Breastfeeding will establish a closer bond with your baby and make parenting easier later on. Therefore, every mother wants her milk to be the best. The question of how to determine the fat content of breast milk is quite relevant, so we decided to talk about it today.
There is still something tender and touching in the process of breastfeeding. This not only brings mother and baby incredibly closer, but also ensures good health for the child for the rest of his life. It has been noticed that babies who have been fed breast milk can boast of stronger immunity: they get sick much less often, and if they do get sick, they recover quickly.
If you decide to feed your baby breast milk, you are giving him the most valuable gift, which is full development and growth. Naturally, every mother worries whether her milk is nutritious and fatty enough. Often these doubts are unfounded, but it also happens that a woman really needs to think about the quality of her milk. How to check the fat content of breast milk is useful for every mother to know. And if suddenly your concerns about insufficient fat content are confirmed, we will tell you how to fix it.
Every milk has its time!
Breast milk tends to change dramatically as the baby “ripens” and grows: for example, the milk of a woman who has literally just given birth will be radically different in fat content and composition from the milk of a mother whose baby is about to reach its first year.
As a rule, breastfeeding specialists distinguish three stages of “maturation” of breast milk: primary milk (colostrum) , transition milk and mature milk . Each of these “products” is extremely beneficial for the baby. We’ll talk about the charms and properties of each of these “varieties” separately and in detail...
But in addition to “age-related” changes in the composition and fat content of breast milk, there are also changes within one feeding - in other words, for the first 5-7 minutes, the baby sucks milk from the breast, the composition is significantly different from what he will suck at the end of feeding ...And we will tell you about this too!
The first milk is colostrum: compound benefits
It is impossible to find food more beneficial for a newborn baby than his mother’s first breast milk, the so-called colostrum. However, colostrum is considered invaluable for the baby’s health not because it has any supernatural fat content. The true benefit of colostrum is that it contains a record amount of nutrients and protective substances.
Interestingly, in its physical and chemical composition, colostrum is more reminiscent of blood than milk. In addition, colostrum has an extremely low water content, which protects the baby’s still immature kidneys from “overload.” But what colostrum contains in abundance are vital immune factors (which provide the newborn with so-called passive immunity) and growth factors - special substances that stimulate the growth and development of the child in the first days of life.
Colostrum is extremely high in calories (its energy value is significantly higher than mature breast milk), so its not too abundant production should not frighten a nursing mother. For example, the protein content of colostrum fluctuates around 11-15% - which is almost three times more than mature human milk.
Therefore, even with a very modest portion of colostrum (as a rule, about 20-30 g of primary milk is produced per feeding), a newborn baby is able to satisfy all his nutritional needs.
But as for the fat content of colostrum, it is slightly lower than that of mature milk - in this way, nature took care of the child, who in the first days of life still finds it difficult to digest and break down more fat. At the same time, the fat content of colostrum is quite sufficient to provide the baby with a slight laxative effect and help get rid of meconium (the first stool), thus reducing the risk of newborn jaundice, the culprit of which is bilirubin, which accumulates in meconium at the time of birth. In this context, many modern neonatologists consider low-fat colostrum not only as food for the baby, but equally as medicine.
What does it consist of?
- Biologically active water. It accounts for up to 90% of the total amount of milk secreted by the mother, provides the baby’s need for fluid and facilitates the body’s absorption of other components of milk.
- Carbohydrates in the form of lactose or milk sugar. They make up up to 7% of the amount of milk, promote the formation of bifidobacteria, substances necessary for the development of the central nervous system, and help the absorption of microelements and vitamins.
- Fats. They make up up to 4% of the amount of milk and are its most nutritious component. Squirrels. Their content does not exceed 1%, but they are the basis for the growth and development of the child’s body. Breast milk proteins are best absorbed by the baby's body, while cow's and goat's milk are only partially absorbed.
- Microelements, vitamins, salts. They are found in breast milk in a form that ensures their maximum absorption by the body. For example, a child's body absorbs 70% of the iron contained in breast milk and only 4% of the iron contained in formula for artificial feeding.
- Natural hormones ensure the growth, physical and mental development of the child, beneficial bacteria help improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, allowing maximum absorption of all beneficial substances.
