What is the norm and interpretation of ultrasound diagnostics of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy?
An ultrasound at the 24th week of pregnancy allows you to examine the baby’s facial features; his build is almost the same as that of a newborn.
3D ultrasound at this stage of pregnancy allows you to take a photo, which makes it possible to capture the baby’s face and determine which parent he resembles. By this period, all skin appendages have formed, and skin tissue accumulates. And if for some reason delivery occurs at the 24th week or the fetus has to be removed, it has every chance of surviving with appropriate medical care and the availability of the necessary equipment and devices, due to the fact that the child is not yet able to independently perform respiratory acts and maintain body temperature. In some cases, a pregnant woman experiences pain in the pelvic and lumbosacral region due to the onset of bone separation. Thus, the bone structures of the birth canal prepare for the process of the birth of the baby. During this period, the load on the musculoskeletal and vascular system of the lower extremities increases significantly.
Therefore, you need to not only give your legs rest, but also try to promote the outflow of blood and lymph from the legs to avoid stagnation and blood clots. To do this, when you are in a lying position, you need to raise your legs up. Some pregnant women develop hemorrhoids during this period of gestation, which require treatment.
Changes in the mother's body
During this period of pregnancy, the expectant mother looks simply beautiful: she is happy, her hair shines, her skin is tender, and her eyes shine.
There are significant changes in the figure of a pregnant woman. The belly is already clearly visible, the chest has become much denser, and the hips are wider. From the back you can see a clearly visible waist.
In addition to these changes in the appearance of the expectant mother, the appearance of such unpleasant sensations as:
- Heartburn;
- Headache;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Frequent urination;
- Back pain;
- Fast fatiguability.
Despite these troubles, the woman’s appetite grows as well as the fetus itself. The size of the uterus also increases. At 24 weeks of pregnancy, its bottom is located approximately at the level of the navel. The mucus plug fills the cervical canal, which is designed to connect the vagina with the uterine cavity.
The uterus is preparing for future birth, so at this time a pregnant woman may experience false contractions, which are called Braxton-Hicks contractions. They are practically painless. If pain is felt during such contractions and discharge appears, this may be evidence of premature birth. If contractions are painful, it is better to call an ambulance.
From the 24th week, profuse sweating and increased pigmentation (pigment spots that disappear after childbirth) may appear. After this week, insomnia appears, which can last for a very long time. Also, the baby's kicks became more noticeable. He can beat his mother with his strong legs at any time of the day.
At this time, skin stretching and veins appear. Stretch marks may appear; they form on the chest, hips, and abdomen.
Pressure surges are also not uncommon at this stage of pregnancy. And mild nausea appears from time to time. The reason for its appearance is the baby’s pushing against the walls of the abdomen and stomach.
Forgetfulness and nasal congestion temporarily appear in many expectant mothers. But there is no need to panic because of this. These symptoms will go away after the baby is born.
Pregnancy at 24 weeks
The period of 24 weeks or 6 obstetric months of pregnancy is an important stage in the life and development of the fetus. It is growing, development is exponential. He still has enough room for free motor activity, so his kicks are very noticeable for his mother. The weight of the fetus grows quickly and is about 0.6 kg.
The baby's sleep during this period should last about 18-20 hours a day; it is believed that the baby is already able to dream. He doesn't necessarily sleep at night. Therefore, quite often the expectant mother wakes up from the tremors of her child, who is no longer able to tumble, but moves from one uterine wall to another.
At week 24, the expectant mother’s belly has grown and become rounder. A pregnant woman regularly experiences heartburn, shortness of breath, and swelling may occur. By this period, prolonged stay in an upright position, including walking, is not recommended. It is worth limiting fluid intake to the physiological norm - 1.5-2 liters. You should not drink liquid at night. A healthy lifestyle during this period is as important as at any stage of the gestational process.
Swelling of the legs during pregnancy at this stage is a common occurrence. The process is associated with a significant increase in the load on the kidneys to which the expectant mother is exposed. In order to neutralize discomfort, it is recommended to limit fluid intake to physiological norms, and also stop drinking fluids at night.
This period is characterized by the appearance of false contractions (Braxton-Hicks training phenomena). These are preparatory contractions for the process of childbirth. As a rule, to alleviate the condition, it is enough to change the position of the body in space. However, if contractions intensify, you should consult a doctor.
Possible problems
Pain
Pain that occurs at 24 weeks is somehow associated with an increase in the size of the uterus. Most often, discomfort occurs in the following areas:
- lumbar region;
- lower abdomen, in the sacrum area;
- in the legs;
- in the anus (due to hemorrhoids);
- in my head.
If the pain in these areas is tolerable and not acute, then there is no cause for concern. However, if the sensations intensify, then it is better not to hesitate and consult a doctor. At this stage there is a high risk of miscarriage. Premature birth is undesirable for the baby; it will be impossible to save his life without special medical equipment.
Fever and colds
It is probably impossible to avoid colds during pregnancy. After all, one way or another, some part of the period falls during the peak of the epidemic. Colds are especially dangerous and can lead to disastrous results in the early stages of pregnancy. This is a period when the position of the embryo in the uterus is unstable, and any negative factor can lead to spontaneous abortion.
The 24th week in the pregnancy calendar is a calmer time when the risk of miscarriage is minimized. However, an advanced cold can have a negative impact on a child’s development. Therefore, it is important to start timely treatment and have an idea of what needs to be done.
- You need to consult a doctor. If your health allows, you can make an appointment and visit the clinic. If the condition is serious, especially if the temperature has risen, you should call a doctor home.
- While waiting for medical help, you can try to alleviate your condition using traditional methods. Gargles and inhalations based on herbal infusions will help relieve a sore throat and cough. It is recommended to drink more warm tea, milk, and berry juice.
- It is not advisable to bring the temperature below 38 degrees. If it reaches this mark, you need to take an antipyretic. It is best to consult a doctor. If the situation is urgent, then you can take paracetomol-based medicine. It will not cause much harm to the child's health.
