Number of views: 26,891
In order to satisfy your curiosity, I placed a special table at the beginning of the article. Next, we will take a closer look at those components of breast milk (HM) that are influenced by the nutrition of a nursing mother.
Table. The influence of a nursing mother's diet on the volume and composition of breast milk
Mother's milk is an important food that influences the development of infants
Breastfeeding your newborn is very important, especially in the first month of life. After all, it is this food that saturates the body with useful vitamins and macroelements, without which it is difficult to imagine proper development. A nursing mother's milk appears due to the synthesis of blood, lymph and water in the body. Human nature is designed in such a way that while a pregnant woman is carrying a baby under her breast, the milk accumulates all the beneficial substances that are needed for feeding and the proper development of the future person, which has a good effect on its benefits and fat content. This composition can be used as the main food for up to 9 months.
All mothers are probably interested in the question: “What kind of milk should be in order for the baby to become healthy, strong and strong?”
The normal calorie content of breast milk is around 280 kJ.
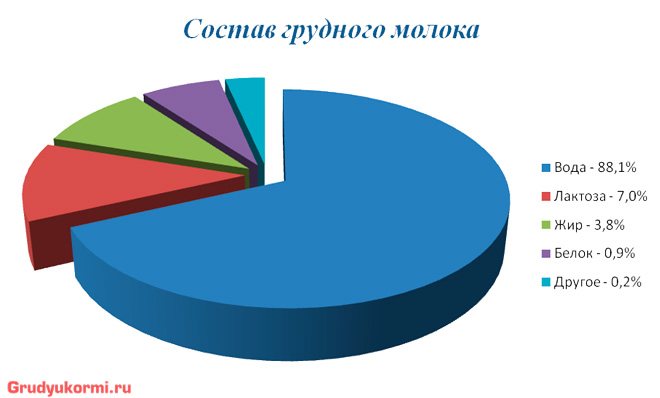
And the nutritional value of the product should be as in this table:
Nutritional value of the product
| Elements found in 100 g of breast milk | Content quantity |
| Calories | 70 kcal |
| Squirrels | 1g |
| Fats | 4.4 g |
| Carbohydrates | 6.9 g |
| Water | 87.5 g |
What determines the quality of breast milk? The properties of this beneficial liquid are influenced by many factors. The most common of them are hormones, heredity, the requirements of the baby’s body, the physiology and psychological health of a woman. Often, among the factors influencing the composition and consistency of the product are the season and time of day. For example, in summer milk is watery because in the heat the child’s body requires more water. At night, such food is characterized by great satiety, which helps the baby sleep sweetly. It acquires a special taste and nutritional value when the baby finishes breastfeeding. That is why it is better for a nursing mother to feed her child with only one breast.
The quality of breast milk is also affected by the nutrition of the nursing mother. Therefore, in order for milk to be truly beneficial, during the lactation period you do not need to exhaust yourself with diets; in an effort to return to its former figure, the child must receive adequate nutrition.
Diet of a nursing mother and its effect on milk
In Ireland, immediately after childbirth, tea and toast with butter and jam are served. In Israel, they bring grapefruit salad for breakfast. In the USA, lunch is served with tomato soup, a sandwich with red fish, coffee and chocolate cake. In Australia, dinner is stewed meat with cabbage and green peas. In post-Soviet countries, immediately after childbirth they give a list of permitted and prohibited products (if they did not have time to give them out during pregnancy).
So does a nursing mother need a diet? And if necessary, which one? In order to answer these questions, it is necessary to understand how the mother’s diet affects the composition of milk.
Milk is produced in the mammary glands from components of the blood plasma; accordingly, the nutrition of a nursing mother affects milk to the same extent as it affects the blood. With a lack of enzymes, food may be poorly broken down and larger proteins will penetrate into the blood, which, once in milk, will be more difficult to absorb by the immature intestines.
Thus, the first thing a mother needs to do is to improve the functioning of her body, tired from pregnancy and overloaded during childbirth. This means that the mother’s diet should be healthy and nutritious. A nutritious diet requires the presence of five food groups in the diet: vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy products and meat (sometimes fish). Recommendations on rational standards for the consumption of food products that meet modern requirements for a healthy diet were approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia N 614 of August 19, 2016. A vegetarian diet is allowed, taking into account the receipt of all necessary substances from plant products and additional intake of vitamin B 12.
