Our clinic provides comprehensive diagnostics of diseases of all organs and systems. The blood system is a universal environment that reflects the state of the entire organism. Any, even minimal, disturbance in the body is instantly reflected in the blood system. Our clinic offers you a comprehensive examination of the body.
- Spleen
- Vessels (arteries and veins) of the legs and arms
- Blood vessels of the abdominal cavity
Watch our video about vascular diagnostics
The blood system includes not only the blood itself (plasma and formed elements: red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets, etc.), but also blood-forming organs (bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes).
In our clinic you can take blood tests 7 days a week
Using a blood test, we can determine the condition:
- Hematopoietic organs. Any disease of the bone marrow, spleen or lymphatic system of the body will give specific changes in a simple blood test.
- General condition of the body. With any disease, characteristic changes appear in the blood. A general blood test helps to distinguish a bacterial infection from a disease of a viral nature, determine the efficiency of the blood coagulation system, etc.
What can we study with blood:
- General blood analysis. A general blood test is the primary link and the beginning of any examination. A general blood test reflects the presence of inflammation, anemia, blood clotting disorders, etc.
- Blood chemistry. Biochemical analysis of the blood reflects the quality of the functioning of organs and systems, helps determine the quality of the liver, kidneys, etc.
- Hormone analysis. Hormones and their metabolic products reflect the work of the endocrine glands. If you need to study your hormonal profile, consult with your doctor about the best time to take the appropriate tests.
- Antibodies to infections . During different periods of an infectious disease, specific antibodies of the acute phase of inflammation (IgM) or chronic phase (IgG) appear in the blood. For rational, effective selection of treatment, it is important to understand what phase the disease is in.
- A blood test for thrombophilia , coagulogram , D-dimer and other studies of blood coagulation ability and susceptibility to thrombus formation are important for the timely prevention of vascular accidents: heart attacks, strokes, thromboembolism.
Spleen examination
The spleen is an important organ of the immune and hematopoietic system, but unlike other organs and systems, we do not notice problems until discomfort appears. The spleen accumulates the formed elements of blood in order to give them to the body at the moment when it is needed and acts as a filter for infectious agents and parasites. Most often, diseases of the spleen are secondary. This means that problems with the spleen are a consequence of some disease and the spleen hurts for some specific reason. The most informative studies of the spleen: general blood test, ultrasound examination of the spleen, beta2-microglobulin, consultation with a therapist.
We will offer you a spleen examination in two directions:
- Study of the structure and condition of the spleen
- Identifying the cause of spleen dysfunction

Study of the structure and condition of the spleen
To study the structure of the spleen and get an accurate idea of its structure, we use ultrasound examination of the spleen. Ultrasound examination helps to assess the condition of the spleen tissue and assess its arterial blood supply, and check how fully the venous outflow is carried out.
If you need a more detailed study of the structure and blood supply of the spleen, we will offer you computed tomography of the spleen or MRI of the spleen.
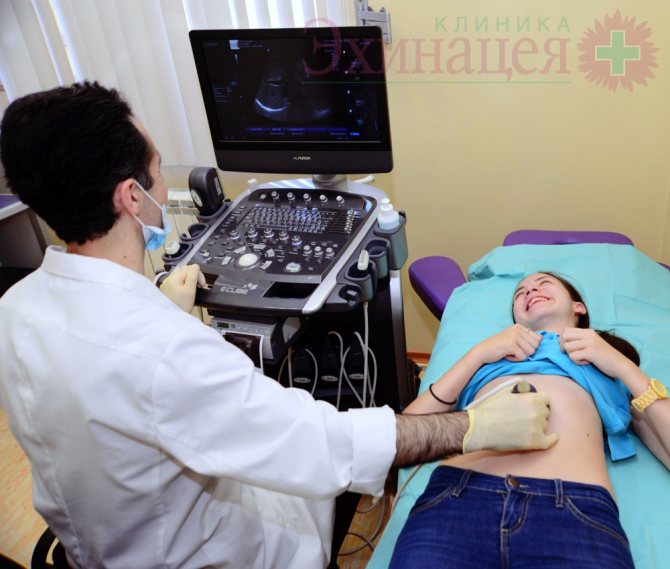
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. Ultrasound of the pancreas, liver, spleen, gall bladder.
Frequent findings during examination of the spleen:
- Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- Spleen cysts (most often caused by parasites);
- Tumors of the spleen.
Possible symptoms of spleen disease:
- Pain in the left hypochondrium (patients often complain that their spleen hurts);
- Anemia and, as a result, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Hypotension (low blood pressure) and tachycardia (increased heart rate per minute).
