What inhalations should you do at home to quickly restore damaged lungs after pneumonia? Do I need to take vitamins and immunomodulators? How to train breathing so that shortness of breath does not develop?
We asked these questions to a pulmonologist with 50 years of experience, Honored Doctor of Belarus, Associate Professor of the Department of General Medical Practice of the Belarusian State Medical University, Ph.D. Irina Lapteva . In the past, Irina Mikhailovna was the head of the clinical department of pulmonology at the Republican Scientific and Practical Center of Pulmonology and Phthisiology, and the chief freelance pulmonologist of the Ministry of Health.
Recovery after pneumonia
You have extensive work experience. What can you say about coronavirus pneumonia: is it worse than the previous ones?
Doctors all over the world encounter viral pneumonia every year. The main difficulty is that new strains of viruses periodically arise, against which there are no vaccines or medicines when they appear. A pandemic occurs when a new virus spreads throughout the world and most people are not immune. This is exactly the situation that is currently observed with the COVID-19 infection due to its very high infectiousness (contagiousness).
COVID-19 is not as deadly as other coronaviruses. It kills about 4%, mostly people with diseases that cause immunodeficiency and the elderly. Children rarely get sick.
In general, are viral pneumonia more severe than bacterial pneumonia?
There are several options for the manifestation of viral pneumonia. Primary viral pneumonia is the most severe. This is pneumonia in the first two days with lightning-fast development of symptoms and involvement of other organs and systems of the body in the process.
Often there are variants of pneumonia that complicate the course of ARVI, when by the end of the first week ARVI is accompanied by pulmonary symptoms: cough with sputum, chest pain when inhaling, coughing. This is a variant of viral-bacterial pneumonia, in which the virus played the role of a conductor of bacterial infection.
A common variant of pneumonia is when the patient has recovered from acute respiratory viral infection, but in the second week the so-called second wave of infection occurs, usually bacterial, which is manifested by fever and pulmonary symptoms. This is secondary bacterial pneumonia.
The volume of lung damage is of great importance. Therefore, it is very important to start treatment in a timely manner and prevent the progression of the disease.
What are the main complications of viral pneumonia?
Viral pneumonia itself is a complication. Its course, in turn, can be complicated by the appearance and progression of shortness of breath, which can be interpreted as severe acute respiratory syndrome, and the development of failure of other organs, such as the kidneys, liver, and heart. Such multiple organ failure is characteristic primarily of primary viral pneumonia, when the virus enters the blood (viremia). In addition, the so-called hemorrhagic syndrome may develop, which was observed in 2009 with viral pneumonia caused by the swine flu strain.
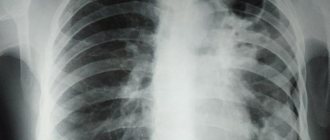
What does pneumonia look like on an x-ray?
The first sign of pneumonia is darkening of the lung tissue with uneven contours, the formation of foci from 3 to 12 mm, shadows of varying color intensity, changes in the pattern of the organ, fluid in the pleural cavity.
The first stage of the disease lasts up to 72 hours and is manifested by a deterioration in general health and the formation of fluid in the alveoli, blurring of the extreme points and an increase in the roots of the organ. Then the lung tissue will thicken and dark spots with light stripes will form. Already during tissue regeneration in the last stages of pneumonia, large darkened elements of the organ pattern will be clearly visible.
Therefore, in case of pneumonia, it is necessary to take x-rays of the lungs several times (at least 3 times) for both adults and children.
About breathing exercises and nutrition
What should you do first for rehabilitation after pneumonia?
One of the main goals is to restore lung function and eliminate residual symptoms, such as prolonged cough. Recovery time can range from one to three months. It is important to practice breathing immediately after finishing antibiotics. You need to start with the simplest exercises so that shortness of breath or cough does not develop.
Breathing exercises include the following exercises:
- holding your breath while inhaling (from 10–15 seconds to 1 minute);
- holding your breath while exhaling (from 5–10 seconds to 40 seconds);
- inhale and exhale quickly for a few seconds;
- breathing with maximum stretching of the chest and all intercostal spaces;
- inflating balloons - to develop the intercostal muscles and diaphragm.

The number of times each person determines for himself individually - according to his condition and well-being.
Rehabilitation at home includes physical education. They are necessary after pneumonia: by increasing the mobility of the chest, they prevent the development of adhesions in the pleural cavity. Do what is familiar to you.
It is important to sleep at least 8 hours at night. Before going to bed, you should take a walk in the fresh air. Even now there is no need to be afraid of it. The lungs need air . At any time of the year, you need to ventilate the apartment twice a day. Wet hygienic cleaning is also required.