You need to eat in small portions, but often. You can forget about the regime at first, just eat according to your appetite. Usually the feeling of hunger comes during or immediately after feeding. Taking into account the fact that at first night feedings cannot be avoided, it is advisable to have something nutritious in stock for a snack, so as not to run to the refrigerator in the middle of the night.
It is advisable to increase the daily calorie content of food consumed by 500-600 calories compared to the pre-pregnancy diet, since milk production requires increased energy consumption.
There is an opinion that when breastfeeding you need to drink a glass of water before and after feeding. However, drinking too much liquid puts a strain on the kidneys, which is a stress factor for the body, and any stress blocks the release of hormones. In addition, excess fluid can lead to swelling of the breast tissue, which can also impair milk flow. Accordingly, excessive fluid intake (as well as thirst) can lead to decreased milk production. It is necessary to drink enough water. Usually this is about 2-3 liters per day, but each body has its own standards, which means you need to listen to your feelings - drink according to thirst.
10-15 minutes before evening feeding (when there is usually less milk), it is advisable to drink a glass of hot tea or other warming drink - this promotes the production of oxytocin and, as a result, better milk flow.
It is widely believed that some foods consumed by a nursing mother can cause gas formation and allergic reactions in the baby. In most cases, it is this misconception that leads to the fact that the mother begins to eat buckwheat and water, which contributes to dysbiosis, vitamin deficiency, calcium deficiency, low hemoglobin, malnutrition and other unpleasant things in both the mother and the child (with insufficient nutrition of the mother, in milk first comes from maternal reserves, but over time these reserves are depleted).
As for gas-forming, strengthening, laxative products, their “hostile” properties do not enter the blood (and therefore into milk). However, if the product consumed has a negative effect on the mother’s digestion, then this can also affect the blood (milk) (you can read more about how to deal with colic and gassy here).
Allergies are often confused with food intolerances. An allergy is a defect of the immune system, which is very often influenced by a hereditary factor, while food intolerance is associated with immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract. In case of intolerance, a dose dependence is often observed. For example, when a mother eats one strawberry, nothing will happen to either the mother or the child. But if the mother eats a bucket right away, pseudo-allergic reactions are quite possible, including in the child.
Along with breast milk, the baby receives only in microdoses the broken down proteins of foods (traces of peanuts, gluten, etc.) consumed by the mother. At the same time, along with these microdoses, the mother’s immunoglobulins, enzymes, lacto- and bifidobacteria enter the milk, which help the baby’s body absorb the resulting protein. Breast milk seems to digest itself. Therefore, if the mother eats a varied diet and does not overuse any particular product, an allergic reaction in the baby, as a rule, does not manifest itself (even if the child later turns out to be allergic, the mother may find out about this at the stage of introducing complementary foods - this often happens with celiac disease).
However, there is an exception - cow's milk protein (cmp). It has not yet been studied why this protein can enter breast milk in an undigested form (logically, it should be broken down by the mother’s body into amino acids). This feature often becomes the reason for the exclusion of all dairy products from a nursing mother’s diet. In most cases, such an exception is unfounded, since, as a rule, only the “hard” bkm contained in whole milk is difficult to digest. At the same time, fermented milk products are absorbed much better. In addition, fresh natural fermented milk products contain beneficial bacteria that promote comfortable digestion for the mother and envelop the walls of her intestines with a protective film, which prevents allergens from entering the blood (and milk).
Thus, breastfeeding should not turn into torture; on the contrary, you need to eat everything. Products that the mother introduces to the baby through breast milk are much easier to introduce during the complementary feeding period and are less likely to cause allergic reactions in the future. At the same time, when a mother unreasonably follows a hypoallergenic diet, this slows down the process of maturation of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract and its adaptation to a new type of diet.
So why do pediatricians so often like to put moms on a useless (and often harmful) hypoallergenic diet? There are several reasons:
1. Previously, it was believed that failure to follow a diet increases the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis in a child. This assumption has long been refuted by modern research, but many doctors do not want (or are unable, due to little free time), to follow new trends in the field of medical science. Even with an existing diagnosis of “atopic dermatitis,” it is advisable to prescribe a diet only for moderate and severe symptoms of the disease (even in this case, the diet is prescribed for a period of 4 weeks, and if no improvements are observed during this time (or they are insignificant), the diet is canceled). Otherwise, the harm from a hypoallergenic diet significantly outweighs the benefits, and after several months of such a diet, the lack of nutrients becomes a new cause of exacerbations.
