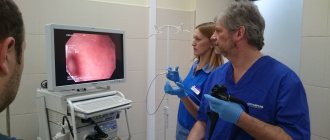
Ultrasound (ultrasound) has now become the most popular method for studying the morphological structures and functions of the human body. Ultrasound is a diagnostic method that can be used to evaluate both changes in the morphology (structure) of an organ, which is most often necessary, and its function. The doctor who conducts such a study is called an ultrasound specialist (USD).
The right to conduct ultrasound diagnostics can be obtained by a doctor of any specialty, basic or specialized, after completing the appropriate training. First, it is necessary to undergo primary specialization for four months, obtain a certificate as an ultrasound specialist, and then periodically undergo training in order to maintain professional competence.
Ultrasound of various organs and systems is specific. In order to conduct high-quality research on a particular organ, extensive experience in this area is required. Therefore, within the specialty itself, a narrow specialization of ultrasound doctors is possible, among the so-called universal ultrasound diagnostic specialists.
Study of the heart and blood vessels
Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels is perhaps the most difficult section of ultrasound. The doctor who performs an ultrasound of the heart and makes a conclusion is a cardiologist .
Ultrasound of the heart helps to identify changes in the structure of the heart muscle, the volume of the heart chambers, the thickness of the septa, changes in the heart valves, the condition of the proximal sections of large vessels, and the presence of effusion in the heart sac.
For ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels, special devices with the Doppler effect are used, and the study is called Dopplerography. This method studies intracardiac hemodynamics (the nature of blood flows inside the heart), the state of blood flow in the vessels, including the heart itself.
Responsibilities of an ultrasound specialist
An ultrasound doctor has a fairly large list of responsibilities. These include the following:
- determining diagnostic tactics depending on the type of patient;
- carrying out diagnostics;
- interaction with the attending physician on examination issues;
- Carrying out equipment serviceability checks;
- work with documents.
In order to work as an ultrasound doctor, you need to know:
- anatomy and physiology;
- stages of pregnancy, features of fetal development;
- symptoms of diseases of internal organs, manifestation;
- research algorithm;
- principles of reading images;
- rules for maintaining medical records.
Thyroid examination
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the first and, practically, the only instrumental examination of the thyroid gland, widely used to diagnose the condition of the tissues of this organ. An endocrinologist performs an ultrasound of the thyroid gland . Therefore, endocrinologists are increasingly seeking to specialize in ultrasound and use this method to identify the condition of the endocrine glands. In regular clinics and city hospitals, this relatively simple study is carried out by both endocrinologists and universal ultrasound specialists.
Features of the profession of an ultrasound doctor
Nowadays, ultrasound machines are available in almost every clinic, so doing an ultrasound is a routine appointment of the attending physician. At the slightest suspicion of organ instability, they are referred for an ultrasound. Moreover, modern devices, as a rule, provide a very high-quality picture. The whole question is how correctly the ultrasound specialist will read the image.
There is a misconception that such research can be done by a medical employee without specialized specialization and without any higher education at all. This is partly true. Of course, he will be able to conduct an examination. But it’s unlikely to interpret the results correctly. To do this, you need not only to train as a doctor, but also to obtain a diploma in the specialty “Ultrasound Diagnostics”. It is this specialty that allows the doctor to perform high-quality ultrasound.
Ultrasound examinations are actively used in the following medical fields:
- gynecology;
- obstetrics;
- oncology;
- gastroenterology.
More often, an uzologist examines the condition of internal organs:
- heart;
- liver;
- kidneys;
- pancreas;
- mammary gland.
A good ultrasound doctor should be familiar with the diseases of these organs, know the symptoms and external manifestations of the diseases. This is extremely important and is what ultrasound technicians are taught in all medical schools.
When monitoring pregnancy, the matter becomes even more complicated. First, the doctor must determine the approximate age of the fetus. Secondly, identify deviations from the norm and instability of organ functioning. It also requires training and knowledge of obstetrics. Therefore, obstetricians and gynecologists often become ultrasound specialists.
In addition, the ultrasound doctor can work with other special equipment. Thus, he can conduct the following studies:
- dopplerography;
- coronary angiography;
- stenting;
- urography;
- colonoscopy;
- ECO.
