Pyelonephritis
Hepatitis
Cystitis
Diabetes
84844 03 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
General urine analysis (with sediment microscopy): indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Indications for prescribing the study
A general urine test is a routine laboratory test aimed primarily at screening for diseases of the urinary system, since pathological processes in the kidneys and urinary tract affect the properties of urine.
With this simple diagnostic test, infectious and inflammatory diseases such as glomerulonephritis
(inflammation of the renal glomeruli),
pyelonephritis
(inflammation of the renal pelvis),
cystitis
(inflammation of the bladder).
Microscopy of urine sediment allows one to suspect injury or infarction of the kidney, urolithiasis, some neoplasms, renal amyloidosis (a systemic disease in which a specific insoluble protein is deposited in the kidneys, which impairs the functioning of the organ).
In addition to diagnosing kidney and urinary tract diseases, the results of a general urine test with sediment microscopy can provide information about your general health.
Urine is formed as a result of ultrafiltration of blood plasma through the glomeruli of the kidneys. With the development of various diseases, pathological metabolic products enter the blood and are excreted from the body, including through the kidneys.
No. 116Clinical urine analysis
General urine analysis (Urine analysis with sediment microscopy) Study of a single morning urine sample, including determination of physical (color, transparency, specific gravity), chemical (pH, protein content, glucose, ketones, urobilinogen, bilirubin, hemoglobin, nitrites and leukocyte esterase), as well as assessment of qualitative and quantitative…
Up to 1 business day
370 rub.
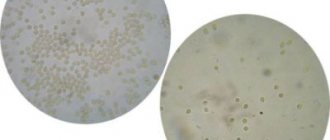
Understanding uraturia
This type of sediment is more common in men, but it also occurs in women. One of the reasons for this can be called the greater commitment of men to meat products, spicy, salty dishes. As a result, the kidneys cannot dissolve and remove so many purines, and they precipitate.
It is important to know! In middle-aged people, urate accumulates in the kidneys; in children and the elderly, sand and pebbles can more often be found in the bladder. Crystals can also be deposited on joints, causing a disease such as gout.
Composition and description of urate deposits
This type of sediment includes the sodium and potassium salts contained in uric acid. Accumulating in large numbers, they form small concretions, often having a rounded shape; often the deposits look like clusters.
The surface of such stones is rough. They are colored reddish or brown, the structure is loose, maybe even porous.
Causes of appearance and norms of content in urine
Normally, urine sediment should not include salt crystals. But if a small amount of them is detected once in a laboratory, this is not a cause for great concern; such a fact does not necessarily mean the presence of a serious pathology. Most likely, the reason lies not in the disease, but in external factors that are easy to eliminate. The doctor will definitely prescribe an additional general urine test. In case of repeated detection, more in-depth studies in the clinic will be recommended.
The reasons why this problem occurred may vary. The main task of the doctor is to identify them and timely therapy. Urates are most often formed under the following conditions:
- poor nutrition;
- infections of the genitourinary organs;
- hereditary predisposition;
- exchange failures;
- fasting;
- hydronephrosis;
- gout;
- violation of the blood formula;
- liver diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- diarrhea;
- vomiting;
- stress.
A hot, dry climate and elevated body temperature can also cause the accumulation of salts in the kidneys and bladder. When these factors are eliminated, the composition of urine is normalized.
Symptoms with high levels
In the initial stages, the problem of the appearance of urates is usually discovered by chance, during a routine medical examination. Progression is accompanied by a number of symptoms that should alert you and prompt you to seek medical help. Warning signs include:
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness;
- hyperthermia;
- pain when urinating;
- frequent urge;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- burning in the urethral area;
- pain in the lumbar region, perineum;
- admixture of blood;
- unexplained change in the color of the secreted fluid.

The appearance of such alarming signals should not go unnoticed. The sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of avoiding such serious complications as urolithiasis and gout, and the appearance of crystals inside the joints.
Consequences of uraturia
If urate is detected in the urine in large quantities, the patient should understand: this means that he has developed a disease such as uric acid diathesis, which has ICD 10 code N20-N23.