After recovery, do not rush to go out in public, visiting public places. The immune system is still weakened and may not be able to cope with a new virus attack. It is better to walk in the park, and at home ventilate the rooms more often.
Discharge at the 24th obstetric week of pregnancy
The discharge at week 24 is almost the same as in the early stages of pregnancy.
The only difference is that their volume may increase slightly, they become more abundant.
Discharge of bright yellow, brown, green color with an unpleasant odor should still cause concern. Changes in consistency are also abnormal: contents streaked with blood, excessively watery and cheesy discharge. They say that you urgently need to see a gynecologist and identify the cause. There may be an inflammatory process.
Condition and level of development of the baby
By this point in the gestational process, the main organs and systems of the fetus have formed; they only have to reach the level of perfection of the newborn. At this stage, the process of receptor development is active. The fetus recognizes the taste characteristics of the food consumed by the mother. At this stage, his food preferences are formed. The main achievements in development at this stage are as follows:
- the child makes independent breathing movements, although he receives oxygen from the blood;
- subcutaneous fat is deposited;
- the formation of the pancreas, which is already producing insulin, has ended;
- skin appendages have formed (hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, marigolds);
- the urinary system works, the child swallows amniotic fluid and produces urine;
- the eyes are open, there are periods of sleep and wakefulness, the baby dreams;
- motor activity is less chaotic and more purposeful.
At the end of the second trimester, the fetal respiratory system is normally formed, including the alveoli, which already have a developed capillary network. But surfactant is not yet produced - a substance with surface activity, which allows it to ensure the expansion of the lungs with the first breath. It does not allow the lung tissue to collapse. Only if there is a sufficient amount of this substance can a newborn breathe on its own.
At week 24, the baby is slowly rehearsing an independent life: he reacts to the taste of food eaten by his mother, can exhibit emotional reactions, sleeps and is awake. During this period, the baby already has hair, fingernails and toenails. He is gradually turning into a real formed baby with a formed respiratory system
There is a rapid development and improvement of the structures of the brain and the apparatus that ensures the maintenance of balance and recognition of the position of the body in space. It is thanks to this that the fetus gains the ability to coordinate the actions of its limbs and shows interest in its body, touching the face, umbilical cord rings, and lower limbs. Right now, an individual pattern is being formed on the skin of the fingers, which is so interesting to fingerprint specialists.
Features of this period of pregnancy for the fetus.
By this moment, the unborn child has completed the formation of all systems and organs, while his body muscles and nerve cells have fully formed. The proportions of the fetal body correspond to the proportions of the newborn. The unborn child's senses actively respond to sounds and light. A pregnant woman can feel quite sensitive tremors.
During this period, the fetus begins to recognize the peculiarities of the taste of amniotic fluid, therefore it is during this period of life that one can begin to form the unborn child’s commitment to certain tastes.
During this period of time, there is a clear differentiation of the fetal sleep and wakefulness patterns. The unborn child may actively react to the body position of the expectant mother and loud sounds. But his schedule may not always coincide with his mother’s sleep and wakefulness schedule.
During this period of development, the skin of the unborn child is thin and has numerous sharp wrinkles. The arms and legs of the unborn child are still thin, and the body itself is thin. The subcutaneous fatty tissue of the unborn child is still poorly developed, but during this period the active accumulation of brown fat begins. The purpose of such accumulations is to form a mechanism for maintaining a constant body temperature.
This period is characterized by the development of sweat glands in the fetus. By this time, the unborn child's bronchi have almost completely developed. The development of the central nervous system is characterized by the formation and development of the cerebral convolutions.
Surfactant begins to form in the lungs of the unborn child - a substance that allows the lungs of the unborn child not to collapse after birth. The size of the fruit reaches a length of 25-30 cm, and its weight is 350 - 500 grams.
Laboratory diagnostics at the end of the second trimester of gestation
The need to monitor the condition of a pregnant woman at the 24th week of pregnancy is no less than in any other period. If there are no indications, the expectant mother undergoes the following tests as standard:
- OAM;
- UAC;
- blood sugar level.
The results obtained are compared with the norm, which makes it possible to determine the development of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, lungs or other organs, the onset of diabetes mellitus and other disorders that may affect the development of pregnancy. At this stage of the gestational process, ultrasound diagnostics can determine the condition of the fetus and the organs that provide its nutrition, growth and development. And also compare the indicators with the norm:
- assess the location, physical and functional state of the baby’s main systems;
- record the baby’s level of motor activity;
- quantity and quality of amniotic fluid;
- condition of the uterus, umbilical cord and placenta.
Additional tests or other types of examinations may be prescribed if the expectant mother’s well-being worsens. Or the obstetrician has reasonable suspicions of gestational complications.
The need for ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnostics after reaching 24 weeks of gestation is not included in the mandatory prenatal screening scheme. The examination in this period is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor to determine defects if there is a danger of negative consequences of pregnancy occurring with complications, or if the second proposed ultrasound procedure is missed.
During the fetal examination procedure, various areas of the body are examined:
- heart;
- brain;
- internal organs;
- spine.
In addition, the specialist examines the condition, the area of attachment of the placenta, as well as the volume of amniotic fluid.
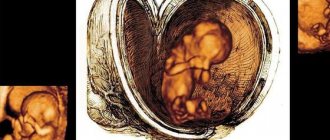
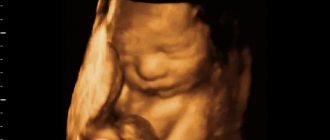
At week 24 you can undergo a 3D ultrasound and see a three-dimensional image of the baby
Doppler ultrasound diagnoses the movement of blood flow in the cardiovascular system, and with the help of 3D ultrasound at the 24th week it is possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the unborn baby.