2. There are pediatricians who are still convinced that a child should have stool at least once a day (and preferably after each feeding) in the form of a yellow mush. With artificial feeding it is possible, but with breastfeeding the situation is completely different. Firstly, with exclusive breastfeeding, after 4-6 weeks the baby may have stool once every few days (and sometimes once every 10 days). In most cases, this is quite normal and is due to the fact that breast milk is absorbed much more easily than formula, and this contributes to a slower filling of the rectal ampoule. However, some doctors prescribe suppositories and enemas for the child, and beets and prunes for the mother (which is absolutely useless, given that milk is produced from blood plasma, and not from the contents of the intestines). Secondly, breast milk is not homogeneous, unlike formula. Its composition changes even during one feeding (not to mention the time of day, age of the child, etc.), accordingly, the color and consistency of the child’s stool can constantly change. This is normal and does not require any diet.
3. Sometimes the pediatrician knows what and how it should be, but it is easier for him to put the mother on a diet, because he does not have the time or desire to explain the essence of the processes occurring in the baby’s body, or there is no contact with the mother. And the doctor prescribes a diet to somehow keep the mother occupied (this is especially common for atopic dermatitis associated with enzyme deficiency - it is often easier for a mother to bring herself to the point of exhaustion in the process of calculating “all allergens” than to simply wait for remission to come, “covering up the problem” ").
Unfortunately, true medical indications for a nursing mother’s diet still exist. A classic example is an allergy or severe intolerance to cow's milk protein (usually manifested by blood in the baby's stool). The complete exclusion of products containing bkm from the mother’s diet eliminates all or almost severe digestive disorders and rashes in the baby, which means that a dairy-free diet is definitely justified for some time.
But it should be noted that a strict diet for a nursing mother is prescribed for false reasons much more often than when there are true objective indications for it.
Based on the above, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1. The nutrition of a nursing mother should be healthy and nutritious. The diet should contain vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy products, meat (sometimes fish);
2. Do not overuse whole milk or any specific product. Milk is made from substances that enter the blood. Accordingly, breast milk protein is synthesized from all the proteins that are in the blood and there will be a little of each there. Even buckwheat consumed in kilograms can cause allergies, since immunoglobulins, enzymes, lacto- and bifidobacteria coming from mother’s milk may not be enough to break down such an amount of buckwheat protein, and the protein of breast milk will be almost identical to buckwheat protein;
3. Milk is formed from blood components; accordingly, the mother’s nutrition affects the composition of milk to the same extent as the composition of the blood. To avoid insufficiently digested proteins and a large number of allergens getting into the blood (milk), the mother needs to improve her digestion;
4. You should not use large amounts of preservatives and dyes, which strongly irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and, as a result, increase the absorption of allergenic substances into the blood (and milk);
5. Some foods can affect the child’s gastrointestinal tract if they contain substances that can penetrate into the blood (milk). These include, but are not limited to, alcohol and caffeine;
6. Any product excluded from the mother’s diet for any reason must be replaced with an equivalent product (in terms of the presence of vitamins and other useful substances);
7. To avoid allergic reactions in your baby, it is necessary to follow measures to prevent atopic dermatitis (a hypoallergenic diet does not apply to this).
In conclusion, I would like to note that breastfeeding is a natural continuation of hemotrophic nutrition (through the umbilical cord); accordingly, after 9 months of intrauterine life, the baby has already become accustomed to the nutrition of a pregnant mother, and a sudden change in the mother’s nutrition will be additional stress for him.
You may be interested in the following posts:
When to introduce complementary foods during breastfeeding and bottle feeding?
Infant colic: concept, causes, how to help
One breast or two?
Causes of atopic dermatitis in infants
About stool standards for babies, and what to do in case of constipation
Why is the fat content of milk so important?
A nursing mother needs to do everything possible to ensure that her breast milk is rich in fat. Why exactly like this? This is easy to explain: full-fat breast milk fully meets the baby’s needs, promoting its development. A well-fed baby becomes cheerful, mobile and active.

And if breast milk is poorly saturated with fats and other beneficial substances, the baby does not gain weight well. In addition to this, other signs appear that indicate that the milk is low-fat:
- after feeding, the baby cries, thus showing that he is not full;
- When expressing, the milk looks like “water” and often takes on a bluish tint.
