Home / Breastfeeding / How to properly express milk during lactostasis and prevent its reoccurrence
16088
1
- How to determine that it is lactostasis?
- Behavior at the first signs of stagnation
- How to express milk correctly during lactostasis
- How to prevent stagnation of breast milk
- Useful video on how to express during lactostasis
Breast milk has been and remains the optimal nutrition option for a baby. Natural feeding helps a woman recover faster after childbirth, normalizes hormonal levels and increases the baby’s immunity, providing him with vitamins and microelements. But often during lactation, stagnation of milk occurs, leading to serious health problems, so every young mother needs to know how to express breasts during lactostasis.
The main danger of such a complication is that it can develop into a severe form - mastitis. Therefore, at the first signs of stagnation of milk in the breast, it is necessary to take measures to express it.
Symptoms
Most often, a woman accidentally discovers a lump in her breast while breastfeeding. A lump in the breast during breastfeeding is an accumulation of milk that for some reason cannot come out. If a small lump has appeared recently, then it does not cause any discomfort. During hygiene procedures, when changing clothes or latching the baby, a nursing mother suddenly feels a lump.
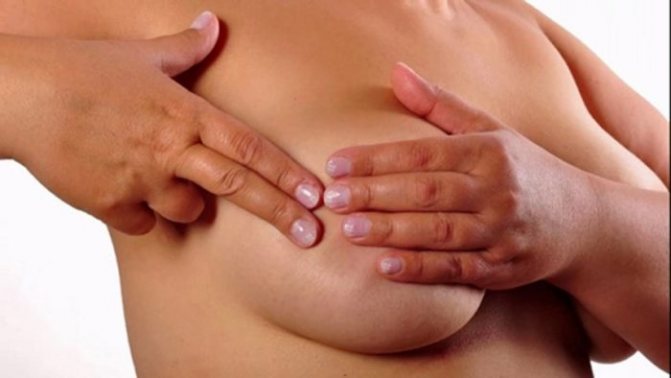
If the lump is large or formed a long time ago, the mother will experience symptoms:
- Changing the shape of the breast. During lactation, the mammary glands differ slightly in shape and size. If a large lump appears, then one breast takes on an unusual shape, swells and becomes larger.
- Tingling and pain. There are many nerve endings in the mammary gland. The lump squeezes them and causes discomfort. A woman's breasts hurt when she is at rest and while feeding her baby.
- Redness of tissues. If the lump in the mammary gland is accompanied by an inflammatory process, the skin changes color. In the area of the lump, the tissue turns red or bluish spots appear on it.
- Temperature increase. Volumetric hard lumps often provoke hyperthermia. Mild lactostasis usually resolves without fever, but the risk of complications cannot be ruled out.
- Difficulty in releasing milk from the breast. When pumping, a woman notices that the stream is weak or the milk flows out drop by drop. The child also notices changes, becomes restless and fusses at the breast.
Severe forms of inflammation worsen a woman’s quality of life. A nursing mother feels weak, drowsy, and does not have enough strength to do her usual activities. In the absence of help, the pathology progresses and brings the woman to the operating table.
Treatment
Today doctors distinguish between surgical and conservative treatment of mastopathy. Conservative treatment, that is, drug treatment, is divided into hormonal and non-hormonal. The main task at the early stage is to find and eliminate the cause of the disease, at the later stage - to relieve pain and remove the disease from the acute phase.
Interesting!
Oddly enough, men also suffer from mastopathy! Not often, but it happens. In the United States, for example, about 850–900 men fall ill each year. The male version of the disease is called differently: gynecomastia, that is, effeminate breasts.
If the disease is not advanced, then, as a rule, it is enough to eliminate the disease in the gynecological area (which provokes hormonal imbalance) and normalize the functions of the liver and nervous system. Hormonal drugs are used that increase the amount of missing hormones or reduce the amount of estrogen. However, hormone replacement therapy is effective at first, then it is also necessary to look for the causes of the imbalance of one’s own hormones and improve the functions of their reproduction naturally.
Nodular mastopathy does not respond well to hormone therapy and requires surgical intervention - excision of nodes as they are detected. However, doctors are skeptical about surgical intervention, since it does not eliminate the cause of the disease. It still needs to be identified and neutralized.
Methods of non-hormonal therapy include a corrective diet, correct selection of a bra, the use of vitamins, diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and drugs that improve blood circulation. For the liver, it is important to use an antioxidant, such as B-keratin, as well as vitamins A, B, E.