Data obtained during ultrasound diagnostics
Usually an ultrasound is not performed at 24 weeks. 2 planned screening is usually timed to the 22nd week of gestation. However, according to indications, ultrasound diagnostics can still be performed:
- late registration period;
- repeat ultrasound if the development of anomalies and chromosomal disorders is suspected;
- repeat ultrasound if a pathology of the placenta, umbilical cord or uterine hypertonicity is suspected.
The obtained fetometry and Doppler data are compared with the standards of this period and the results of past studies. The norms of fetometric data are indicated in Table 1, the norms of blood flow indicators in Table 2.
Table 1. Fetometry at 24 weeks of gestation
| Fetometric data | Normal, cm | |
| Size | biparietal | 55-67 |
| fronto-occipital | 71-85 | |
| Circle | heads | 20,1-23,7 |
| belly | 17,2-22,4 | |
| Length of tubular bones | femoral | 40-48 |
| ray | 33 | |
| shoulder | 36-44 | |
| ulnar | 37 | |
| shins | 36-44 | |
When performing an ultrasound at 24 weeks, the prognostic data for delivery and the postpartum condition of the child and mother are favorable, in the case of normal Doppler and fetometry data. During this period, utero-fetal-placental blood flow is assessed by assessing the state of the MAG of the fetus, placenta and uterus. The body weight of the fetus at the 24th week ranges from about 63 to 0.69 kg, and its growth indicators are 30-32 centimeters. During this period, the maturity of the placenta can be determined; it should still be zero. In the case of hypotension in a pregnant woman, a moderate expansion of the intervillous space of the placenta is possible.
Fetal development at this stage
The fetus at 24 weeks of gestation is already quite large. It is believed that a fetus weighing more than 500 grams and a gestation period older than 22 weeks can already be born and nursed after a caesarean section. The weight of the unborn child is approximately 630 grams.
- In the brain, grooves and convolutions are already forming, differentiation of nerve cells into gray and white matter occurs, and the process of myelination of nerve fibers occurs.
- As for the auditory and visual analyzers, they are quite mature. At week 24, the brow ridges, eyebrows and ears are formed, but the eyes are still closed.
- The face of the unborn child is already quite formed.
- The cardiovascular system has been developed since the 8th week and continues to mature during the further period of development. The unpaired organs of the abdominal cavity after the rotation of the organs (at 8–11 weeks) also continue to mature, and the intestinal tube lengthens.
- Regarding the respiratory system, at 24 weeks of pregnancy the alveolar ducts finish forming and the alveolar sacs begin, which indicates that the baby’s lungs are not yet as mature (there is little surfactant) as other vital systems. This is an important point in the possible development of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome if they are premature.
- In the kidneys at the 24th week of pregnancy, the filtration apparatus, the renal glomeruli, continues to form.
- The gonads have already been differentiated into male or female gonads, in addition, the external genitalia have already been formed, so at 24 weeks (and earlier) the sex of the fetus can be determined using ultrasound.
- The fetal skeleton is also already fully formed.
- The unborn child already has nails, but no hair yet; a special lubricant is formed on the surface of the skin.
What is the need for ultrasound diagnostics at 24 weeks?
In this period of the gestational process, ultrasound makes it possible to determine the danger to the life and development of the baby and prevent the pathological condition of the mother. At this stage, you can see how the fetal skeletal system, its organs and systems, the location of the internal organs and the condition of the baby’s external membranes develop. Ultrasound at the 24th week is of great importance to study the condition of the uterus, umbilical cord and placenta. Their condition allows us to predict the normal process of delivery. Also, timely diagnosed pathology allows you to avoid a lot of problems for mother and baby. At this stage, you can make a 3-D and 4-D recording of fetal activity, you can take photographs or videos. At this stage of gestation, the mother herself is able to assess the external characteristics of the baby using a highly accurate diagnostic procedure.
Source
Recommendations for the expectant mother

- During flu and acute respiratory infections epidemics, stay away from crowded places. Eat germ-killing foods like onions and garlic. Ventilate the room more often and postpone visiting.
- If the mild swelling, which is often observed during this period, intensifies, consult a specialist. If not treated in time, preeclampsia may develop - a serious disease that affects the heart, nervous system, kidneys, liver, placenta and fetus.
- Be careful to avoid falls and injuries. Of course, the child is reliably protected from negative external influences, but an abdominal injury does not bring anything good.
- Communicate with your child, talk to him more often. He already distinguishes his mother's voice from everyone else and reacts to touch. Calm conversations with your baby and gentle stroking will bring you closer even before birth.
It is necessary to do vaginal exercises to prepare the genital tract for the upcoming birth. It is especially beneficial to do Kegel exercises regularly.
Dietary recommendations
At 24 weeks of pregnancy, you must adhere to the same diet as before. The daily menu should include fruits and vegetables, berries, cereals, bread, pasta, olive oil, beans, nuts, and herbs. At least once a week you should eat fish and seafood, white meat, eggs, cheese, yogurt and sour cream.

It is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol and minimize the consumption of unhealthy foods: flour and sweet, spicy, peppery and salty. High-calorie foods do not bring any benefit, but they cause very strong weight gain. At the same time, salty foods cause swelling.
The diet must include foods high in iron (to prevent anemia - beef, buckwheat, persimmon, pomegranate juice), ascorbic acid (cherries, bell peppers, seaweed), fiber (fruits and vegetables). You should drink at least 1-2 liters of still water. It is advisable to drink and eat little and often.
Vitamins at 24 weeks of pregnancy
It is not always possible to get all the necessary vitamins from food, so gynecologists recommend that expectant mothers take multivitamin preparations. They are especially often prescribed when pregnancy occurs during the cold season. Another indication is age over 30 years or food allergies, due to which the woman is limited in her diet.

Before going to the pharmacy and purchasing a vitamin complex, you need to consult your doctor. Only a gynecologist who monitors the course of pregnancy knows which drug is suitable for the mother and will not harm the child. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage.
Physical activity
Physical activity plays an important role in maintaining the health of mother and baby. Constantly sitting at the computer or in front of the TV, interspersed with lying down, will not bring anything good. The result will be excess weight, complicating pregnancy, pain in different parts of the body and a lethargic state of the mother.
