Cholesterol is an organic compound found in cell membranes. Necessary for cell construction, synthesis of sex hormones, bile acids, and nutrient metabolism. It plays an important role in the human body, but sometimes causes significant harm.
There are two types of cholesterol in the blood: “good” (HDL) and “bad” (LDL). An increase in the concentration of the latter becomes the main cause of the formation of plaques in blood vessels, resulting in an increased risk of stroke and heart attack. High cholesterol levels are dangerous to health, so they need to be reduced. The most effective methods will be discussed in the article.
What causes cholesterol to rise?
Up to 80% of total cholesterol is synthesized by the human body from fats and only 20% comes to us with food. Moreover, this organic substance is contained exclusively in products of animal origin.
Until recently, it was the abuse of animal fats that was considered the main cause of high cholesterol, but as it turns out, this is not an entirely correct assumption. There are no high or low density lipoproteins in food; they become so during processing in our body. Therefore, metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases, diseases of the liver, intestines and adrenal glands are the main causes of high cholesterol.
At risk of increased LDL and early development of atherosclerosis are:
- patients with diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- people with endocrine diseases, for example, hypothyroidism, deficiency of sex hormones;
- women over 50 years of age, as well as men over 35 years of age;
- people with bad habits;
- patients with diseases of the kidneys, liver, pancreas;
- patients with a hereditary predisposition;
- women who have been taking hormonal medications for a long time.
People at risk should definitely undergo a blood cholesterol test. Because they are susceptible to heart and vascular diseases.
The risk of high blood cholesterol increases with predisposing factors. These include a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, overeating, an abundance of unhealthy and fatty foods, deficiency of vitamin D, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the diet.
High cholesterol in women is more often due to excess weight or low estrogen levels. Typically, this problem occurs during menopause. High cholesterol in men occurs at a younger age, after 35 years. The reason for this is bad habits and poor nutrition.
Properties of cholesterol in the body in women
Cholesterol is an alcohol that contains fats. Cholesterol molecules accompany the human body from birth to the last day of life. 1.0 grams of cholesterol molecules are synthesized in 24 hours.
The main part of lipids in the female body is produced by liver cells, this amounts to 50.0%, up to 20.0% is absorbed into the blood from the small intestine, the remaining lipid molecules enter the blood plasma from the skin, adrenal glands, as well as their female reproductive glands .
The metabolic process is quite complex, it involves more than 100 reactions, and more than 300 different proteins and protein compounds take part in the synthesis.
Cholesterol can only be transported throughout the body by lipoprotein molecules.
Low molecular weight lipoprotein delivers cholesterol to every cell of the female body, and high molecular weight lipoprotein (HDL) collects unused fat and transports it back to the liver cells for further utilization with the help of bile acid.
Low cholesterol leads to lipid metabolism disorders, when there is a decrease in high molecular density lipoproteins and an increase in the concentration of low density lipids.
Reduced cholesterol
Normal cholesterol levels
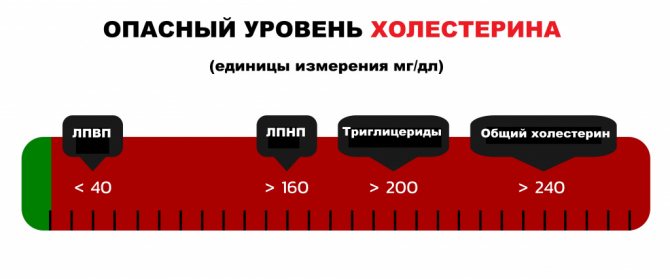
On average, a healthy person contains about 2 g of cholesterol per 1 kg of body weight. If we talk about laboratory standards, then this is 3.6-7.8 mmol/l. However, when deciphering the results, it is important to understand what kind of cholesterol we are talking about. There are the following varieties:
- HDL – high-density lipoproteins, “good” cholesterol, which utilizes excess “bad” cholesterol;
- LDL - low-density lipoproteins, the main carriers of cholesterol in the blood, have a second name - “bad” cholesterol;
- VLDL are very low density lipoproteins that transport endogenous lipids.