In most cases, pain in the spleen is the only symptom that the patient pays attention to.
Identifying the cause of spleen dysfunction
To determine the cause of the enlarged spleen, we will offer you several examinations:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- PCR for some viral infections (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis B, C, etc.);
- Immunological examination. In some cases, infectious diseases are difficult to detect in the blood using the PCR method due to the low viral load, however, if there is a virus in the blood, the body always produces antibodies against them;
- An immunogram will allow us to determine what disorder in the immune system gave the microorganism the opportunity to enter the body.
Our task is not only to cure spleen disease, but also to prevent its occurrence in the future; comprehensive diagnosis is the key to effective treatment.
Possible diseases of the spleen
Acute spleen diseases usually require hospitalization, so if you have severe pain or your spleen hurts very badly, we recommend seeking emergency care.
The most common causes of chronic splenic dysfunction are:
- Viral hepatitis B, C;
- Some cardiovascular diseases;
- Leukemia, hereditary anemia;
- Infectious and parasitic diseases.
Spleen size in children
In children, the normal size of the spleen depends not only on age, but also on height, therefore individual fluctuations in indicators in children are acceptable within 10% of the age norm. The sizes of the organ for children of different ages are presented in the table.
| Age | Length (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
| Newborn | 45 | 20 |
| 1 year | 52 | 25 |
| 3 years | 65 | 30 |
| 5 years | 75 | 35 |
| 7 years | 90 | 40 |
| 10 years | 105 | 50 |
| 14 years | 130 | 55 |
If the indicators go beyond the normal range, the following pathologies may be suspected:
- hematological syndrome.
- anemia.
- leukemia.
- Congenital heart defect.
- typhoid fever.
- tuberculosis.
Often, an enlarged spleen in children indicates liver problems.
Examination of the blood vessels of the arms and legs
Diseases of the blood vessels of the arms and legs rarely appear on their own; most often there is a specific reason for this. Our task is to determine the degree of vascular damage and identify the cause of the disease.
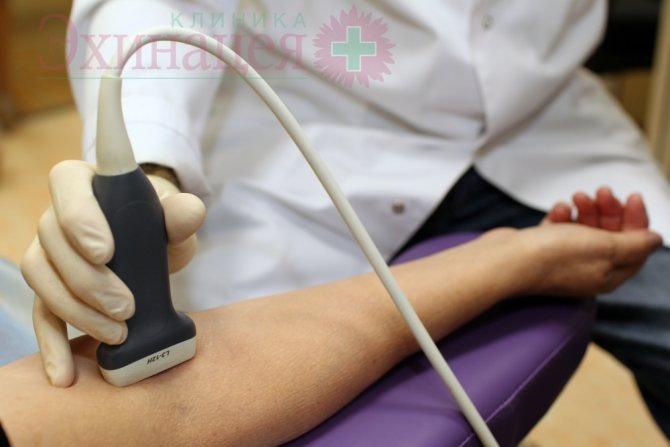
The main methods of vascular examination that we will offer you: Doppler ultrasound (vascular ultrasound) of the arms and legs, consultation with a vascular surgeon. If necessary, we will offer you additional examination methods and assistance from a doctor of the appropriate specialty.
Examination of the vessels of the arms and legs in our clinic is carried out in two directions:
- Examination of the structure of blood vessels and the quality of blood flow; both arteries and veins can be examined;
- Search for the cause of damage, vascular disease.
examination of the structure of blood vessels and the quality of blood flow
- Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the arms and legs. During an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the arms and legs, our task is to determine the diameter of the vessel, determine the presence of narrowing of the vessel, and exclude the presence of cholesterol plaques, blood clots, and pathological dilation of the vessel (aneurysm). Of great importance in the diagnosis of vascular diseases of the lower extremities is determining the quality of the valve apparatus. Ultrasound scanning of the lower extremities is important in the diagnosis of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, and the presence of blood clots in the veins of the legs. Ultrasound examination of the vessels (arteries and veins) of the upper extremities is advisable for Raynaud's disease, impaired thermoregulation of the hands (in cases where the hands are constantly cold).
1 – Healthy vessel, 2- Narrowed vessel with poor blood flow
Search for the cause of vascular damage.
- Biochemical blood test. First of all, we are interested in indicators of fat metabolism (including cholesterol).
- Coagulogram and examination for antiphospholipid syndrome . If there is a blood clotting disorder, there is a risk of increased thrombosis. Including in the venous system of the lower extremities. This situation is dangerous due to the detachment of a blood clot and blockage of blood vessels in vital organs: pulmonary arteries, cerebral vessels, and heart.
