Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is synthesized by chorionic tissue after attachment to the walls of the uterus. In gynecological practice, hCG analysis is actively used to establish the fact of conception, early detection of the risk of threatened miscarriage and non-developing pregnancy. The method is also used as part of a comprehensive diagnosis of pregnancy pathologies, as well as defects in the child.
What is hCG?
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), hCG (chorionic gonadotropin) is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 36.7 kilodaltons.
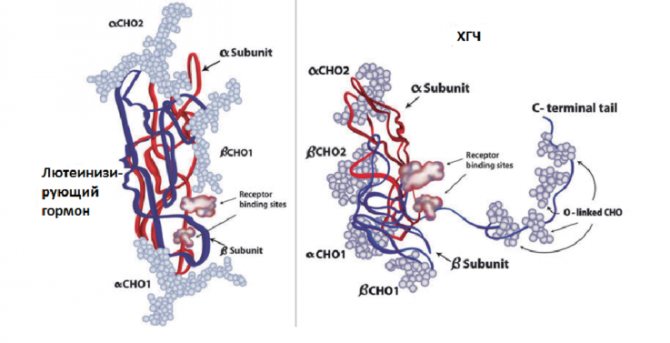
In its structure, hCG is similar to pituitary gonadotropins, for example, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH). Human chorionic gonadotropin, like them, consists of two subunits (alpha and beta), which are connected by non-covalent bonds.
The structure of the hCG molecule
The alpha subunit is similar in all four hormones. It has a molecular weight of 14.5 kDa and is encoded by a single gene. The alpha subunit consists of 92 amino acids. The main difference between hormones is provided by the structure of the beta subunit.
The beta subunit of pituitary gonadotropins consists of 114–145 amino acid residues. In hCG, it has a molecular weight of about 22 kDa. Figure 1 shows a diagram of the homology (similarity) of the beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin with LH, FSH, TSH.
Most of all, the beta subunit of hCG is similar to luteinizing hormone (75%). This is due to the fact that they interact with the same receptor. The degree of homology with follicle-stimulating hormone is approximately 35%, and with thyrotropin – 46%.
The beta subunit is designated free β-HCG (free β-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin) or free beta chain of hCG (β-hCG).
The definition of human chorionic gonadotropin refers to studies of the level of the beta subunit or β-hCG, that is, there is no difference between these two concepts.
Where is human chorionic gonadotropin synthesized?
The main site of synthesis is the trophoblast (syncytial layer). Let's try to figure out how it is formed from the moment of conception. After fertilization of an egg by a sperm, intensive cell division occurs. At the end of the first week, an embryo is formed, the outer part of which is called the trophoblast. The trophoblast fuses with the endometrium to form a syncytiotrophoblast. In the future, it will develop into the chorion, which will serve as the beginning for the development of the placenta.
Thus, the trophoblast ensures the attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus (endometrium) and promotes the development of the placenta, the main function of which is to ensure metabolism between mother and child.
In the pregnant state, the chorion secretes chorionic gonadotropin. The synthesis of progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovary is also important. HCG maintains a constant concentration of progesterone, then it begins to be secreted by the placenta.
The absence of the corpus luteum and, as a consequence, low progesterone levels can lead to miscarriage (miscarriage).
Functions performed by hCG
The main role of hCG is:
- maintaining the secretion of progesterone by the corpus luteum and placenta;
- promotes the formation of chorion, increasing the number of villi, their nutrition;
- increasing the synthesis of hormones of the adrenal cortex - adaptation of the body to pregnancy. Glucocorticoids suppress immune reactions aimed at rejecting the child by the mother's body, since the fetus consists of 50% foreign antigens of the father;
- promotes the production of sex hormones (estrogens), the maturation of the male reproductive system.
Almost all women know that the level of hCG is a sign of an existing pregnancy. This is based on the mechanism of action of test strips. The bottom line is that using an immunochromatographic test, you can determine the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine. Its presence indicates a 90% probability of pregnancy.

In men and women, this hormone can be determined in the presence of a tumor.
Messages sometimes pop up on forums that the hCG level did not indicate pregnancy, but later it turned out that the woman was pregnant. This situation could arise due to incorrect introduction of the ovulation calendar, which led to the test being taken early.
hCG calculator can help you correctly calculate the gestational age . You need to enter the day of your cycle, after ovulation or missed period, as well as the hCG level, after which the calculator will calculate your approximate period in weeks. Studying the level of human chorionic gonadotropin over time will allow you to assess the development of pregnancy. The calculator will tell you the rate of hormone growth and explain whether this corresponds to the norm or not.