At any stage of mastopathy, physiotherapy, as well as visiting the bathhouse, sun and artificial tanning are prohibited.
Possible reasons
The cause of tightness in the chest during breastfeeding is:
- Stagnation of milk. There are many milk ducts in the mammary glands. They transport food for the baby from the lobes to the nipple. At the beginning of feeding, milk stagnation is considered normal, since the volume of fluid in the breast increases sharply. However, the cause of stagnation is sometimes pathological conditions and violation of the rules for caring for lactating breasts.
- Lactostasis. Having discovered a lump in the chest during breastfeeding, women talk about lactostasis. This condition is characterized by persistent stagnation of milk due to blockage of the milk duct. The cause may be physiological processes, tight underwear, hypothermia or inflammation.
- Mastitis. This inflammation in the mammary glands is caused by infection. Mastitis often develops after lactostasis or stagnation of milk in the breast. The causative agents of inflammation penetrate through cracks in the nipples or enter the gland through the lymphatic system.
- Neoplasms. Lumps in the breast during lactation are not always caused by breastfeeding. Sometimes women develop benign or malignant tumors during this period. The main provocateur of tumor growth is considered to be changes in hormonal levels.
Most often, lumps in the breast are an accumulation of milk in the ducts. Causes:
- an uncomfortable nursing bra that squeezes the gland and pinches the ducts;
- incorrect position when feeding, when the mother pressed the tissues with her fingers;
- sleeping on your stomach, which compresses your chest;
- excessive pumping, which produces a lot of milk;
- hypothermia, causing spasm of blood vessels and ducts;
- untimely emptying of the breast, which often happens when feeding by the hour;
- injuries and bruises, after which hematomas appear.
Bumps appear if the mother independently tries to stop breastfeeding with the help of her grandmother’s advice. When the breast is pulled or the baby is abruptly weaned, lumps form quickly and often lead to complications.
Hormonal storm
A woman's breast is like an orange - the glandular tissue (the same one that supplies milk to the nipple during the feeding period) is divided into 15-20 lobes. There is dense connective tissue between the lobes, which allows the breast to be firm and supports the lobes.
Article on the topic
Mastopathy: truth and myths about breast health The key to a healthy breast is the correct ratio of these tissues. This delicate balance is regulated by hormones.
Hormones involved in the functioning of the mammary glands are produced by the ovaries and pituitary gland. There are a great many of these hormones, not all have been fully studied, but we are interested in their most striking representatives: estrogens, progestins and prolactin.
In the first phase of the cycle, estrogens and prolactin are actively produced. Both of these hormones stimulate increased division of all breast cells. In the second phase, the ovaries begin to produce progestin, which limits cell division, returning them to normal. As soon as the hormonal balance is disturbed, the processes get out of control - and mastopathy can develop.
Blood test to identify causes
Any imbalance in the production of the hormones listed above can cause mastopathy. Of course, if you have the slightest doubt about your own health, you should contact a specialist. And don’t listen to doctors’ arguments like “all this is nonsense, come back in six months.” The earlier the disease is detected, the sooner treatment is started, the faster there is a chance to get rid of discomfort and possible consequences. Therefore, a competent mammologist will refer you for a consultation with an endocrinologist to look for the causes of mastopathy. And they are looked for first of all with the help of a blood test. It is necessary to donate blood for hormones in the first and second phases of the cycle, and then determine whether there are any violations. Having found out in which direction the shift is observed, the endocrinologist will prescribe medications to normalize the situation.
How to deal with seals
If a lump is detected in the breast while breastfeeding, action should be taken immediately. You should not expect the lump to resolve on its own. Often, delay leads to the fact that the usual stagnation of milk is complicated by the inflammatory process. In severe cases, the woman ends up on the operating table.
It will be better if a mammologist examines the lump and prescribes treatment. Sometimes a small examination is required to make a diagnosis. Medicines for lumps in the chest are prescribed if it is impossible to do without medications. Most often this occurs with mastitis of an infectious nature. More serious treatment is prescribed if tumors are detected.

If the lump appears due to stagnation of milk, then it can be broken using simple methods.
- Milk stagnation is caused by narrowing of the ducts. To make it easier for baby food to come out of the breasts, it is necessary to expand them. Heat helps relieve spasm. It is recommended to take a warm shower or drink a hot drink before feeding your baby. Heat should not be applied if lactostasis is accompanied by inflammation. Characteristic signs of mastitis are redness of the skin at the site of the lump and severe pain.