Alcohol consumption should be avoided. If possible, stop smoking. If you are bothered by a strong cough and are unable to give up a bad habit, it is recommended to reduce the number of cigarettes and smoke less than before the illness. .
You should also avoid hypothermia.

What to change in nutrition and diet?
Proper nutrition is the basis for restoring lung function. During pneumonia, the body spends a lot of energy to overcome the infection. You can restore your strength by consuming enough proteins (meat, fish, legumes). At the same time, it is necessary to limit fried and spicy foods, as these dishes cause stress in the functioning of internal organs, which leads to worse recovery of the respiratory system. You also need to drink plenty of water: mineral waters, herbal teas with thyme, mint, lemon balm - this helps flush out bacterial toxins and tissue breakdown products and speed up the recovery of the lungs.
Types of shading
The location of the dark spots, their size and shape depend on the developed pathological lesion of the lung. There are several types of dark spots in the lungs:
- Focal
- Focus
- Segmental
- Shading of an indeterminate shape
- Share
- Darkening with liquid
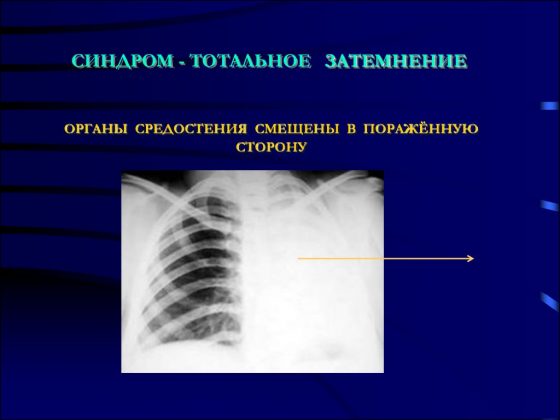
Total blackout syndrome
Total darkening of the lung on an x-ray is a complete or partial darkening (at least 2/3 of the lung field). In this case, gaps are possible in the upper or lower part of the lung. The main physiological reasons for the manifestation of this syndrome are the lack of air in the lung cavity, an increase in the density of the tissue of the entire surface of the lung, the content of fluid or any pathological content in the pleural cavity.
Diseases that can cause such a syndrome include:
- Bronchoscope in the bronchiWhat is bronchoscopy?
- atelectasis;
- cirrhosis;
- exudative pleurisy;
- pneumonia.
To carry out differential diagnosis of diseases, it is necessary to rely on two main signs. The first sign is to assess the location of the mediastinal organs. It can be regular or offset, usually in the direction opposite to the darkening focus. The main landmark in identifying the displacement axis is the shadow of the heart, located mostly to the left of the midline of the chest, and less to the right, and the stomach, the most informative part of which is the air bubble, always clearly visible on the images.
The second sign that makes it possible to identify a pathological condition is an assessment of the uniformity of darkening. Thus, with uniform darkening, atelectasis can be diagnosed with a high degree of probability, and with heterogeneous darkening, cirrhosis can be diagnosed. Interpretation of the results obtained using the radiographic method consists of a comprehensive assessment of all visually detected pathological elements in comparison with the anatomical features of each individual patient.
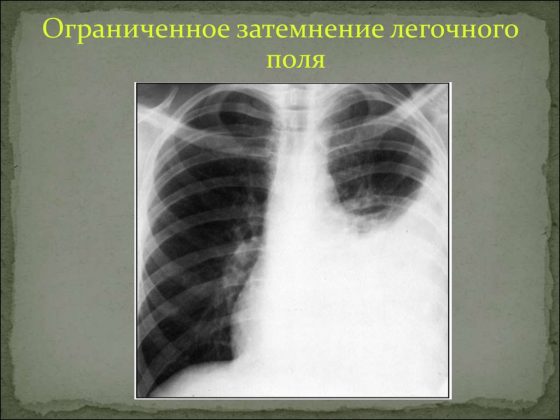
Limited dimming syndrome
To identify the causes of limited darkening of the pulmonary field, it is necessary to take an image in two directions - in direct projection and lateral. Based on the results of the obtained images, it is important to assess the localization of the darkening focus. If the shadow in all photographs is located inside the pulmonary field and is similar in size to its contours or has a smaller volume, it is logical to assume a lung lesion.