Fat content and composition of milk during the transition period
3-5 days after birth, primary breast milk gradually begins to change in composition and quantity, turning into more mature milk - the protein content drops significantly, but the fat and sugar content increases. All these changes are determined solely by the needs of the newborn, who is gradually adapting to life “outside, not inside.” The baby needs strength for growth and the final formation of organs and tissues (therefore, his food becomes rich in fats and sugars), but at the same time he does not yet need a developed muscular “framework” - since he is not yet able to move much, run, jump, etc. P. So the protein content in transition milk is fairly low - as they say: what is the demand, so is the supply.
The composition and fat content of breast milk changes - accordingly, its taste and color change. Compared to colostrum (which has a “thick” yellowish tint), transition milk becomes noticeably lighter and sweeter. The taste changes due to a decrease in the amount of salts and an increase in sugar and fat in the composition, and color and density - due to the fact that the milk gradually becomes richer in water.
Does breast milk beat cancer? One of the most amazing things about transitional breast milk is its ability to kill cancer cells. During the period of transformation of colostrum into finally mature milk, substances appear in it, which, when they enter the baby’s stomach, form a special complex - the so-called HAMLET (Human Alpha-Lactalbumin Made Lethal to Tumor Cells).
The HAMLET complex is formed only in breastfed children. Why is it good and important? It causes programmed death (in medical terms - apoptosis) of tumor cells, primarily cancer cells.
Namely: the HAMLET complex, which is a “friendly” union of alpha-lactalbumin (the whey protein of breast milk, which begins to be produced just during the transition period of breastfeeding) and oleic acid (a substance found in most animal fats and some vegetable fats) when interacting with cancer cells, it “pushes” them to complete self-destruction.
The HAMLET complex was first discovered in the stomach of newborns. Nowadays, scientists are placing great bets on this discovery to finally create an effective drug against cancer.
What should you eat during the lactation period?
The main reason for low-quality milk is the mother’s body not receiving the necessary substances. That is why it is imperative to eat foods that increase the fat content of breast milk. Many mothers neglect this rule and use absolutely the wrong thing. What foods increase the fat content of breast milk? This biological fluid is saturated with nutritional value and usefulness through the use of:
- sour cream;
- butter;
- milk cream;
- hard cheese;
- fatty fish;
- cauliflower;
- porridge and muesli with milk;
- red meat (pork, lamb, beef);
- sunflower seeds;
- hazelnuts and walnuts.

If you are interested in how to make breast milk fattier and more satisfying, you need your own approach to preparing dishes from the above products. For example, meat and fish dishes can only be stewed, baked or steamed. A mother who wants to increase lactation and fat content should absolutely not eat anything fried or smoked, including sausages. Otherwise, such food will only do harm. The same goes for chicken meat, which can cause allergies.
Cauliflower can also increase the nutritional value of milk. It must be boiled or added to vegetable salad. By the way, it is better to dress salads with sour cream, and not with mayonnaise or sunflower oil, which is absolutely forbidden to do if you want to make breast milk fattier.
If you are still wondering how to improve the fat content of milk, walnuts are just right. They are very useful because they give strength and vigor. But these products often provoke an allergic reaction in a newborn. Therefore, mother needs to eat 3 fruits a day, no more. The same goes for almonds.
Women, not knowing how to increase lactation correctly, often use a spread instead of butter. And this is wrong, because the substitutes do not contain the beneficial substances that are found in natural oil. Therefore, it is better to give your preference to butter. It can be used to season both milk porridges and various soups. Sandwiches made with butter and hard cheese are also perfect for increasing the fat content of milk. This snack is best eaten with green tea with milk or cream.
Also, nursing mothers, wondering what to eat during lactation, probably ask the question: “Can I eat sweets?” Yes, you can, but only in small quantities, otherwise there will be a high probability of flatulence and colic in the baby.
Another method to increase the fat content of breast milk is to eat seeds, both sunflower and pumpkin. It is better to eat them roasted, a small handful every day.
Dairy and fermented milk products, for the production of which cow and goat milk are used, also perfectly increase the fat content of the nutrient liquid. Particular attention should be paid to the consumption of cottage cheese, whole milk, kefir, cream, and sour cream.
Fat content of mature milk - is it really that important?
Normally, the fat content of mature milk is approximately 4.1 - 4.5%. Not cream at all, as many mothers believe, but not a lean product either. However, it is not the percentage of fat that is considered a measure of the quality of mother's milk! So-called high-quality breast milk is milk that is complete in composition.
