Is it possible to take contraceptives during breastfeeding?
During breastfeeding, many women choose lactational amenorrhea as a means of contraception. This is a natural method of birth control with a high percentage of reliability (95%) in the first six months after birth.
But it only works under the following conditions:
- putting the baby to the breast frequently (every 2 hours or on demand);
- consuming only breast milk without complementary feeding or drinking;
- active lactation.
Contraception during breastfeeding should be prescribed by a doctor.
Even with such a high degree of protection, pregnancy can occur, so it is recommended to select other means of contraception. Oral contraceptives are effective and safe.
They are allowed to be taken 6 weeks after birth. The degree of protection against conception when taken is 99%. Suitable pills (if there are no contraindications) will be prescribed by a gynecologist after examination and a series of tests.
The need for contraception after childbirth
Contraception is protection against conception, which for some reason is undesirable. Why is contraception so important after childbirth? Even if the family plans to have another child, it is necessary to wait time so that the woman’s body can fully recover after 9 months of increased stress. According to doctors, the minimum time that should pass after childbirth before the next pregnancy occurs is 2 years. Research results have shown that pregnancies that occur earlier than this period often have complications for both the mother and the fetus. If the spouses no longer intend to have children, they must approach the issue of birth control with even greater responsibility.
After resuming sexual relations, it becomes necessary to choose the right method of contraception
When should you start protecting yourself?
Despite the fact that the female body will need several more years to recover after childbirth, the reproductive system can be ready for conception within 4-6 weeks. In non-breastfeeding women, the first ovulation most often occurs between 1.5 and 3 months, although deviations to a smaller extent are possible when conception becomes possible after 25 days. In nursing mothers, ovulation resumes on average after 2–6 months, and this period is associated with feeding habits.
The choice of contraceptive methods and the initiation of their use depend on the intensity of breastfeeding.
- If you are not breastfeeding, you need to start using protection from the very beginning of sexual relations. You are not limited in your choice of contraceptive methods and means.
- If your baby is on mixed feeding, you do not breastfeed him often enough or introduced complementary foods early, you must use contraception, as in the first case, immediately after returning to sexual activity. It is permissible to use only those contraceptives that cannot affect milk production and the health of the child.
- If you breastfeed on demand, you can rely on the lactational amenorrhea method for the first six months and delay the use of other contraceptives for 6 months.
- In case of emergency cessation of breastfeeding, you should start using contraceptives on the day of your last feeding.
Advantages and disadvantages of oral contraceptives for breastfeeding
Contraception during breastfeeding has the following priorities:
- Normalization of hormonal levels.
- Does not degrade the quality of breast milk.
- Minimize the occurrence of inflammation, diseases of the genitourinary system, and oncology.
- Prevention of disorders in the musculoskeletal system and metabolism due to hormonal imbalance.
- Reducing pain during menstruation, normalizing the cycle.
- Reducing menstrual flow reduces the risk of developing anemia with significant blood loss.
- Suppressing PMS symptoms.
- Normalization of weight.
- Ease of use.
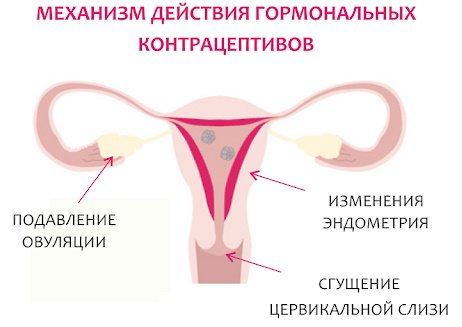
Along with the advantages, there are also a number of disadvantages:
- Irregular, scanty menstrual bleeding.
- The appearance of spotting between periods.
- In the first month of use, you may experience headache, nausea, and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- Decreased libido.
- Slight weight gain is possible.
- You must strictly adhere to the rules for taking pills.
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
- The risk of blood clots and the development of polycystic ovary syndrome increases.
- High price.
What contraceptive drugs are allowed while breastfeeding?
Birth control medications that can be used while breastfeeding should not contain estrogen. This hormone disrupts lactation and slows down the development of the child.

Approved medications include one-component tablets with progestin (an analogue of the hormone progesterone). It is contained in tablets in a microdose - 300-500 mcg, which is why such preparations are called mini-pills.
Hormonal tablets with estrogen are approved for use when the child reaches six months.