To keep your body in good shape, it is enough to take long walks in the fresh air. But you need to remember that five minutes of walking along the streets is not enough. It is best to go outside the city; in extreme cases, parks and squares are suitable for walking. If you have the opportunity and desire, you can sign up for special classes for pregnant women. Fitness clubs offer them in abundance. This includes water aerobics, yoga, and gym classes. The main thing in this matter is regularity and measure.
Intimate life
Intimate life at 24 weeks of pregnancy should be calm - without sudden movements or experiments. Mother and father should not forget about the comfort of their baby, avoiding pressure on the stomach. There are no other restrictions.
A doctor may recommend stopping sexual relations if the mother’s health leaves much to be desired and there is a risk of miscarriage. Possible causes include gestosis, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, and cervical injury. Intimacy should be exercised with caution during multiple pregnancies.
Changes in the baby's body at 24 weeks of pregnancy:
The child’s hearing becomes quite acute, and light perception improves.
All facial structures are already fully developed, the eyes have eyelashes, the eyelids are able to open and close, the eyebrows can frown and wonder. All facial structures can be especially clearly seen and assessed using 3d-4d ultrasound during pregnancy. With an ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, the face is fully formed, you can see who your baby looks like!
The child's head is covered with hair. It is not yet clear whether the child will be blond, brunette or red-haired - the pigment appears much later, now the hair is bright white.
Your baby continues to receive oxygen through the placenta, but his lungs begin to produce a substance called surfactant. Surfactant is a substance that allows you to keep the alveoli of the lungs open, prevents them from sticking together and ensures normal breathing and oxygenation of the child’s tissues. When enough surfactant has been produced, the baby will be able to take his first breath and continue breathing on his own. During an ultrasound scan of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, the echogenicity of the lungs indicates their immaturity. If there is a threat of premature birth, the hormone dexamethasone is administered to the mother according to the scheme in order to accelerate the maturation of the fetal lung tissue. If this is done within a certain time frame, the child’s chances of survival are much higher. If you still did not have time to do dexamethasone injections, or not enough time has passed since they were administered (the injections were done late), the child is given an artificial surfactant after birth.
The child forms his own periods of sleep and wakefulness. These periods may not coincide with yours! For example, a child can have a dance at 2 am. Most babies sleep 18 to 20 hours a day from 24 weeks of pregnancy until 4 months outside the womb.
Well-being of a pregnant woman at 24 weeks
The 24th week of pregnancy is a relatively calm time for the expectant mother, because she already clearly feels how the baby moves, can determine the periods of his sleep and wakefulness, and notices how quickly her belly is growing. At 24 weeks of pregnancy, the baby sleeps about 18-20 hours a day. Sometimes your baby kicks at night, or when you go to rest during the day. This may indicate that he is hungry. Allow yourself a light, healthy snack to help calm your baby's movements. Experts recommend that expectant mothers follow a daily routine and diet, thus teaching babies to stay awake and sleep at the same time.
Fetometry (fetal size) during fetal ultrasound at 24 weeks of pregnancy is normal:
- BDP (biparietal size). With an ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, the biparietal size is 55-67 mm.
- LZ (fronto-occipital size). Ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy shows 71-85mm.
- OG (fetal head circumference). With an ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, the head circumference corresponds to 201-237 mm.
- OB (fetal abdominal circumference) - with ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy it is 102 mm 172 -224 mm.
Normal sizes of long bones during fetal ultrasound at 24 weeks of pregnancy:
- Femur 40-48 mm
- Humerus 36-44 mm
- Forearm bones 31-39 mm
- Tibia bones 36-44 mm.
With an ultrasound of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, the time comes for Doppler to diagnose the prognosis of normal or abnormal development of the pregnancy. With normal Doppler characteristics and the absence of fetal malformations (visible on fetal ultrasound at 24 weeks of gestation), the prognosis for labor and the postpartum period is favorable.
An ultrasound scan of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy evaluates blood flow in the umbilical cord arteries on both sides and the umbilical artery. These studies are recorded in the ultrasound protocol and characterize the processes of utero-fetal-placental circulation.
The structure of the placenta is also assessed during fetal ultrasound at 24 weeks of pregnancy. Normally, the placenta should be homogeneous; moderate expansion of the intervillous spaces is allowed, especially in women with low blood pressure. The degree of placental maturity is 1 or higher and normal Doppler readings require ultrasound monitoring of the dynamics of the child’s development rate with an assessment of its intrauterine state.
Checklist for 24 weeks of pregnancy
- Strengthen your back muscles with swimming and special exercises for pregnant women: this will reduce the load on your lower back.
- Swimming is also useful because it creates additional conditions for the baby’s vestibular training. Many mothers note that while swimming they feel active movements of the fetus, flips and somersaults.
- Don't forget about Kegel exercises: by doing them regularly, you will strengthen your pelvic floor muscles and reduce the risk of postpartum complications.
Ask all your questions about the 24th week of gestation to the specialists of the Women's Medical Center. Pregnancy management at the MLC is an individual approach and care for each patient.
Changes in the mother's body at 24 weeks of pregnancy
It's time for an important pregnancy test - blood glucose levels. The usual time to take this screening test is 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, when the risk of developing gestational diabetes is highest.
A glucose tolerance test is performed on an empty stomach, after which a certain amount of glucose is drunk and the blood sugar level is repeated. This way you can determine the body's ability to process glucose normally.
If your tests are abnormal, your doctor will give you dietary recommendations, and sometimes insulin may be necessary. Women with diabetes have a high probability of giving birth to large (sometimes even gigantic) children up to 6 kg, which requires a cesarean section.
You may feel numbness in your hands. This condition is called carpal tunnel syndrome. This syndrome is caused by sprained ligaments that put pressure on the median nerve of the wrist due to the influence of pregnancy hormones. If the numbness is severe and is accompanied by a feeling of weakness in the hand, perform an ultrasound of the joints (wrist joint). After childbirth, these symptoms will go away.