If there is darkening adjacent to the diaphragm or mediastinal organs with a wide base, extrapulmonary pathologies (fluid inclusions in the pleural cavity) can be diagnosed. Another criterion for evaluating limited shades is size. In this case, two possible options should be considered:
The size of the darkening clearly follows the contours of the affected part of the lung, which may indicate an inflammatory process;
The size of the darkening is smaller than the normal size of the affected segment of the lung, which indicates cirrhosis of the lung tissue or blockage of the bronchus.
Particular attention should be paid to cases in which there is a darkening of normal dimensions, in the structure of which light foci (cavities) can be traced. First of all, in this case, it is necessary to clarify whether the cavity contains liquid. To do this, a series of photographs are taken in different positions of the patient (standing, lying down or bending over) and changes in the level of the estimated upper limit of the liquid contents are assessed. If fluid is present, a lung abscess is diagnosed, and if it is not present, then the likely diagnosis is tuberculosis.
Important! The detection of several cavities with limited darkening of the lung is characteristic of pneumonia caused by staphylococcus. Such a lesion has an unfavorable prognosis, and often treatment is only possible through surgery.
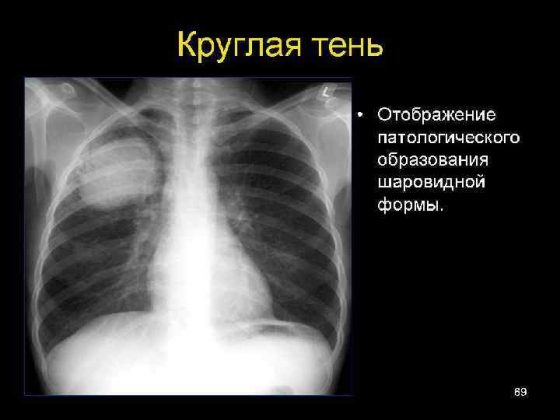
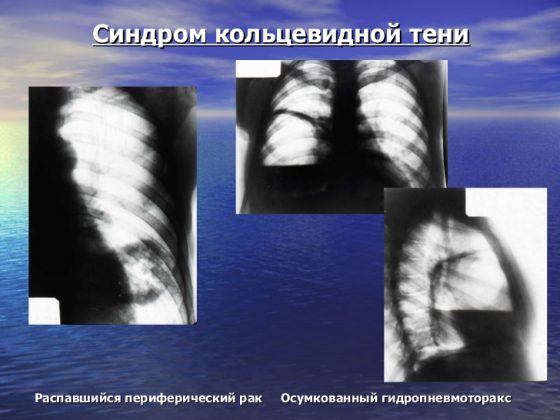
Round shadow syndrome
I identify round shadow syndrome when the spot on the lungs has a round or oval shape on two photographs taken perpendicular to each other, that is, from the front and the side. To decipher the results of radiography when a round shadow is detected, they rely on 4 signs:
- form of shading;
- localization of darkening relative to nearby organs;
- clarity and thickness of its contours;
- structure of the internal shadow field.
Since the shadow reflected on the image within the lung field may actually be located outside it, assessing the shape of the darkening can greatly facilitate diagnosis. Thus, a round shape is characteristic of intrapulmonary formations (tumor, cyst, infiltrate filled with inflammatory contents). An oval shadow in most cases is the result of compression of a round formation by the walls of the lung.
The structure of the internal shadow field is also highly informative. If, when analyzing the results, the heterogeneity of the shadow is obvious, for example, lighter foci, then with a high degree of probability, it is possible to diagnose the disintegration of necrotic tissue (with disintegrating cancer or disintegration of tuberculous infiltrate) or the formation of a cavity. Darker areas may indicate partial calcification of tuberculoma.
A clear and dense contour indicates the presence of a fibrous capsule, characteristic of an echinococcal cyst. Round shadow syndrome includes only those shadows that are more than 1 cm in diameter; shadows with a smaller diameter are considered lesions.
Ring shadow syndrome
A ring-shaped spot on the lung on an x-ray is the easiest syndrome to analyze. As a rule, a ring-shaped shadow appears on an x-ray as a result of the formation of a cavity filled with air. A mandatory condition under which the detected darkening is classified as ring-shaped shadow syndrome is the preservation of a closed ring when taking pictures in all projections and in various positions of the patient’s body. If in at least one of the series of photographs the ring does not have a closed structure, the shadow can be considered an optical illusion.
If a cavity is detected in the lung, the uniformity and thickness of its walls should be assessed. Thus, with a large and uniform thickness of the contour, one can assume the inflammatory origin of the cavity, for example, a tuberculous cavity. A similar picture is observed with an abscess, when purulent melting of tissue occurs and the contents are removed through the bronchi. However, with an abscess, the remains of pus most often remain in the cavity and their complete removal is quite rare, so usually such a cavity is a tuberculous cavity.