Classification of drugs, list of safe drugs
There are several classifications of hormonal drugs that are safe during lactation. The table below shows their main types and names.
| Classification | Kinds | Drug names |
| Oral contraceptives (pills) | Combined | Janine, Diane-35, Jess, Silhouette |
| Progestin (mini-pills) | Laktinet, Exluton, Microlut, Ovret, Charozetta, Femulen | |
| Prolonged | Injections (done every 8-10 weeks, contain progesterone) | "Implanton" |
| Subcutaneous capsules (the implant is inserted under the skin in the shoulder area for 5 years, contains progesterone) | Depo-Provera | |
| Emergency contraception | Preparations with levonorgestrol, taken after unprotected sexual intercourse no later than 72 hours later, are not used for continuous use | Postinor, Exapela |
Lactinet: review, composition, price, instructions
Lactinet contains the hormone desogestrel (75 mcg) - this is a 3rd generation synthetic gestagen. The action of the tablets is based on inhibition of ovulation processes: progesterone and luteotropic hormones do not increase in the blood, and the uterine mucus becomes more viscous.

To achieve a high degree of protection against conception, the tablets are used daily without interruption (it is recommended to take them at the same time of day). If you skip a pill, the contraceptive effect lasts up to 12 hours. The Laktinet package contains 28 tablets, the cost is about 800 rubles.
The drug is used 1 pc. per day, after finishing the tablets in the blister, start taking the next package. The first tablet is taken on the 1st day of menstruation. During lactation, administration begins 6 weeks after birth.
Charosetta
Taking the drug Charozetta, produced in the USA, is similar to Lactinet. It contains desogestrel (75 mcg), stearic acid, vitamin C and excipients. The action of the tablets is aimed at suppressing ovulation.
They do not affect the metabolic process in the body. When taken, a small part of the drug enters the baby’s body through breast milk. But this does not cause any developmental problems.
Women may experience headaches, acne, mood swings, and nausea. These manifestations disappear within the first 2 months from the start of treatment. Charozette is allowed to be taken 21 days after natural childbirth. For caesarean section, administration begins on the 28th day. The cost of the drug is about 1500 rubles.
Microlute
The active ingredient of the drug Microlut is the hormone levonorgestrel (0.03 mg). It prevents the release of the egg, suppresses the active production of luteotropic and follicle-stimulating hormones. The effectiveness of the drug is achieved by taking tablets daily at the same time interval.
Due to the content of low doses of the Microlut hormone:
- Not recommended for overweight women.
- After 1 year of use, its contraceptive effect decreases. It is recommended to switch to medications with a high content of hormones.
The drug package contains 35 tablets, the blister is enough for use for 5 weeks.
Exluton
The active ingredient of Exoluton is the hormone linestrenol (500 mcg). The drug helps normalize the menstrual cycle, is approved for use in cases of renal failure, hypertension, disruption of the cardiovascular system, and the likelihood of developing thromboembolism.
When taking Exoluton, you must strictly adhere to the time of taking the tablets. A delay in taking the drug for more than 3 hours reduces the contraceptive effect. If vomiting and diarrhea occur, the protective effect of the drug also decreases. Contraindications for use are liver disease, uterine bleeding, pregnancy and the risk of developing ectopic pregnancy.
Side effects of taking Exoluton are:
- swelling of the legs;
- headaches and dizziness;
- swelling and tenderness of the breast.
The cost of a package of tablets (28 pieces in a blister) averages 2,000 rubles.
Femulen
Contraceptives for breastfeeding Femulen contain 2 active ingredients - levonorgestrol and norethindrone. They have a gestagenic (suppression of the production of gonadotropins by the pituitary gland) effect on the female body, and have virtually no contraindications.
The drug is approved for use for:
- frequent headaches and migraines;
- high likelihood of blood clots;
- being overweight;
- diabetes;
- elevated blood pressure levels.
The contraceptive effect of Femulene lasts for 24 hours. If diarrhea or vomiting occurs, you must take the pill again.
Mini-pill
Mini-pills are an effective replacement for combined pills during lactation in the following cases:
- Presence of cardiovascular system disorders.
- Smoking – nicotine and combination pills increase the risk of blood vessel blockage.
- Painful menstruation.
- Psychoemotional disorders during PMS and menopausal disorders.