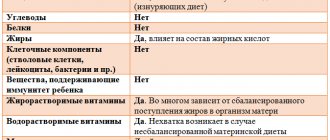
What and how much should be contained in breast milk? On average, the composition of mature breast milk is approximately as follows (per 100 g of product):
- Water - 87.5 g
- Proteins - 1.1 g
- Fat (total) - 4.4 g saturated - 2 g monosaturated - 1.6 g polyunsaturated - 0.5 g
- Carbohydrates (disaccharides) - 6.9 g
- Retinol (vitamin A) – 60 mcg
- Beta-carotene - 7 mcg
- Thiamine (vitamin B1) - 0.014 mg
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2) - 0.036 mg
- Niacin (vitamin B3) - 0.177 mg
- Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) - 0.223 mg
- Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) - 0.011 mg
- Folacin (vitamin B9) – 1.5 mcg
- Cobalamin (vitamin B12) - 0.05 mcg
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) – 5 mg
- Tocopherol (vitamin E) - 0.08 mg
- Vitamin K - 0.3 mcg
- Calcium - 32 mg
- Iron - 0.03 mg
- Magnesium - 3 mg
- Phosphorus – 14 mg
- Potassium - 51 mg
- Sodium - 17 mg
- Zinc - 0.17 mg
You will be surprised, but today it is reliably known that the composition (including fat content) of breast milk is practically in no way affected by the mother’s diet, or her age and maternal experience, or even her mood. The only real factor that determines the composition and fat content of breast milk is the needs of the breastfed baby.
In other words, a young, 13-year-old mother from the socially disadvantaged corners of Nigeria, and a well-to-do 26-year-old mother from Russia, Switzerland or the USA will have almost the same composition and fat content of breast milk. In this sense, nature has managed to equalize all people on Earth - by feeding on breast milk, we all get approximately the same start for future development and growth.
Diet
In order to bring the fat content of breast milk back to normal, you need to pay special attention to your diet. The female body must receive vitamins, minerals, proteins and many other useful substances. Therefore, nutrition must be correct. Your daily diet should include foods that contain the following:
- carbohydrates (7 g);
- fats (4.2 g);
- proteins (1.3 g).
During the lactation period, a new mother should not constantly go on a diet, nor should she overeat. After all, all this has a bad effect on the nutritional value of breast milk. A woman who is breastfeeding her baby needs to eat portions, preferably in small portions. It is very important that the diet be varied. It is better if it includes all the important substances and elements that support and increase lactation.
Fat content of breast milk and mother's diet: what is the connection?
Let us repeat: the composition of breast milk is more or less the same for every nursing mother. More precisely, it is determined solely by the needs of the baby’s growing body. For example, if at some stage of growth and development a baby urgently needs calcium, then this same calcium will increase in his mother’s milk.
It is important to understand that it is not you, as a nursing mother, who shapes the composition of your breast milk, but your baby, who needs certain nutrients.
And no matter how carefully you adjust your diet, by and large it does not affect the fat content, composition and taste of breast milk. This is a pure myth - the theory that a baby “eats” the same thing as its mother. No, that's not true.
A joint study by Norwegian and British scientists showed that in nature there are only two products that can significantly affect the taste and composition of breast milk. Only two! It's garlic and alcohol. But if babies suck “garlic” milk with pleasure and thirst, then on the contrary, they don’t like breast milk “under the influence” - they don’t like it so much that they may give up breastfeeding altogether.
A newborn and an older baby, being breastfed, receive the set of nutrients that he needs depending on his state of health, period of development, etc. If a nursing mother allows a certain deficiency of certain substances in her daily diet (consumes little protein, or, for example, little calcium), the baby will still take his dose. Only to the detriment of the mother’s health.
A nursing mother needs a complete, balanced diet, first of all, for the mother herself. Because if there is a deficiency of certain substances, the baby will still take them, but not from the mother’s diet, but from the mother’s body.
With fat content, the story is exactly the same as with the general composition of milk - mother’s milk will have exactly the same percentage of fat content that is necessary to meet the nutritional needs of a growing child. On average, we recall that mature human milk has a fat content of 4.1 - 4.6%.
Another thing is that due to typical mistakes when breastfeeding, the mother may unwittingly not give the baby some of the fatty milk he needs. The fact is that mature breast milk is conventionally divided into :
- foremilk (has more water and less nutrients)
- hind milk (it is denser and contains maximum fat and nutrients)
Foremilk , which the baby sucks out at the beginning of feeding, is essentially a drink for the baby; it quenches thirst rather than hunger. The baby receives foremilk in the first minutes of attachment to the breast.
But hind milk is nothing more than a nourishing, complete “breakfast, lunch and dinner” for the baby. The baby begins to receive hind milk after the front milk has dried up.