- Immunological examination is important in the search for immune factors that damage blood vessels in Raynaud's disease and various vasculitis. These systemic diseases harm not only the vessels of the arms and legs, but also the entire body as a whole. in this case, the aggression of the immune system is directed not only at the vessels of the arms and legs, but also at the vessels of other organs.
- Determination of antibodies to infection. In some cases, vasculitis-like diseases with damage to the veins of the arms and legs occur when blood vessels are damaged by viruses or toxins. Our task is to accurately identify the pathogen and carry out targeted treatment.
In more complex cases, various options for angiography, CT, MRI, and capillary studies (capillaroscopy) can be used.
The vessels of the legs are arteries that supply blood to the legs and veins that carry blood that has given off oxygen back to the heart. The arteries and veins of the legs can be examined either together or separately, depending on the purposes of the diagnostic study. If we are talking mainly about varicose veins, then there will be no need to study the arteries.
Study of the arteries of the legs
Ultrasound examination of the arteries of the legs is usually indicated when it comes to insufficient blood flow to the legs, which can occur due to atherosclerosis, when atherosclerotic plaques narrow the lumen of the vessel or when the artery is blocked by a blood clot. Other causes are much less common and require more detailed examination.
Examination of leg veins
Vein examination is often prescribed for venous insufficiency, when varicose veins and swelling of the legs occur. But it is important to know that swelling of the legs can be caused by problems with the heart (heart failure) and then it would be advisable to conduct a heart examination along with the examination of the vessels of the legs.
Most often, when examining the vessels of the legs, it is enough to take a few steps:
- Perform an ultrasound examination of arteries and veins;
- Assess blood clotting for risk of blood clots
- Determine blood cholesterol levels to assess the risk of atherosclerotic plaque deposition and vasoconstriction and blood glucose levels for diabetes mellitus.
If these studies are not enough, we can offer you a more detailed and comprehensive diagnosis.
The main methods for studying the veins and arteries of the lower extremities used in our clinic:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the legs (duplex scanning) - using an ultrasound diagnostic device, the doctor determines the structure of the vessels of the legs, assesses their condition, blood flow speed, the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques and aneurysms. Usually, an ultrasound scan of the leg veins is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis of varicose veins.
- Angiography of the vessels of the legs using X-rays, computed tomography with contrast injection, or MRI. These studies are needed quite rarely - if an ultrasound of the blood vessels of the legs does not provide the doctor with the necessary information.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Preparation for an ultrasound scan of the spleen occurs as follows: in 2-3 days you will need to eliminate from the diet foods that cause gas formation, which may interfere with diagnosis. On each day of preparation, you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid, this will cleanse the digestive system. You should not eat food 5-6 hours before the procedure. Exceptions: pregnant women, infants and diabetics. If necessary, the doctor can prescribe medications that improve the secretory function of the digestive system.
Examination of the blood vessels of the abdominal cavity
In our medical practice, the following diagnostic methods are most often used to study the vessels of the abdominal cavity:
- Vascular ultrasound
- Vascular MRI (MR angiography)
- Vascular CT (CT angiography)
- Classical radiography of blood vessels
Ultrasound of abdominal vessels allows you to see the vessels “from the inside”, in real time. This is possible due to the property of red blood cells to reflect ultrasonic waves. This property is called the Doppler effect, from which the name of the research method itself comes - Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels. Ultrasound Dopplerography of blood vessels makes it possible to identify any change in blood flow in the vessels of the abdominal cavity, which may be associated with spasm of the walls of blood vessels, narrowing of their lumen or thrombosis.
Ultrasound shows large vessels: the abdominal aorta, its main branches, and the inferior vena cava. We will measure the diameter of the vessels, evaluate their lumen, and identify, if any, blood clots and/or atherosclerotic plaques. In the case of thrombosis, we can determine its size and monitor changes in its structure during treatment.
Ultrasound of the pancreas.
MR and CT (MSCT) angiography . The main advantage of CT and MRI of vessels is the ability to examine vessels with contrast and create their 3D model for more detailed diagnostics. Thus, it is possible to examine the abdominal aorta and its branches going to the kidneys, liver, spleen, intestines, etc., for dissection of the wall and aortic aneurysm, thrombosis, compression of the vessel by a tumor, narrowing of the lumen of the vessel (narrowing of the renal arteries is one of possible causes of hypertension). In addition to the arteries, we can evaluate the condition of the vessels for thrombosis (simple and inflammatory, i.e. associated with sepsis), etc.
Classic X-ray angiography (X-ray of blood vessels with contrast). At the moment, vascular x-ray is used less frequently due to its greater technical complexity compared to CT or MRI of blood vessels.