Excessive production of breast milk causes a lot of inconvenience to a nursing mother. She is forced to regularly resort to additional pumping to prevent stagnation and further troubles with her breasts.
The babies of such mothers also have a difficult time: it can be difficult for them to suckle due to an overly active flow of milk, feeding becomes nervous and fussy. These difficulties are accompanied by less significant but unnerving moments - unpleasantly overfilled breast pads, excessive milk leakage, more dirty diapers and nappies. But if a mother wants to reduce her breast milk production, she first needs to understand whether she really has too much milk.
When is it necessary to reduce lactation?
The need to slow down the rate of milk production usually occurs in case of hyperlactation. The main symptom of this condition is very rapid breast fullness. For example, the baby ate only half an hour ago, and has not yet expressed readiness to suck again.
And my mother’s breasts are already engorged and are experiencing noticeable discomfort and even pain. If under such conditions a woman does not express at least a little secretion, the risk of swelling, blockage of the ducts, lactostasis and subsequent mastitis (inflammation) increases. Therefore, women often find themselves in a vicious circle: they cannot help but relieve their condition by pumping, and frequent emptying of the breasts leads to even greater milk production.
Excess milk often accompanies the first three months of a baby's life. The mother's body adapts to the child's needs gradually, and by three months the secretion production stabilizes. That is, the breast produces exactly as much nutrition as the baby sucks. Supply equals demand. And at first there is an abundance of milk, because, figuratively speaking, the woman’s body does not understand how many children need to be fed.
Pumping
If feeding is inconvenient for a woman, for example, it is painful for a mother to feed her baby, you can use an alternative method - pumping. For this, the mother will need a breast pump. Breast milk is expressed, then the baby is bottle-fed. Regularly expressing and preparing milk for a baby takes a lot of time. But the mother can be calm about the baby’s digestion. Since the breasts are emptied during hot flashes, a woman will be able to avoid stagnation of milk, mastitis and other breast diseases.
The problem of excess lactation
Most babies whose mothers experience hyperlactation gain weight too quickly. Their natural desire is to suck frequently, and not just for the sake of getting food. But with each attachment, the child receives another portion of nutrition. Therefore, increases can be significantly higher than normal.
The opposite situation also happens: the baby’s weight increases more slowly than is acceptable for an infant. The reason for this may be a lack of milk supply, since the baby finds it difficult to cope with its strong flow. He may nurse frequently but not actually get enough milk. Regurgitation due to swallowing air during feeding can also interfere with weight gain.
Signs
When a mother has a lot of milk, other features may appear in her well-being and the baby’s behavior during breastfeeding. They may or may not accompany this condition, so they cannot be considered reliable evidence of excess milk production. Other possible signs of hyperlactation include the following.
- Constant and abundant leakage of milk. When the baby suckles on one breast, milk actively flows out from the other side. This situation can also happen between feedings. Sometimes mothers have to change several diapers on their chest while the baby is sucking. And during the day, throw away more than one bra pad. However, copious leakage of secretions also occurs in women without hyperlactation.
- Restless behavior of the child at the breast. Babies from very milky mothers often fuss, get nervous and cry during feedings. They take and release the breast, hiccup, spit up and cannot cope with the strong flow of fluid.
- The milk flows out in an active stream. This is a completely normal situation to start feeding. But it happens that the force of the flow does not weaken even after a few minutes.
- Short but frequent applications. Since the abundance of milk does not allow the baby to suckle comfortably, he may ask for the breast too often. In this case, the duration of application may not exceed several minutes. Although, normally, healthy children are able to get enough after five to seven minutes of effective sucking.
- Excessive gas and strange stools. Babies from mothers with hyperlactation often have abnormal stools: foamy, watery, greenish in color.
- Repeated blockages of the ducts, lactostasis and mastitis. Excess secretion and its untimely removal often lead to problems with the mammary gland. However, these consequences also have other reasons (errors in attachment, infectious disease, rare feedings).

Causes
Hyperlactation can be caused by hormonal characteristics of the female body. It can also be encountered by mothers who carefully follow the advice to express “to the last drop” after each feeding. Excess milk also appears when breasts are changed frequently during one feeding. That is, the baby is transferred to the other side before he has completely emptied the first. This happens even if you follow the recommendations to keep the baby at each breast for a certain number of minutes so that he is sure to receive milk from both glands at the same time.
How does it affect the child?
Abundant milk production, it would seem, is not a problem at all. After all, many mothers are struggling to increase its volume. Meanwhile, hyperlactation can seriously worry the baby. Frequent and short sucking with constant breast changes leads to the fact that the baby does not empty the gland completely.
He receives mainly “foremilk”, rich in lactose (milk sugar). It has a very low percentage of fat, so it is less nutritious. Normally, the baby drinks it at the very beginning of feeding. With prolonged sucking, particles of fat are added to it. And the longer the feeding, the more high-calorie milk the baby sucks out.
If the baby is breastfed often, but not for long, and at the same time moves from one breast to the other during one feeding, he gets the “fore milk”. The intestines are filled with an excess amount of lactose with a reduced fat content. This disrupts normal digestion processes and leads to rumbling in the stomach, excessive gas accumulation, and foamy and green stools. Naturally, these problems bother the baby and spoil his mood.
What's the result? Frequent attachments, crying and nervousness of babies at the breast make mothers think that they have little milk. Or it is not nutritious enough to satisfy the child's needs. Although, in reality, there is more nutrition than is needed. Thus, unreasonable supplementary feeding with formula may appear in the baby’s life.