Determination of hCG
Every woman who has gone through the procedure of artificial insemination wants to find out as quickly as possible whether the embryo has taken root. It’s not worth judging an “interesting situation” based on the first signs. You can verify your pregnancy by donating blood for an hCG test. This hormone begins to be synthesized from the moment of conception. A pharmacy test is an easy way to detect pregnancy.
In order to determine a “healthy” pregnancy, it is necessary to find out the hormone content. Elevated hCG or, conversely, a lack of the hormone indicates trouble.
To assess the nuances of pregnancy as accurately as possible, doctors recommend that women after artificial insemination monitor hCG every two to three days.
Preparing for hCG analysis
The material for the study is venous blood. The preparation is simple and consists of the following:
- blood must be donated on the 4th – 5th day of missed menstruation for a more accurate result to confirm the pregnant status;
- you should refrain from physical and emotional overload, and not only because this relates to preparing for the analysis (pregnant women should take care of their body);
- It is preferable to donate blood on an empty stomach so that it is suitable for research;
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol before any test, and especially if pregnancy is suspected.
You should not overeat before taking any test. It is best to donate biological material on an empty stomach, unless this applies to those cases where the doctor has previously agreed on specialized preparation for the analysis. For example, excess lipids in the blood (lipemia) make the blood unsuitable for testing, resulting in the need for repeated sampling.
What are the indications for prescribing a hCG test?
A blood test for hCG is prescribed for the purpose of:
- confirmation of pregnancy and assessment of its progress;
- when performing an abortion, the quality of its implementation is judged;
- find out the reason for the absence of menstrual bleeding (pregnancy has been refuted);
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasia of the ovaries and testicles (in men, women without pregnancy);
- diagnosis of formations capable of secreting this hormone.
There are indicators (triple test) that can be used to determine whether there are disorders on the part of the mother or the fetus. These include human chorionic gonadotropin, estriol and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP).
Normal hCG levels
In men and women who are not pregnant, the hCG content normally does not exceed 5 mU/ml or 5 U/l. During pregnancy, the concentration of hCG increases with increasing gestational age.
The development of pregnancy is monitored by hCG levels. This indicator will allow timely detection of deviations from the norm.
Table 1 presents reference values for hCG levels depending on the stage of pregnancy.
Table 1. Weeks of pregnancy and hCG levels
| Gestational age | Human chorionic gonadotropin level |
| First - second weeks | 5 – 25 mU/ml |
| Third - fourth weeks | 25 – 156 honey/ml |
| Fourth – fifth weeks | 101 – 4870 honey/ml |
| Fifth – sixth weeks | 1110 – 31500 mU/ml |
| Sixth – seventh weeks | 2560 – 82300 mU/ml |
| Seventh – eighth weeks | 23100 – 151000 mU/ml |
| Eighth – ninth weeks | 27300 – 233000 mU/ml |
| Ninth – thirteenth weeks | 20900 – 291000 mU/ml |
| Thirteenth – eighteenth weeks | 6140 – 103000 mU/ml |
| Eighteenth – twenty-third weeks | 4720 – 80100 mU/ml |
| Twenty-third – forty-first weeks | 2700 – 7810 honey/ml |
The maximum concentration of hCG reaches in the 11th week up to 291,000 mU/ml. Then, from the second trimester, the hCG content begins to decrease, as part of the functions of hormone synthesis is taken over by the placenta.
The degree of growth of the hormone may depend on the number of embryos: the concentration will increase in proportion to the number of embryos.
When the hCG content in the blood is 5 - 25 mU/ml, it does not allow us to say with 100% certainty about the presence of pregnancy. It is necessary to donate blood again after a couple of days, where an accurate conclusion about the presence of an embryo will be more likely.
If there are abnormalities in the development of pregnancy, the hCG level will be reduced or increased. Careful monitoring of the course of pregnancy is necessary.

HCG and its functions
HCG is often called the pregnancy hormone, since it appears only after the successful implantation of a fertilized egg and is produced by the chorion, or more precisely by its trophoblast (the precursor of the placenta). The hCG level is an important indicator indicating the course of pregnancy and fetal development.
