical) treatment. Most often, conservative treatment of MFC is performed. In the event that there are large cysts and significant compactions that are not amenable to conservative treatment or if therapy is unsuccessful, surgical treatment is performed.
Conservative treatment
The usual tactics for managing women suffering from mastopathy were developed back in the 60s and 70s, so at the moment they are not very effective. New drugs introduced into practice have increased the effectiveness of treatment at the initial stage. However, these drugs turned out to be ineffective for women with fibrocystic mastopathy who had a history of close relatives (mother, grandmother, sister, aunt) suffering from breast cancer.
For drug treatment, the following drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers - relieve pain and help restore sleep;
- vitamin complexes - strengthen the immune system;
- homeopathic remedies - strengthen the body's defenses;
- antidepressants and sleeping pills - necessary for depression, irritability, insomnia (symptoms accompanying fibrocystic mastopathy);
- iodine preparations - it is especially important to use them at the initial stage of treatment, as they improve the functioning of the thyroid gland, contribute to the normal functioning of the reproductive system and regulation of the menstrual cycle;
- diuretics [2] - eliminate swelling of the breast tissue, improve the outflow of blood through the veins and its circulation in the breast tissue. These drugs also reduce the levels of potassium and magnesium in the blood, without which the normal functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems is difficult. Therefore, diuretics are usually taken together with drugs containing potassium and magnesium.
Hormone therapy
This treatment method is prescribed in complex cases of FCM. Normalization of hormonal balance is aimed, first of all, at eliminating pain. Stabilizing the condition of the endocrine glands and gastrointestinal tract helps prevent the appearance of new formations, reduce the size of existing ones, and reduce or eliminate pain. However, proliferative forms of fibroadenomatosis and fibrocystic or fibromatous mastopathy do not respond well to this method of treatment.
The use of hormonal drugs is prescribed individually and is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Medicines are used in the form of tablets, injections or gels that are applied to the mammary gland. Patients of reproductive age may be prescribed hormonal contraceptives. Systemic hormone therapy should be carried out by a highly qualified specialist who can monitor hormonal status.
Hormonal therapy involves the use of antiestrogens, oral contraceptives, gestagens, androgens, prolactin secretion inhibitors, gonadotropin releasing hormone analogues (LHRH). Treatment with analogues
LHRH is applicable to women with mastodynia (breast pain) in the absence of effective treatment with other hormones. The action of gestagens is based on an antiestrogenic effect at the level of breast tissue and inhibition of the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland. Their use in complex therapy of mastopathy increased the therapeutic effect to 80%.
For the treatment of mastopathy in women under 35 years of age, oral monophasic combined estrogen-progestogen contraceptives are used. Their contraceptive reliability is almost close to 100%. Most women, while using these drugs, experience a significant reduction in pain and engorgement of the mammary glands, as well as restoration of the menstrual cycle.
Currently, a fairly effective external drug is used in the treatment of mastopathy. It contains micronized progesterone of plant origin, identical to endogenous. The drug is released in the form of a gel. Its advantage lies precisely in its external use - this way the bulk of progesterone remains in the tissues of the mammary gland, and no more than 10% of the hormone enters the bloodstream. Thanks to this effect, there are no side effects that occurred when taking progesterone orally. In most cases, continuous application of the drug 2.5 g to each mammary gland is recommended, or its application in the second phase of the menstrual cycle for 3-4 months.
Non-hormonal therapy
Methods of non-hormonal therapy are: diet correction, correct selection of a bra, the use of vitamins, diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that improve blood circulation. Latest Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been used for a long time in the treatment of diffuse mastopathy.
Indomethacin and brufen, used in the second phase of the menstrual cycle in the form of tablets or suppositories, reduce pain, reduce swelling, promote the resorption of lumps, and improve the results of ultrasound and x-ray examinations. The use of these drugs is especially indicated for the glandular form of mastopathy. However, for most women, homeopathy or herbal medicine may be sufficient.
Conservative treatment of mastopathy should consist not only of long-term use of sedatives, but also of vitamins A, B, C, E, PP, P, since they have a beneficial effect on breast tissue:
- vitamin A reduces cell proliferation;
- vitamin E enhances the effect of progesterone;
- vitamin B reduces prolactin levels;
- vitamins P and C improve microcirculation and reduce local swelling of the mammary gland.
Since mastopathy is considered a precancerous disease, long-term use of natural antioxidants is required: vitamins C, E, beta-carotene, phospholipids, selenium, zinc.
In addition to vitamins and sedatives, patients are advised to take adaptogens for four months or more. After a four-month course, the use of the drug is stopped for a period of two months, and then the treatment cycle is resumed for four months. A total of at least four cycles must be carried out. Thus, the full course of treatment may take approximately two years.
Diet for mastopathy
When treating mastopathy, it is necessary to improve the functioning of the digestive system.[1] Therefore, recovery can be accelerated by following a special diet. To do this, you need to reduce your calorie intake by eliminating carbohydrates. First of all, it is important to completely get rid of the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, honey, jam and flour products) and increase the proportion of vegetables, unsweetened berries and fruits consumed.