Attention! In the future, without properly selected treatment, the risk of complications is high. One of them can be called the formation of stones. This leads to disruption of the functioning of the urinary system, difficult and lengthy recovery. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, there is a high risk of disability and organ loss.
Features of the disease in pregnant women and children
Uric acid diathesis, symptoms of the appearance of urates in women during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, are most often a consequence of toxicosis. At this time, many expectant mothers have poor appetite, drink little fluids, and suffer from bouts of vomiting. All this leads to dehydration of the body and accumulation of toxins. In the absence of other pathological manifestations, it is usually enough to adjust the diet and water regime, and the problem will gradually disappear.
Uraturia can also occur in a baby: there are frequent cases of sediment being detected not only in infants, but also in newborns. This happens due to the mother’s poor nutrition and complementary feeding disorders. Also, insufficient water consumption, diseases accompanied by high fever, and long-term use of antibiotics are complicated by the presence of acid crystals in the urine. It is necessary to normalize the diet and repeat the general analysis. If the amount of sediment becomes significantly smaller or disappears completely, there is no need to worry, just continue to follow the recommended diet.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for a general urine test begins the day before the collection of biomaterial.
Certain foods, the amount of fluid you drink, taking medications and dietary supplements, and intense physical activity can distort the results of the study. The day before collecting urine, you should avoid foods that can affect the color of your urine: for example, beets and blueberries give your urine a reddish tint; consuming large amounts of carrots or carotene supplements may change the color of your urine to orange.
On the eve of urine collection, it is not recommended to drink alcohol, coffee, dietary supplements or strong tea. If possible, you should limit your intake of diuretics (diuretics). It is necessary to exclude serious physical activity, as well as visiting a bathhouse or sauna.
Women during menstruation are not recommended to donate urine for testing, since even a small amount of blood will significantly distort the test result.
You should warn your doctor about the medications you are taking, as well as about invasive examinations (for example, cystoscopy) on the eve of the test.
Method of collecting urine for general analysis
- It is necessary to prepare in advance a disposable sterile container for collecting urine (can be purchased at a pharmacy or taken from the INVITRO medical office).
- Before collecting urine, hygienic treatment of the external genitalia should be carried out, without using antibacterial and disinfectants.
For children, you need to adhere to the following rules: girls are washed from front to back (from the pubis to the tailbone) so that bacteria that populate the intestines do not enter the urinary tract. Only wash the skin with soap, since contact with mucous membranes causes irritation, dryness and itching. In boys, the glans penis is fused with the foreskin (physiological phimosis), so it is not recommended to forcefully open the glans penis, as this leads to trauma to the delicate tissue. You just need to slightly pull the skin and rinse with water, but it is unacceptable to direct a stream of water into the opening of the urethra. - For general analysis, as a rule, the first morning urine sample is collected. First, release a small amount of urine into the toilet, then, without interrupting urination, place a container and collect approximately 50 ml of urine. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the container does not touch the skin and mucous membranes.
- After collecting urine, close the container tightly with a screw cap.
- Special urinals have been developed for newborns and infants. You should not use urine squeezed out of a diaper or diaper - the results will be unreliable, since the diaper is a kind of filter for microscopic elements of urine, which are counted during the study.
- When taking the test during the day, it is not recommended to drink large amounts of water, tea, coffee or diuretics to stimulate urination.
The turnaround time for a general urine test is usually 1 business day.
Therapeutic diet if urate is detected in the urine

If urate crystals in the urine are elevated, corrective nutrition is required. In advanced cases, when diet therapy is ineffective, medications that suppress the formation of uric acid are prescribed. Example – Allopurinol, Febuxostat. The content of urate salts in large quantities leads to gout or urolithiasis, so you need to normalize your diet to prevent complications.
With an increased content of sediment in the urine in children and adults, dietary table number 6 is indicated. The essence of the diet is a reduced intake of foods that trigger the formation of uric acid.
What foods are prohibited to eat:
- Offal - brains, liver, kidneys, ventricles and heart.
- Young meat is prohibited - veal, chicken, lamb, piglets. The same goes for fish.
- Fried, salted, smoked food.
- Extractive dishes, including pickles and broths.
- Semi-finished products - cheeses, sausages, dumplings.
