The issue of choosing a method of contraception during the postpartum period is relevant, since the newborn is still too small, and the woman’s body has not had time to recover. When choosing suitable contraceptives, consider their effect on lactation and all sorts of side effects. Otherwise, there is a risk of impaired milk production, an allergic reaction is possible, and an incorrectly selected product can harm the baby.
There are many methods of contraception, the most natural of which is lactational amenorrhea. In addition, lactating women use barrier, intrauterine, hormonal and other methods of contraception. The gynecologist will select the appropriate method of protection against unwanted pregnancy for a woman who is breastfeeding.
Woman in the postpartum period
The body of a lactating woman requires restoration: weakened immunity, hormonal changes, energy consumption for lactation. Not all mothers have ideal health and can become pregnant 3-5 months after giving birth. This is possible, but dangerous to health. For a woman to fully recover during lactation, she needs at least 2 years.
The balance of hormones during intrauterine development was adjusted over a period of 9 months. After the birth of a child, a woman’s body is rebuilt again, the hormonal background changes. As a result, the woman becomes impressionable, absent-minded, and quick-tempered. The body needs about 3 months to regulate the production of the necessary hormones. A new pregnancy will only worsen the woman’s already unstable condition.
There are no periods during breastfeeding for at least 2 months, maximum – the entire period of natural feeding. After about a year, the menstrual cycle is restored. At the very first menstruation, there is a risk of pregnancy, even if the woman is breastfeeding.

Consider the fact that ovulation precedes menstruation. Therefore, if the first unprotected sexual intercourse occurred during the first ovulation, then menstruation will not begin, as pregnancy occurs.
Prevention is an important point in the postpartum period. After all, a lactating woman must take care of her health in order to recover faster and feed the child. And an unplanned pregnancy with such a short interval is additional stress for the body. The gynecologist will select the appropriate contraceptive to save you from dangerous consequences.
Lactational amenorrhea
Physiological amenorrhea is a condition in which there are no periods during the postpartum period. This is due to excess prolactin in the body, which blocks ovulation. This is the most natural method of protection against unplanned pregnancy.

The method will work if the following points are met:
- The newborn is less than six months old.
- A lactating woman has not yet started her period.
- The baby is breastfed without complementary foods or additional fluids.
- The first feeding occurred within an hour after birth.
- The baby is often put to the breast during the day (at least 10 times).
- Feeding at night is mandatory.
This method of contraception has a lot of advantages: savings, naturalness, lack of side effects. There are also disadvantages: lactational amenorrhea lasts 6 months, a woman is not protected from sexual diseases.
It is not recommended to use this type of protection for women who cannot adhere to the schedule; any violation (missing the feeding time by at least an hour) and the method ceases to work. If you properly establish breastfeeding, then this method of birth control during lactation is 98% effective.
Is it possible to get pregnant immediately after giving birth?
After the birth of a child, a restructuring occurs in a woman’s body: the uterus contracts and cleanses. Cleansing occurs through fairly copious bleeding called lochia. Typically, they last up to eight weeks, gradually fading away. It is absolutely impossible to get pregnant during this period, since sex is completely contraindicated. It can lead to infection of the healing uterus. It is best to begin restoring sexual activity after an examination by a gynecologist, if the doctor gives permission. Although many women begin having sex immediately after the cessation of lochia.
Barrier contraception
Barrier contraception includes condoms, caps, and diaphragms. Doctors allow women to use this method of protection when breastfeeding. Barrier contraceptives are safe for breastfeeding and the newborn.

Condoms with spermicidal preparations guarantee an effectiveness of about 99%. Vaginal caps and diaphragms are used after 1 month and 2 weeks. The gynecologist will help you choose the right size product, which is administered only after its appointment. The cap is more effective (92%) than the diaphragm (87%).
Barrier methods
The simplest and most affordable method of protection when breastfeeding is the use of condoms for men or cervical caps, diaphragms and sponges for women.
- Not everyone likes to use condoms, and some are allergic to latex. Many note that childbirth affects the tone of the vaginal muscles, so the first time sensations during sexual intercourse may not be the same as they were before childbirth.
- Diaphragms and caps are selected by the doctor individually for each woman. The diaphragm is placed by the doctor for a long time, and the caps can be inserted by the woman immediately before PA. This is a suitable method of contraception for nursing mothers, and is especially effective for the first six months in combination with the lactational amenorrhea method.
If you used a barrier method of contraception before giving birth, you can opt for a diaphragm or a cap. Just be sure to keep in mind that the size of your ring and cap is now different, so be sure to consult a gynecologist.