A high level of the last two types is a predisposing factor for the development of atherosclerosis.
What cholesterol is considered high? Any (general, “good” or “bad”), if its concentration is above 5 mmol/l. If previously there were no limits for HDL, now scientists have come to the conclusion that its optimal level for men is 1.9 mmol/l, for women – 2.4 mmol/l. It is important that its concentration does not fall below 1.5 mmol/l, as this will cause an increase in LDL cholesterol.
If the level of “bad” cholesterol is within 5-6 mmol/l, then it is moderately elevated. If it reaches 7 mmol/l or more, it is life-threatening.
Studies have confirmed that extremely high cholesterol in men increases the risk of premature death by 106%. For women, this figure will be 68%. But the situation is no better in the case of extremely low HDL levels. An excessive decrease in “good” cholesterol also adversely affects health and increases the likelihood of early mortality.
Increased cholesterol levels
Hepatitis
Atherosclerosis
Diabetes
28634 March 18
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Increased cholesterol levels: reasons for the increase, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Cholesterol is a fat-soluble alcohol molecule and is a very important element of cell membranes, a precursor to hormones. However, as Paracelsus said: “Everything is poison and everything is medicine, only the dose makes it one way or the other.” The same is true for cholesterol. An increase in its level in the blood leads to many diseases, and it is important to control cholesterol levels to prevent, first of all, cardiovascular pathology.
The presence of problems with the metabolism of fats in the body can be indicated by specific external manifestations: subcutaneous deposits of cholesterol under the skin of the eyelids (xanthelasmas) and in the area where the tendons pass (xanthomas); cholesterol deposits can also be detected in the form of a grayish-white rim along the edges of the cornea of the eye.
Types of increased cholesterol
Cholesterol is an indicator of fat metabolism in the body, and it is important to evaluate its level in combination with other indicators of the lipid (fat) spectrum of the blood.
Depending on the ratio of cholesterol and other blood fats, several phenotypes of dyslipidemia (lipid metabolism disorders) are distinguished:
Phenotype I – cholesterol levels are normal or slightly elevated, while triglyceride levels are very high;
Phenotype IIa – cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels are increased. This phenotype and all subsequent ones have varying degrees of atherogenicity, that is, they are a factor in the development of atherosclerosis;
II b phenotype - in addition to increasing blood cholesterol levels, the level of triglycerides and low and very low density lipoproteins (LDL and VLDL) increases;
III phenotype - characterized by increased levels of triglycerides, cholesterol and intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL);
IV phenotype – predominantly increased levels of VLDL and triglycerides;
Phenotype V – the level of cholesterol, triglycerides, chylomicrons and VLDL is significantly increased.
This classification allows the doctor to interpret the results of the lipid profile and provides the opportunity to make the right decision on prescribing lipid-lowering therapy.
Possible causes of increased cholesterol levels in the blood
Lipid metabolism in the body is disrupted due to three groups of factors:
- Hereditary predisposition in combination with unfavorable environmental factors.
- Secondary dyslipidemias are disorders of fat metabolism that occur in various diseases.
- Alimentary dyslipidemia is a change in the balance of fats that directly depends on dietary habits.
More often than others, doctors are faced with nutritional hypercholesterolemia
, which is primarily observed in the first day after consuming large amounts of fatty and fried foods.
If you regularly eat large amounts of fat, then constant hypercholesterolemia occurs.
Primary dyslipidemia
is explained by a mutation in the parents' genes, which is inherited and causes a disruption in the synthesis and use of cholesterol in the body.
Among the causes of secondary dyslipidemias
One of the leading positions is occupied by diseases of the thyroid gland. With hypothyroidism, the content of the hormone T3 decreases, which leads to a decrease in the formation of receptors for LDL and a decrease in the utilization of cholesterol contained in the LDL molecule. Diabetes mellitus also disrupts cholesterol metabolism in the body - blood glucose levels increase, and its utilization occurs through fat metabolism, changing the balance of this system.