In case of mastopathy that has developed as a result of problems with the thyroid gland, it is necessary to limit the consumption of meat dishes, since protein stimulates the release of thyroid hormones, on which the level of the female sex hormone, estrogen, depends.
If mastopathy appears against the background of hypertension, then it is necessary to limit the consumption of fats, especially butter and lard, to reduce hormonal stimulation of the breast.
To provide the body with the necessary amount of calcium, which regulates the functions of the hormonal glands and has an anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect, you should consume kefir, yogurt and cottage cheese. Among other things, it is advisable to include in your diet seafood that contains iodine - fish, squid, shrimp and seaweed. This trace element is also present in large quantities in walnuts and mushrooms.
Treatment with folk remedies
In addition to the general course of treatment, you can also take herbal decoctions that help improve sleep and relieve pain, have a diuretic effect and contain beneficial elements.
Surgery
Surgical removal of affected tissue is prescribed in the following cases:
- rapid growth of the tumor;
- malignant degeneration of mastopathy detected by biopsy.
During the operation, a separate sector of the mammary gland is removed, in which cysts and lumps are found (sectoral resection). The operation lasts 40 minutes under general anesthesia.
After surgery, antibiotics and vitamins are prescribed. If necessary, pain relief and sedatives are administered. Hormone therapy may be used to prevent relapses. In this case, patients need to treat the underlying disease that caused the imbalance of hormones.
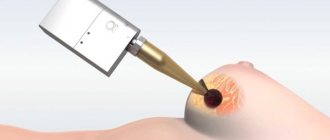
For large cysts, laser coagulation of these formations is possible. This technique is quite young and not widely used due to expensive equipment. For this procedure, a modern BioLitec laser device is used, which allows coagulation of the cystic formation without incisions or anesthesia. Also, with this procedure there is no risk of infection; a stay in an inpatient department is not required.
Thermal procedures, including physiotherapy, are not recommended for the treatment of FCM, as they can intensify inflammatory processes.
Contraindications to treatment
Hormonal treatment is contraindicated in cases of suspected malignancy, allergies and individual intolerance to drugs. In addition, each medicine has its own contraindications - for example, hormonal contraceptives are contraindicated for bleeding disorders, liver diseases and varicose veins. Therefore, if you have chronic diseases, it is important to tell your doctor about them.
Surgery is indicated for suspected malignant tumors. In other cases, diffuse FCM is treated conservatively.
Risk group
We have already found out that the cause of FCM is hormonal imbalance. Accordingly, women with diseases that disrupt the production of sex hormones - estrogen, progesterone, prolactin - are at risk. Most often, such changes overtake women between the ages of 18 and 40 years. Much less often - men. Long-term treatment with hormonal drugs also increases the risk of developing fibrocystic mastopathy, as well as a large number of births and abortions. Hormonal imbalances can result from refusal to breastfeed and prolonged absence of pregnancy (after 30 years).
Secondary factors can be considered everything that indirectly relates to hormonal imbalances. These are diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and disorders of the pituitary gland. Heredity, including if fibrocystic mastopathy was identified in close relatives. And of course, nutrition problems, bad habits and regular stress. All this negatively affects women's health in general and the health of the mammary glands in particular.
It is also important for women to protect themselves from injuries to the mammary glands. For example, squeezing your breasts with a tight bra can have a very negative impact on your breast health3.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
To carry out diagnostics, you need to see a mammologist. The specialist conducts a visual examination and analyzes the patient’s complaints. The first step is palpation. The patient stands up, raises her arms, then lies down on the couch and does the same. The doctor determines not only the appearance, but also the presence of signs of asymmetry, enlargement of one gland relative to another
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo one or more diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound examination;
- CT;
- mammography (not performed for women under 35 years of age or for pregnant and lactating women);
- pneumocystography;
- checking hormonal status;
- performing a biopsy (sampling of biological material) of the mammary glands.
What is mastopathy of the mammary glands and why is it dangerous?
Breast mastopathy is a pathological proliferation of breast tissue. There are different types of disease depending on the type of expanding breast tissue.
- Fibrous mastopathy is an excessive proliferation of connective tissue.
- Cystic mastopathy is excessive growth and obstruction (blockage) of the ducts, the formation of cysts.
- Adenomatosis is an excessive proliferation of glandular ducts.
There are also mixed types of mastopathy, for example, fibrocystic.
It is also important how exactly the tissue begins to grow. There are diffuse and nodular mastopathy. When it is not possible to determine clear boundaries of tissue changes, such mastopathy is called diffuse. And when the heterogeneity is clearly localized, they speak of nodular mastopathy.
It is important to understand that mastopathy can be benign (when the compaction does not threaten the body) or malignant. To determine the type of tumor, a biopsy or puncture is usually done. The sooner the type of compaction is established, the easier it will be to cope with the problem, especially in the case of a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of mastopathy.