Intrauterine contraception
The contraceptive device is a reliable method of contraception. The device is valid for 3–5 years, and short-term ones – from 1 to 1.5 years. The spiral is safe during lactation, as it acts locally. Intrauterine contraception is effective during lactation and guarantees a result of about 99.99%.
The contraceptive device shortens the duration of menstruation and prepares the uterus for the next planned pregnancy. The gynecologist will remove the IUD at any time at the request of a lactating woman. The ability to bear children is restored after 3–6 months.
The selection and installation of a contraceptive device should be carried out by a professional gynecologist. Otherwise, injuries and dangerous complications may occur. An ultrasound examination is performed before and after insertion of the spiral.
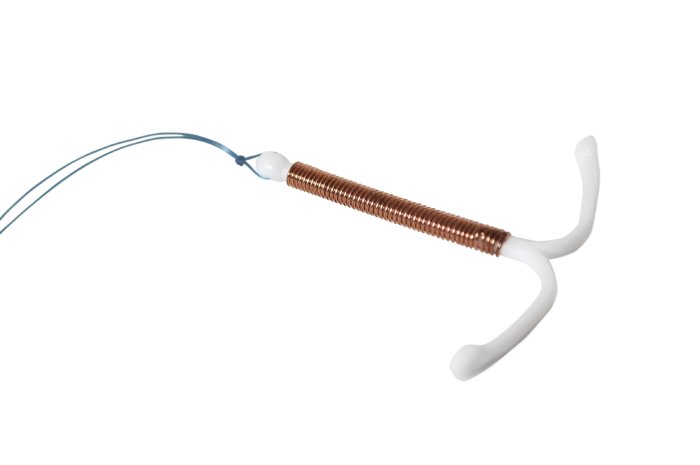
Disadvantages of intrauterine contraception:
- Heavy discharge during menstruation.
- Long menstruation.
- Decreased sensitivity during sexual intercourse.
- The uterus is constantly open, so you need to pay special attention to intimate hygiene.
Thus, the intrauterine method of contraception is effective and lasts for 5 years. It is important to understand that there is no 100% method of protection against unplanned pregnancy, and therefore the risk exists even when a woman is breastfeeding.
Hormonal contraceptives
Oral hormonal medications should not be used during breastfeeding, regardless of the level of hormonal substances. Contraceptives negatively affect lactation, as a result, the volume and quality of milk decreases. In addition, the drugs negatively affect the newborn’s body.

A lactating woman can be protected using tablets (mini-pills) with microdoses of the hormone progestin. This contraceptive is safe for babies and does not affect lactation. If you strictly follow the dosage schedule, the drug is quite effective (99%). Read more about the choice and effect of birth control pills during lactation in the article at the link.
After unprotected intimacy, use an emergency contraceptive drug, for example, Postinor. This hormonal drug should be taken with caution if a woman is breastfeeding. The drug has not undergone medical studies, and therefore its effect on lactation and the newborn is not fully known. Breastfeeding is allowed only 36 hours after taking Postinor. The degree of protection of the drug is not higher than 98%.
Spermicides are single-use preparations
Spermicides in the form of vaginal suppositories, gels, tablets and creams are approved for use during lactation, as they have a local effect and are not absorbed into breast milk.
The most popular drugs are Erotex, Patentex Oval, Pharmatex. Their main active ingredient is benzalkonium hydrochloride, which has a detrimental effect on sperm. It is imperative to follow the rules for using spermicides, which are indicated in the instructions:
- Use only clean water for washing.
- The drug must be administered strictly on time. For example, suppositories are administered 5 minutes before the act.
- Remember the rule: 1 candle (tablet) = only 1 act.
Spermicidal contraception
Spermicidal preparations (Patentex Oval, Pharmatex, etc.) have a low level of reliability. Spermicides are produced in the form of suppositories (vaginal suppositories), foam, jelly, cream, etc. The drug envelops the vagina and uterine cavity, and the chemical components that make up it destroy sperm.

Spermicides help fight atrophic vaginitis (drying of the vaginal mucosa), this problem is typical for women in the postpartum period. Gynecologists recommend using them in combination with barrier agents. The effectiveness of spermicidal contraception is from 59% to 96%.
How not to get lost in the variety of contraceptive methods? Are they allowed for a nursing mother?