- The child qualitatively empties the mammary glands. If there is stagnation, you need to put the baby on the affected breast more often. It is recommended to position the baby so that the chin points towards the bump. The baby makes intense sucking movements with the lower jaw, so the duct with compaction will be emptied better.
- A cabbage leaf compress speeds up the resorption of the lump. You need to take a leaf, rinse it with clean water, beat it a little until the juice appears and apply it to the seal. This compress can be left on for several hours or overnight.
Alternative medicine offers many ways to combat compactions during hepatitis B. Women make compresses from a decoction of chamomile, honey, and cottage cheese. Every mother finds a method that helps her cope with a delicate problem. Usually lactostasis goes away within 1-5 days. Every day my mother notices improvements. If the lump becomes larger, redness appears, and severe pain is felt during feeding, you should consult a doctor.

If you have lumps in your chest, you should not:
- Pump until it hurts. By pumping, which was practiced in Soviet times, women damage breast tissue. This inevitably leads to problems in the future.
- Make alcohol compresses. Alcohol is well absorbed into tissues and passes into breast milk. In addition, ethanol blocks the production of oxytocin, a hormone that is responsible for milk excretion.
- Warm with salt or a heating pad. Complicated lactostasis and mastitis are sometimes accompanied by suppuration. During warming up, the risk of infection spreading and abscess opening increases.
- Drink medications without a doctor's prescription. Most medications are not compatible with breastfeeding. Therefore, even taking anti-inflammatory medications is contraindicated. Treatment is performed only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Stop breastfeeding. Mothers make a big mistake when they interrupt breastfeeding due to lumps. Abrupt refusal leads to excess milk in the breast and enlarged lumps. If you follow this scheme, it is easy to develop complications and end up on the operating table.
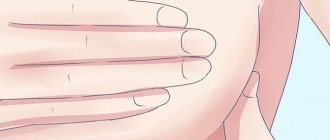
How to express milk correctly during lactostasis
There are several rules for expressing milk during lactostasis. The procedure should begin after high-quality warming of the chest and should be carried out as follows:
- Place the palm and four fingers under the mammary gland, the thumb and index finger as close as possible to the areola of the nipple.
- Using your thumb and forefinger, gently press on the breast, moving from top to bottom from the periphery to the edge of the nipple.
- During the pumping process, change the position of your fingers, trying to use the entire breast.
- Make sure that the movements remain slow and rhythmic; if there is pain or swelling, add light massaging.
- If the breasts are swollen and hardened unevenly, then pumping should be done more actively in the part where stagnation is detected.
At the end of the procedure, you can apply it to the baby's chest. If pumping does not bring relief or after a few hours lactostasis appears again and does not go away for more than 2 days, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination.

Prevention
To avoid the appearance of lumps in the mammary gland, it is recommended:
- Feed your baby on demand, not by the hour. The baby regulates milk production himself.
- Apply the baby correctly. The baby empties the breast fully only when the areola is captured. If the child sucks only the nipple, then the woman constantly develops lumps and cracks.
- Avoid bottles and pacifiers. Auxiliary accessories are harmful to lactation. They cause incorrect sucking technique and inadequate grip of the areola.
- Rest and avoid stress. Oxytocin is required to empty the milk ducts. Fatigue and stress block its production.
- Don't get too cold. Lumps in the breast appear due to narrowing of the milk ducts. One of the causes of spasms is hypothermia.

In Soviet times, doctors recommended expressing until the last drop so that there would be no lumps in it. However, pumping provokes hyperlactation - one of the causes of lactostasis. Therefore, regular pumping, feeding by the hour, supplementary feeding from a bottle and using pacifiers is a direct path to hyperlactation and compactions.
Preparing to pump
If you feed the baby not according to a set schedule, but according to his desire, then additional emptying of the mammary glands is not required. But if a nursing woman already has lactostasis, it is necessary to remove the milk from the breast where it has accumulated as soon as possible.
How to properly strain milk stagnation? First of all, you need to prepare your breasts. Before expressing, it is important to warm up the tissues with a hot shower, as the heat helps to remove blockages in the glandular ducts. Then you need to get a massage. It must be remembered that with lactostasis, you can empty the mammary glands only with your hands, and in no case with a breast pump. Before pumping, many doctors advise using cabbage leaf lotions with a thin layer of honey. These compresses eliminate pain and relieve swelling, but they should be applied for no more than fifteen minutes.