Requirements for an ultrasound specialist
A doctor must meet the following requirements to work:
- higher medical education;
- a valid certificate in the field of “Ultrasound Diagnostics”;
- PC skills;
- ability to provide first aid.
It is also worth noting that the presence of diseases that have a negative impact on attentiveness, vision and hand motor skills can cause significant difficulties with employment.
Where can I learn to become an ultrasound specialist?
It is possible to master this profession in medical universities. To do this, you first need to complete six years of training in one of the following specialties:
- "Medicine";
- "Pediatrics".
This is followed by residency training in the field of Ultrasound Diagnostics, which will take two years. After completing the training, the doctor receives a certificate with which he can begin medical practice in the chosen field.
As previously mentioned, ultrasound equipment is regularly updated and is becoming more efficient and also somewhat affordable for the average person. For example, many expectant mothers perceive 3D images of a child as their first photographs. And such development requires that the doctor be able to use various techniques and constantly study.
What kind of research is this and in what cases is it performed?
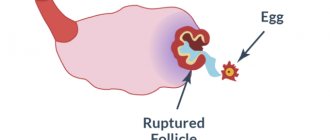
Ultrasound examination is a method that doctors and patients have dreamed of for a long time, since it can be used to look inside a person without cutting into the patient’s body. The doctor sees the condition of the organs, and the patient does not experience any pain. When creating ultrasound, scientists were guided by the principle used by dolphins for underwater orientation. The dolphin emits waves that travel through the water. Then they are reflected from surrounding objects and return to the owner, that is, the dolphin. And from them he receives accurate information about what is going on around him.
The operation of an ultrasonic device is based on this principle. During the examination, the doctor uses a sensor that emits ultrasound and receives a reflection back. The doctor moves this sensor over the patient's skin. It is connected to a computer that processes the received data. The device's monitor shows a cross-section of the organs. All components are painted in different shades. Dense tissues look white, liquids are black, and the image of all internal organs consists of grayish shades.
What does the examination reveal?
Sonography during pregnancy has advantages over other examination methods:
- speed of implementation in two-dimensional (black and white) mode - up to 15 minutes. 3d and 4d ultrasound during pregnancy takes longer - at least 40-50 minutes;
- determination of pathological markers. Their detection is not a 100% sign of pathology, but they are an indication for an in-depth examination, including expert ultrasound;
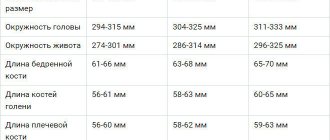
- highly accurate determination of gestational age;
- no discomfort or pain during the procedure;
- the ability to monitor (up to 4 times a day) if problems arise during pregnancy;
- early detection of genetic abnormalities, deformities, defects incompatible with life, when the timing allows for a medical or other type of abortion;
- timely diagnosis of developmental disorders, when therapeutic correction will allow you to maintain pregnancy, carry and give birth to a healthy baby;
- identifying abnormalities in the second and third trimesters, which allows you to determine the tactics of postpartum treatment of the child or draw up a plan for surgical intervention.
- Ultrasound is the most quickly accessible method that can be used in the event of unforeseen changes in a woman’s condition, if something went wrong with the pregnancy as it should be for a specific period.
What is ultrasound?
This is a research method in which ultrasonic waves (high-frequency sound waves) are passed through tissue using a special device and an image is obtained on the monitor from the reflected waves. Internal organs and tissues are an obstacle to sound waves, so they are reflected (partially or completely), and the specialist sees an image: formations with fluid (cysts, vessels) are displayed on the screen as darker and are called hypoechoic, bone structures (as well as stones) are displayed as light and are called hyperechoic.
Ultrasound is the most important diagnostic method, which gives the doctor a lot of information. However, sometimes in addition to ultrasound it is also necessary to perform a CT or MRI. Many patients do not see the difference between these diagnostic methods, but it is very significant. The safest, most accessible and widely used is ultrasound, which is often performed right in the doctor’s office.
CT and MRI are performed only if there are appropriate indications for them.
Ultrasound, CT, MRI are different research methods and are not interchangeable. These methods are based on different physical principles: ultrasound is based on the propagation, absorption and reflection of ultrasonic waves, CT is based on X-ray radiation, and MRI is based on nuclear magnetic resonance.