Immediately after conception, the embryo is a small bubble, the walls of which include actively reproducing cells. Some of them subsequently form the embryo, and the other the trophoblast, which develops into the chorion (the membrane of the embryo) and then into the placenta.
After successful implantation of the embryo into the endometrium, the chorion begins to synthesize hCG, which affects the body of the woman and the fetus. HCG during pregnancy is necessary to create favorable conditions for the development of the fetus, the formation of the placenta, and the activation of the corpus luteum, which is responsible for the synthesis of progesterone. It is worth noting that it is progesterone that maintains the optimal condition of the endometrium, ensures strong fixation of the embryo and its nutrition. Normally, in the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development and resolves, but hCG helps to preserve it and stimulates its performance.
Therefore, high and low hCG are among the signs of the development of pregnancy pathology, allowing it to be identified in the early stages and prevent the formation of negative consequences, in particular fetal death.
Low hCG levels
A low hCG content may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, threatened miscarriage, or pathology of the placenta. An expanded list of causes of low levels of human chorionic gonadotropin is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Causes of low hCG levels
| In pregnant women | In non-pregnant women and men |
|
|
Ectopic pregnancy is a condition accompanied by implantation of the embryo in places other than the uterus, for example, in the ovary, oviduct (fallopian tube), or abdominal wall. The absence of an increase in hCG concentration along with ultrasound serves as a criterion for making this diagnosis.
A low concentration of hCG requires careful attention to the patient, as this can affect the development of the fetus, causing a delay in the maturation of organs and tissues, and has a negative effect on the placenta, as a result of which the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus is disrupted.
Why is hCG low?
Starting from week 11, hCG gradually decreases, which is a natural process. The unborn child's need for this hormone is highest in the first 2-3 months. But with the threat of miscarriage or placental abruption, human chorionic gonadotropin rapidly decreases in the early stages. False-negative results are possible in case of ectopic pregnancy and the study is carried out before 2-3 weeks of pregnancy.
Low levels of human chorionic gonadotropin during pregnancy may indicate the presence of serious disorders:
- fixation of the embryo outside the uterine cavity, which slows down the production of hCG;
- non-developing pregnancy;
- various disorders in fetal development;
- risk of miscarriage;
- placental insufficiency.
Experts make the final diagnosis based on several studies and the results of other diagnostic procedures, including ultrasound.
High hCG levels
A high concentration of hCG in a pregnant woman may indicate an incorrectly determined period or number of embryos, as well as gestosis or diabetes. More details about the reasons for the increase in human chorionic gonadotropin levels are described in Table 3.
Table 3. Elevated hCG concentration with possible causes
| Causes of high hCG in pregnant women | Causes of high hCG in non-pregnant women and men |
|
|
A little about pathology
I would like to dwell in a little more detail on those pathological conditions that can be indicated by changes in the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, in order to convey to patients the importance of determining hCG, if someone does not fully understand.
Preeclampsia
A high level of hCG may indicate the development of gestosis. Preeclampsia is a condition that is a complication of pregnancy, which is accompanied by increased blood pressure (hypertension), the appearance of edema, and proteinuria (protein in the urine). It is not necessary that all three manifestations occur simultaneously. There are different combinations of symptoms of gestosis.
preeclampsia and eclampsia - pose a danger to mother and child .
The reason for this is vasospasm due to endothelial dysfunction. The volume of circulating blood decreases, the blood thickens, and plasma escapes through the vessel wall into the interstitium. The functioning of the kidneys is impaired, fetal development is delayed and hypoxia occurs.
Treatment of gestosis is carried out inpatiently. Therapy is symptomatic, that is, they lower blood pressure, improve microcirculation, and anticonvulsants if necessary.

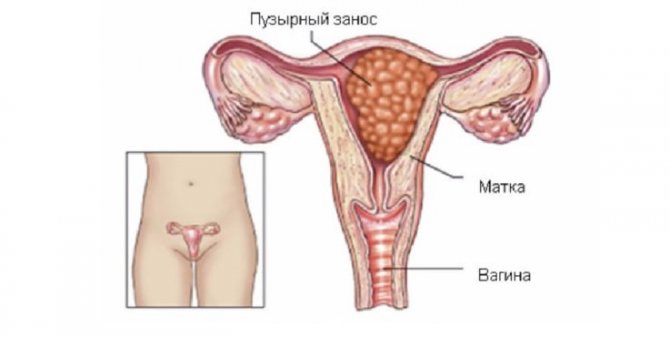
Hydatidiform mole
Hydatidiform mole is a rather rare pathology. Due to an unformed placenta, the death of the fetus occurs, and cysts filled with fluid form instead. The reason for this is considered to be chromosomal abnormalities. There are complete and partial hydatidiform moles.