The unevenly wide walls of the ring indicate the process of decay of lung cancer. Necrotic processes in tumor tissue can cause the formation of a cavity, but since necrosis develops unevenly, tumor masses remain on the inner walls of the cavity, creating the effect of an “uneven” ring.
Important! The main difficulty in assessing the ring-shaped shadow is determining the localization of the formation, since in most cases a similar syndrome is observed in extrapulmonary processes (deformation of the ribs, gases in the intestines, gases in the pleural cavity).
About probiotics and vitamins
Should I take probiotics and for how long?
When treating pneumonia while taking antibiotics, the intestinal microflora dies. In this case, discomfort in the abdomen, bloating, loss of appetite, nausea, belching, and aversion to a certain type of food may occur. In addition, disruption of the intestinal microflora can have long-term consequences: decreased immunity, allergies to foods that previously did not cause problems, weight gain. In this regard, doctors often recommend a probiotic containing lacto- and bifidobacteria. It is better to take the drug simultaneously with an antibiotic, observing a three-hour interval. And then switch to kefir and yogurt, which contain lactic acid bacteria.

Do I need to take vitamin complexes and adaptogens?
Yes. You can take multivitamins, but not more than one month. The instructions will tell you more about the dosage regimen.
The ability of adaptogens to restore the body's strength under the most extreme conditions is well known. The strongest are considered to be Leuzea, Eleutherococcus, Echinacea and ginseng. Then come lemongrass and aralia. Golden root, pollen, rose hips, and royal jelly are also used. Incorporating herbal adaptogens into the treatment of pneumonia may prevent adverse antibiotic reactions and accelerate clinical improvement. But you need to know that their use has a lot of contraindications and some seasonal restrictions. In the summer, especially in the heat, it is better not to take these drugs at all, since at this time of year they have virtually no therapeutic effect, but can cause headaches and rapid heartbeat. Take adaptogens no more than once a day, preferably in the morning. And the doctor selects the dosage.
Can immunodeficiency occur after pneumonia?
During the inflammatory process in the lungs, the immune system is activated to fight the pathogen. During treatment, immune mechanisms may become depleted, which can lead to a new infection or relapse of the disease. To prevent undesirable consequences, herbal immunomodulators are used: tinctures of Chinese lemongrass, echinacea, and eleutherococcus.
Types of blackouts
Pulmonary diseases are generally accompanied by compactions in the lung tissues. This occurs due to a decrease or absence of air permeability in certain areas of the organ. X-rays show darkened spots. This symptom may indicate not only pathological processes in the lung itself.
Blackouts, the causes of which are associated with pulmonary pathologies, vary in their intensity, clarity, quantity and size. Darkening may indicate:
- on inflammatory processes and tissue compaction;
- on nodes of tumor formations;
- to an area impassable for air - collapse of the lung;
- on the development of tuberculosis;
- for the presence of fluid in the pleural area of the lungs (pleura is the membrane covering the lungs and chest cavity);
- for inflammation in the pleural area, possibly purulent (abscesses).
Pulmonary opacities, which appear due to problems with other organs, may also be visible on the images. These may include:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- formations on the ribs or spine;
- problems with the esophagus, for example, its enlargement.
About physiotherapy
Due to the fact that it is not worth visiting clinics now, what physical procedures can be performed at home?
In the first days of the recovery period, it is necessary to continue removing residual sputum (mucus) from the respiratory tract. To do this, you can use alkaline inhalations at home: breathe warm mineral water through an inhaler. Inhalations with drugs that dilate the bronchi are also possible, especially if you feel difficulty breathing (as prescribed by a doctor). If you don’t have an inhaler, you can breathe under a towel with a warm soda solution (40 g of soda per liter of water).
When the borders open, where is the best place to go on vacation after suffering from pneumonia?
A person recovers faster and more effectively in familiar, familiar conditions. Spa treatment is indicated only several months after pneumonia. Rest in a sanatorium is the last stage of rehabilitation. The most favorable resorts for the respiratory system are forested areas.
How to cheer up after severe pneumonia amid a pandemic?
Everything depends on ourselves. It is in our power to adequately and correctly assess the situation: a panicked or sad mood will not contribute to success. Cultivate positive emotions.
Your recommendations for prevention: how to support and strengthen the body and lungs so as not to get sick or easily suffer a new infection?
Necessary:
- Timely vaccination (seasonal flu, pneumonia)
- take vitamin and mineral complexes
- exercise regularly
- eat well
- have a good rest
- observe the rules of hygiene.