CT and MRI are prescribed as additional procedures if an accurate diagnosis cannot be made using ultrasound, as well as if examination of bones, joints, and nervous tissue is necessary (their condition cannot be accurately assessed with ultrasound). Tomography is also necessary to detect small tumor formations that are invisible on ultrasound.
Who does the ultrasound?
Ultrasound is performed using different techniques, using equipment of different classes, with the participation of doctors of different qualifications. The optimal option for examining a patient is when a medical examination and ultrasound diagnostics are performed by the same specialist, for example, ultrasound of blood vessels is performed by a vascular surgeon, ultrasound of the female genital organs by an obstetrician-gynecologist; Ultrasound of joints - orthopedic surgeon and so on. In this case, the study will be complete and accurate, since the specialist is familiar with the specifics of the pathologies of his field of medicine and knows what and how to look for during ultrasound diagnostics. All the nuances are important here - from the correct placement of the ultrasound sensor to the interpretation of the result on the screen (two doctors can evaluate the results differently).
Ultrasound techniques, equipment:
- two-dimensional ultrasound: obtaining a two-dimensional flat “picture”; Usually, with 2D ultrasound, the doctor receives all the necessary information;
- 3D, or three-dimensional ultrasound: obtaining a three-dimensional volumetric image, the quality of which is comparable to that of magnetic resonance imaging; 3D ultrasound is widely used in gynecology and is recommended if fetal pathology is suspected; it is not mandatory during pregnancy;
- 4D, or four-dimensional ultrasound, which produces a three-dimensional image in real time, that is, it allows you to see not just a three-dimensional image, but also the movement of an object;
- Doppler ultrasound with blood flow assessment (speed, direction, volume); indicated for identifying cardiovascular problems (blood clots, incompetent venous valves, heart valve defects, etc.), if fetoplacental insufficiency is suspected during pregnancy, for identifying heart defects in the fetus and other pathologies.
To carry out ultrasound diagnostics, the most sophisticated medical equipment is used - ultrasound scanners. They come in different classes: simple, medium, advanced and high, they have different resolution and sensitivity, and the diagnostic accuracy depends on these characteristics. To work with ultrasonic devices of the highest (expert) class, a qualified expert doctor (with an appropriate certificate) is required.
Who is an ultrasound diagnostic doctor and what does he do?
Many inquisitive people are interested in which doctor does ultrasound, keeping in mind the doctor’s specialization. Usually in medical institutions such a professional is called an ultrasound specialist. If the institution is specialized, then most often the ultrasound examination is performed by a specialized doctor. For example, in cardiovascular hospitals, ultrasound is performed by a vascular surgeon. In regular clinics, this is most likely a general practitioner.
The quality of the ultrasound result depends on the doctor’s experience and equipment. If the device is more functional, then you can expect better results from it. Not all small provincial hospitals have an ultrasound machine. Usually it is one for several institutions. A doctor of any specialization who has undergone additional training works on it. To make an accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound specialist examines many systems and organs. With some experience, he can take biopsies under ultrasound guidance. This is very important for various neoplasms. An ultrasound doctor performs pregnancy screening, which helps determine the following parameters:
- gestational age;
- condition of the placenta;
- position of the baby in the uterus;
- fetal development;
- estimated time of birth.
The ultrasound doctor performs diagnostics, but does not provide treatment. You can contact such a specialist on your own or under the direction of your treating doctor.
The ultrasound doctor will confirm the diagnosis or be able to make it himself for such pathologies as:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- thyroid lesions;
- ailments of the male sphere;
- diseases of the female genital organs and much more.
The patient should prepare for the ultrasound examination. If an abdominal examination is to be performed, then a number of foods should not be taken for 2 days. These are vegetables and fruits, legumes, carbonated drinks, black bread and everything that causes excessive gas formation. It is advisable to drink activated carbon. You can eat food before the ultrasound 20 hours before, no later. On the day of the study, you should not drink, brush your teeth, rinse your mouth, or take medications in the morning. If the doctor recommends something else, then you should listen to it.
When examining the organs of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to come to the procedure with a full bladder. To do this, you should drink a certain amount of liquid and not visit the toilet for 4 hours.