- Complete hydatidiform mole - there are no maternal chromosomes, but a double set of paternal chromosomes. The fetus dies, but the uterus continues to grow. This type of hydatidiform mole is characterized by a high risk of malignant degeneration.
- Partial hydatidiform mole - there is a set of maternal and two paternal chromosomes. Is detected in the 8th – 12th week of pregnancy.
If a hydatidiform mole moves into the walls of the uterus (invasive), internal bleeding may occur.
Treatment consists of removing the hydatidiform mole surgically by curettage. The hCG level will help evaluate the quality of the therapy. If the hormone does not return to normal, it means that pathological growths remain in the uterus and repeated curettage is necessary.
Vacuum aspiration is offered to those who wish to have children in the future. The material obtained as a result of removal of a hydatidiform mole is sent for research to exclude the possibility of its degeneration.
Chorionepithelioma
Chorionepithelioma is a malignant tumor of the chorionic villi. The neoplasm damages blood vessels and promotes the spread of metastases. Chorionepithelioma occurs as a result of hydatidiform mole. Clinical manifestations are uterine bleeding, increased body temperature, pain of various localizations, nausea, vomiting. Chorionepithelioma is treated with chemotherapy and antitumor drugs. A favorable outcome occurs if the tumor does not metastasize and affects only the uterus.
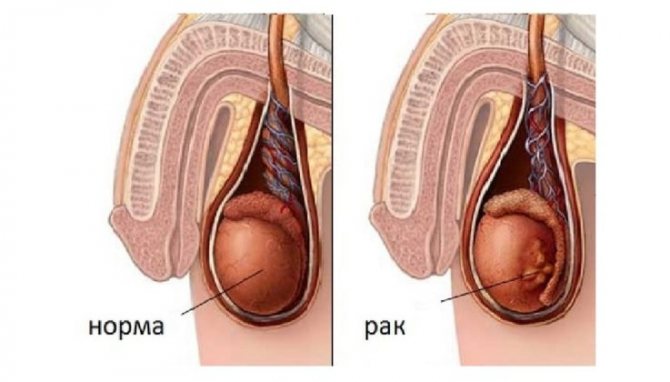
Malignant testicular tumors
Malignant testicular tumors include:
- seminoma is the most common neoplasm, which is characterized by early development of metastases;
- teratomas;
- chorionic carcinoma;
- embryonic cell carcinoma.
The development of neoplasms is influenced by heredity, cryptorchidism (undescended testicles into the scrotum), and an increased amount of estrogen. But this does not mean that in the presence of these risk factors a tumor will necessarily develop. You just need to take into account the likelihood of developing a neoplasm.
Every year there are advances in the combined treatment of testicular tumors. A number of treated patients experience restoration of reproductive functions.
HCG norms
HCG is detected in the blood 6-8 days after successful implantation of the embryo. HCG norms are quite arbitrary and depend not only on the duration of pregnancy, but also on the number of fetuses, medications taken, methods for detecting the hormone, laboratory equipment and other factors. Therefore, each laboratory presents its own tables to interpret the results. In addition, it is recommended to carry out the hCG test in the same laboratory to obtain reliable and truthful data.
The first hCG test is carried out to determine whether pregnancy has occurred. It can be done at home using rapid tests. Of course, hCG appears in urine later than in blood, but this simple diagnostic method is available to many women and is effective in 98% of cases. In this case, using an express test, you can suspect low hCG - the strip will be dim and weakly expressed. The hormone level can also be determined by taking a blood test - this is the most accurate diagnostic method.
The second analysis is carried out at 10-12 weeks of pregnancy simultaneously with an ultrasound. It is during this period that the highest level of hCG in the blood is determined. If poor results are obtained, the test is repeated, sometimes the test is prescribed right up to the birth.
It is worth noting that not only the hCG level is important, but also the degree of its increase.
Indeed, in the first trimester, its concentration doubles every 2-3 days, reaching a maximum at 10-12 weeks. Therefore, to identify pathological conditions, tests are often prescribed at intervals of 2-3 days.