Your uterus has already risen above your navel. Wear a brace to reduce stress on your spine during pregnancy. During an ultrasound scan of the fetus at 24 weeks of pregnancy, it is also necessary to assess the tone of the uterus and the condition of the cervix. If there is a threat of premature birth, the bandage is necessary to support the fetal head and will not allow it to drop too much and put pressure on the cervix.
Watch for swelling. A slight pastiness (swelling) of the face, legs and arms is normal during pregnancy. If you begin to gain weight of 1 kg in a week or more, you experience visual hallucinations, and your blood pressure rises, consult a doctor immediately! These may be the first signs of preeclampsia or late gestosis (toxicosis).
read more: 25 weeks of pregnancy
Source
How the baby develops at 24 weeks
At 24 weeks, the baby is approximately the size of a Chinese cabbage.
At week 24, your Baby is about 27-28 cm tall and weighs approximately 500-600 g:
- the development of the brain, motor skills and vestibular apparatus allows the Baby to learn to control his body: he bends and unbends his arms and legs, tries to reach his heels, strokes his face;
- Two layers of skin are formed: a superficial layer - the epidermis and a deeper layer - the dermis. The epidermis is responsible for the formation of skin patterns on the tips of the fingers, palms and feet, which are determined by the genetic program. The dermis, located under the epidermis, forms small outgrowths containing blood vessels and nerve endings.
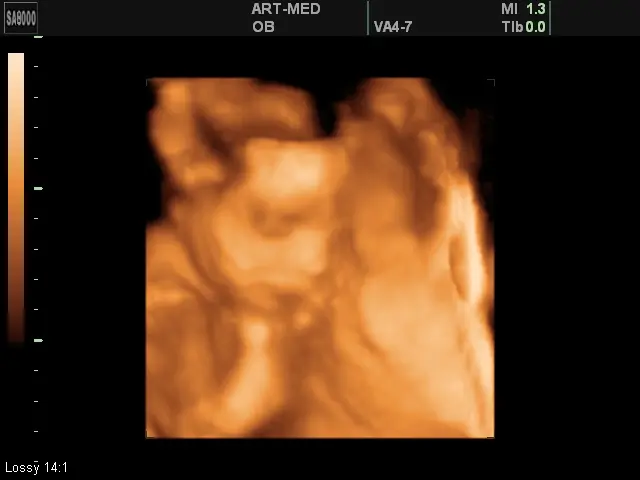
Ultrasound at 24 weeks of pregnancy
Ultrasound of the fetus: tasks, norms and deviations in three trimesters
All pregnant women carrying a child must undergo routine ultrasound examinations of the fetus in each of the three trimesters.
This is a requirement of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Fetal ultrasound allows you to fully monitor the condition of the woman and child, while the examination is absolutely safe and most informative. Appointment with a gynecologist - 1000 rubles. Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound - 1000 rubles. Ultrasound during pregnancy - from 1300 rubles. Appointment based on ultrasound or test results - 500 rubles (optional)
Ultrasound at 24 weeks during pregnancy
The second trimester is already nearing its end, the belly of the expectant mother protrudes very noticeably forward. When performing ultrasound diagnostics, you can see a fully formed small person on the monitor. The development of the baby in the woman’s body continues. He continues to push in the mother’s womb, the baby is already becoming a little cramped in the mother’s womb.
Changes in the mother's body
During this period of pregnancy, the expectant mother looks simply beautiful: she is happy, her hair shines, her skin is tender, and her eyes shine.
There are significant changes in the figure of a pregnant woman. The belly is already clearly visible, the chest has become much denser, and the hips are wider. From the back you can see a clearly visible waist.
Timing of planned ultrasound scans during pregnancy and indications for unscheduled examinations
Routine fetal screenings are carried out within the following framework:
- The first screening is from the 10th to the 14th week.
- The second screening is from the 20th to the 24th week.
- The third screening is from the 30th to the 32nd week.
However, most women undergo the procedure more often. The reasons for non-screening ultrasound are the following:
Up to ten weeks:
- The need to confirm the fact of pregnancy and determine the due date.
- There is experience of miscarriage due to miscarriage, habitual miscarriages, missed pregnancies.
- Pregnancy took place through the use of assisted reproductive technology
- There have been negative experiences with fetal pathologies in the past.
- There was a multiple pregnancy in the family.
- Determination of intrauterine or ectopic pregnancy.
After the first ultrasound, you need to undergo an unscheduled examination if you have:
- Nagging pain in the area of the reproductive organs - lower abdomen.
- Presence of bleeding or unusual discharge.
- The size of the uterus is inappropriate for the given period, the belly is too large.
- Suspicion of leaking amniotic fluid.
- The need to control insufficiency (weakness) of the cervix.
You also need to be examined to confirm or refute the conclusions of doctors from previous ultrasound examinations that showed pathologies.
General indications for all three trimesters:
- Bleeding, discharge.
- Stomach ache.
- A uterine size that is not appropriate for the current week is noticed during an examination by a leading gynecologist - then an ultrasound is necessary to exclude an undeveloped pregnancy
Objectives of ultrasound throughout pregnancy
The main task of fetal ultrasound is to monitor the growth, development and well-being of the baby. But each trimester has its own characteristics and clarifying tasks.
In the first trimester, the doctor needs to:
- Determine the location of the fertilized egg. If the pregnancy turns out to be ectopic, urgent surgery will be required, otherwise the organ where the embryo is attached will burst over time. In this case, the woman will at least lose her tube, and there are also deaths.
- Specify the deadline. Knowing the due date will allow you to calculate the due date.
- Find out the exact number of fruits. This is important, since multiple pregnancies often occur with pathologies and end in early birth.
- Analyze extracorporeal circulation and calculate the amniotic fluid index.
- Diagnose non-compliance with the norms of fetal development. During this period, you can refuse a pathological pregnancy and have a medical abortion or vacuum aspiration.
