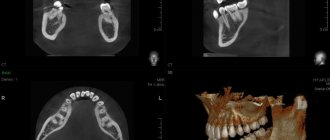
Every parent is wary of any manipulations concerning the health of their child. Many of us have no idea how diagnostics affect the body, or which examination method is best to choose (this is in cases where alternative options exist). That is why we want to cover the issue of computed tomography examination in more detail. The question of whether CT is harmful for a child is always relevant for parents. In many cases, the benefits of high-quality diagnostics will outweigh any possible risks. The child’s body reacts completely differently to certain influences. This is due to the fact that a child’s immune system is more vulnerable than that of an adult. It is worth considering that the physiology, namely the structure of cells, in children differs from that of an adult body, so a regular x-ray examination sometimes does not provide the necessary information. Pediatric CT is not a whim of doctors, but an extreme necessity.
At what age can children have a CT scan?
This is the most common and frequently asked question from parents. It is not surprising, since the examination is based on ionizing radiation, and not every parent is fully aware of what dose the tomograph produces and what standards are generally acceptable. Yes, we can say with confidence that if there is an alternative to x-ray examination, then it is better to use it, but this is not always possible. For example, MRI has a number of contraindications, although it is based on a harmless magnetic effect. CT examinations are performed from birth. But there must be a good reason for the doctor to order a CT scan for the baby. Such examinations are carried out only by children's hospitals. And one more nuance - the examination process requires the patient to remain motionless. Try to put the children to bed calmly! Yes, older children can lie down quietly during the procedure, especially if one of their relatives is nearby (this is allowed, there are restrictions for pregnant mothers). But very young children cannot lie without moving for even a couple of minutes. In this case, the examination is performed under anesthesia.
What is the essence of the study?
Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI of the brain is used to diagnose various diseases. Modern pediatric neurology cannot be imagined without the use of this highly accurate diagnostic method. Every day, thousands of children living in different parts of the world undergo this study.
The medical community first started talking about MRI of the brain at the end of the last century. This method was an absolute breakthrough in the diagnosis of various diseases. Quite often, brain pathologies remained “silent.” Many malignant tumors and neoplasms were detected only in late stages. The capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging have made it possible to recognize even the most dangerous pathologies at the initial stage of their development.
Magnetic resonance imaging equipment is being improved every day. There are several well-known leaders in this industry in the world. These corporations are located in Japan and America. European tomographs also provide decent quality in research. Various models allow examination of children of different ages, including the youngest patients.
Using magnetic resonance, doctors obtain an accurate descriptive picture of all the anatomical structures of the brain. To correctly assess the result obtained, the study is carried out in several projections at once. This gives specialists and clinicians a spatial description of where a specific pathology is located. For correct interpretation, a systematic analysis of all the projections made at once is necessary.
Editorial: Coma after traumatic brain injury
This safety of the study allows it to be widely used even in infants. In America, not a single clinical examination is performed without an MRI of the brain. Before making a diagnosis, doctors send all patients for magnetic resonance imaging.
The essence of the study is to conduct high-frequency pulses generated in a tomograph to the organs of the central nervous system. In most cases, this procedure is non-invasive (non-contact). Only in some situations is it necessary to first introduce a special dye - contrast. It has a targeted and selective effect and accumulates only in nervous tissue.
Contrast studies are carried out mainly in complex diagnostic situations, when simple magnetic resonance imaging is not enough to obtain a correct diagnosis. Typically, such invasive procedures have contraindications and are carried out only on the strict recommendation of the attending physician who is observing the child.
Magnetic resonance imaging has a number of advantages over conventional diagnostic methods that are performed daily. These include:
- No radiation exposure. When performing radiography, exposure to x-rays is significant. Such a high radiation dose is only possible for a limited period of time, so the examination can only be carried out a maximum of a couple of times a year. There are no such deadlines for magnetic resonance imaging. It can be carried out as long as necessary to establish a correct and complete diagnosis.
- High resolution. Some brain diseases are almost impossible to detect using ultrasound examination. In this case, MRI comes to the rescue. It shows pathologies of the brain and spinal cord even at the earliest stages.
The need for anesthesia during CT examinations of children
Most often, diagnostics using anesthesia are performed by the children's city hospital, since it is equipped in accordance with all the requirements for diagnostics in children. The use of anesthesia is a responsible procedure and must be carried out by a special pediatric anesthesiologist. When using anesthesia, many factors are taken into account: the presence of allergic reactions, the weight of the child, or the development of an inflammatory process in the body (banal ARVI).
Report any physiological abnormalities in your child; this is primarily important for your child. It is worth understanding that, first of all, CT scanning under anesthesia will allow for high-quality diagnostics. Currently, gentle medications - sedatives - are used for children. They act for a short time, suppressing the consciousness of a small patient. The dose is calculated according to the child's weight.
Advice for mothers: the use of anesthesia and a contrast agent is provided only on an empty stomach. Therefore, try to have your last meal no later than 6-8 hours before the examination.
How dangerous is CT scanning for children, or what should parents be guided by when choosing a diagnosis?
It is definitely impossible to answer the question whether CT is harmful for a child. On the one hand, we understand that radiation exposure on a child’s body is not beneficial. But if we think from the point of view of what harmful disease can be diagnosed with 100% certainty, then the risk here is clearly justified. It is worth saying that currently there is multislice computed tomography, which causes minimal harm to the child’s body. The examination time is reduced significantly, so the child receives a small dose of radiation. Before the examination, check what equipment the clinic uses. According to experts, this examination cannot be carried out “just in case,” since the consequences of CT scanning for children can be disastrous. Radiation can provoke genetic diseases, or give impetus to the development of a cancerous tumor. But these are just assumptions of experts; there are no reliable statistics.