Therefore, if the child has not eaten enough and is capricious, then it is necessary to take some measures to increase the fat content of breast milk. But there is no need to rush in this matter. After all, if the percentage of fat in milk is high, then the baby may experience gastrointestinal disorders.
4% fat is considered optimal. Before increasing the fat content of milk, it is advisable to first consult with your pediatrician. Dr. Komarovsky gives very good advice, recommending that mothers focus on drinking liquids (compotes, herbal teas, juices), fruits and vegetables, which are so necessary to improve the quality of breast milk.
What foods should you not eat while breastfeeding?
Despite recommendations for a varied diet, are there any prohibited foods during breastfeeding that should never be eaten?
There are no prohibited foods for a nursing mother: you can eat almost everything, but in acceptable quantities, then the food will not cause any harm to either the mother or the baby. However, there are some things that should be limited.
What exactly?
While breastfeeding, you should limit your intake of caffeine, alcohol, and certain types of fatty fish.
What will happen if, out of ignorance, a nursing woman still eats something from this list in large quantities? And what are the general norms for using these products?
Caffeine passes through breast milk, and too much can make your baby restless and disrupt sleep. Therefore, it is permissible to consume only no more than 200-300 milligrams of caffeine per day - this is about 2 cups of coffee or 3-4 cups of tea. It's always worth considering caffeine, which is also found in other foods, such as chocolate and energy drinks.
If a mother decides to breastfeed her baby, she is not recommended to consume more than 1 serving (140 grams) of oily fish per week. Among the varieties one can distinguish mackerel, herring, and sardine.
Canned fish is not taken into account. You can also eat no more than one serving of swordfish, shark and marlin meat per week.
You should also not indulge in foods that are rich in sugar and saturated fat, particularly margarine. But a small amount of 5–10% of the daily diet is acceptable.
What about alcohol?
Drinking alcohol is not recommended for a nursing woman, just like any other adult. However, it is believed that 1 serving of alcohol - for example, 1 glass of dry wine per week - does not have a negative effect on the child.
It is important to observe a pause between drinking alcohol and feeding: at least 2-3 hours should pass. If you plan to drink alcohol, you first need to feed the baby or express breast milk, after which you can drink alcohol, but you can feed the baby again only after 120–180 minutes. This is due to the utilization of alcohol from breast milk: during this time it is almost completely eliminated. Excess alcohol in milk can cause increased drowsiness in a child and have a negative effect on his nervous system.
Checking milk for fat content
Before you learn how to make breast milk more filling, you need to check the fat content of the liquid. Every woman's body is structured differently. But, regardless of this, each mother’s breast milk is conventionally divided into two parts: front and back. The former consists of 90% water, while the latter is oilier. First, the baby sucks out the front fluid, thereby quenching thirst, and at the end of feeding, the back fluid, saturating its body with useful substances.
If you need to find out the real picture regarding the fat content of breast milk, then you can do this at home using a special test:
- take a clean transparent test tube or glass, mark a line on the container with a marker (10 cm from the bottom);
- Express the milk into the container up to the mark and set it aside for 6 hours. This time is enough for milk to separate into liquid and fats;
- after 6 hours, take a ruler and use it to measure the thickness of the layer of collected cream. As a rule, 1 mm = 1% fat content. If breast milk has normal fat content, then the figure will be 4%. If this figure is lower, then it needs to be brought back to normal.
It is important to know:
This fat content analysis is not always accurate. In most cases it shows approximate results. This is due to the fact that the composition of breast milk changes during feeding in a nursing mother. Therefore, not even every modern laboratory can fully test milk and find out what its exact fat content is. Therefore, it is worth taking a close look at parameters such as the baby’s weight, mood and well-being.
Knowing what the fat content of breast milk depends on, you can begin to improve its quality. This is done in many ways. But which one should you choose? How to make milk not only nutritious, but also tasty?
The most effective method is a special diet, which we will talk about below.
Diet
In order to bring the fat content of breast milk back to normal, you need to pay special attention to your diet. The female body must receive vitamins, minerals, proteins and many other useful substances. Therefore, nutrition must be correct. Your daily diet should include foods that contain the following:
- carbohydrates (7 g);
- fats (4.2 g);
- proteins (1.3 g).