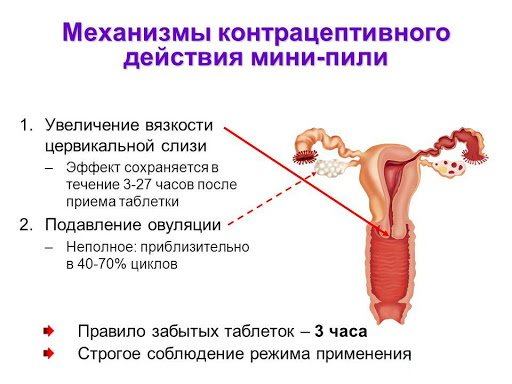
The contraceptive effect of the mini-pill is lower than that of combination drugs and is 95%. This is due to different mechanisms of action on the body.
Combination pills completely suppress ovulation. When using the mini-pill, the usual menstrual cycle is maintained.
Their contraceptive effect is based on 2 features:
- The structure of the mucous membranes of the cervix changes - increased viscosity does not allow sperm to penetrate to the egg.
- The proliferation of the epithelium of the uterine mucosa prevents the attachment of a fertilized egg.
Contraindications

The doctor can prescribe contraceptive pills during breastfeeding after carefully clarifying the restrictions on the part of the mother. If there are contraindications, these drugs should be avoided, as the drugs may contribute to a serious complication such as pulmonary embolism (PE) or venous thrombosis of the lower extremities.
Main contraindications to the use of these drugs:
- congenital bleeding disorders,
- atrial fibrillation,
- deep vein thrombosis of the legs,
- history of pulmonary embolism,
- smoking more than 15 cigarettes per day,
- severe diseases of the liver tissue and kidneys,
- diabetes,
- suspected pregnancy
- hormone-dependent cancer
- feeding the baby in the first 2 months after birth.
Precautions when taking medications
Contraceptives during breastfeeding require care and caution when taken.
Necessary:
- take into account existing contraindications before starting treatment;
- visit a gynecologist every 3 months;
- in the first week of taking the pills, use additional contraceptives;
- follow the dosage schedule (it is better to take the pills in the evening to smooth out side effects);
- in case of intestinal dysfunction for more than 5 days, consult with your doctor and, if necessary, choose another drug;
- if bleeding occurs for more than 7 days or absence of menstruation for more than 3 cycles, immediately contact a gynecologist;
- do not change the drug or dosage yourself;
- When taking certain enzyme-inducing drugs (antibiotics, antiretrovirals, St. John's wort), additional contraception is required (for a period of up to 28 days).
Other methods of protection
Non-hormonal contraceptives allowed during lactation are presented in the table below.
| Methods | Peculiarities |
| Barrier (condoms, diaphragms, caps) | When used correctly, they provide 98% protection against pregnancy. Condoms additionally protect against a number of diseases. |
| Spermicides (gels, suppositories, creams) | The effectiveness of protection is 80%, they have a local effect and can cause allergic reactions. |
| Intrauterine device | Protection is 99.2%, for a period of 3-5 years. |
| Calendar | The effectiveness is up to 60%; it consists in determining the period of ovulation by tracking the menstrual cycle and measuring basal temperature. |
| Interruption of sexual intercourse | An ineffective method, the probability of pregnancy is 30-40%. |
| Medical sterilization | Irreversible method, suitable for people who no longer want to have children. |
Mini-pill contraceptives during lactation are safe drugs, provided there are no contraindications for the mother and child.
Natural methods of contraception
Coitus interruptus
During intercourse, a man withdraws his penis from the vagina before ejaculating. But the thing is that some of the sperm may be contained in lubricant, which is released even before orgasm. And thus get into the vagina and fertilize the egg. After childbirth, using this method of birth control is completely unsafe.
Efficiency: 50%
Basal temperature measurement
An increase in basal temperature in the rectum indicates the onset of favorable days for conception. By regularly measuring basal temperature, the days of ovulation are calculated. This method should not be considered effective after childbirth. During postpartum recovery, temperature may fluctuate due to changes in the pelvic organs or due to lactation hormones. In addition, basal temperature is measured after a full night's sleep, without getting out of bed. But mothers of infants can hardly afford uninterrupted sleep at night. So you shouldn’t rely on this type of contraception.
Efficiency: no more than 60%
Calendar method
Keeping a calendar of dangerous and safe days after childbirth is not a reliable method of birth control. After childbirth, the cycle is established within several months. This method is also not suitable for a woman who is breastfeeding because even after the cycle has been established, menstruation may be delayed. This depends on the surge in lactation hormones. Prolactin “clogs” ovulation, it can be delayed for several days or even weeks.
Efficiency: less than 50%