In the second trimester, during a fetal ultrasound, the gynecologist will be able to:
- Examine the woman’s uterus to rule out threats of miscarriage.
- Study the features of the umbilical cord, its loops and the presence of entanglements.
- Inspect the amniotic fluid for its quantity and purity.
- An exploration of the maturity and texture of a child's place.
- Diagnose in detail all the formed organs of the fetus, record the number of heartbeats.
- Determine the sex of the child.
- Carry out fetal fetometry in the context of the current period.
- Determine the position of the fetus.
- Study fetal mobility.
In case of serious developmental disorders, a surgical abortion can be performed during this period. By law, such a procedure is available only if indicated.
The third trimester is considered crucial in terms of the quality of childbirth. Using ultrasound, a gynecologist-obstetrician can:
- Monitor placental blood flow and its effect on fetal development.
- Determine the size of the fetus and its correspondence to the given period.
- Study the location and “age” of the placenta
- Record the location of the fetus relative to the uterine outlet
- Consider the presence and number of entanglements of the fetus with the umbilical cord.
- Identify late-onset pathologies and current diseases of the fetus.
- Determine the condition of the amniotic fluid.
- Study the features of the structure and functioning of internal organs, in particular the brain and heart.
- Specify the due date.
The information obtained from ultrasound during this period is important for determining possible options for delivery. If the fetal position is abnormal, the doctor will prescribe a caesarean section. In case of placental abruption, threat of fetal suffocation, etc., artificial early labor can be performed with stimulation of the process.
Preparation for fetal ultrasound, procedure progress
No special actions are required from the woman to prepare for the ultrasound examination, since all internal organs are displaced by the uterus and do not interfere with the view. But you will have to adhere to several recommendations to make the pregnant woman feel as comfortable as possible.
The doctor will recommend:
- Avoid foods rich in allergens one week before the procedure. Allergies are dangerous not only for the woman - her poor health will certainly affect the behavior of the fetus.
- In a couple of days you need to give up fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods. These products stimulate the secretion of bile and affect the liver - it increases in size.
- For 24 hours, do not consume carbonated water and foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. Air bubbles obstruct vision, distorting echogenicity characteristics.
- Immediately before the ultrasound, control the amount of food and liquid consumed so that the natural urge to empty the intestines and bladder does not constrain the pregnant woman
Failure to follow these recommendations certainly affects the results obtained during the ultrasound, but not so significantly as to refuse diagnosis if you ate a piece of meat or drank a glass of soda the day before.
The procedure is painless. As usual, the woman lies on her back on the couch, and the specialist rubs her stomach, which was lubricated a minute earlier with the gels necessary as conductors. The procedure lasts on average from 10 minutes to half an hour.
Often in the first trimester, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed - a sensor with a condom on it is inserted into the pregnant woman’s vagina. This does not cause pain, the procedure lasts no more than a few minutes. Transvaginal ultrasound may be repeated in the second trimester if a detailed examination of the cervix is necessary.
How is the examination carried out?
An ultrasound scan at 24 weeks of pregnancy, which falls in the second trimester, is performed by the doctor in two ways:
- transvaginally - the sensor is inserted into the vagina, after putting a condom on it;
- transabdominal - a special device is moved along the anterior abdominal wall.
In this case, ultrasound is reflected from echogenic formations, after which the echo is converted into an image or graph.
A woman may also be referred for Doppler ultrasound. This is an ultrasound diagnostic method that is necessary to assess the intensity of blood flow in the vessels of the umbilical cord and uterus.
What can a specialist see on an ultrasound?
First trimester
The first planned ultrasound examination is a mandatory part of screening a pregnant woman and, by law, must be carried out no later than the sixth day of the thirteenth week. Globally, it is aimed at excluding pathologies or risk factors for their occurrence. If you suspect any abnormalities after an ultrasound, you may need an additional examination of the amniotic fluid or a chorionic villus biopsy.
In detail, a study in the first trimester provides the following fetometric data:
- The size and weight of the fetus, which confirms or refutes the expected date. Only three values are taken into account: the distance from the head to the coccyx (KTR), between the parietal bones of the head (BPR), and the volume of the fertilized sac (FV).
- Data on the size and structure of the brain - whether its hemispheres are symmetrical, the presence of the necessary structures.
- Information about the work and structure of the fetal heart.
- Development of the digestive, nervous and cardiovascular systems in accordance with the current week of pregnancy.
- Are the fetal limbs normally developed?
- The presence of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down and Edwards syndrome.
Second trimester
The main purpose of ultrasound from the 20th to the 24th week is to examine the size and organs of the fetus to exclude anomalies and developmental deviations, as well as to monitor the condition of the pregnant woman’s organs to avoid premature birth. The data obtained in many cases helps to maintain pregnancy and improve the vital functions of the fetus using medication.
- Location and structure of the children's place. The specialist can see the presentation, low location (in these cases, measures are required) or normal. Compaction of the structure of the placenta (more than 4.5 cm) indicates hydrops fetalis, diabetes or rhesus conflict. Its thickness serves as an indicator of maturity - if it is less than 2 cm, then premature aging is diagnosed, due to which the fetus does not receive the nutrients it needs. If placental abruption occurs, a woman must be hospitalized urgently.
- The amount and purity of amniotic fluid. Their volume is constantly changing and if oligohydramnios is suspected, it is necessary to check this parameter at unscheduled ultrasounds. The reason for the insufficient amount of water may be leakage or lack of kidneys in the fetus. Polyhydramnios is caused by Rh conflict or infection. The latter is evidenced by the presence of flakes in the waters.
- Vessels, loops and entanglements of the umbilical cord.
- Uterine tone, the presence of myomatous nodes, the condition of scars after previous surgery.
- The cervix is measured to exclude isthmic-cervical insufficiency. Its length during this period should be 35 millimeters, at least 33 for the first pregnancy and 22 for repeated ones. The opening of the cervix is also controlled.