During the lactation period, a new mother should not constantly go on a diet, nor should she overeat. After all, all this has a bad effect on the nutritional value of breast milk. A woman who is breastfeeding her baby needs to eat portions, preferably in small portions. It is very important that the diet be varied. It is better if it includes all the important substances and elements that support and increase lactation.
How to eat for breastfeeding vegetarian women
Is the number of calories a breastfeeding mother needs different from the average woman?
If before giving birth a woman needed 1800 calories per day, then during breastfeeding the energy requirement increases to 2300 calories, that is, nursing mothers need an additional 500 calories daily. To replenish them, just add a couple more snacks to your regular diet.
How should a woman eat in order to get all the necessary nutrients and fit into the number of calories when eating if she is a vegetarian?
She should eat a nutritious, balanced vegan diet. The diet of such a nursing mother should include legumes and whole grain cereals every day. To get a source of omega-3 fatty acids, she should definitely consume nuts and seeds, including flax, hemp or chia.
A vegetarian mother needs at least 3 servings of vegetable protein per day: 1 cup of cooked legumes - chickpeas, lentils, beans, 150 grams of tofu and a serving of nuts - 40 grams.
Plant-based alternatives such as soy yogurt, soy or other plant-based milk are suitable sources of calcium. Additionally, you need to take vitamin B12, D, iodine. For iron deficiency, doctors usually prescribe special medications.
What should you eat during the lactation period?
The main reason for low-quality milk is the mother’s body not receiving the necessary substances. That is why it is imperative to eat foods that increase the fat content of breast milk. Many mothers neglect this rule and use absolutely the wrong thing. What foods increase the fat content of breast milk? This biological fluid is saturated with nutritional value and usefulness through the use of:
- sour cream;
- butter;
- milk cream;
- hard cheese;
- fatty fish;
- cauliflower;
- porridge and muesli with milk;
- red meat (pork, lamb, beef);
- sunflower seeds;
- hazelnuts and walnuts.

If you are interested in how to make breast milk fattier and more satisfying, you need your own approach to preparing dishes from the above products. For example, meat and fish dishes can only be stewed, baked or steamed. A mother who wants to increase lactation and fat content should absolutely not eat anything fried or smoked, including sausages. Otherwise, such food will only do harm. The same goes for chicken meat, which can cause allergies.
Cauliflower can also increase the nutritional value of milk. It must be boiled or added to vegetable salad. By the way, it is better to dress salads with sour cream, and not with mayonnaise or sunflower oil, which is absolutely forbidden to do if you want to make breast milk fattier.
If you are still wondering how to improve the fat content of milk, walnuts are just right. They are very useful because they give strength and vigor. But these products often provoke an allergic reaction in a newborn. Therefore, mother needs to eat 3 fruits a day, no more. The same goes for almonds.
Women, not knowing how to increase lactation correctly, often use a spread instead of butter. And this is wrong, because the substitutes do not contain the beneficial substances that are found in natural oil. Therefore, it is better to give your preference to butter. It can be used to season both milk porridges and various soups. Sandwiches made with butter and hard cheese are also perfect for increasing the fat content of milk. This snack is best eaten with green tea with milk or cream.
Also, nursing mothers, wondering what to eat during lactation, probably ask the question: “Can I eat sweets?” Yes, you can, but only in small quantities, otherwise there will be a high probability of flatulence and colic in the baby.
Another method to increase the fat content of breast milk is to eat seeds, both sunflower and pumpkin. It is better to eat them roasted, a small handful every day.
Dairy and fermented milk products, for the production of which cow and goat milk are used, also perfectly increase the fat content of the nutrient liquid. Particular attention should be paid to the consumption of cottage cheese, whole milk, kefir, cream, and sour cream.
Some important tips
In addition to the products necessary to increase the usefulness of biological breast fluid, there are also important nuances regarding how to make breast milk fatty and nutritious:
- if you often put your child to your breast and allow him to suck every drop, then lactation will work like clockwork, and the fat percentage will stabilize;
- in order for the baby to suck the entire breast, including the fatty part, it is necessary to express a little foremilk;
- if you need your breast milk to be full-fat, feed your baby on one breast, and the next time on the other;
- factors that increase the usefulness of milk are proper sleep and peace of mind. It is very important for a nursing mother to sleep at least 8 hours and not succumb to nervous disorders.
As you can see, there are many answers to the question of how to increase the fat content of milk while breastfeeding. The main thing is to monitor your diet, health and emotional state. And then your child will be fed, healthy and happy.