Video on the topic Mama Lara about excess breast milk
Chest tug
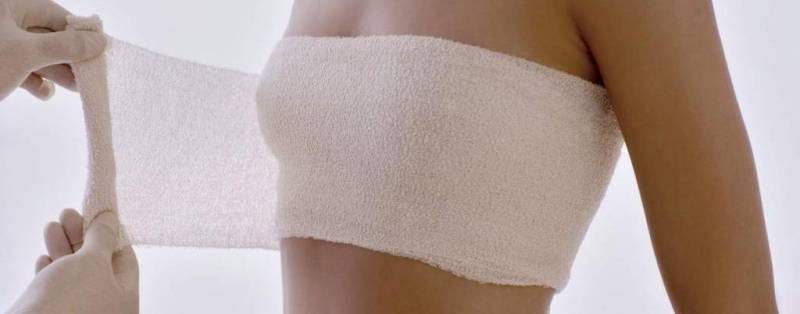
There is an opinion that tying the breasts is the best method for stopping milk production. For this technique, a woman first expresses all the milk, then bandages her breasts with a sheet or elastic bandage. After hot flashes or a feeling of heaviness in the chest, the bandage is removed, the breasts are re-expressed until relief is achieved and bandaged again.
Women note that milk disappears after the third dressing. But this technique causes discomfort in the woman. Moreover, there is a high risk of developing breast diseases. During tight tugging, a woman can simply injure the milk ducts, causing stagnation of milk. If medical care is not provided during this period, mastitis develops. In this case, the woman needs to immediately visit a doctor to begin treatment.
Bad advice and myths
In attempts to “tame” lactation, nursing mothers often make the same type of mistakes. Because of this, they not only cannot cope with excess milk, but also aggravate the situation.
What a mother with hyperlactation should not do:
- constantly use a breast pump;
- express after each feeding;
- try to express your breasts “to the bottom”;
- often shift the baby from one side to the other during one feeding;
- change breasts every feeding;
- ignore the feeling of painful fullness in the chest;
- crush, crush, traumatically strain the gland;
- uncontrollably take herbs and medications to suppress lactation;
- tightening your breasts and wearing tight underwear.

Medicinal ways to get rid of milk
Having firmly decided for yourself that you completely trust modern pharmaceutical products, do not be too lazy to consult a doctor. For example, if a woman’s prolactin level is off the charts, this feature needs to be taken into account, since it will be more difficult for her to get rid of lactation, there is a risk of edema, followed by blockage of the ducts and mastitis.
Typically, anti-lactation drugs contain hormones, they are taken from several days to a couple of weeks, the course depends on the individual characteristics and specifics of the drug.
Known drugs:
- Duphaston;
- Turinal;
- Utrozhestan;
- Acetomepregenol;
- Bromocriptine;
The latter, by the way, is banned in the USA due to many side effects.
Contraindications
For kidney and liver diseases, diabetes mellitus, thrombophlebitis, hormonal imbalance, etc., there is no need to buy these medications. This is another argument in favor of the need to consult a doctor who can select a drug specifically for each patient.
It should be remembered that as soon as you take the first dose of the medicine, you will no longer be able to feed the baby.
Decreased milk production when complementary foods are introduced
Nursing mothers with excessive milk secretion make a lot of efforts to establish lactation in a comfortable manner. Many of them then strive to feed their babies for as long as possible. Therefore, the slightest changes in breastfeeding rhythms cause concern and anxiety. For example, there is an opinion that when you introduce complementary foods, the amount of milk decreases. In fact, complementary feeding products complement, rather than replace, mother's milk.
Breastfeeding remains approximately the same daily amount (10-12 times), but they are distributed differently throughout the day. An older baby breastfeeds mainly around dreams and at night. During the day he eats regular food. Therefore, if you maintain a sufficient number of latch, milk production will not change even during this period.
But when a child is weaned, milk secretion actually decreases. With the physiological completion of lactation, this occurs smoothly and painlessly. But here, too, the need to periodically express is not excluded. When the number of feedings is reduced, the breast does not immediately adjust to the new regime. From time to time she needs help - to pump up the discomfort until she gets relief. This applies not only to mothers with excess milk production, but also to mothers with normal secretion production.
Related video Nina Zaichenko talks about the problem of hyperlactation
Hyperlactation leaves mothers wondering how to reduce their breast milk supply. There are simple and effective ways to do this that you just need to try in practice. There is another alternative: not to fight the abundant “rivers of milk”, but to use them for the benefit of other children. Some mothers choose to become breast milk donors. They donate the surplus to a special milk bank. And from there he is taken by women who, for various reasons, are not able to feed their children themselves. So addressing hyperlactation can be a wonderful way to help other babies stay healthy.
Folk remedies
Ways to reduce milk production using folk remedies can bring significant relief. It is advisable to avoid tugging the mammary glands. This method may cause the development of mastitis.
To reduce lactation, you can take sage in the form of a decoction three times a day. Compresses on the chest made from cabbage leaves and ice can bring minor relief. Medicinal herbs have a diuretic effect and help reduce lactation. Lingonberry leaves, black alder and other compounds are used. Peppermint tea has a calming effect and helps reduce milk production.
It is better to coordinate the use of folk remedies with a doctor, and observe moderation when using them.
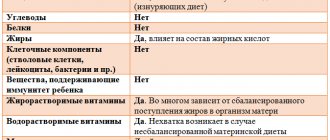
We recommend reading: Breast milk analysis