Cholesterol is involved in the formation of bile acids, therefore, when the outflow of bile is disrupted, for example, with cholelithiasis, “unused” cholesterol accumulates in the blood.
The opposite situation can develop when liver function is impaired (with cirrhosis, hepatitis) - cholesterol synthesis decreases, and a state of hypocholesterolemia is observed in the blood.
Taking certain medications (beta blockers, glucocorticosteroids, some diuretics, estrogens, immunosuppressants) leads to an increase in blood cholesterol levels.
Arterial hypertension is also a factor that affects the metabolism of fats in the body and increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis. Damage occurs to the vascular wall, where “warrior cells” - macrophages - rush. If the level of cholesterol and other lipid fractions is high, then lipids are captured by these cells. “Fed” cells linger in the vascular wall and gradually form an atherosclerotic plaque.
Metabolic syndrome is another pathological condition that involves increased cholesterol levels in the blood. Metabolic syndrome is a complex of metabolic disorders and hormone regulation, including abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, arterial hypertension and atherogenic dyslipidemia (dyslipidemia phenotype II–V).
The development of metabolic syndrome entails many other pathologies: coronary heart disease, severe forms of obesity, type 2 diabetes, stroke, thrombosis, infertility.
Which doctors should I contact if my cholesterol is high?
An increase in cholesterol levels is a pathological symptom and requires consultation with a doctor - first of all, to identify the causes of this condition. The doctor will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental examinations and refer you for consultations to specialized specialists, among whom may be: an endocrinologist.
Diagnosis and testing for high cholesterol levels
Establishing the cause of increased cholesterol levels is possible only with the help of laboratory research methods. You can suspect an increase in cholesterol levels by the presence of xanthomas and xanthelasmas, as well as by the appearance of symptoms of atherosclerosis and its consequences - coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities. Depending on the symptoms, the doctor may prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
- (blood glucose levels, control of cholesterol levels, very low, low and high density lipoproteins, blood electrolytes - potassium, sodium, calcium, creatinine levels, liver enzyme levels - ALT and AST, CPK (19) levels of total and direct bilirubin). Cholesterol levels should be checked in children from the age of two if there is a family predisposition to high cholesterol levels;
Complications from high cholesterol
High cholesterol is dangerous because it increases the likelihood of developing the following diseases:
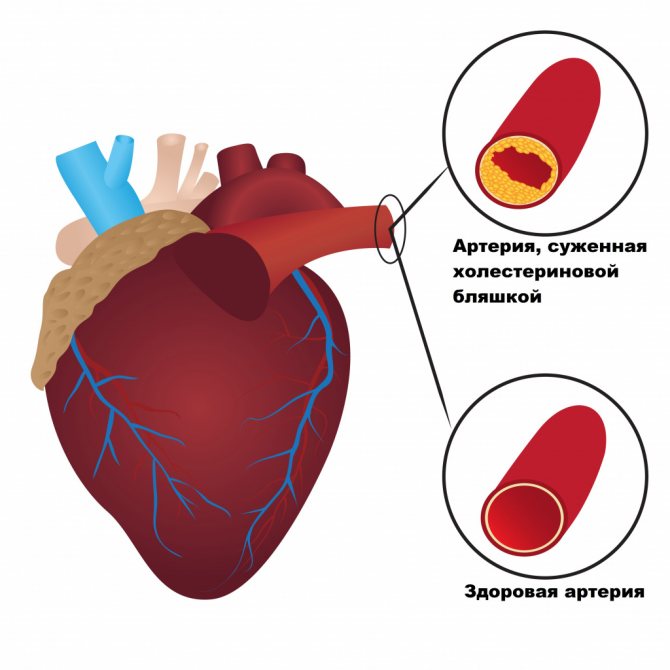
- atherosclerosis – accompanied by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, decreased elasticity of vessel walls, and narrowing of the arteries;
- coronary heart disease – accompanied by narrowing of the coronary artery, which causes myocardial hypoxia and disrupts its functioning;
- hypertension - manifests itself as high blood pressure, against the background of which stroke, heart attack, heart failure and other serious complications are likely;
- stroke - an acute disorder of cerebral circulation as a result of blockage or rupture of a cerebral vessel;
- heart attack – death of a section of the heart muscle due to loss of blood supply.