The lactational amenorrhea method is based on the suppression of ovulation by the hormone prolactin, which stimulates lactation. The method is effective only with strict adherence to the rules of breastfeeding and it must be combined with other methods of contraception when reducing the amount of milk and introducing complementary foods.
Calendar method. It is not recommended to use after childbirth, since it is difficult to determine the date of ovulation and first menstruation. The effectiveness of the method is no more than 50% when performed correctly; the method requires special counseling for the couple.
Intrauterine device (IUD). A fairly reliable method, however, this method of contraception in the postpartum period can only be used after complete restoration of the uterus, but not earlier than 6 weeks after birth.
Hormonal contraception. Prescription and use are carried out under the strict supervision of the attending gynecologist. If you do not follow the rules of taking pills and skip taking pills, the effectiveness of this method is sharply reduced. Estrogen-containing medications are contraindicated in the first few weeks after birth due to the high risk of venous thrombosis. In addition, they affect the quantity and quality of breast milk and reduce the duration of lactation.
Barrier contraception. A condom protects against sexually transmitted diseases, but it also has a number of disadvantages:
- the condom may break during sexual intercourse;
- allergic reactions to latex are possible;
- the material is susceptible to destruction when exposed to high temperature, sunlight or oil-based lubricants, which are sometimes necessary for women in the postpartum period, because natural vaginal secretion is not restored immediately;
- decreased sexual sensations in partners during sexual intercourse.
Spermicides are means of local non-hormonal contraception. Preparations based on them (for example, Farmatex) can be used during breastfeeding and, if necessary, combined with other methods of contraception.
Pharmatex (active ingredient - benzalkonium chloride) destroys sperm membranes, which leads to the impossibility of fertilization of the egg. In addition, under its influence, cervical mucus thickens, which leads to loss of sperm motility and creates a barrier to their movement to the cervix.
Pharmatex:
- does not have a systemic effect on the body and does not penetrate the blood, therefore it can be used as a contraceptive in nursing women;
- does not affect the menstrual cycle, libido and fertility;
- does not affect the normal microflora of the vagina, including lactobacilli;
- 4 vaginal forms of the drug - suppositories (suppositories), capsules, tablets and cream - allow partners to choose the most convenient option.
The advantage of using spermicides in the form of creams and suppositories is the formation of additional lubrication during sexual intercourse, which makes it more comfortable for nursing women who experience vaginal dryness.
Pharmatex is used not only during breastfeeding. The drug is a means of local contraception for women of reproductive age, and especially: in the postpartum period; after termination of pregnancy; with irregular sexual intercourse; if there are contraindications to the use of hormonal contraceptives or intrauterine contraception; as an additional method of contraception.
Sterilization
Voluntary surgical sterilization is a fundamental method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. This is an operation as a result of which an artificial obstruction of the fallopian tubes is created, and the woman is deprived of reproductive function. The effectiveness of this method is 99%, but the consequences of surgical intervention are irreversible, so before making a decision, weigh the pros and cons. Entrust the operation to a professional, otherwise pregnancy is possible.
There are many more methods of contraception, among which you can choose the most suitable option.
However, it should be remembered that it is not recommended to take hormonal drugs while breastfeeding. Otherwise, side effects occur in the form of bleeding of varying intensity. In addition, hormonal drugs negatively affect lactation and the body of the newborn. The gynecologist selects and prescribes a contraceptive. Subscribe to our VKontakte group
Contraception for a nursing mother
If you want to protect yourself from re-conception, then you should think about contraceptive methods and choose the most suitable one. Of course, the best advisor in this matter is a gynecologist. There are the following methods of contraception that do not affect milk production and are harmless to the baby:
- Barrier contraception. This is a reliable way to avoid pregnancy. True, female contraceptives of this classification should be used no earlier than two months after childbirth and only as prescribed by a doctor. Typically, gynecologists recommend protecting yourself with condoms.
- Spermicides. These are topical contraceptives. They are absolutely harmless for both mother and baby. The only disadvantage of this type of protection is its low reliability compared to other methods. It is within 80%.
- Hormonal pills. The lion's share of such drugs suppresses milk production. The exception is progesterone-based medications. The principle of their action is simple, they change the structure of the cervical mucus, making it thick, which prevents the passage of sperm into the female body. The use of such drugs should be discussed with your doctor; usually gynecologists are not against giving permission to use this method of protection.
- Hormonal implants and injections. They have a high degree of reliability - up to 99%. At the same time, they have absolutely no effect on milk production and the baby’s health.
- Spiral. The intrauterine device is an excellent method of contraception. But until the size of the uterus is completely restored, it should not be used, since there is a high probability of prolapse. It is necessary to check the position of the spiral with a gynecologist twice a year.
Contraceptive methods that worked well before pregnancy may not work for a nursing mother . These are methods of natural pregnancy prevention, such as calendar and temperature. This state of affairs is associated with dramatic changes in a woman’s body after childbirth, so it is no longer worth protecting yourself with them.
If you are not sure about your method of contraception, it is better to visit a gynecologist and choose another method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. Most married couples during this period prefer condoms. The popularity of this method of barrier contraception is largely due to the complete absence of contraindications and the need to consult a doctor.