What tomography shows: possible deviations
Magnetic resonance imaging, with a magnetic intensity of at least 1.5 - 2 Tesla, especially when performed with contrast, makes it possible to obtain clear images of the brain and identify deviations of 1 mm in size. Diagnosis of anomalies at an early stage of their development allows timely treatment to begin without serious consequences for the child.
The answer to the question of what an MRI of a child’s brain shows is that, first of all, tomography is used to diagnose:
- congenital brain defects such as micro- and macroencephaly;
- cystic dysplasia;
- hypo- or aplasia of the corpus callosum;
- brain cysts;
- hydrocephalus;
- traumatic injuries and concussions;
- congenital or acquired (infectious, traumatological) anomalies of the structure and growth of various nerves - auditory, facial, ophthalmic;
- the extent of meningitis, meningoencephalitis, tumor lesions of the pituitary gland;
- organic diseases of various structures of nerve cells, which include multiple sclerosis.
Editorial: Symptoms, stages and treatments for paranoid schizophrenia
There is another diagnostic technique - MRI of brain vessels in children, which is aimed at examining vascular structures in children - angiography. It is almost always performed with contrast, since blood vessels are not clearly visible on a standard magnetic resonance image. The examination shows the presence of cerebral circulation disorders and thereby determines the cause of headaches, fatigue, drowsiness, and fainting in children. It can also be used to identify tumors of various types and other neoplasms - not only their location in the brain tissue is visualized, but also their contours, linear dimensions, as well as their effect on surrounding tissues.
Many newborn babies suffer from jaundice - in particular from its hemolytic form, which is associated with the synthesis of bilirubin in large quantities. There is a phenomenon called “kernicterus,” which is damage to the brain by increased concentrations of bilirubin. A tomogram of the brain of newborns with jaundice and an examination by a neurologist can determine the presence of jaundice-related disorders in babies.
Contraindications for tomography
There are a number of contraindications to this type of tomography, which are divided into relative and absolute. Relative contraindications include the presence of dental and inner ear implants, nerve stimulators, prosthetic heart valves, braces, and retainers in a young patient.
Absolute contraindications include if the child has a pacemaker, ferromagnetic implants, or hemostatic clips installed during neurosurgical surgery. If prostheses or implants were made of ferromagnetic materials, then under the influence of a strong electromagnetic field they will heat up and even shift, which can lead to unpredictable complications.
Indications for brain MRI in children include:
- traumatic injuries to the skull;
- concussions;
- suspicion of the presence of a tumor in the brain tissue;
- dizziness, spots before the eyes;
- general weakness;
- frequent fainting and headaches;
- difficult birth with possible injuries and deformations of the baby’s skull;
- intracranial hypertension;
- Congenital heart defect;
- causeless headaches;
- constant physical activity (for example, among athletes).
Some statistics about CT examination
Currently, children's CT of ENT organs is so common that it should no longer cause panic among parents. The main thing here is to understand why CT for tuberculosis in children is a priority diagnostic method. According to experts, if mantoux is positive for tuberculosis, it is better to do a computed tomography scan rather than a regular x-ray. Radiation diagnostics produces detailed, step-by-step images of changes in the lungs, bronchi and lymph nodes during the course of the disease. This way the doctor sees the whole picture and can confidently make a diagnosis. If previously tuberculosis most often occurred in people with an unhealthy lifestyle (alcohol, smoking, etc.), now the percentage of the disease in children from one to three years of age is rapidly growing from year to year. It is worth noting that this disease affects not only the lungs, but the entire human body. Therefore, it is very important to prevent the development of the disease. A correct diagnosis will help you begin treatment in a timely manner.
Is this dose of radiation acceptable?
Computed tomography is performed using high-precision digital equipment. Modern devices use minimal doses of radiation. The radiation dose is slightly higher than with x-rays, but the scanning results are more accurate and informative.
Modern tomographs are adjusted in accordance with the purposes of the study and the age of the patient. For children, lower doses of X-rays are used than for adults. In some cases, it is impossible to significantly reduce the radiation dose, since this will adversely affect the quality of the images (when studying head structures, etc.)
Given the risk of negative consequences in the long term, pediatricians try to resort to x-ray diagnostic methods as rarely as possible. When prescribing a CT scan, the doctor is guided by specific medical indications. Safer procedures are used whenever possible.
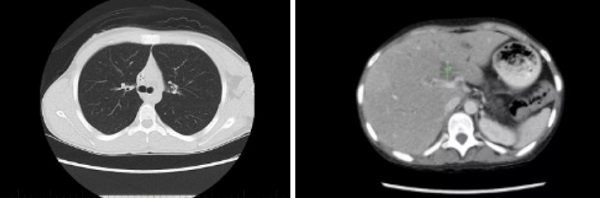
Computer tomograms of the child’s chest and abdominal organs
Where can I get a CT scan for my child?
If your child is scheduled for a CT scan, feel free to call the number provided and make an appointment for a consultation. If you do not have the opportunity to come to the clinic in advance and clarify the details, ask about this by phone. A call to the citywide recording service is completely free. Experts will advise in which areas of the city there are clinics where CT scans for children in St. Petersburg and Moscow are most often performed. If you still have doubts, you can always find on forums discussions of parents who performed a CT scan on a small child, reviews of medical centers and specialists.
Children is our future! Parents, be careful and responsible for the future generation.