Most of these diseases are known to be fatal.
High cholesterol at a young age causes early disability and mortality. Due to the increased concentration of LDL, the walls of blood vessels become less elastic, atherosclerotic plaques are deposited on them, which impede blood flow. As a result, blood clots form, which cause heart attack and stroke.
Signs of High Cholesterol:
- heart pain, angina attacks;
- heaviness, pain in the legs even after minor physical exertion;
- the appearance of blood clots with mild bleeding;
- yellow spots on the skin, mainly in the eye area, wen.
More severe symptoms of high cholesterol in men and women appear when LDL levels are at critical levels. This may be a pre-stroke or pre-infarction condition.
The earlier high cholesterol and its causes are identified, the more effective the treatment.
How to treat high cholesterol
To reduce LDL levels, it is important to address the cause of high cholesterol and any predisposing factors. First, you should do a lipid profile. The examination shows how serious the increase is . High cholesterol is treated by a general practitioner or cardiologist. There is also a more specialized specialist - a lipidologist.
To reduce high cholesterol levels in the body, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a diet. Namely, reduce the consumption of animal fats, “fast” carbohydrates, and foods with trans fats. Nutritional correction reduces LDL levels by 10-15%.
- To refuse from bad habits. Moreover, not only active smoking, but also passive smoking is detrimental to health.
- To live an active lifestyle. It is useful to walk in the fresh air and set aside time for physical exercise. Exercise for at least 30-60 minutes. in a day.
- Control your weight. Fat deposits in the abdominal area are especially dangerous.
- Control blood sugar levels. This recommendation applies to patients with diabetes, as well as people who are predisposed to this disease.
- Cure endocrine diseases, normalize hormonal levels.
Sometimes statins are needed to treat high cholesterol. They produce an immediate effect, but scientists are increasingly talking about their shortcomings. Drugs in this group do not have a selective effect, they reduce everything - both “bad” and “good” cholesterol, and also negatively affect the functioning of the liver. However, their harm is less than the complications of critically high LDL levels.
How to avoid violations of the norm
It is necessary to regularly monitor the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and keep it within acceptable limits. To do this, it is recommended to regularly take a lipid profile at intervals, depending on age.
To avoid cholesterol problems for as long as possible, you need to adhere to certain generally accepted recommendations. You need to be careful about your diet and eat right . Diet restrictions should be reasonable; foods containing harmful cholesterol should be consumed in moderation. These products include: high-fat cottage cheese, eggs, butter, sour cream, animal fat, cheeses, fatty meats. Preference should be given to low-fat foods, for example, dairy products with a low fat content.

You need to add more vegetables and fruits . Be sure to limit, or better yet completely eliminate, fried foods and products with transgenic fats (chips, crackers, puff pastries, donuts, etc.). It is advisable to eat less sweets (fast carbohydrates).

Products that need to be limited
I would like to say right away that it is impossible to recover with diet alone. Treatment for high cholesterol is complex. However, some dietary restrictions are simply necessary.
If your LDL level is high, limit your consumption of the following foods:
- meat - beef, veal, lamb, pork;
- bird – duck, goose;
- lard, animal by-products;
- sausages, smoked meats;
- canned food;
- high fat dairy products;
- seafood - caviar, shrimp, oysters;
- margarine, mayonnaise;
- chicken yolk;
- coffee;
- sugar, flour products;
- fast food, convenience foods, chips, crackers and other unhealthy foods;
- salt (it prevents the breakdown of fats).
The consumption of fried foods is also limited, but it is impossible to completely remove all animal fats from the diet. If the body feels a lack of cholesterol coming from outside, it will increase its synthesis. When planning a diet, it is important to consult a nutritionist.