Mother’s milk (this means hind milk) can be super-nutritious and quite fatty, but if the mother often changes breasts during feeding, then in the end it turns out that the baby drinks front milk all the time, simply not having time to “get” what he needs rich and rich hindmilk.
The result is a situation in which the mother has full-fat and dense milk, but her child is losing weight day by day, as if he were eating only water...
Controlling fat content
Like any nutritious product, human milk contains a sufficient amount of fat . They make up 4%. This amount is quite enough to provide the child’s body with additional energy, because the fats in milk are perfectly balanced. An infant receives from 30 to 50% of his daily energy requirement from this fat. The optimal combination of fats and carbohydrates provides the energy needs of a child in the first year of life by 100%, and in the second and third years of life by 50%.
In human milk, fats are found in the form of microscopic balls, smaller in size than in cow's milk. This makes them easier to digest. The mechanisms for the absorption of fats in an infant are still immature, so breast milk, in addition to the fats themselves, also contains a special enzyme, lipase. Most mammals do not have such enzymes in their milk. Lipase helps the baby break down fat.
The ideal balance of fats in human milk is associated with an optimal ratio between saturated and long-chain unsaturated fatty acids. Breast milk contains more unsaturated fatty acids than saturated fatty acids. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential for brain development. Of particular importance among them are linoleic and arachidonic acids. The content of these two fatty acids in human milk is almost four times higher than in cow's milk; Prostaglandins, the synthesis of which depends on the presence of these two essential fatty acids, influence many physiological functions that activate digestion and promote the maturation of intestinal cells.
Fats are the most variable component of all milk components. The level of fat fluctuates not only during the day, but even during the same feeding. In some women, the concentration of fat in milk at the end of feeding is 4-5 times higher than at the beginning. This increase in fat content towards the end of feeding acts as a kind of satiety regulator. The last fat droplets usually do not flow out of the breast in a continuous stream. The child receives them through prolonged sucking, often during sleep. Having received a signal that he has enough fat, the baby usually finishes feeding himself. It turns out that the most high-calorie part of the milk reaches the baby only at the end of feeding, so the time of any feeding should not be arbitrarily limited! Only unlimited feeding on demand will provide the child with a sufficient amount of fat, and therefore calories.
How to check the fat content of breast milk at home?
There is a simple way to check how much fat your breast milk is. However, don't rely too much on this indicator - in reality, it means absolutely nothing. In 95% of cases, mothers, having measured the fat content of their milk, “fall” into the statistical norm (from 3.6 to 4.6% fat). But even if your specific milk turns out to be a little less or a little more fatty than these numbers, this will only indicate the individual characteristics and needs of you and your baby, that’s all. The main indicator that is directly related to the baby’s nutrition (that is, it demonstrates how fully and sufficiently the child is fed) and to his health are always the same: this is the dynamics of the baby’s height and weight gain.
And yet, if you are itching to measure the fat content of your breast milk, go ahead. Take an ordinary test tube (at any pharmacy) and express hindmilk (this is important!) into it to a height of 10 cm. Then leave the tube for about 5-5.5 hours at room temperature. Over time, the milk will separate into fractions, the topmost being fat. Measure this creamy layer with a ruler: how many mm is the result, so is the percentage of fat in your milk.
Laboratory at home
Analysis of breast milk for its fat content can be carried out using simple manipulations that any mother can handle. If it turns out to be optimal in terms of fat content, you will calm down and discard unnecessary worries. And if you discover in a timely manner that the milk is not nutritious enough, then you will take the necessary actions to correct the problem. Checking the fat content is quite simple. This mini-study to determine the fat content of a baby’s food will not interfere with any mother who is breastfeeding.
So, to conduct the experiment we need:
- glass flask;
- ruler;
- marker.
Now let's talk about how to find out the fat content coefficient. It's not difficult at all.

The action plan for determining the fat content of breast milk is as follows:
- In a glass container, measure a distance of 10 mm, in the direction from the bottom up.
- Place a mark at the measurement location with a marker.
- After this, you need to pour hind milk into the flask. We wrote a little higher how to calculate it. The important point is that for the experiment you must use fresh milk, directly after expressing.
- After this, you need to leave the flask in a vertical position at room temperature for 6-7 hours. Do not touch or move the container during this time. Also, do not cover the milk.
- After the required hours have passed, you will find an oily layer of cream on top of the milk, which you need to measure using a ruler.
Now it's time to learn how to understand these measurements and how they can indicate the fat content of your breast milk.