- You should not eat vegetables and fruits that are a source of oxalic acid - almost all green leafy ones (parsley, sorrel, dill), as well as those with a sour aftertaste (lemons, apples).
- Chocolate, sweets, cocoa and coffee, and baked goods are prohibited.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Legumes.
Recommended products include:
- Milk and low-fat fermented milk products - cottage cheese, kefir and sour cream.
- Sweet fruits - raspberries, strawberries and wild strawberries.
- Vegetables - cauliflower, potatoes, zucchini, squash, pumpkin, peppers, carrots, cucumbers.
- Vegetarian soups with pureed vegetables.
- Crackers from black or gray bread.
The amount of salt is limited to 5-6 grams per day. At the same time, the amount of water you drink should increase. It is recommended to drink 2-3 liters of water per day, not counting the liquid included in cooked dishes. It is believed that drinking more water will help clear salt deposits from the kidneys.
What may affect the results
Factors that may distort the results of the study:
- Violation of hygiene procedures and urine collection techniques.
- Drinking large or small amounts of water.
- Consuming foods, medications, or dietary supplements that change the color of urine.
- Menstruation.
- High blood pressure.
- Intense physical and psycho-emotional stress on the eve of urine collection.
- Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, hypothermia.
- Carrying out invasive procedures on the urinary tract a week before the test.
You can take a general urine test at the nearest INVITRO medical office.
A list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory research is presented in the “Addresses” section. Urine examination includes the study of physical and chemical properties, as well as microscopy of sediment.
Physical properties: quantity, color, odor, transparency, relative density (specific gravity), urine reaction (pH).
Chemical properties: determination of protein, glucose, ketone bodies, urobilinogen, bilirubin, hemoglobin, nitrites, leukocyte esterase.
Microscopy: identification of erythrocytes, leukocytes, cells of flat, transitional and renal epithelium, cylinders, crystals, mucus, bacteria, fungi.
Nutritional Features
To reduce the amount of uric acid salts in urine, the patient is advised to radically review his menu. It is also important to control your water balance - drink enough fluid per day. The urate diet prohibits the consumption of salty, fatty, smoked, and fried foods.
In case of such a violation, it is strictly forbidden to add the following products to your diet:

- alcohol;
- mineral water;
- canned food and spices;
- offal;
- concentrated meat broths;
- trans fats and margarine;
- natural dark chocolate and coffee;
- beef, pork and veal.
The urate diet requires strict adherence to nutritional rules. In this case, it is recommended to limit the intake of: various seasonings; fresh onions, cabbage; legumes; bread and baked goods.
The patient's menu for urate in the urine must include a list of the following products: oatmeal; fresh vegetables and fruits; fermented milk products; eggs; white grapes; baked or stewed potatoes; bell pepper; citrus. If you follow the rules of dietary nutrition, recovery occurs very quickly, and the effectiveness of therapeutic measures increases significantly.
Attention! To get rid of the presence of urea crystals in the discharge, it is important to control the caloric content of the food consumed. The daily dose of nutrients should not exceed 2800-3000 kcal. It is recommended to include a minimum amount of protein and some fat in the diet - replacing the rest with carbohydrates.
Normal indicators
| Index | Result |
| Quantity | 50 ml |
| Color | Colorless, light yellow, straw yellow, yellow, amber yellow |
| Smell | Odorless or non-specific |
| Transparency | Transparent |
| Relative density of urine (specific gravity) | 1003-1035 |
| Urine reaction (pH) | 5.0-8.0 (in children under 1 month – 5.0-7.0) |
| Protein | > 0.140 g/l |
| Glucose | > 2.8 mmol/l |
| Ketone bodies | > 1 mmol/l |
| Urobilinogen | > 34 mmol/l |
| Bilirubin | Not detected |
| Hemoglobin | Not detected |
| Leukocyte esterase | Not detected |
| Nitrites | Not detected |
| Red blood cells | Up to 2 cells per field of view |
| Leukocytes | Up to 5 cells in field of view |
| Epithelium | Up to 5 squamous epithelial cells per field of view |
| Cylinders | Not detected |
| Crystals | Little or no detectable amounts of urates, calcium oxalates, amorphous phosphates |
| Slime | In small quantities |
| Bacteria | Not detected |
| Fungi | Not detected |