Fetometrics of the fetus:
- Dimensions: length of the femur and ulna, ridge, diameter of the head, chest, abdomen,
- weight in grams and height in millimeters. Based on these data, we can conclude that the physical development of the fetus corresponds to the current period.
- The study of facial bones is aimed at excluding Down syndrome pathologies such as cleft lip or cleft palate.
Internal organs of the fetus:
- The head section is examined for double contour, abnormal shapes, and integrity of the cranial bones.
- The brain is assessed by the size of the ventricles and the presence of tumors.
- The lungs are examined for maturity.
- The structure of the heart, blood vessels, and whether the heart rate corresponds to the norms are checked.
- The presence of abnormalities and defects in the kidneys, digestive tract and diaphragm is examined.
Timing for fetal ultrasound
At what stage (trimesters) of pregnancy is ultrasound performed? This is one of the main questions of interest to future parents.
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 457 of December 28, 2000, the mandatory examination of pregnant women, along with biochemical screening (blood test for the content of specific proteins), includes an ultrasound, which is carried out at 11-13 weeks, as well as 2 morphological ultrasounds during second and third trimesters. A total of three screening ultrasound examinations are performed during pregnancy.
Planned fetal ultrasounds by week of pregnancy are performed at the following times:
- 1st trimester screening - at 11-13 weeks;
- 2nd trimester screening - at 20-24 weeks;
- 3rd trimester screening - at 32-34 weeks.
Additional (unscheduled) ultrasound examinations can be carried out on the recommendation of a doctor at any stage of pregnancy. This should not frighten the patient, since ultrasound does not have a harmful effect on the body. Repeated procedures may be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis or, if a particular pregnancy pathology is detected, to take the necessary measures to improve the health of the woman and fetus.
The first ultrasound of the fetus helps to establish the exact gestational age, obtain data on the size and number of embryos, hear the fetal heartbeat, assess the degree of its development, and detect possible abnormalities.
Heart rate, formation of the nasal bone, thickness of the nuchal region and coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) are extremely important parameters by which the formation of the fetus is judged. Significant deviations from the norm, coupled with the corresponding laboratory test results, will indicate the presence of pregnancy pathology.
Important! The screening should be deciphered by a professional. This is the only way you can be sure that no pregnancy pathology has gone unnoticed. Attempts to independently evaluate the results of an ultrasound will not provide an objective picture of what is happening and will only add anxiety to an already emotionally difficult period for future parents.
At the second ultrasound during pregnancy, the gynecologist checks whether the size of the fetus corresponds to the current stage of pregnancy. The length of the child’s limbs, the size of his head, internal organs, the volume of the chest and abdomen, etc. are assessed. It is equally important during this period to monitor whether the internal organs, spine, and cardiovascular system are developing normally.
Also, during ultrasound screening of the 2nd trimester, the condition of the walls and cervix, appendages, location, thickness and structure of the placenta, and the number of vessels in the umbilical cord are assessed.

1 fetal ultrasound

2 fetal ultrasound
3 Fetal ultrasound
The third ultrasound of the fetus is key. At this stage, the doctor carefully analyzes the compliance of the anatomical and functional state of the fetus with screening standards for a given period of pregnancy. It is extremely important to identify late developmental defects.
If the results of the 3rd trimester screening show some delay in fetal development, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostics (assessment of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, embryo and umbilical cord). The doctor also analyzes the state of the “uterus-placenta-fetus” system. Close attention is paid to the placenta - its attachment zone, degree of maturity and thickness.
Determining the sex of a child during the third planned screening reaches 90% accuracy.
You can read more information about prenatal screenings
Unscheduled ultrasounds during pregnancy are performed if:
- the patient experiences pain in the lower abdomen;
- suffered an infectious disease;
- does not feel fetal movement after the 20th week;
- has bloody or other discharge;
- premature labor has begun;
- contractions appeared at 36-40 weeks;
- there are other complications of pregnancy.
Detailed explanation of fetal ultrasound results, norms and pathologies
Since the goals and subjects of medical interest in ultrasound examinations of different trimesters differ, the abbreviations and abbreviations in the reports are different.
First trimester
Estimated date of birth (EDD) - in fact, this is the same thing as the exact date of pregnancy, only from a different angle. Determined by data on the menstrual cycle and the size of the fetus
- The cervical-neck space (CN) is the main criterion for ultrasound examination in the first trimester. The norm is from 1.5 mm at the 10th week to 2.7 mm at the 13th. If the indicator is increased, the pregnant woman needs to undergo further examination.
- The coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) is one of the main parameters for assessing the size of the fetus. Normally, it should range from 41 mm at week 10 to 73 mm at week 12
- Heart rate - (HR, heart rate) normally for the first trimester should be 146-179 beats per minute, and this figure is lower the longer the pregnancy period
- Nasal bone - starting from the 12th week should be at least 3 mm, otherwise Down syndrome is suspected
- Biparietal size (BSD) should be from 14 mm at 10 weeks to 26 and higher at 13.
- The yolk sac is studied as an indicator of gestation-appropriate development. It grows in the first weeks and then decreases. Should be round in shape and 4-6 mm in diameter. If the shape is different, and the internal length of the incision is less than 2 mm at 8-12 and more than 6 mm after 10 weeks, a frozen pregnancy is stated.