It is logical that each millimeter will indicate the percentage of fat content. The optimal indicator would be 4 millimeters, corresponding to 4% fat content. This result would fall within the healthy fat content of milk, which ranges from 4.1 to 4.5%.
How to increase the fat content of breast milk?
No way. Firstly, solely because this action makes no sense. Even if you manage to increase the fat content of your “product” to 6-7%, this will not affect the baby in any way - he will take his 4%, and the rest of the fat will remain with you, gradually increasing your waist circumference.
Also, keep in mind that by consuming fatty foods in your diet, you will not be able to change the overall fat content of your breast milk, but you will be able to change the fat composition. Breastfeeding specialist Irina Ryukhova warns: “The composition of milk fats depends on the mother’s nutrition, but not the total fat content, so it makes no sense to lean on fatty foods. The milk will simply become more viscous and the likelihood of stagnation (lactostasis) will sharply increase.” In addition, given the increase in the density of milk, prepare for the fact that it will become more difficult for the baby to suck it out, and he may simply refuse to breastfeed.
Factors affecting quality
- Nutrition. If one of the family members is allergic to any foods, then the mother needs to be extremely careful in adding them to her diet or eliminating them completely. A baby prone to allergic reactions will most likely react negatively to nuts, eggs, berries, chocolate, honey, and citrus fruits in the mother's diet. A nursing mother should consume all food groups so that the nutrition is balanced and the baby receives all the vitamins and microelements he needs with milk.
- Beverages. Occasionally, a mother can drink a little coffee or wine, but it is necessary to understand that some of the caffeine will enter the child’s body. The process of lactation causes an increase in the amount of fluid needed by the body. To avoid dehydration, a woman should drink more than usual, but she should not do this forcefully, because excess fluid will not affect the amount of mother’s milk, and the quality of the milk may deteriorate.
- Presence of stressful situations and proper rest. A nursing mother should get a good night's sleep and avoid noisy companies or crowded places. Try not to participate in conflict situations, disputes, and be less nervous. Excessive physical activity reduces the amount of beneficial proteins and vitamins in milk.
- Taking medications. The instructions for all medications must include information about the possibility of using this medication during lactation, since some medications can suppress it. In any case, before starting to take medications, it is better to consult a doctor, and for the mother to carefully monitor the behavior and health of the baby. Most drugs affect the child's body only during the first two months of life, and then children become less susceptible to drugs that pass into breast milk.
- Ecology. The presence of toxins in mother's milk sharply reduces its quality. Therefore, a nursing woman should avoid smoky places and areas with large concentrations of cars. You should not eat foods grown in urban areas or near the road, as most likely they contain significantly higher levels of heavy metals. For the same reason, you should not eat fish caught in polluted waters, or mushrooms collected in a city park. It is necessary to avoid inhaling vapors of solvents, varnishes and paints, gasoline (while refueling the car, you should get out of it and step aside), use nail polish remover and nail polishes as little as possible.
- Women's health. The condition of the breasts and the general condition of a woman’s body affect the quantity and quality of milk produced. Illnesses accompanied by high temperatures can lead to “burnout” of milk and cessation of lactation.
Read also:
Breastfeeding pads
Milk is worth its weight in gold!
There is no need to philosophize over the composition and fat content of breast milk, trying, like a real alchemist, to turn into “gold” what is already worth a lot. Your breast milk - just as it is - is the most useful, priceless, vital food for your baby. You should not try to experiment with changing its quality, quantity or fat content.
The wisest and most correct thing you can do on the way to the well-deserved title “Ideal Nursing Mother” is to put your baby to the breast as often as possible (and pump correctly from time to time). In this case, nature and your own brain will do their job: the milk will become both quantitatively and qualitatively absolutely ideal for your little one.
Useful tips
- The entire feeding process should be natural. You should not express your front milk and feed your baby only your hind milk.
- It is not possible to influence the amount of water in milk by drinking more liquid. All efforts aimed at increasing the concentration of fat and nutritional value through such a method are doomed to failure.
- Feed your baby on demand, don’t take him off the breast prematurely, make sure he’s latching correctly, and then your baby will be provided with healthy milk that is normal in fat content.
Unfortunately, there are no products that increase the fat content of breast milk. The same answer awaits women who are wondering how to reduce the fat content of breast milk. Food must be balanced and contain sufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements. In addition, to obtain high-quality milk, the woman’s general condition, her emotional health, and adherence to sleep and rest patterns are also important.