Norms of fetal ultrasound indicators in the first trimester in the summary table
| Term | BPR | Yolk sac | Nasal bone | Heart rate | KTR | VP |
| 10 weeks | 14 mm | 4-6 mm, but not less than 2 | Yes, but not measured during this period | From 161 to 179 beats/min | From 41 mm | 1.5 to 2.2 mm |
| 11 weeks | 17 mm | 4-6 mm, begins to decrease | Yes, but not measured during this period | From 153 to 177 beats/min | 1.6 to 2.4 mm | |
| 12 weeks | Not less than 20 mm | Disappears | Not less than 3 mm | From 150 to 174 beats/min | up to 73 mm | 1.6 to 2.5 mm |
| 13 weeks | Approximately 26mm | Disappears | Not less than 3 mm | From 141 to 171 beats/min | 1.7 to 2.7 mm |
Second trimester
The ultrasound report from the 20th to the 24th week contains the following abbreviations:
- BPR - biparietal size of the fetal head;
- LZR - fronto-occipital size;
- BPR/LZR - cephalic index;
- AB - abdominal circumference;
- RS - heart size;
- DG—tibia length;
- DP - shoulder length;
- DB - thigh length;
- OG - head circumference;
- s/b or heart rate - heartbeat;
- IUGR—intrauterine growth restriction;
- DgRK - chest diameter;
- AFI - amniotic fluid index - an indicator of the amount of amniotic fluid;
- ICI - isthmic-cervical insufficiency - the cervix with this pathology is not long enough for full gestation.
So what does an ultrasound show and what can actually be seen there?
The first ultrasound examination of the fetus was carried out in 1958 by the British doctor D. Donald. He was the first to measure the size of the head of a fetus in the uterus using ultrasound.
First ultrasound
, as a rule, is done when a woman realizes that she is pregnant. Pregnancy can be seen by ultrasound from 3 weeks. You can already see the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, and a week later - its resident and even hear its heartbeat. The length of the body of a 4-week embryo is no more than 5 mm, and the heartbeat frequency reaches 100 beats per minute. By the 6-7th week from the moment of conception, the head and torso, arms and legs of the embryo are clearly visible.
In the first trimester, ultrasound allows you to determine the gestational age of the fetus
with an accuracy of 2–3 days. It is this age, and not the date of the last menstruation, that obstetricians focus on in all difficult situations.
All pregnant women without pregnancy complications undergo three ultrasound examinations, at 10–14 weeks, at 20–24 weeks and at 32–34 weeks.
Up to 10 weeks, ultrasound is performed, as a rule, if there are special indications:
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- suspicion of an undeveloped, frozen pregnancy;
- miscarriage in the past (history);
- pregnancy resulting from the use of assisted reproductive technologies - for example, in vitro fertilization (IVF);
- fetal malformations during previous pregnancies;
- possible multiple pregnancy.
Ultrasound in the early stages of pregnancy allows you to exclude an ectopic pregnancy, identify a threat of miscarriage or a pathology such as “hydatidiform mole”.
If there are no such indications, then for the first planned ultrasound
a woman arrives at a period of
10 to 14 weeks
. This ultrasound allows you to identify severe malformations of the fetus; its cervical-collar space is necessarily measured. Ultrasound at this stage makes it possible to diagnose a number of gross pathologies in the fetus that are incompatible with life or guarantee severe disability. The exclusion of some pathologies is carried out using invasive prenatal diagnostics, again performed using ultrasound.
Next scheduled ultrasound
is carried out already in the second trimester, between the
20th and 24th weeks
of pregnancy. This is the most informative study. The correspondence of the size of the fetus to the gestational age is examined, the sizes of all internal organs are assessed, and the condition of the placenta is diagnosed - its size, age, place of attachment.

At the same time, an ultrasound examination of the blood flow in the vessels of the placenta (Doppler ultrasound) is performed. This study allows us to assess how the fetus is supplied with oxygen and assess the risk of preeclampsia and premature birth.
In the second trimester, a specialist can examine every vertebra of the baby, every finger, and therefore exclude congenital malformations. Ultrasound also allows you to assess the amount of amniotic fluid.
If an ultrasound has revealed placenta previa, then the pregnant woman is prescribed an ultrasound scan every 4 weeks.
During a routine ultrasound in the second trimester, as a rule, parents are told the gender of the baby
.
Ultrasound examination in the third trimester
allows you to assess the presentation of the fetus - pelvic or cephalic, assesses the amount of water, the specialist looks to see if there is any entanglement in the umbilical cord, makes a forecast of the child’s weight at the time of birth and specifies the due date.
Norms of fetal ultrasound indicators in the second trimester in the summary table
| Term | BPR | LZR | coolant | DP | DG | OG | Heart rate | DgRK | DB |
| 20 weeks | From 43 to 53 mm | From 56 to 68 mm | From 124 to 164 mm | From 26 to 34 mm | From 26 to 34 mm | From 154 to 186 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 48mm | From 29 to 37 mm |
| 21 weeks | From 46 to 56 mm | From 60 to 72 mm | From 137 to 177 mm | From 29 to 37 mm | From 29 to 37 mm | From 166 to 200 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 50mm | From 32 to 40 mm |
| 22 weeks | From 48 to 60 mm | From 64 to 76 mm | From 148 to 190 mm | From 31 to 39 mm | From 31 to 39 mm | From 178 to 212 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 53mm | From 35 to 43 mm |
| 23 weeks | From 52 to 64 mm | From 67 to 81 mm | From 160 to 201 mm | From 34 to 42 mm | From 34 to 42 mm | From 190 to 224 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 56mm | From 37 to 45 mm |
| 24 weeks | From 56 to 67 mm | From 71 to 85 mm | From 172 to 224 mm | From 36 to 44 mm | From 36 to 44 mm | From 201 to 237 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 60mm | From 40 to 48 mm |
Third trimester
The last planned ultrasound examination is the most extensive and consists of measuring and studying the following fetal data:
- BPR - biparietal head size;
- LZR - fronto-occipital size;
- OG - head circumference;
- AB - abdominal circumference;
- DG - length of the tibia;
- DB - length of the femur;
- DP - length of the humerus;
- Height - 430 -470 mm;
- Weights - 1400 - 2400 grams;
- Beclair's nuclei - with normal development less than 5 mm;
- Thickness of placenta;
- The maturity of a child's place;
- Placenta placement, its presentation and the presence of abruption;
- AFL - the amount of amniotic fluid - is considered the norm to be 1-1.5 l;
- The length of the neck is considered normal to be from 30 to 35 mm.